跟同事合作前后端分离项目,自己对 WebApi 的很多知识不够全,虽说不必要学全栈,可是也要了解基础知识,才能合理设计接口、API,方便与前端交接。
晚上回到宿舍后,对 WebApi 的知识查漏补缺,主要补充了 WebAPi 的一些方法、特性等如何与前端契合,如何利用工具测试 API 、Axios 请求接口。
本文主要写 WebApi 前端请求数据到 API 、后端返回处理结果,不涉及登录、跨域请求、前端 UI 等。(难一点我不会了。。。看张队的公众号,篇篇都看不懂。。。)
前提:会一点点 VUE、会一点 Axios、会一点点 Asp.net Core。
工具:Visual Studio 2019(或者其它版本) + Visual Studio Code + Swagger +Postman
由于 Visual Studio 2019 写 ASP.NET Core 页面时,没有 Vue 的智能提示,所以需要使用 VSCode 来写前端页面。
本文 代码 已发布到 GitHub https://github.com/whuanle/CZGL.IKonwWebApi
一. 微软WebApi
1. 安装 Swagger
二. 数据绑定与获取
1,默认不加
2, [FromBody]
3, [FromForm]
4, [FromHeader]
5, [FromQuery]
6, [FromRoute]
7, [FromService]
三. action 特性方法
1, [Route]
2, [Bind]
3, [Consumes]、[Produces]
4, [HttpGet]、[HttpPost]、[HttpDelete]、[HttpPut]
四,返回类型
1, 查询备忘表
2, 返回的数据类型
3, 直接返回基元或复杂数据类型
4, IActionResult 类型
一. 微软WebApi
| 特性 | 绑定源 |
|---|---|
| [FromBody] | 请求正文 |
| [FromForm] | 请求正文中的表单数据 |
| [FromHeader] | 请求标头 |
| [FromQuery] | 请求查询字符串参数 |
| [FromRoute] | 当前请求中的路由数据 |
| [FromServices] | 作为操作参数插入的请求服务 |
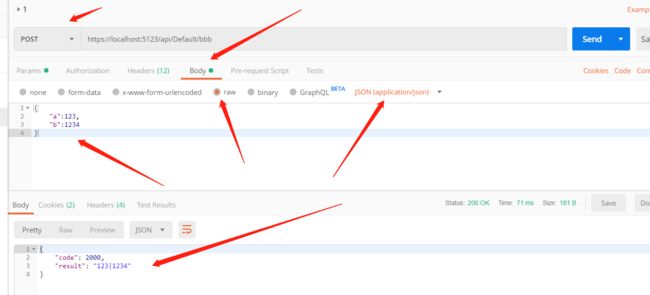
来一张 Postman 的图片:
HTTP 请求中,会携带很多参数,这些参数可以在前端设置,例如表单、Header、文件、Cookie、Session、Token等。
那么,上面的表格正是用来从 HTTP 请求中获取数据的 “方法” 或者说 “手段”。HttpContext 等对象不在本文讨论范围。
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc 命名空间提供很多用于配置Web API 控制器的行为和操作方法的属性:
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| [Route] | 指定控制器或操作的 URL 模式。 |
| [Bind] | 指定要包含的前缀和属性,以进行模型绑定。 |
| [Consumes] | 指定某个操作接受的数据类型。 |
| [Produces] | 指定某个操作返回的数据类型。 |
| [HttpGet] | 标识支持 HTTP GET 方法的操作。 |
| [HttpPost] | 标识支持 HTTP POST 方法的操作。 |
| ... ... ... | ... ... ... |
WebApi 应用
首先创建一个 Asp.Net Core MVC 应用,然后在 Controllers 目录添加一个 API 控制器 DefaultController.cs。(这里不创建 WebApi 而是 创建 MVC,通过 MVC 创建 API 控制器)。
创建后默认代码:
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class DefaultController : ControllerBase { }
1. 安装 Swagger
在 Nuget 中搜索 Swashbuckle.AspNetCore,或打开 程序包管理器控制台 -> 程序包管理器控制台 ,输入以下命令进行安装
Install-Package Swashbuckle.AspNetCore -Version 5.0.0-rc2
打开 Startup 文件,添加引用
using Microsoft.OpenApi.Models;
在 ConfigureServices 中添加服务,双引号文字内容随便改。
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "My API", Version = "v1" }); });
添加中间件
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseCookiePolicy(); // 添加下面的内容 app.UseSwagger(); app.UseSwaggerUI(c => { c.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "My API V1"); });
