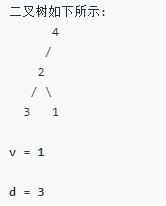LeetCode-树(解题技巧总结一)
为递归而生——树
递归的两个重要环节:
反复调用自身
终止条件
这两个条件务必注意。
有时候需要进行比大小操作,需要使用int类型的数据作为标识符,此时使用INT_MIN和INT_MAX
https://www.cnblogs.com/yangxin6017/p/9500867.html
以下所有的试题存出自LeetCode,每个题的解法思路均有参考和对比LeetCode上官方及各位大神们的题解(非常感谢平台和大家无私的分享),有些题的解法较为繁多,此处并未全部写出思路或者解题代码。
目录
0基本操作:
0.1各种遍历(迭代完成)
0.2N叉树
0.3二叉搜索树
1广度优先遍历(BFS)
2深度优先遍历(DFS)
3基础问题升级
3.1重构二叉树
4路径问题
0基本操作:
求树的深度,叶子结点的个数,对树进行遍历,这些都是最基本的操作,如果在这些基础操作的基础上,稍加难度,应该如何应对。
计算叶子结点个数/计算深度
void leafpointNum(BiNode * root)
{
if(nullptr == root)
return;
if(nullptr == root->lchild&&nullptr == root->rchild)
num++;
leafpointNum(root->lchild);
leafpointNum(root->rchild);
}//树的高度
int getTreeHigh(BiNode * root)
{
if(nullptr == root)
return 0;
int Lheight = getTreeHigh(root->lchild);
int Rheight = getTreeHigh(root->rchild);
int max = Lheight>Rheight ? Lheight+1:Rheight+1;
return max;
}以上都是最基本的递归,那么如果不使用递归,使用迭代算法,该如何做呢?
0.1各种遍历(迭代完成)
144. 二叉树的前序遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
94. 二叉树的中序遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
关于二叉树的前/中/后序遍历的迭代方法:
如果是递归,就方便很多,但是迭代就会有难度,这是为什么呢?因为递归最终会回到根结点,完成左子树后继续右子树,但是迭代可就没有这种优势了,和单向量表一样,都是单程路线,此时,就需要在单程路线中记录下需要需要回头才能处理的点。
前序:根->左->右
1->2->4->5->3->6->7 ,从根开始,先把根结点的元素压入栈中,然后左子树,然后右子树
但是如果左孩子又是一颗新树的根,那么还需要继续深入,那么右子树怎么办?把右子树压入栈中,先进后出,等遍历到
最左侧的叶子结点(1->2->4->),此时就需要将栈中的右子树弹出,进行打印(5->3);同样的,右孩子树也可以是另一颗树的根结点,因此弹出栈顶元素后,对其重复上述操作即可。
前序遍历:
要记住右子树元素的地址
class Solution {
public:
vector preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector Res;
if(root == nullptr) return Res;
stack Right;
TreeNode* temp = root;
Right.push(nullptr);
while(!Right.empty())
{
while(temp)
{
Res.push_back(temp->val);
Right.push(temp->right);
temp = temp->left;
}
temp = Right.top();
Right.pop();
}
return Res;
}
}; 其中第一个while的条件,也可以换成
while(temp||!Right.empty())中序遍历:
要记住根结点元素的地址
class Solution {
public:
vector inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector Res;
if(nullptr == root) return Res;
stack Saveroot;
Saveroot.push(nullptr);
TreeNode* temp = root;
while(!Saveroot.empty())
{
while(temp)
{
Saveroot.push(temp);
temp = temp->left;
}
temp = Saveroot.top();
Saveroot.pop();
if(!temp) break;
Res.push_back(temp->val);//根
temp = temp->right;
}
return Res;
}
}; 后序遍历是最难的,最讨巧的方法,就是反转!
