利用RawSocket篡改UDP源地址
补充交流:
私下交流的时候,宝哥哥提到为何不考虑TGW或者LVS作为解决方案?
经过一番调研,无论是TGW还是LVS的DR模式,所谓的session保持功能主要还是基于TCP长连接而言(TGW支持基于客户端IP的保持功能),其实并不特别适用于这里的业务场景。
一般后台Server之间出于性能考虑,往往通过TCP长连接进行通信,而该连接是由全量用户所共享的。与正常客户端的Per-Conn-Per-User模式并不一样,所以继续基于Connection做session保持就不适用了。
有童鞋对于代码中的PseudoUdpHeader部分感到疑惑,笔误?
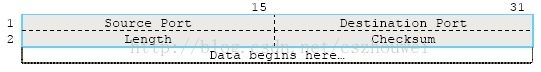
图1 IP包头格式
’图2 UDP包头格式
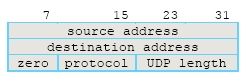
这里重点解释一下IP包头和UDP包头各自Checksum字段的计算方法。IP包头的Checksum比较简单,checksum(ip_header),计算时的checksum字段为0。UDP包头的Checksum计算方法有点复杂,checksum(pseudo_header+udp_header+data+padding),其中:pseudo_header如下图所示,data为实际用户数据,padding用于非2字节对齐的部分补零,计算时udp_header的checksum字段为0。
图3 Pseudo Header
而最终实际发送的IP包格式为:ip_header+udp_header+data
有了这些背景知识,对于代码里pseudo_header相关部分就很容易理解了,无非为了减少数据拷贝开销,临时征用了ip_header空间,完成udp_checksum的计算后再覆盖为真实的ip_header。
———————————————————————————————————————————————— 问题描述:
最近在voip项目开发过程中,碰到一种业务场景,接入层通过两种途径对外提供访问入口:
- CMLB——外部Server
- SSO——移动终端
由于我们的接入层存在session的概念,因此,一旦session在接入节点X建立后,后续请求都必须由节点X进行处理。但是,无论CMLB还是SSO,都属于无状态负载均衡分发系统,前后请求并无逻辑关联。
解决思路:
为了提高系统的可扩展性,我们将session存储于公司的ckv系统,接入节点每次接受请求后,首先尝试从ckv获取相应session,若无则设置自身为处理节点,反之则检查自身是否初始处理节点,若非则将请求转发至正确节点进行处理。
存在问题:
其实这里面临的问题和"Dispatcher-Worker"模式非常类似,假设请求流的走向为“Client->Dispatcher->Worker”,最终响应流的走向存在两种选择:
- Worker->Client:节省资源,但可能导致Client校验异常
- Worker->Dispatcher->Client:浪费资源,但确保Client侧的通用性
改进手段:
通过RawSocket篡改源地址,Worker伪装成Dispatcher进行回包。具体实现这里不展开叙述,可以下载附件源码,自行测试。
存在风险:
目前我在多台不同IDC的内网机器测试均表现正常,但不确定会不会哪天网平的兄弟们配置一些安全策略,然后就歇菜了?这一块如果有经验的同事还请多多指教!