访问 /swagger 可以访问到 Swagger 的 UI 界面。
为了便于查看输出和固定端口,打开 Progarm,cs ,修改内容
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) => WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args) .UseUrls("https://*:5123") .UseStartup<Startup>();
不要使用 IIS 托管运行。
注意:本文全部使用 [HttpPost] ;全局使用 JsonResult 作为返回类型。
二. 数据绑定与获取
1,默认不加
直接写 action,不使用特性
[HttpPost("aaa")]
public async Task<JsonResult> AAA(int? a, int? b) { if (a == null || b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 2000, result = a + "|" + b }); }
打开 https://localhost:5123/swagger/index.html 查看 UI 界面 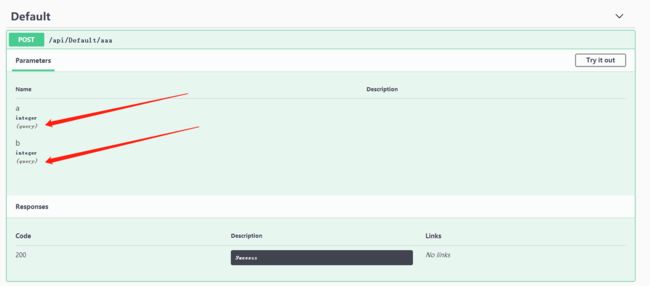
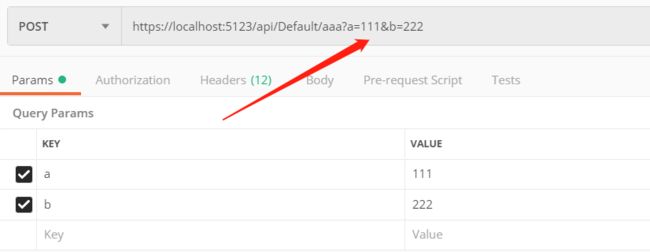
也就是说,创建一个 action ,什么都不加,默认是 query。
通过 Postman 提交数据、测试接口
对于 Query 的 action 来说, axios 的写法
postaaa: function () {
axios.post('/api/default/aaa?a=111&b=222' ) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) }
在网上查找资料时,发现有人说通过 params 添加数据也可以,不过笔者测试,貌似不行。
讲道理,别人可以,为啥我不行。。。
axios 代码:
postaaa: function () {
axios.post('/api/default/aaa', { params: { a: 123, b: 234 } } ) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) }
包括下面的,都试过了,不行。
axios.post('/api/default/aaa', {
a:1234,
b:1122
}
axios.post('/api/default/aaa', {
data:{
a:1234,
b:1122
}
}
把 [HttpPost] 改成 [HttpGet] ,则可以使用
axios.post('/api/default/aaa', {
params: { a: 123, b: 234 } } ... ...
提示:
... ...
.then(res => {
console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); })
.then 当请求成功时触发,请求失败时触发 catch 。res 是请求成功后返回的信息,res.data 是请求成功后服务器返回的信息。即是 action 处理数据后返回的信息。
在浏览器,按下 F12 打开控制台,点击 Console ,每次请求后,这里会打印请求结果和数据。
2, [FromBody]
官方文档解释:请求正文。[FromBody] 针对复杂类型参数进行推断。 [FromBody] 不适用于具有特殊含义的任何复杂的内置类型,如 IFormCollection 和 CancellationToken。 绑定源推理代码将忽略这些特殊类型。
算了,看得一头雾水,手动实际试试。
刚刚开始的时候,我这样使用:
public async Task<JsonResult> BBB([FromBody]int? a, [FromBody]int? b)
结果编译时就报错,提示只能使用一个 [FromBody],于是改成
[HttpPost("bbb")]
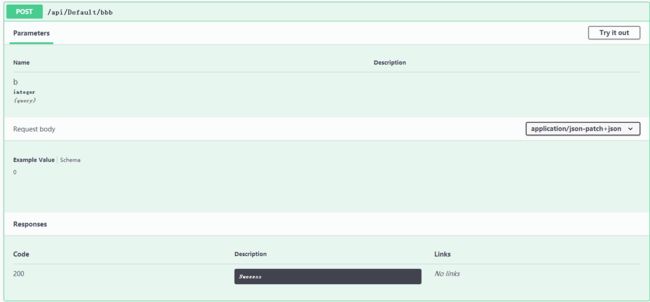
public async Task<JsonResult> BBB([FromBody]int? a, int? b) { if (a == null || b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 2000, result = a + "|" + b }); }
打开 Swagger UI 界面,刷新一下
从图片中发现,只有 b,没有 a,而且右上角有下拉框,说明了加 [FromBody] 是 json 上传。
那么说明 [FromBody] 修饰得应当是对象,而不是 字段。
修改程序如下:
// 增加一个类型
public class AppJson
{
