- 【解决 NumPy meshgrid 函数的 ‘indexing‘ 参数错误】
weixin_48705841
报错numpy深度学习transformer计算机视觉
解决NumPymeshgrid函数的'indexing'参数错误解决NumPymeshgrid函数的'indexing'参数错误问题描述解决NumPymeshgrid函数的‘indexing’参数错误最近在使用NumPy的meshgrid函数时,遇到了一个奇怪的错误:“TypeError:meshgrid()gotanunexpectedkeywordargument‘indexing’”。经过一
- 用opencv生成视频流,然后用rtsp进行拉流显示
hunter206206
pythonopencvpython人工智能
importcv2importnumpyasnpimporttimefromdatetimeimportdatetimeimportgiimportsocketimportsysgi.require_version('Gst','1.0')try:gi.require_version('GstRtspServer','1.0')fromgi.repositoryimportGst,GLib,Gst
- android备忘录app设计er图,图、流程图、ER图怎么画及常见画图工具(流程图文章汇总)...
weixin_39714164
跟我一起写Makefile---变量(嵌套变量+追加变量+overrid+多行变量+环境变量+目标变量+模式变量)目录(?)[-]使用变量一变量的基础二变量中的变量三变量高级用法四追加变量值五override指示符六多行变量七环境变量八目标变量九模式变量使用变量————在Makefil...UVA10537TheToll!Rev
- 多张图片读入后组成一个矩阵。怎么读取图片,可以让其读入的形式是:ndarray(a,b,c)分别的含义:a为多少张图片,b*c为图片大小
洛水微寒
矩阵线性代数
不显示通道数:要将多张图片读取为一个NumPy数组(ndarray),其中a表示图片数量,b和c分别表示每张图片的高度和宽度(不显示通道数),你可以使用Python中的PIL(Pillow)库和NumPy库。下面是一个示例代码,展示了如何实现这一点:代码示例importnumpyasnpfromPILimportImageimportosdefload_images_from_folder(fol
- Python中判断列表是否包含某个元素的方法
五月天的尾巴
python判断列表是否包含元素
文章目录1、成员运算符in和notin2、使用count()方法3、使用any()函数4、使用set转换5、使用numpy库6、使用any()和生成器表达式7、使用index()方法8、使用itertools.chain()函数9、使用collections.Counter类10、使用pandas库以下整理几种判断列表中是否包含某个元素的方法。以下代码基于python2.7执行。1、成员运算符in
- 2024微短剧行业生态洞察报告汇总PDF洞察(附原数据表)
数据挖掘深度学习
原文链接:https://tecdat.cn/?p=39072本报告合集洞察从多个维度全面解读微短剧行业。在行业发展层面,市场规模与用户规模双增长,创造大量高收入就业岗位并带动产业链升级。内容创作上,精品化、品牌化趋势凸显,题材走向多元以满足不同受众需求。商业生态中,多种商业模式并存,端原生微短剧崭露头角,品牌营销与电商布局拓展盈利空间。行业价值体现于AI赋能、大小屏融合、助力地方经济与信息传播等
- 174所地信遥感测绘等专业考研报考学校及专业参考汇总表分享
新中地GIS开发老师
考研arcgisGISGIS开发地信地理信息科学大学生
地信遥感测绘等地理学考研和想要考研到地信遥感专业的小伙伴绝对不能错过的宝藏资料!!!表格中包含了各个高校的名称、所在省市、是否自主划线、所属院系、专业、总分以及各科目的分数要求等。
- 跨平台物联网漏洞挖掘算法评估框架设计与实现项目概述与调整
XLYcmy
漏洞挖掘网络安全漏洞挖掘物联网跨架构静态检测项目报告二进制
1.1项目研究目的与创新点复述1.1.1.研究目的本研究的研究目的主要有以下两个:1、基于此领域的相关方法,通过实验找出各个架构的最优方法2、通过设计实验,比较跨架构解决方案和各架构最优方法组合解决方案在函数识别、漏洞挖掘上的优劣性1.1.2.创新点1、通过构建数据集和设计实验,本研究汇总性地得到各个架构下物联网漏洞挖掘静态方法的最优方法2、在以往的研究中,只是做了某个架构内或者跨架构方法之间的比
- NocoBase 本周更新汇总:详情区块联动规则
汇总一周产品更新日志,最新发布可以前往我们的博客查看。NocoBase目前更新包括的版本更新包括三个分支:main,next和develop。main:截止目前最稳定的版本,推荐安装此版本。next:包含即将发布的新功能,经过初步测试的版本,可能存在部分已知或未知问题。主要面向测试用户,用于收集反馈和进一步优化功能。适合愿意提前体验新功能并提供反馈的测试用户。develop:开发中的版本,包含最新
- NocoBase 本周更新汇总:优化移动端
