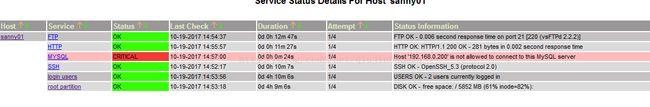
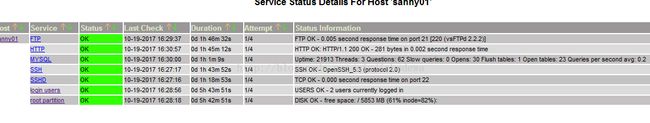
nagios监控数据库错误
Question1:
有两种解决方法
1)使用check_tcp 监听22号端口[root@localhost objects]# vim 192.168.0.201.cfg
define service{
use local-service
host_name sanny01
service_description SSHD
check_command check_tcp!22
}
检查配置文件
#/usr/loca/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/nagios.cfg
重启服务2)在被监控机上给主监控机的IP授权
被监控机器:
mysql> grant all on *.* to root@'192.168.0.200';
mysql> flush privileges;
mysql> show grants;
+---------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for root@localhost |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
在监控机器上试一下
首先mysql要开启的状态
#mysql -uroot -h 192.168.0.201 -----确定已经连通
重启nagios服务
service nagios restart
总结:
监听Mysql要进行授权
Question2:mysql连接失败 在Status Information下面显示Connection host are denyed
Solution:
在监控机上测试是否可以连通被监控机 ----------可以
检查配置文件
cd /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects
vim commands.cfg
发现mysql 那里的command_line 写错了,所以连接不上
检查配置文件
#/usr/loca/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
重启服务 -----------成功
总结:
要深刻理解nagios配置文件的运作过程
#cat /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
...
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/contacts.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/timeperiods.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/templates.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/192.168.0.201.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/services.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/hosts.cfg
...
#ls /usr/local/naios/libexec/check_*
........
check_apt check_file_age check_load check_nt check_rpc check_ups
check_breeze check_flexlm check_log check_ntp check_sensors check_users
check_by_ssh check_ftp check_mailq check_ntp_peer check_simap check_wave
check_clamd check_http check_mrtg check_ntp_time check_smtp negate
check_cluster check_icmp check_mrtgtraf check_nwstat check_spop urlize
check_dhcp check_ide_smart check_mysql check_oracle check_ssh utils.pm
check_dig check_ifoperstatus check_mysql_query check_overcr check_ssmtp utils.sh
check_disk check_ifstatus check_nagios check_ping check_swap
check_disk_smb check_imap check_nntp check_pop check_tcp
check_dns check_ircd check_nntps check_procs check_time
check_dummy check_jabber check_nrpe check_real
.........
#ls /usr/local/nagios/etc/object/
192.168.0.201.cfg printer.cfg commands.cfg hosts.cfg templates.cfg windows.cfg
localhost.cfg services.cfg contacts.cfg switch.cfg timeperiods.cfg
nagios.cfg这个文件是主配置文件
在里面加载其他的与程序运作的文件
例如:
我新建了一个192.168.0.201.cfg 是我要监控的机器,里面放的是这个机器里面的我要监控的服务
如httpd sshd mysql ftp
服务可以统一放在services.cfg里面,但是要监控很多机器就会很乱的,为了避免产生混乱,我们依照services.cfg里面服务编写的模式,新建以机器IP地址为名的cfg文件,如我创建的192.168.0.201.cfg,创建好了,我们在里面对要监控的服务进行定义。
#vim 192.168.0.201.cfg
define service{
use local-service
host_name sanny01
service_description login users
check_command check_nrpe!check_users ###监控软件的检测###
}
define service{
use local-service
host_name sanny01
service_description HTTP
check_command check_http ###http的检测###
}
define service{
use local-service
host_name sanny01
service_description SSH
check_command check_ssh ###ssh的检测###
}
define service{
use local-service
host_name sanny01
service_description FTP
check_command check_ftp ###ftp的检测###
}
define service{
use local-service
host_name sanny01
service_description MYSQL
check_command check_mysql ###mysql的检测###
}
define service{
use local-service
host_name sanny01
service_description port test
check_command check_tcp!22 ##端口的检测 加上这一块省去了对mysql授权那一步###
}
上面的是对服务的定义,接下来我们讲一下check_command.这一项来源于commands.cfg,check_command的名字的必须与commands.cfg里面相应 的command_name相同,我们看一下commands.cfg与http,ssh,mysql,ftp相对应的内容
#Vim commands.cfg
# 'check_http' command definition
define command{
command_name check_http
command_line $USER1$/check_http -I $ARG1$ $HOSTADDRESS$
}
# 'check_ssh' command definition
define command{
command_name check_ssh
command_line $USER1$/check_ssh $ARG1$ $HOSTADDRESS$
}
# 'check_mysql' command definition
define command{
command_name check_mysql
command_line $USER1$/check_mysql $ARG1$ -H $HOSTADDRESS$
}
# 'check_ftp' command definition
define command{
command_name check_ftp
command_line $USER1$/check_ftp -H $HOSTADDRESS$ $ARG1$
}
值得注意的是,mysql的定义这里面是没有的,需要我们自己定义。定义的时候command_line要在/usr/local/nagios/libexec里面的check_XXX列中。command_name可以自己定义。还需要定义后面的参数部分
以mysql为例:
参看/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_mysql --help ##我贴出来选项
Options:
-h, --help
Print detailed help screen
-V, --version
Print version information
-H, --hostname=ADDRESS
Host name, IP Address, or unix socket (must be an absolute path)
-P, --port=INTEGER
Port number (default: 3306)
-s, --socket=STRING
Use the specified socket (has no effect if -H is used)
-d, --database=STRING
Check database with indicated name
-u, --username=STRING
Connect using the indicated username
-p, --password=STRING
Use the indicated password to authenticate the connection
==> IMPORTANT: THIS FORM OF AUTHENTICATION IS NOT SECURE!!! <==
Your clear-text password could be visible as a process table entry
-S, --check-slave
Check if the slave thread is running properly.
-w, --warning
Exit with WARNING status if slave server is more than INTEGER seconds
behind master
-c, --critical
Exit with CRITICAL status if slave server is more then INTEGER seconds
behind master
command_line $USER1$/check_mysql $ARG1$ -H $HOSTADDRESS$
定义主机名就可以了,用-H