高效程序有两个重要指标:速度,内存,移动app中内存比重要多一些,为此在速度相差不是很大的时候,优先考虑内存,container是一个重要部分,对此google对一些原java容器设计新的容器进行替换Map结构。在写程序时使用Map类大部份情况都会用到,尤其是HashMap使用频率相当高,使用HashMap会涉及一个要求key与value必须为对象类型,
而不能为基本类型,这就导致了本可以基本类型的数据必须转换为其对象包装类型(int->Integer,long->Long......)这就涉及到需要占用更多内存以及拆箱装箱频繁转换问题。
例如:Map
这里涉及一个引用类型计算问题,引用java规范;
在Java中,一个空Object对象的大小是8byte,这个大小只是保存堆中一个没有任何属性的对象的大小。
看下面语句:
Object ob = new Object();
这样在程序中完成了一个Java对象的生命,但是它所占的空间为:4byte+8byte。4byte是Java栈中保存引用的所需要的空间。而那8byte则是Java堆中对象的信息。
因为所有的Java非基本类型的对象都需要默认继承Object对象,因此不论什么样的Java对象,其大小都必须是大于8byte。
包装类型已经成为对象了,因此需要把他们作为对象来看待。包装类型的大小至少是12byte(声明一个空Object至少需要的空间),而且12byte没有包含任何有效信息,同时,因为Java对象分配内存时其大小是8的整数倍,因此一个基本类型包装类的大小至少是16byte。这个内存占用是很恐怖的,它是使用基本类型的N倍(N>2),有些类型的内存占用更是夸张(随便想下就知道了)。因此,可能的话应尽量少使用包装类。
为此google专门设计了当key为基本类型时的替换Map数据结构容器,在android.util包下,根据文档介绍如下
SparseArray -> map integer to Object
SparseBooleanArrays -> map integers to booleans
SparseIntArrays -> map integers to integers
SparseLongArrays -> map integers to longs
LongSparseArray -> map longs to Objects
可以看出key为integer时情况较多,原理是key存储在int[] mKeys数组内,value存储在对应的(int,long,object)[] mValues数组内,采用二分法计算索引位置
SparseArray实现
public class SparseArray implements Cloneable {
private static final Object DELETED = new Object();
private boolean mGarbage = false;
private int[] mKeys;//使用array存储int key
private Object[] mValues;//使用array存储泛型Value
private int mSize;
/**
* Creates a new SparseArray containing no mappings.
*/
public SparseArray() {
this(10);//默认容量10
}
public SparseArray(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0) {
mKeys = EmptyArray.INT;
mValues = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
mValues = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedObjectArray(initialCapacity);
mKeys = new int[mValues.length];
}
mSize = 0;
}
public E get(int key) {
return get(key, null);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E get(int key, E valueIfKeyNotFound) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);//使用二分查找查找key
if (i < 0 || mValues[i] == DELETED) {//没有找到key或者Value已经被deleted
return valueIfKeyNotFound;
} else {
return (E) mValues[i];
}
}
public void put(int key, E value) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);//二分查找key是否存在,如果没有找到时,这里返回的是-low,也就是待插入位置取反
if (i >= 0) {//存在直接替换value
mValues[i] = value;
} else {
i = ~i;//待插入位置
if (i < mSize && mValues[i] == DELETED) {//pos在size范围内,并且该pos被deleted直接赋值
mKeys[i] = key;
mValues[i] = value;
return;
}
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {//是否需要回收处理
gc();
// Search again because indices may have changed.
i = ~ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);//扩容key处理
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mValues, mSize, i, value);//扩容value处理
mSize++;
}
}
......