真前序遍历:根->左->右
伪前序遍历:根 ->右->左 反转 左->右->根 就是后续遍历,只要把前序遍历中的一部分改变即可
s.push(temp->left);
temp = temp->right;
reverse(Res.begin(),Res.end());最后记着反转即可。
同类型的一道二叉搜索树的题目:
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/
本题两种解法,第一种中序遍历整个树,然后找第K小的数
第二种是使用中序遍历,在遍历的过程中,完成查找(加快速度,找到就停止,不在继续找)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//一般方法:中序遍历
// int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
// vectorNum;
// DFS(root,Num);
// return Num[k-1];
// }
// void DFS(TreeNode* root,vector & Num){
// if(root == nullptr) return;
// DFS(root->left,Num);
// Num.push_back(root->val);
// DFS(root->right,Num);
// }
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
//遍历完成
stackS;
TreeNode * temp = root;
S.push(root);
int num = 0;
while(S.size())
{
while(temp)
{
S.push(temp);
temp = temp->left;
}
temp = S.top();S.pop();
if(temp) num++;
if(num == k) return temp->val;
temp = temp->right;
}
return -1;
}
}; 0.2N叉树
二叉树的遍历很简单,那么N叉树呢?
589. N叉树的前序遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-ary-tree-preorder-traversal/submissions/
590. N叉树的后序遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-ary-tree-postorder-traversal/
(深度优先遍历DFS迎刃而解)
559. N叉树的最大深度 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/
(宽度优先遍历BFS最好理解)
0.3二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树,最大的特点就是比根小的放在左孩子结点,比根大的放在右孩子结点,二叉搜索树的中序遍历,是一个有序数组。
这是二叉搜索树的重要特点,也是解题关键。
二叉树 三个特性:
- 二叉搜索树的中序遍历的序列是递增排序的序列
- 在二叉搜索树中的插入、删除、搜索的复杂度等于树高,即(log(n))
- 在二叉搜索树中找最小节点和最大节点也很方面,如要找最小节点,只需从根节点开始,一直找左子树,当某个节点没有左子树时,该节点就是最小节点,即终止节点就是最小节点。同理,如果要找最大节点,那么从根节点开始一直找右子树即可,当某个节点没有右子树时,该节点就是最大节点。
下面这个题目充分体现了这个特点:
以下解法来自leetcode官方:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/solution/shan-chu-er-cha-sou-suo-shu-zhong-de-jie-dian-by-l/
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
一起看一下二叉搜索树的删除:
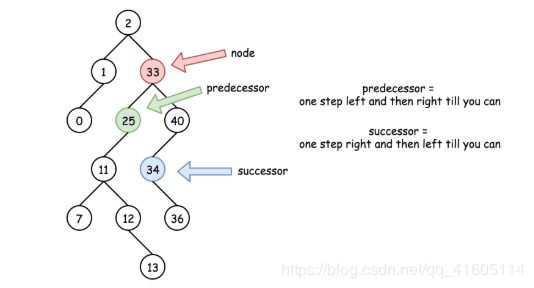
首先看一下在二叉搜索树中前驱后驱的定义,和普世的前后驱不同
三种情况:
如果 key > root.val,说明要删除的节点在右子树,root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key)。
如果 key < root.val,说明要删除的节点在左子树,root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key)。
如果 key == root.val,则该节点就是我们要删除的节点,则:
如果该节点是叶子节点,则直接删除它:root = null。
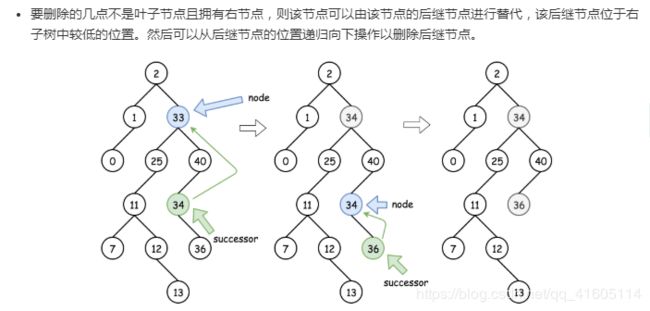
如果该节点不是叶子节点且有右节点,则用它的后继节点的值替代 root.val = successor.val,然后删除后继节点。
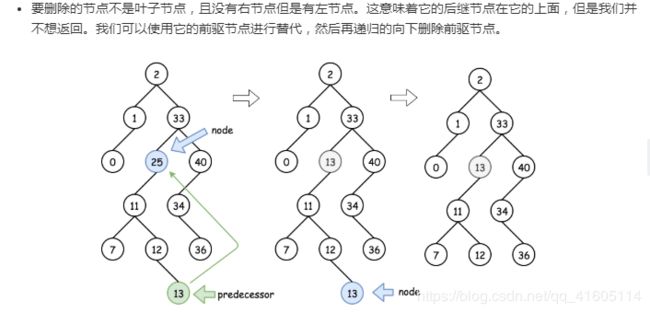
如果该节点不是叶子节点且只有左节点,则用它的前驱节点的值替代 root.val = predecessor.val,然后删除前驱节点。
返回 root。
作者:LeetCode
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/solution/shan-chu-er-cha-sou-suo-shu-zhong-de-jie-dian-by-l/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。下面是代码实现:
代码和上面的解释稍有区别,下面的三个情况和上面不一样,但是思想都是一样的。
- 没有左子树,右子树替换为根;
- 没有右子树,左子树替换为根;
- 左右子树都有,那么直接找后驱(右子树中的左叶子结点)