参考文献:
http://www.tenouk.com/Module43.html
源码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef struct
{
uint8_t ip_hl:4;
uint8_t ip_v:4;
uint8_t ip_tos;
uint16_t ip_len;
uint16_t ip_id;
uint16_t ip_off;
uint8_t ip_ttl;
uint8_t ip_p;
uint16_t ip_sum;
uint32_t ip_src;
uint32_t ip_dst;
} __attribute__ ((packed)) IpHeader;
typedef struct
{
uint16_t source;
uint16_t dest;
uint16_t len;
uint16_t check;
} __attribute__ ((packed)) UdpHeader;
typedef struct
{
uint32_t src_ip;
uint32_t dst_ip;
uint8_t zero;
uint8_t protocol;
uint16_t udp_len;
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PseudoUdpHeader;
static uint16_t CalcChecksum(void *data, size_t len)
{
uint16_t *p = (uint16_t *)data;
size_t left = len;
uint32_t sum = 0;
while (left > 1) {
sum += *p++;
left -= sizeof(uint16_t);
}
if (left == 1) {
sum += *(uint8_t *)p;
}
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xFFFF);
sum += (sum >> 16);
return ~sum;
}
int SendFakeUdp(const void *msg, size_t len, const char *src_ip, uint16_t src_port, const char *dst_ip, uint16_t dst_port)
{
if (!msg || len <= 0 || !src_ip || !dst_ip) {
return -1;
}
static int fd = -1;
if (fd == -1) {
if ((fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW)) == -1) {
return -2;
}
int on = 1;
if (setsockopt(fd, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, &on, sizeof(on)) == -1) {
close(fd);
fd = -1;
return -3;
}
}
static char buf[65536];
IpHeader *ip_header = (IpHeader *)buf;
UdpHeader *udp_header = (UdpHeader *)(ip_header + 1);
char *data = (char *)(udp_header + 1);
PseudoUdpHeader *pseudo_header = (PseudoUdpHeader *)((char *)udp_header - sizeof(PseudoUdpHeader));
if (sizeof(*ip_header) + sizeof(*udp_header) + len + len % 2 > sizeof(buf)) {
return -4;
}
uint32_t src_ip_v = 0;
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, src_ip, &src_ip_v) <= 0) {
return -5;
}
uint32_t dst_ip_v = 0;
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, dst_ip, &dst_ip_v) <= 0) {
return -6;
}
uint16_t udp_len = sizeof(*udp_header) + len;
uint16_t total_len = sizeof(*ip_header) + sizeof(*udp_header) + len;
pseudo_header->src_ip = src_ip_v;
pseudo_header->dst_ip = dst_ip_v;
pseudo_header->zero = 0;
pseudo_header->protocol = IPPROTO_UDP;
pseudo_header->udp_len = htons(udp_len);
udp_header->source = htons(src_port);
udp_header->dest = htons(dst_port);
udp_header->len = htons(sizeof(*udp_header) + len);
udp_header->check = 0;
memcpy(data, msg, len);
size_t udp_check_len = sizeof(*pseudo_header) + sizeof(*udp_header) + len;
if (len % 2 != 0) {
udp_check_len += 1;
*(data + len) = 0;
}
udp_header->check = CalcChecksum(pseudo_header, udp_check_len);
ip_header->ip_hl = sizeof(*ip_header) / sizeof (uint32_t);
ip_header->ip_v = 4;
ip_header->ip_tos = 0;
ip_header->ip_len = htons(total_len);
ip_header->ip_id = htons(0); //为0,协议栈自动设置
ip_header->ip_off = htons(0);
ip_header->ip_ttl = 255;
ip_header->ip_p = IPPROTO_UDP;
ip_header->ip_src = src_ip_v;
ip_header->ip_dst = dst_ip_v;
ip_header->ip_sum = 0;
//协议栈总是自动计算与填充
//ip_header->ip_sum = CalcChecksum(ip_header, sizeof(*ip_header));
struct sockaddr_in dst_addr;
memset(&dst_addr, 0, sizeof(dst_addr));
dst_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
dst_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = dst_ip_v;
dst_addr.sin_port = htons(dst_port);
if (sendto(fd, buf, total_len, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&dst_addr, sizeof(dst_addr)) != total_len) {
return -7;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 6) {
printf("Usage: %s msg src_ip src_port dst_ip dst_port\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
int ret = SendFakeUdp(argv[1], strlen(argv[1]), argv[2], strtoul(argv[3], NULL, 0), argv[4], strtoul(argv[5], NULL, 0));
if (ret != 0) {
printf("SendFakeUdp fail. ret=%d\n", ret);
return -1;
}
printf("SendFakeUdp succ.\n");
return 0;
}