汇总一周产品更新日志,最新发布可以前往我们的博客查看。NocoBase目前更新包括的版本更新包括三个分支:main,next和develop。main:截止目前最稳定的版本,推荐安装此版本。next:包含即将发布的新功能,经过初步测试的版本,可能存在部分已知或未知问题。主要面向测试用户,用于收集反馈和进一步优化功能。适合愿意提前体验新功能并提供反馈的测试用户。develop:开发中的版本,包含最新
- python代码转exe
xuaman
pythonpythonexe编译
1.打开cmd控制台,跳转之python目录下的scripts.2.输入:pipinstallnumpy3.第二步成功后,输入:pipinstallPyInstaller4.第三步完成后,输入:pyinstaller-Fpy文件路径5.第四步完成后,在当前目录下出现,dist文件夹,里面就是编译成功的同名exe文件如有问题可以留言。
- sklearn.datasets
SilenceHell
机器学习实战学习笔记
fromsklearn.datasets.california_housingimportfetch_california_housinghousing=fetch_california_housing()type(housing)Out[21]:sklearn.utils.Bunchtype(housing.data)Out[23]:numpy.ndarrayhousing.data[0]Out
- 岭回归预测PM2.5
qianjinwang
python
#-*-coding:utf-8-*-#@File:demo2.py#@Author:CJH#@Date:2019/4/9#@Software:PyCharm#@Desc:天气PM2.5预测importcsvimportnumpyasnpfromnumpyimport*importmatplotlib.pyplotaspltfromsklearnimportlinear_modeltraining
- HarmonyOS 开发实践——基于设置应用的应用权限、通知设置跳转
六号嘉宾
鸿蒙开发移动开发HarmonyOSharmonyos架构ui鸿蒙鸿蒙系统移动开发鸿蒙开发
往期学习笔录:鸿蒙(HarmonyOS)北向开发知识点记录~鸿蒙(OpenHarmony)南向开发保姆级知识点汇总~鸿蒙应用开发与鸿蒙系统开发哪个更有前景?嵌入式开发适不适合做鸿蒙南向开发?看完这篇你就了解了~对于大前端开发来说,转鸿蒙开发究竟是福还是祸?鸿蒙岗位需求突增!移动端、PC端、IoT到底该怎么选?记录一场鸿蒙开发岗位面试经历~持续更新中……场景描述引导用户跳转到系统设置页进行权限,通知
- python爬虫——pandas的简单使用
张謹礧
python爬虫+可视化python网络爬虫pythonpandas爬虫
pandas作为爬虫中最重要的包之一,我们要想学好爬虫,就必须要深入了解pandas直接上代码importpandasaspdimportnumpyasnpdata=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(16).reshape((4,4)),index=['a','b','c','d'],#如果不写列索引默认为0,1,2,3columns=['a','b','c','d'])print(d
- transformer模型代码
地瓜不是呱
学习笔记transformer深度学习pytorch
importnumpyasnpimporttorchimporttorch.nnasnnimporttorch.optimasoptimimportmatplotlib.pyplotaspltimportmathdefmake_batch(sentences):input_batch=[[src_vocab[n]forninsentences[0].split()]]output_batch=[[
- 自动化办公python脚本_Python自动化办公
weixin_39834281
自动化办公python脚本
在公司购买的OA系统上,很多功能都是软件商开发好的,如果有什么自定义的需求,也很难实现。现实情况下需要将一个工单的各类信息汇总整理为一份Excel,看似简单的需求,却需要在OA系统上反复点击多次,人工汇总。本章我们看看如何使用Python爬虫帮同事解决这个问题的。点击工单号之后才可以看到更多信息一、技术路线requests_html二、环境准备fromrequests_htmlimportHTML
- hive电影数据分析系统 Springboot协同过滤-余弦函数推荐系统 爬虫2万+数据 大屏数据展示 + [手把手视频教程 和 开发文档]
QQ-1305637939
毕业设计大数据毕设计算机毕业设计hivespringboot爬虫
hive电影数据分析Springboot协同过滤-余弦函数推荐系统爬虫2万+数据大屏数据展示+[手把手视频教程和开发文档]【功能介绍】1.java爬取【豆瓣电影】网站中电影数据,保存为data.csv文件,数据量2万+2.data.csv上传到hadoop集群环境3.MR数据清洗data.csv4.Hive汇总处理,将Hive处理的结果数据保存到本地Mysql数据库中5.Springboot+Vu