这里注意到一个Deleted标识,这个是什么呢?就是前面类的一个object成员变量,当执行delete,remove时value[i]被标记
public void delete(int key) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
if (mValues[i] != DELETED) {
mValues[i] = DELETED;
mGarbage = true;
}
}
}
public void removeAt(int index) {
if (mValues[index] != DELETED) {
mValues[index] = DELETED;
mGarbage = true;
}
}
这样标记的一个好处就是避免array频繁移动元素,对数据频繁的delete,removed,put操作时,在一定程度上可以提供效率,只有当执行gc时才进行回收处理
private void gc() {
int n = mSize;
int o = 0;
int[] keys = mKeys;
Object[] values = mValues;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Object val = values[i];
if (val != DELETED) {
if (i != o) {
keys[o] = keys[i];
values[o] = val;
values[i] = null;
}
o++;
}
}
mGarbage = false;
mSize = o;
// Log.e("SparseArray", "gc end with " + mSize);
}
对于常用的基本类型google已经有对应实现类,例如:SparseLongArray,SparseIntArray,SparseBooleanArray
对于key不是Integer,Long的基本类型情况,在api 19时可以使用ArrayMap,原理:与SparseArray类似处理,hash值存储在int []mHashes,value存储在Object[] mArray中,
ArrayMap实现:
public final class ArrayMap implements Map {
...
/**
* @hide Special immutable empty ArrayMap.
*/
public static final ArrayMap EMPTY = new ArrayMap(true);
...
/**
* Special hash array value that indicates the container is immutable.
*/
static final int[] EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS = new int[0];
int[] mHashes;//存储key的hashCode
Object[] mArray;//存储key(偶数索引存储key)与value(奇数索引存储value)
int mSize;
int indexOf(Object key, int hash) {//查找hash code索引位置
final int N = mSize;
// Important fast case: if nothing is in here, nothing to look for.
if (N == 0) {
return ~0;
}
int index = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mHashes, N, hash);//二分查找hash code的index
// If the hash code wasn't found, then we have no entry for this key.
if (index < 0) {//未查找到
return index;
}
// If the key at the returned index matches, that's what we want.
if (key.equals(mArray[index<<1])) {//查找到index,对应到mArray位置中指定的key index
return index;
}
// Search for a matching key after the index.
int end;
for (end = index + 1; end < N && mHashes[end] == hash; end++) {
if (key.equals(mArray[end << 1])) return end;
}
// Search for a matching key before the index.
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0 && mHashes[i] == hash; i--) {
if (key.equals(mArray[i << 1])) return i;
}
return ~end;
}
private void allocArrays(final int size) {
if (mHashes == EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("ArrayMap is immutable");
}
......
mHashes = new int[size];//指定hash array size
mArray = new Object[size<<1];//mArray大小为size x2,因为这里使用一个array即存储key,又存储value
}
public void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {//容量不足时扩容处理
if (mHashes.length < minimumCapacity) {
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(minimumCapacity);
if (mSize > 0) {
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, mSize);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, mSize<<1);
}
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, mSize);
}
}
@Override
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return indexOfKey(key) >= 0;
}
public int indexOfKey(Object key) {
return key == null ? indexOfNull() : indexOf(key, key.hashCode());
}
int indexOfValue(Object value) {//查找指定value的索引位置
final int N = mSize*2;
final Object[] array = mArray;
if (value == null) {//null分开查找,value存储在奇数位置,每次+2跳步
for (int i=1; i>1;
}
}
} else {
for (int i=1; i>1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
return indexOfValue(value) >= 0;
}
@Override
public V get(Object key) {
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
return index >= 0 ? (V)mArray[(index<<1)+1] : null;
}
@Override
public V remove(Object key) {
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
if (index >= 0) {
return removeAt(index);
}
return null;
}
public V removeAt(int index) {
final Object old = mArray[(index << 1) + 1];
if (mSize <= 1) {
// Now empty.
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: shrink from " + mHashes.length + " to 0");
freeArrays(mHashes, mArray, mSize);
mHashes = EmptyArray.INT;
mArray = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
mSize = 0;
} else {
if (mHashes.length > (BASE_SIZE*2) && mSize < mHashes.length/3) {//hash array长度>预定baseSize 2倍,元素个数小于3分之一时,进行容量缩减处理
// Shrunk enough to reduce size of arrays. We don't allow it to//减少内存占用,提供使用效率
// shrink smaller than (BASE_SIZE*2) to avoid flapping between
// that and BASE_SIZE.