public int? a { get; set; } public int? b { get; set; } } [HttpPost("bbb")] public async Task<JsonResult> BBB([FromBody]AppJson ss) { if (ss.a == null || ss.b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 2000, result = ss.a + "|" + ss.b }); }
再看看微软的文档:[FromBody] 针对复杂类型参数进行推断。,这下可理解了。。。
即是不应该对 int、string 等类型使用 [FromBody] ,而应该使用一个 复杂类型。
而且,一个 action 中,应该只能使用一个 [FromBody] 。
打开 Swagger 界面(有修改需要刷新下界面,下面不再赘述)。
这样才是我们要的结果嘛,前端提交的是 Json 对象。
用 Postman 测试下
证实了猜想,嘿嘿,嘿嘿嘿。
前端提交的是 Json 对象,遵循 Json 的格式规范,那么 [FromBody] 把它转为 Object 对象。
前端 axios 写法:
methods: {
postaaa: function () {
axios.post('/api/default/bbb', { "a": 4444, "b": 5555 }) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) } }
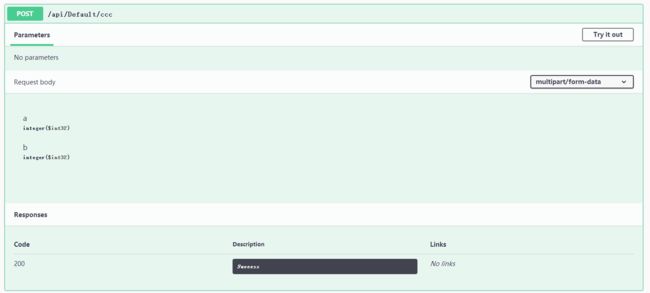
3, [FromForm]
[HttpPost("ccc")]
public async Task<JsonResult> CCC([FromForm]int? a, [FromForm]int? b) { if (a == null || b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = a + "|" + b }); }
当然,这样写也行,多个字段或者对象都可以
[HttpPost("ccc")]
public async Task<JsonResult> CCC([FromForm]AppJson ss) { if (ss.a == null || ss.b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = ss.a + "|" + ss.b }); }
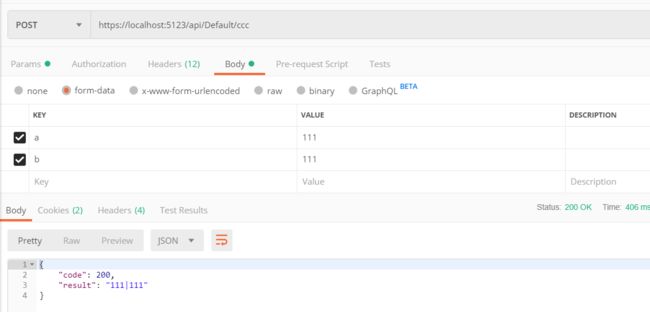
根据提示,使用 Postman 进行测试
事实上,这样也行 ↓
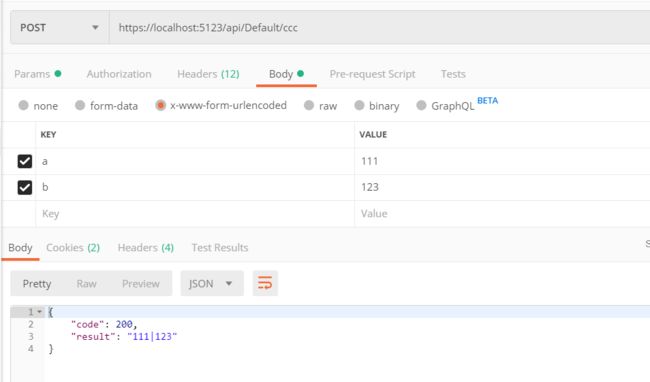
form-data 和 x-www.form-urlencoded 都是键值形式,文件 form-data 可以用来上传文件。具体的区别请自行查询。
axios 写法(把 Content-Type 字段修改成 form-data 或 x-www.form-urlencoded )
postccc: function () {
let fromData = new FormData() fromData.append('a', 111) fromData.append('b', 222) axios.post('/api/default/ccc', fromData, { headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' } }) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) }
4, [FromHeader]
[FromHeader] 不以表单形式上传,而是跟随 Header 传递参数。
[HttpPost("ddd")]
public async Task<JsonResult> DDD([FromHeader]int? a, [FromHeader]int? b) { if (a == null || b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = a + "|" + b }); }
axios 写法
postddd: function () {
axios.post('/api/default/ddd', {}, { headers: { a: 123, b: 133 } }) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) }
需要注意的是,headers 的参数,必须放在第三位。没有要提交的表单数据,第二位就使用 {} 代替。
params 跟随 url 一起在第一位,json 或表单数据等参数放在第二位,headers 放在第三位。
由于笔者对前端不太熟,这里有说错,麻烦大神评论指出啦。
5, [FromQuery]
前面已经说了,Action 参数不加修饰,默认就是 [FromQuery] ,参考第一小节。
有个地方需要记住, Action 参数不加修饰。默认就是 [FromQuery] ,有时几种参数并在一起放到 Action 里,会忽略掉,调试时忘记了,造成麻烦。
6, [FromRoute]