下面写的非常精妙。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {
if (!root) return root;
if (root->val < key) {
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); // 如果key大于root->val, 递归到右子树删除
return root;
}
if (root->val > key) {
root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); // 如果key小于root->val, 递归到左子树删除
return root;
}
if (!root->left) {
TreeNode* tmp = root->right; // 如果key = root->val,且左子为null,根变成右子根
delete root;
return tmp;
}
if (!root->right) {
TreeNode* tmp = root->left; // 如果key = root->val, 且右子为null,根变成左子根
delete root;
return tmp;
}
TreeNode* tmp = root->right;
while (tmp->left) tmp = tmp->left; // 找到右子树中最小值,与root->val交换
swap(root->val, tmp->val);
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); // 再在交换过的树中删除key
return root;
}
};
作者:yuexiwen
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/solution/c-di-gui-by-yuexiwen-3/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。以上两种情况都是一样的,本题是二叉搜索树中序遍历性质精髓的体现。
面试题54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-cha-sou-suo-shu-de-di-kda-jie-dian-lcof/
此题解法较多,逆向中序遍历,就是最好理解的一种
class Solution {
public:
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector Res;
DFS(root,Res);
return Res[k-1];
}
void DFS(TreeNode* root, vector & Res){
if(root == nullptr) return;
DFS(root->right,Res);
Res.push_back(root->val);
DFS(root->left,Res);
}
}; 不使用额外的空间:
class Solution {
public:
int Res;
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
DFS(root,k);
return Res;
}
void DFS(TreeNode* root, int& k){
if(root == nullptr) return;
DFS(root->right,k);
if(k == 1)
Res = root->val;
k--;
DFS(root->left,k);
}
};核心还是利用树的中序遍历的性质
以下两个题也是体现了这种性质,注意细节
二叉树展开为链表
114. 二叉树展开为链表 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
897. 递增顺序查找树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/increasing-order-search-tree/
这两道题都可以使用暴力解法完成求解,也就是中序遍历后,利用中序遍历的结构重新创建一个链表
当然了,暴力法也是下下策,原地完成是最好的。思路如下:
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
while (root != nullptr) {
if (root->left != nullptr) {
auto most_right = root->left; // 如果左子树不为空, 那么就先找到左子树的最右节点
while (most_right->right != nullptr) most_right = most_right->right; // 找最右节点
most_right->right = root->right; // 然后将跟的右孩子放到最右节点的右子树上
root->right = root->left; // 这时候跟的右孩子可以释放, 因此我令左孩子放到右孩子上
root->left = nullptr; // 将左孩子置为空
}
root = root->right; // 继续下一个节点
}
return;
}
};参考:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/solution/biao-biao-zhun-zhun-de-hou-xu-bian-li-dai-ma-jian-/
注意技巧,怎么找左子树的最右结点
auto most_right = root->left; // 如果左子树不为空, 那么就先找到左子树的最右节点
while (most_right->right != nullptr) most_right = most_right->right; 这种方法也出现在二叉搜索树中。
此题非常考验观察能力,原地完成有一定的难度
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/
排序依据不再是难事了,那么寻找众数,该用什么方式呢?