final int n = mSize > (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (mSize + (mSize>>1)) : (BASE_SIZE*2);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: shrink from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n);
mSize--;
if (index > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: copy from 0-" + index + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, index << 1);
}
if (index < mSize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: copy from " + (index+1) + "-" + mSize
+ " to " + index);
System.arraycopy(ohashes, index + 1, mHashes, index, mSize - index);
System.arraycopy(oarray, (index + 1) << 1, mArray, index << 1,
(mSize - index) << 1);
}
} else {
mSize--;
if (index < mSize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: move " + (index+1) + "-" + mSize
+ " to " + index);
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index + 1, mHashes, index, mSize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, (index + 1) << 1, mArray, index << 1,
(mSize - index) << 1);
}
mArray[mSize << 1] = null;
mArray[(mSize << 1) + 1] = null;
}
}
return (V)old;
}
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
final int hash;
int index;//根据key为null,不为null两种方式查找index
if (key == null) {
hash = 0;
index = indexOfNull();
} else {
hash = key.hashCode();
index = indexOf(key, hash);
}
if (index >= 0) {//查找到已有key,则替换新值,返回旧值
index = (index<<1) + 1;
final V old = (V)mArray[index];
mArray[index] = value;
return old;
}
index = ~index;//等到插入位置
if (mSize >= mHashes.length) {//扩展array大小
final int n = mSize >= (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (mSize+(mSize>>1))
: (mSize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE*2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n);
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + mSize + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, mSize);
}
if (index < mSize) {//移位腾出指定位置空间,待插入位置
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: move " + index + "-" + (mSize-index)
+ " to " + (index+1));
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index, mHashes, index + 1, mSize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, index << 1, mArray, (index + 1) << 1, (mSize - index) << 1);
}
mHashes[index] = hash;
mArray[index<<1] = key;
mArray[(index<<1)+1] = value;
mSize++;
return null;
}
/**
* Special fast path for appending items to the end of the array without validation.
* The array must already be large enough to contain the item.
* @hide
*/
public void append(K key, V value) {//快速插入指定key-value,当array容量够大,元素较少时使用,去掉了扩容,处理使用抛异常替代
int index = mSize;//在最后一个元素位置后执行添加
final int hash = key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode();
if (index >= mHashes.length) {//hash array边界检测
throw new IllegalStateException("Array is full");
}
if (index > 0 && mHashes[index-1] > hash) {
//hash array采用升序排序存储,即前面hash code <后面元素,当插入元素<最后元素时,说明需要进行元素移动
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException("here");
e.fillInStackTrace();
Log.w(TAG, "New hash " + hash
+ " is before end of array hash " + mHashes[index-1]
+ " at index " + index + " key " + key, e);
put(key, value);//执行移动元素
return;
}
mSize = index+1;
mHashes[index] = hash;
index <<= 1;
mArray[index] = key;
mArray[index+1] = value;
}
ArraySet用来替换HashSet,实现与ArrayMap类似,只不过ArraySet实现Collection
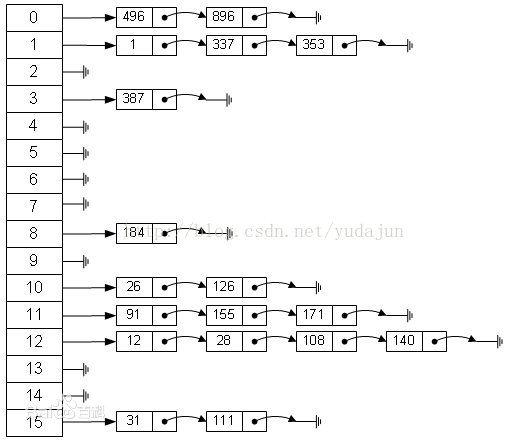
HashMap结构是以array存储链表的头结点,找到头结点后在进行遍历查找,如下图:
从图示中可以看出当HashMap扩容容量过多,元素较少时会产生内存使用不平衡,即浪费不少内存,而ArrayMap则不会有过多的内存浪费问题,
虽然效率比Hashmap低一些但是内存使用率有很大提高,采用时间换空间方式解决移动设备内存问题。
summary:
1,android中采用用时间换空间的方式,平衡移动设备内存问题而使用SparseArray,ArrayMap替换HashMap
2,SparseArray使用int[],为Integer类型key存储,Object[]为value即双数组一一对应的方式实现存储,替HashMap
3,当key为int类型value为reference object可以使用SparseArray,value为基本类型时使用使用SparsexxxArray,当key为其它引用类型时使用ArrayMap