获取路由规则,这个跟前端上传的参数无关;跟 URL 可以说有关,又可以说无关。
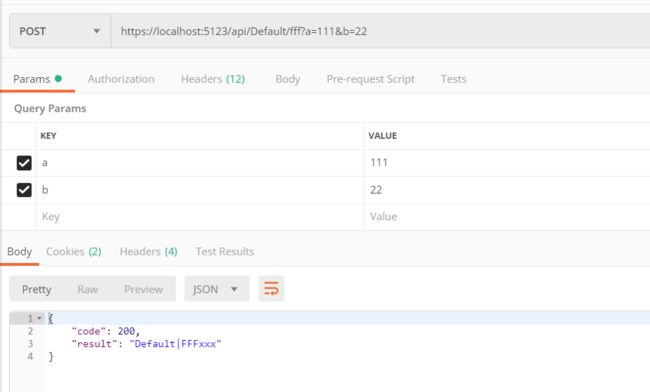
[HttpPost("fff")]
public async Task<JsonResult> FFFxxx(int a,int b, [FromRoute]string controller, [FromRoute]string action) { // 这里就不处理 a和 b了 return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = controller+"|"+action }); }
[FromRoute] 是根据路由模板获取的,上面 API 的两个参数和路由模板的名称是对应的:
[FromRoute]string controller, [FromRoute]string action
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute( name: "default", template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); });
当然,还可以加个 [FromRoute]int? id
[FromRoute] 和 [FromQuery] 区别
以此 URL 为例
https://localhost:5123/api/Default/fff?a=111&b=22
Route 会查到 controller = Default ,action = FFFxxx 。查询到的是代码里的真实名称。
Query 会查询到 a = 111 和 b = 22
那么,如果路由规则里,不在 URL 里出现呢?
[HttpPost("/ooo")]
public async Task<JsonResult> FFFooo(int a, int b, [FromRoute]string controller, [FromRoute]string action) { // 这里就不处理 a和 b了 return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = controller + "|" + action }); }
那么,访问地址变成 https://localhost:5123/ooo
通过 Postman ,测试
说明了 [FromRoute] 获取的是代码里的 Controller 和 Action 名称,跟 URL 无关,根据测试结果推断跟路由表规则也无关。
7, [FromService]
参考 https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/mvc/controllers/dependency-injection?view=aspnetcore-2.2
这个是与依赖注入容器有关,跟 URL 、路由等无关。
新建一个接口、一个类
public interface ITest
{
string GGG { get; } } public class Test : ITest { public string GGG { get { return DateTime.Now.ToLongDateString(); } } }
在 ConfigureServices 中 注入
services.AddSingleton<ITest, Test>();
在 DefaultController 中,创建构造函数,然后
private readonly ITest ggg;
public DefaultController(ITest ttt) { ggg = ttt; }
添加一个 API
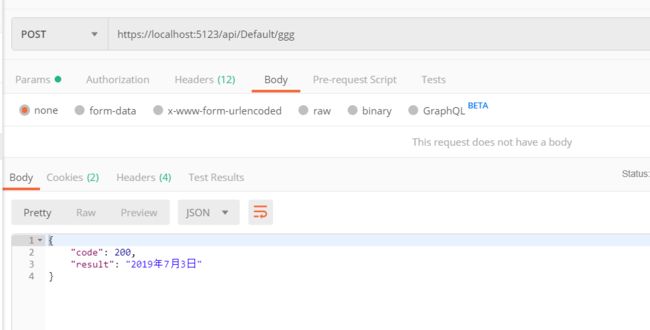
[HttpPost("ggg")]
public async Task<JsonResult> GGG([FromServices]ITest t) { return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = t.GGG }); }
访问时,什么参数都不需要加,直接访问此 API 即可。
[FromService] 跟后端的代码有关,跟 Controller 、Action 、URL、表单数据等无关。
小结:
特性可以几种放在一起用,不过尽量每个 API 的参数只使用一种特性。
优先取值 Form > Route > Query。
IFromFile 由于文件的上传,本文就不谈这个了。
关于数据绑定,更详细的内容请参考:
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/mvc/models/model-binding?view=aspnetcore-2.2
三. action 特性方法
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc 命名空间提供可用于配置 Web API 控制器的行为和操作方法的属性。
下表是针对于 Controller 或 Action 的特性.