注意,所有的众数,众数可不一定就只有一个,最简单的方法就是中序遍历二叉搜索树,然后在中序遍历中寻找众数
参考:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/solution/zhong-xu-bian-li-vectorqiu-zhong-shu-by-jesse-42/
class Solution {
public:
vector v;
vector res;
int max=1;
int cur=1;
vector findMode(TreeNode* root) {
inOrder(root);
if(v.size()==0) return res;//处理输入为空的情况
res.push_back(v[0]);//初始化res数组
for(int i=1;imax)
{
res.clear();
max=cur;
res.push_back(v[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
void inOrder(TreeNode* root)//中序遍历
{
if(root==NULL) return;
inOrder(root->left);
v.push_back(root->val);
inOrder(root->right);
}
}; 108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/
面试题 04.02. 最小高度树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-height-tree-lcci/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return nullptr;
int Length = nums.size();
int mid = Length/2+1;
TreeNode* Root = new TreeNode(nums[mid-1]);
vector Left(nums.begin(),nums.begin()+mid-1);
// cout<<*nums.begin()<<" "<<*(nums.begin()+mid-1);
vector Right(nums.begin()+mid,nums.end());
// cout<<*(nums.begin()+mid)<<" "<<*(nums.end());
Root->left = sortedArrayToBST(Left);
Root->right = sortedArrayToBST(Right);
return Root;
}
}; 最小高度,最好的办法就是二叉搜素树,从给定的数组中的中间值开始,注意vector的用法
783. 二叉搜索树结点最小距离 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-distance-between-bst-nodes/
1038.https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/
合理运用性质
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* bstToGst(TreeNode* root) {
int sum = 0;
DFS(root,sum);
return root;
}
void DFS(TreeNode* root,int &sum){
if(root == nullptr) return;
DFS(root->right,sum);
root->val +=sum;
sum = root->val;
DFS(root->left,sum);
}
};
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insert-into-a-binary-search-tree/
综上我们能看到,在树中,递归为DFS(深度优先遍历),迭代为BFS(广度优先遍历),那么下面就介绍这两种最为经典的遍历方法:
面试题33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-cha-sou-suo-shu-de-hou-xu-bian-li-xu-lie-lcof/
此题和利用前序遍历和中序遍历创建二叉树非常相似,给的是后序遍历,但是树是二叉搜索树,那么终归还是一个找规律的问题:根结点很好找,就是后序遍历中的最后一个元素,那么在整个序列中,左子树的元素都小于根结点,右子树的元素都大于根结点。
可以把除了根结点以外的序列分割,分割为左右子树,然后在递归,判断依据就是根结点的值大于左子树的结点值,小于右子树的值。
class Solution {
public:
bool verifyPostorder(vector& postorder) {
return DFS(postorder,0,postorder.size()-1);
}
bool DFS(vector& postorder,int begin,int end){
if(begin>=end) return true;
int LeftB = begin;
while(LeftBpostorder[end]) LeftE++;
if(LeftE != end) return false;
return DFS(postorder,begin,LeftB-1)&&DFS(postorder,LeftB,LeftE-1);
}
}; 第一个循环是为了找到左子树的区间(都小于根),第二个循环是为了找到右子树的区间(都大于根)
1广度优先遍历(BFS)
广度优先遍历(借助队列这个数据结构)
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
class Solution {
public:
vector> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector> Res;
if(root == nullptr) return Res;
queue q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int qsize = q.size();
vector Vtemp;
