源码分析String的substring()在jdk1.6,jdk1.7的区别
String中有很多方法,其中substring是面试常考也是工作常用的,很有必要去分析了解它的实现。
substring方法,用于截取字符串中指定位置并返回子字符串。用法比较简单,但它的实现在不同JDK版本却有一定的差异。
public static void main(String[] args){
String str = "subtring";
str = str.substring(2, 5);
System.out.println(str);
}为了展示效果,我安装了2个版本的JDK来分析
jdk1.6中substring实现:
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[]; //字符数组
/** The offset is the first index of the storage that is used. */
private final int offset; //数组的偏移量
/** The count is the number of characters in the String. */
private final int count; //包含的字符的个数public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
if (endIndex > count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
}
if (beginIndex > endIndex) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex - beginIndex);
}
return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == count)) ? this : //如果开始位置等于且结束为止等于count字符个数。那么就返回本身
new String(offset + beginIndex, endIndex - beginIndex, value); //否则创建一个新的字符串对象
} String(int offset, int count, char value[]) {
this.value = value;
this.offset = offset;
this.count = count;
}它通过创建一个新的字符串对象,传入改变后的偏移量(offset +beginIndex),count字符数个数与value。这样就通过偏移量跟count获取到了这个范围内的值并返回。
到这里,没发现任何毛病,但是,毛病就new String那里的构造函数,this.value = value。
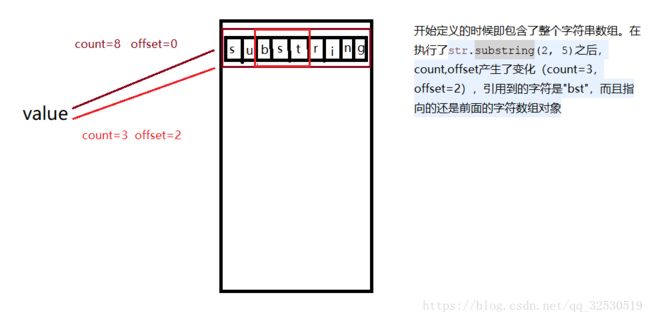
数组对象是放在内存区域中的堆位置,这里我画了一个简单的图:
JDK1.6这个方法的问题就在这,可以想想,当它改变偏移量跟count之后,引用的字符数组还是原来那个(value),用到的字符数组是"str"这三个,那其它是不是就没用了,我们知道java会不定时清除没用的对象,但是前提是没被引用的。这个"substring"字符数组在被截取后还是被引用着,但是仅仅只有str这三个位置需要使用,其它就浪费了,回收不了。假设,我们需要截取一个很长很长的字符串中很短的字符串,截取后真正用到的就只有那很短的字符串,那很长的字符就会一直占据着那些没用到的位置,那就可能会造成内存泄露。
大家能想到的是我再创一个String对象不就好了吗,是的,就是这么干。在截取后的字符串+""
str = str.substring(2, 5)+""从这里也能看出,jdk1.6也通过这样提升了效率(共用字符数组),但是却存在这样的问题。来看JDK1.7的substring
jdk1.7中substring实现:
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
if (endIndex > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
}
int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this
: new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}方法前面是一些判断是否越界的操作,重点代码就是这行代码:
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);此方法是在数组截取后返回一个新数组,按照上面的例子,就是在堆里创建了一个字符为bst的字符数组。这样原来截取的那个字符数组就会在不定时被回收掉,就不会存在内存泄漏的问题了。JDK1.8也是使用Arrays.copyOfRange的方式。