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| [Route] | 指定控制器或操作的 URL 模式。 |
| [Bind] | 指定要包含的前缀和属性,以进行模型绑定。 |
| [Consumes] | 指定某个操作接受的数据类型。 |
| [Produces] | 指定某个操作返回的数据类型。 |
| [HttpGet] | 标识支持 HTTP GET 方法的操作。 |
| ... | ... |
下面使用这些属性来指定 Controller 或 Action 接受的 HTTP 方法、返回的数据类型或状态代码。
1, [Route]
在微软文档中,把这个特性称为 属性路由 ,定义:属性路由使用一组属性将操作直接映射到路由模板。
请教了大神,大神解释说,ASP.NET Core 有路由规则表,路由表是全局性、唯一性的,在程序运行时,会把所有路由规则收集起来。
MVC 应用中设置路由的方法有多种,例如
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute( name: "default", template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); });
[Route("Home/Index")]
public IActionResult Index() { return View(); }
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class DefaultController : ControllerBase { }
路由是全局唯一的,可以通过不同形式使用,但是规则不能发生冲突,程序会在编译时把路由表收集起来。
根据笔者经验,发生冲突,应该就是在编译阶段直接报错了。(注:笔者不敢确定)
关于路由,请参考 :
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/mvc/controllers/routing?view=aspnetcore-2.2#token-replacement-in-route-templates-controller-action-area
2, [Bind]
笔者知道这个是绑定模型的,但是对原理不太清楚。ASP.NET Core 自动生成的可读写的 Controller ,默认都是使用 [Bind] 来绑定数据。
文档定义:用于对复杂类型的模型绑定。
有下面几种相近的特性:
[BindRequired][BindNever][Bind]
微软文档提示:如果发布的表单数据是值的源,则这些属性会影响模型绑定。
就是说,上面的特性是针对类、接口等复杂类型(下面统称模型),对于 int、string 这些类型,可能出毛病。
[BindRequired] 、[BindNever] 只能应用于模型的属性,如
public class TestB
{
[BindNever]
public int ID { get; set; } [BindRequired] public string Name { get; set; } }
但是 [BindRequired] 、[BindNever] 不在讨论范围内,这里只说 [Bind]。
[Bind] 用于类或方法(Controller、Action),指定模型绑定中应包含的模型属性。
在微软官方文档,对于[Bind] 的解释:
[Bind]属性可用于防止“创建”方案中的过多发布情况 。 由于排除的属性设置为 NULL 或默认值,而不是保持不变,因此它在编辑方案中无法很好地工作;- 因为
Bind特性将清除未在 某个 参数中列出的字段中的任何以前存在的数据。
一脸懵逼。
下面是我的踩坑过程,不感兴趣的话直接跳过吧。笔记笔记,记得当然是自己觉得要记的哈哈哈。
新建一个类
public class TestBind
{
public string A { get; set; } public string B { get; set; } public string C { get; set; } public string D { get; set; } public string E { get; set; } public string F { get; set; } public string G { get; set; } }
新建 API
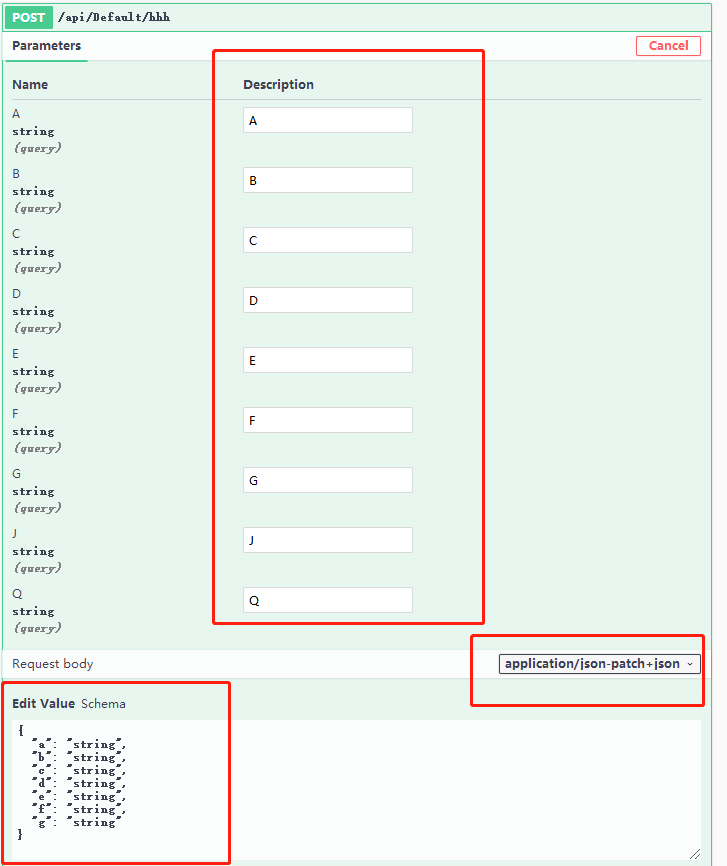