for(int i = 0;ileft) q.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right) q.push(temp->right);
Vtemp.push_back(temp->val);
}
Res.push_back(Vtemp);
}
return Res;
}
}; 这是典型中的典型,典型的广度优先遍历,最适合这种层层遍历的题目,本体可以说是模板中的模板,此结果务必牢记。
同类型的衍生问题如下:
107. 二叉树的层次遍历 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/submissions/
面试题32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cong-shang-dao-xia-da-yin-er-cha-shu-lcof/
面试题32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cong-shang-dao-xia-da-yin-er-cha-shu-ii-lcof/
637. 二叉树的层平均值https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/
993. 二叉树的堂兄弟节点 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cousins-in-binary-tree/
都是在BFS模板上稍加修改即可完成
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/
合理运用标志位和reverse函数,此题不难
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/submissions/
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/submissions/
面试题32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cong-shang-dao-xia-da-yin-er-cha-shu-iii-lcof/
如果用DFS会较难理解,使用DFS,更容易理解,主要技巧,在一次循环中完成next的指向
面试题 04.03. 特定深度节点链表 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/list-of-depth-lcci/submissions/
class Solution {
public:
vector listOfDepth(TreeNode* tree) {
vector Res;
if(tree == nullptr) return Res;
queue q;
q.push(tree);
while(!q.empty())
{
int qsize = q.size();
ListNode dummy(INT_MIN);
ListNode* listtemp = &dummy;
for(int i = 0;ival);
listtemp->next = insert;
listtemp = insert;
q.pop();
if(temp->left) q.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right) q.push(temp->right);
}
Res.push_back(dummy.next);
}
return Res;
}
}; 623. 在二叉树中增加一行 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-one-row-to-tree/
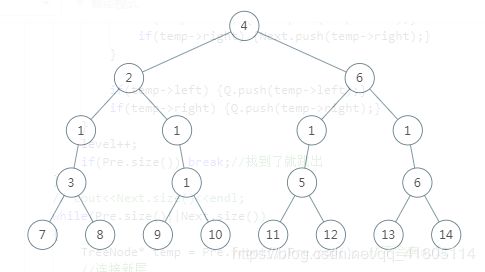
本题难度一般,但是细节非常多,整个编写过程思路要非常清晰,看懂题意,摸清规律和法则,然后利用代码复现过程即可。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
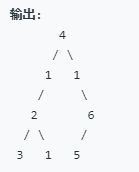
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int v, int d) {
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
queueQ,Pre,Next;
Q.push(root);
int level = 1;
//在第一层加入内容
if(d == 1)
{
TreeNode* NewHead = new TreeNode(v);
NewHead->left = root;
return NewHead;
}
while(Q.size())
{
int qsize = Q.size();
for(int i = 0;ileft) {Next.push(temp->left);}
if(temp->right) {Next.push(temp->right);}
}
if(temp->left) {Q.push(temp->left);}
if(temp->right) {Q.push(temp->right);}
}
level++;
if(Pre.size()) break;//找到了就跳出
}
// cout<left&&temp->left == Next.front()) //左子树存在
{NewLeft->left = Next.front();Next.pop();}
// else if()Next.pop();
// cout<right&&temp->right == Next.front())//右子树存在
{NewRight->right = Next.front();Next.pop();}
// else Next.pop();
temp->left = NewLeft;temp->right = NewRight;
}
return root;
}
}; 从题意我们可以看到,选择BFS较好理解也较好操作
我们要在第K层增加一行,有两个部分的内容需要我们做
(1):在第k-1层的非空结点,都创建值为v的左右子树,那么显然,我们需要得到k-1层的非空结点地址
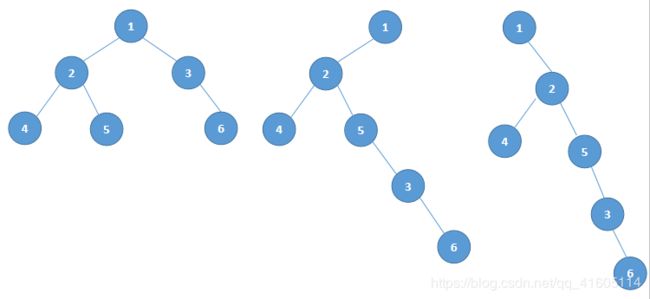
(2):原先的左子树,依旧是左子树,但是根结点变更,右子树也是一样的。我们看示例:
再看一个例子:输入 层数第三层,v= 1
对于两个操作部分的第一个部分,很好办,我们找到k-1行,保存即可,但是因为第二步需要用到原来树中第k行的内容,我们也进行保存
如上图所示,我们要在第三层增加,那么就要保存第二层和第三层的内容,具体程序如下:
while(Q.size())
{
int qsize = Q.size();
for(int i = 0;ileft) {Next.push(temp->left);}//保存k层的结点
if(temp->right) {Next.push(temp->right);}
}
if(temp->left) {Q.push(temp->left);}
if(temp->right) {Q.push(temp->right);}
}
level++;
if(Pre.size()) break;//找到了就跳出
} 做好了第一步,下面我们看第二步,增加一行,这部分代码如下:
while(Pre.size()||Next.size())
{
TreeNode* temp = Pre.front();Pre.pop(); //不会有null
//连接新层
TreeNode* NewLeft = new TreeNode(v);
TreeNode* NewRight = new TreeNode(v);
temp->left = NewLeft;temp->right = NewRight;
}那么我们还是需要知道,新结点和原树第k层如何连接
现在我们先判断原来树第k-1层子树的情况,左子树存在,那么就将其连接在新增层左孩子结点处
如果不存在那么就不需要管
注意:我们在BFS的时候,只保存了存在的第k层,此时队列里面,从左到右依次是存在的孩子结点,那么我们只需要判断原来这个部分有没有孩子结点,对接到新增层即可。
代码如下:
if(temp->left&&temp->left == Next.front()) //左子树存在
{NewLeft->left = Next.front();Next.pop();}
if(temp->right&&temp->right == Next.front())//右子树存在
{NewRight->right = Next.front();Next.pop();}
关于对称二叉树
101. 对称二叉树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/symmetric-tree/submissions/
面试题28. 对称的二叉树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/dui-cheng-de-er-cha-shu-lcof/
使用BFS当然可以,每层都比较数据即可,但是有点复杂了,如果使用深度优先遍历呢?
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return true;
return dfs(root->left, root->right);
}
private:
bool dfs(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2){
if(!root1 && !root2) return true;
if(!root1 || !root2) return false;
if(root1->val != root2->val) return false;
return dfs(root1->left, root2->right) && dfs(root1->right, root2->left);
}
};使用DFS就会非常讨巧了,对输入参数进行简单的修改即可。
那么下面就详细介绍一下DFS
199. 二叉树的右视图 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/
典型的对层序遍历的考察,我们保存每一行最好的答案即可。
class Solution {
public:
vector rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
//BFS
if(root == nullptr) return {};
vectorRes;
queueQ;
Q.push(root);
// Res.push_back();
while(Q.size())
{
int size = Q.size();
for(int i = 0;ileft) Q.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right) Q.push(temp->right);
if(i == size - 1) Res.push_back(temp->val);
}
}
return Res;
}
}; 如果是左视图呢?也很简单
改一下判断语句即可:
if(i == 0) Res.push_back(temp->val);2深度优先遍历(DFS)
其实在正式介绍DFS前,已经用了很对次的DFS了。
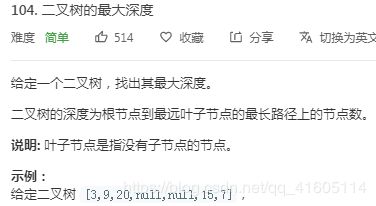
104. 二叉树的最大深度 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/submissions/
典型的深度优先遍历:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int Depth = 0;
return DFS(root,Depth);
}
int DFS(TreeNode* root,int Depth){
if(root == nullptr)
return Depth;
Depth++;
int leftD = DFS(root->left,Depth);
int rightD = DFS(root->right,Depth);
return max(leftD,rightD);
}
};110. 平衡二叉树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/submissions/
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
return true;
int Depth = 0;
int Result = DFS(root,Depth);
if(Result == -1)
return false;
return true;
}