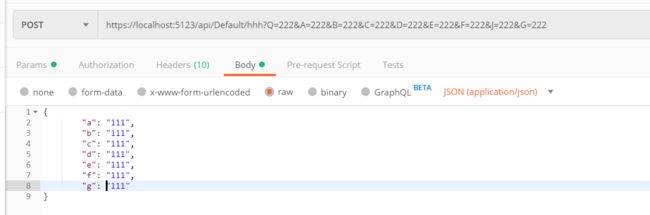
[HttpPost("hhh")]
public async Task<JsonResult> HHH([Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test) { if (ModelState.IsValid == true) return new JsonResult(test); return new JsonResult(new { Code = 0, Result = "验证不通过" }); }
使用 Postman 进行,测试,发现必须使用 Json 形式,才能访问到这个 Action ,其它方式会直接 返回 错误。
{
"errors": {
"": [ "A non-empty request body is required." ] }, "title": "One or more validation errors occurred.", "status": 400, "traceId": "0HLO03IFQFTQU:00000007" }
通过两次 Postman 进行测试
经过测试,我猜想
ModelState.IsValid 跟模型里的验证规则有关系,跟 [Bind] 没关系(尽管用于测试的 TestB 类中没有写验证规则),因此不能使用 ModelState.IsValid 验证 [Bind] 是否符合规则。
Action 的参数:[Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test,刚开始的时候我以为请求的数据中必须包含 A、B、C。
测试后发现不是。。。再认真看了文档 :因为 Bind 特性将清除未在 某个 参数中列出的字段中的任何以前存在的数据。
我修改一下:
[HttpPost("hhh")]
public async Task<JsonResult> HHH( string D, string E,[Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test) { if (ModelState.IsValid == true) return new JsonResult(new { data1 = test, data2 = D, data3 = E }); return new JsonResult(new { Code = 0, Result = "验证不通过" }); }
参数变成了 string D, string E,[Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test
使用 Swagger 进行测试:
{
"data1": {
"a": "string", "b": "string", "c": "string", "d": "string", "e": "string", "f": "string", "g": "string" }, "data2": null, "data3": null }
改成
[HttpPost("hhh")]
public async Task<JsonResult> HHH([Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test, string J, string Q) { if (ModelState.IsValid == true) return new JsonResult(new { data1 = test, data2 = J, data3 = Q }); return new JsonResult(new { Code = 0, Result = "验证不通过" }); }
返回结果
{
"data1": {
"a": "string", "b": "string", "c": "string", "d": "string", "e": "string", "f": "string", "g": "string" }, "data2": null, "data3": null }
文档中对 [Bind] 描述最多的是:防止过多发布。
通过上面的测试,首先肯定的是一个 Action 里,有多个参数 如
[Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test, string D, string E string J, string Q。
注意,下面的结论是错的!
那么 D、E 因为于 除了 Test, J、Q就会无效,通过百度,[Bind] 修饰的 Action ,前端请求的数据只有 Test 里面的数据有效,其它 Query等形式一并上传的数据都会失效,防止黑客在提交数据时掺杂其它特殊参数。应该就是这样理解吧。
上面是一开始我的结论,直到多次测试,我发现是错的。
可是有一个地方不明白,
[Bind("A,B,C")]
[Bind("A,B,C,D,E,F,G")]
这两者的区别是是什么。还是没搞清楚。
突然想到 Query,当字段没有使用特性修饰时,默认为 Query 。
最终踩坑测试代码
模型类
public class TestBind
{
public string A { get; set; } public string B { get; set; } public string C { get; set; } public string D { get; set; } public string E { get; set; } public string F { get; set; } public string G { get; set; } }
Action
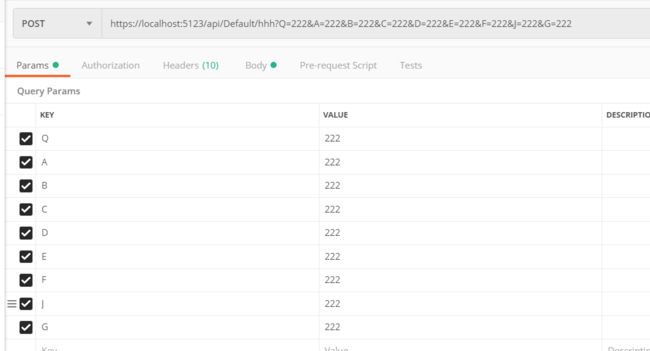
[HttpPost("hhh")]
public async Task<JsonResult> HHH( string A, string B, string E, string F, string G, [Bind("A,B,C,D")] TestBind test, string C, string D, string J, string Q) { if (ModelState.IsValid == true) return new JsonResult(new { data1 = test, dataA = A, dataB = B, dataC = C, dataD = D, dataE = E, dataF = F, dataG = G, dataJ = J, dataQ = Q }); return new JsonResult(new { Code = 0, Result = "验证不通过" }); }
Swagger 测试
Postman 测试
{
"data1": {
"a": "111", "b": "111", "c": "111", "d": "111", "e": "111", "f": "111", "g": "111" }, "dataA": "222", "dataB": "222", "dataC": "222", "dataD": "222", "dataE": "222", "dataF": "222", "dataG": "222", "dataJ": "222", "dataQ": "222" }
再在 Swagger 或 Postman ,换着法子尝试各种不同组合的输入。
我懵逼了。试了半天试不出什么。
实在不理解 [Bind] 里,“防止过多发布” 是什么意思
[Bind("A,B,C")]
[Bind("A,B,C,D,E,F,G")]
这两者的区别是是什么。还是没搞清楚。算了,不踩了。
我再到 stackoverflow 提问题,地址 https://stackoverflow.com/questions/56884876/asp-net-core-bind-how-to-use-it/56885153#56885153
获得一个回答:
What's the difference between [Bind("A,B,C")] and [Bind("A,B,C,D,E,F,G")]?
The former tells the model binder to include only the properties of TestBind named A, B and C. The latter tells the model binder to include those same properties plus D, E, F and G.
Are you testing by posting data for all properties of your model? You should notice that the values you post for the excluded properties are not bound.
算了,嘿嘿,测试不出来,放弃。
3, [Consumes]、[Produces]
[Consumes("application/json")]
[Produces("application/json")] [Produces("application/xml")] [Produces("text/html")] ... ...
目前只了解到 [Consumes]、[Produces] 是筛选器,用来表示 Controller 或 Action 所能接受的数据类型。大概就是像下面这样使用:
[Consumes("application/json")]
[Produces("application/json")]
public class DefaultTestController : ControllerBase
{
}
但是如何实际应用呢?我找了很久,都没有找到什么结果。在 stackoverflow 找到一个回答:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41462509/adding-the-produces-filter-globally-in-asp-net-core
4, [HttpGet]、[HttpPost]、[HttpDelete]、[HttpPut]
修饰 Action ,用来标识这个 Action 能够通过什么方式访问、访问名称。
例如:
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class DefaultController : ControllerBase { [HttpPost("aaa")] public async Task<JsonResult> AAA(int? a, int? b) { if (a == null | b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = a + "|" + b }); } }
访问地址 https://localhost:5123/api/Default/aaa
使用时,会受到 Controller 和 Action 路由的影响。
但 本身亦可控制路由。以上面的控制器为例
[HttpPost("aaa")] //相对路径
访问地址 xxx:xxx/api/Default/aaa
[HttpPost("/aaa")] //绝对路径
访问地址 xxx:xxx/aaa
四,返回类型
1, 查询备忘表
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc 命名空间中,包含控制 MVC 的各种操作方法和类型,笔者从命名空间中抽出与 MVC 或 API 返回类型有关的类型,生成表格:
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| AcceptedAtActionResult | An ActionResult that returns a Accepted (202) response with a Location header. |
| AcceptedAtRouteResult | An ActionResult that returns a Accepted (202) response with a Location header. |
| AcceptedResult | An ActionResult that returns an Accepted (202) response with a Location header. |
| AcceptVerbsAttribute | Specifies what HTTP methods an action supports. |
| ActionResult | A default implementation of IActionResult. |
| ActionResult | A type that wraps either an TValue instance or an ActionResult. |
| BadRequestObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Bad Request (400) response. |
| BadRequestResult | A StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a Bad Request (400) response. |
| ChallengeResult | An ActionResult that on execution invokes AuthenticationManager.ChallengeAsync. |
| ConflictObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Conflict (409) response. |
| ConflictResult | A StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a Conflict (409) response. |
| ContentResult | |
| CreatedAtActionResult | An ActionResult that returns a Created (201) response with a Location header. |
| CreatedAtRouteResult | An ActionResult that returns a Created (201) response with a Location header. |
| CreatedResult | An ActionResult that returns a Created (201) response with a Location header. |
| EmptyResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will do nothing. |
| FileContentResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will write a binary file to the response. |
| FileResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will write a file as the response. |
| FileStreamResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will write a file from a stream to the response. |
| ForbidResult | An ActionResult that on execution invokes AuthenticationManager.ForbidAsync. |
| JsonResult | An action result which formats the given object as JSON. |
| LocalRedirectResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302), Moved Permanently (301), Temporary Redirect (307), or Permanent Redirect (308) response with a Location header to the supplied local URL. |
| NotFoundObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Not Found (404) response. |
| NotFoundResult | Represents an StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a Not Found (404) response. |
| OkObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed performs content negotiation, formats the entity body, and will produce a Status200OK response if negotiation and formatting succeed. |
| OkResult | An StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce an empty Status200OKresponse. |
| PartialViewResult | Represents an ActionResult that renders a partial view to the response. |
| PhysicalFileResult | A FileResult on execution will write a file from disk to the response using mechanisms provided by the host. |
| RedirectResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302), Moved Permanently (301), Temporary Redirect (307), or Permanent Redirect (308) response with a Location header to the supplied URL. |
| RedirectToActionResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302), Moved Permanently (301), Temporary Redirect (307), or Permanent Redirect (308) response with a Location header. Targets a controller action. |
| RedirectToPageResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302) or Moved Permanently (301) response with a Location header. Targets a registered route. |
| RedirectToRouteResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302), Moved Permanently (301), Temporary Redirect (307), or Permanent Redirect (308) response with a Location header. Targets a registered route. |
| SignInResult | An ActionResult that on execution invokes AuthenticationManager.SignInAsync. |
| SignOutResult | An ActionResult that on execution invokes AuthenticationManager.SignOutAsync. |
| StatusCodeResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will produce an HTTP response with the given response status code. |
| UnauthorizedObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Unauthorized (401) response. |
| UnauthorizedResult | Represents an UnauthorizedResult that when executed will produce an Unauthorized (401) response. |
| UnprocessableEntityObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Unprocessable Entity (422) response. |
| UnprocessableEntityResult | A StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a Unprocessable Entity (422) response. |
| UnsupportedMediaTypeResult | A StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a UnsupportedMediaType (415) response. |
| ViewComponentResult | An IActionResult which renders a view component to the response. |
| ViewResult | Represents an ActionResult that renders a view to the response. |
| VirtualFileResult | A FileResult that on execution writes the file specified using a virtual path to the response using mechanisms provided by the host. |
留着写 WebApi 时查询备忘嘿嘿。
那些类型主要继承的两个接口:
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| IActionResult | Defines a contract that represents the result of an action method. |
| IViewComponentResult | Result type of a ViewComponent. |
注意的是,上面有些是抽象类,例如 FileResult,而 FileStreamResult 实现了 FileResult 。有些类是继承关系。
2, 返回的数据类型
- 特定类型
- IActionResult 类型
- ActionResult 类型
Action 的 return ,返回的数据类型必定是上面三种。
3, 直接返回基元或复杂数据类型
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<Product> Get()
{
return _repository.GetProducts(); }
4, IActionResult 类型
响应状态码、Json、重定向、URL 跳转等,属于 IActionResult。
MVC 的 Controller 与 API 的 Controller 有很多相同的地方,亦有很多不同的地方。
API 的 Controller 继承 ControllerBase
MVC 的 Controller 继承 Controller而 Controller 继承
Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IFilterMetadata, IAsyncActionFilter, IDisposable
API 里的 Controller 是最原始的。
API 里的 返回类型需要实例化, new 一下; MVC 里的返回类型,“不需要实例化”。
当然,有些例如 FileResult 是抽象类,不能被实例化。
API:
[HttpGet("returnaaa")]
public async Task<IActionResult> ReturnAAA() { return new ViewResult(); return new JsonResult(new { code="test"}); return new RedirectToActionResult("DefaultController","ReturnAAA",""); return new NoContentResult("666"); return new NotFoundResult(); ... }
MVC
public async Task<IActionResult> Test()
{
return View(); return Json(new { code = "test" }); return RedirectToAction("DefaultController", "ReturnAAA", ""); return NoContent("666"); return NotFound(); ... }
MVC 中,Action 默认是 [HttpGet],不加也可以被访问到;
而 API 的Action,不加 [Httpxxx],则默认不能被访问到。