int DFS(TreeNode* root,int Depth)
{
if(root == nullptr)
return Depth;
Depth++;
int Dleft = DFS(root->left,Depth);
int Dright = DFS(root->right,Depth);
if(Dleft == -1||Dright == -1)
return -1;
if(abs(Dleft-Dright)>1)
return -1;
return max(Dleft,Dright);
}
};面试题27. 二叉树的镜像 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-cha-shu-de-jing-xiang-lcof/
公共祖先
这个部分体现了深度遍历,根结点的回溯,这也是递归的特点,也体现了难点,如果将题目中的内容转变为代码。
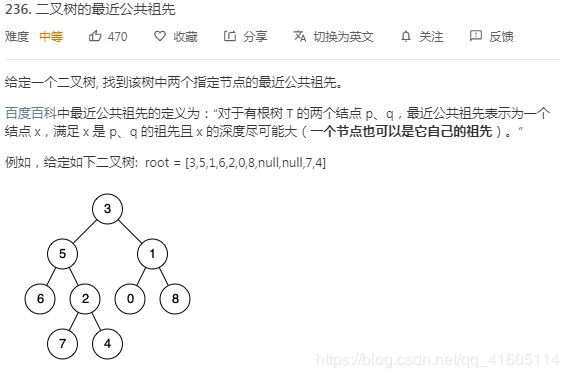
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
面试题68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-cha-shu-de-zui-jin-gong-gong-zu-xian-lcof/
面试题 04.08. 首个共同祖先 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/first-common-ancestor-lcci/submissions/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
if(root->val == p->val||root->val == q->val) return root;
TreeNode* Left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
TreeNode* Right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
if(Left&&Right) return root;
return Left?Left:Right;
}
};404. 左叶子之和 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/ 典型的DFS类型题目
关于左叶子结点的判断,还是需要注意这个细节的
if(root->left&&root->left->left == nullptr&&root->left->right == nullptr)稍有难度一点的DFS题目,如下:
572. 另一个树的子树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/
面试题 04.10. 检查子树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/check-subtree-lcci/submissions/
典型的DFS,注意调用自身时候传递的参数
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t) {
if(!s) return false;
return DFS(s,t)||isSubtree(s->left,t)||isSubtree(s->right,t);
}
bool DFS(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t){
if(!s&&!t) return true;
if(!s||!t) return false;
if(s->val == t->val) return DFS(s->left,t->left)&&DFS(s->right,t->right);
return false;
}
};面试题26. 树的子结构 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-de-zi-jie-gou-lcof/submissions/
此题比上面的同类型的题目,增加了难度,因为判断条件放宽了。
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubStructure(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
if(!A||!B)
return false;
return Jadge(A,B)||isSubStructure(A->left,B)||isSubStructure(A->right,B);
}
bool Jadge(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B){
if(!A&&!B) return true;
// if(!A||!B) return !B?true:false;
if(!A&&B) return false;
if(!B) return true;
if(A->val == B->val) return Jadge(A->left,B->left)&&Jadge(A->right,B->right);
else return false;
}
};872. 叶子相似的树:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/leaf-similar-trees/
513. 找树左下角的值 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/(DFS/BFS都是好办法)
508. 出现次数最多的子树元素和https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/most-frequent-subtree-sum/solution/si-lu-hou-xu-bian-li-qiu-ge-zi-shu-de-he-bing-cun-/(Hash&DFS)
面试题36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-cha-sou-suo-shu-yu-shuang-xiang-lian-biao-lcof/
中序遍历加hash
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
queue Index;
DFS(root,Index);
Node * pre = Index.front();
Node * frist = Index.front();
Index.pop();
Node * Cur;
while(!Index.empty())
{
Cur= Index.front();
Index.pop();
pre->right = Cur;
Cur->left = pre;
pre = Cur;
}
pre->right = frist;
frist->left = pre;
return frist;
}
void DFS(Node* root,queue&Index){
if(root == nullptr) return;
DFS(root->left,Index);
Index.push(root);
DFS(root->right,Index);
}
}; 3基础问题升级
3.1重构二叉树
此类型的题目,难点其实是找规律加上对vector的使用和理解,尤其是vector的构造函数。
面试题07. 重建二叉树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zhong-jian-er-cha-shu-lcof/
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/submissions/
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/
参考:链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zhong-jian-er-cha-shu-lcof/solution/cjian-dan-shi-xian-di-gui-by-theowu/

利用前序遍历,找到根结点,利用从中序遍历中找到左右子树,然后分割vector,之后直接递归即可。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector& preorder, vector& inorder) {
if(inorder.size() == 0) return nullptr;
vector::iterator division = find(inorder.begin(),inorder.end(),preorder[0]);
int dis = division - inorder.begin();
vector preLeft(preorder.begin()+1,preorder.begin()+1+dis);
vector inLeft(inorder.begin(),inorder.begin()+dis);
vector preright(preorder.begin()+1+dis,preorder.end());
vector inright(inorder.begin()+dis+1,inorder.end());
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
root->left = buildTree(preLeft,inLeft);
root->right = buildTree(preright,inright);
return root;
}
}; 606. 根据二叉树创建字符串 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-string-from-binary-tree/
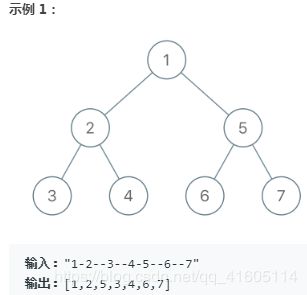
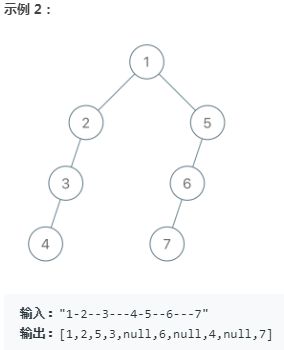
1028. 从先序遍历还原二叉树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/recover-a-tree-from-preorder-traversal/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* recoverFromPreorder(string S) {
int begin = 0;
return DFS(S,begin,0);
}
TreeNode* DFS(string S,int& begin,int pos)//begin表示本层元素的值,pos表示在第几层
{
if(begin>S.size()) return nullptr;
int val = Getnum(S,begin);//首先计算出结点的值
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(val);//赋值
//计算下一个元素的位置,看是否需要继续递归
int newpos = 0;
while(beginpos) //继续递归,在下一层
{
root->left = DFS(S,begin,newpos);//优先左子树
// 进入一段判断,判断我们是继续构建右子树
//此时因为左子树的递归,begin指向了下一个结点的值,我们需要计算该结点的层数
int backbegin = begin-1,backpos = 0;
while(backbegin>=0&&S[backbegin]=='-') {backpos++;backbegin--;}
//计算完层数之后,我们和当前比较,判断当前是不是根结点,所以pos+1
//如果是,那么就建立右子树,不是,那么我们继续返回,往上一层找,这个歌过程begin不变
if(backpos == pos+1) root->right = DFS(S,begin,backpos);
else root->right = nullptr;//继续往上找
}
else //在上一层,本层已经完成
{
root->right = nullptr;
root->left = nullptr;
}
return root;
}
//都是正数,不存在负数,但是存在多位数
int Getnum(string S,int& begin)
{
int Num = 0;
while(begin
LeetCode-树(解题技巧总结二——路径问题)
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41605114/article/details/105857839