- hadoop电影数据分析系统 Springboot协同过滤-余弦函数推荐系统 爬虫2万+数据 大屏数据展示 + [手把手视频教程 和 开发文档]
QQ-1305637939
计算机毕业设计毕业设计大数据毕设hadoopspringboot爬虫
全套视频教程全套开发文档hadoop电影数据分析系统Springboot协同过滤-余弦函数推荐系统爬虫2万+数据大屏数据展示【Hadoop项目】1.java爬取【豆瓣电影】网站中电影数据,保存为data.csv文件,数据量2万+2.data.csv上传到hadoop集群环境3.data.csv数据清洗4.MR数据汇总处理,将Reduce的结果数据保存到本地Mysql数据库中5.Springboot
- spark电影数据分析系统 Springboot协同过滤-余弦函数推荐系统 爬虫2万+数据 大屏数据展示 + [手把手视频教程 和 开发文档]
QQ-1305637939
毕业设计大数据毕设计算机毕业设计sparkspringboot爬虫大数据电影推荐电影分析
spark电影数据分析系统Springboot协同过滤-余弦函数推荐系统爬虫2万+数据大屏数据展示+[手把手视频教程和开发文档【功能介绍】1.java爬取【豆瓣电影】网站中电影数据,保存为data.csv文件,数据量2万+2.data.csv上传到hadoop集群环境3.MR数据清洗data.csv4.Spark汇总处理,将Spark处理的结果数据保存到本地Mysql数据库中5.Springboo
- 大数据分析专业毕业设计最新最全选题精华汇总--持续更新中⑤
源码空间站11
pythondjango大数据分析数据可视化hadoophive大数据分析毕设
目录前言开题指导建议更多精选选题选题帮助最后前言大家好,这里是源码空间站学长大数据分析专业毕业设计毕设专题!大四是整个大学期间最忙碌的时光,一边要忙着准备考研、考公、考教资或者实习为毕业后面临的升学就业做准备,一边要为毕业设计耗费大量精力。学长给大家整理了大数据分析专业最新精选选题,如遇选题困难或选题有任何疑问,都可以问学长哦(见文末)!以下是学长精心整理的一些选题:21.基于Hadoop和Spa
- NumPy学习第十课:一文通俗了解NumPy中的数学函数
HappyAcmen
Numpy基础知识学习numpy学习pythonpycharm开发语言
前言导读在前面NumPy的学习过程当中,我们知道NumPy库是一个特别擅长处理大型矩阵或者说存储大型数据的这么一个库,与Python自身相比较在处理数据的时候更加的高效,所以我们在数学中常见到的计算函数,NumPy库中基本上也都已经涵盖了。而且已经封装好了很多的函数,我们在实际的使用过程当中,只需要引入NumPy库,并调用相应的函数方法就可以了,非常的便捷。这一节我们就先来了解了解NumPy中的数
- 关于sklearn.svm.SVC与.NuSVC的区别以及参数介绍
_Magic
机器学习实战withpython
0.区别SVC与NuSVC是类似的方法,但是接受稍微不同的参数集合并具有不同的数学公式,并且NuSVC可以使用参数来控制支持向量的个数,以下代码默认的是多分类1.SVC#coding:utf-8fromsklearnimportsvmfromnumpyimport*X=array([[0],[1],[2],[3]])y=array([0,1,2,3])clf=svm.SVC()clf.fit(X,
- 计算机网络基础知识点简记
UV Youth
计算机网络网络
OSI七层网络模型TCP/IP四层网络模型模型图解IP地址与子网划分基础概念IPV4与IPV6的区别子网划分的目的子网掩码的使用CIDR表示法路由器与交换机TCP与UDP协议HTTP与HTTPS协议DNS域名系统网络攻击与防御机制网络安全协议网络性能优化云计算基础
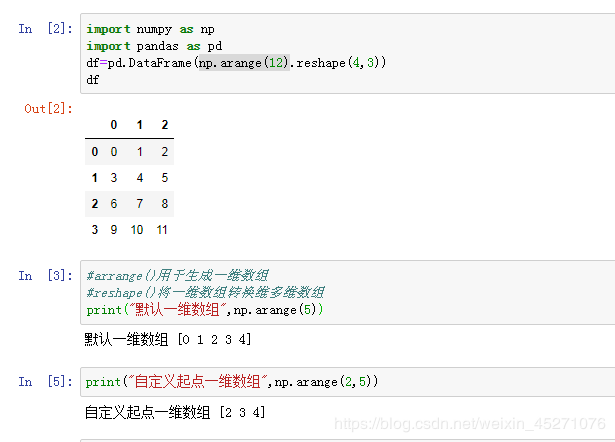
- Numpy基础01(Jupyter基本用法/Ndarray创建与基本操作)
XYX的Blog
数据分析与可视化numpyjupyter
内容一:Jupyter开发环境IPython是一个增强型的Python交互式解释器,提供了自动补全、命令历史、魔法命令等功能。它支持与操作系统命令交互、内联绘图和多语言扩展,并可与JupyterNotebook集成,适用于数据分析和科学计算。IPython还支持远程访问、包管理和插件扩展,是一个功能强大且灵活的开发工具。JupyterNotebook是IPython的开发环境。1.1Jupyter
- python封装成exe文件
wenangou
python
这篇文章主要介绍了一个有趣的事情,具有一定借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下。希望大家阅读完这篇文章后大有收获,下面让小编带着大家一起了解一下。Python打包exe文件方法汇总【4种】Python作为解释型语言,发布即公开源码,虽然是提倡开源但是有些时候就是忍不住想打包成exe,不仅仅是为了对代码进行加密,而是为了跨平台。防止有些没有安装py环境的电脑无法运行软件小神猪。目录对python代码打包成
- vscode开发stm32的编译环境配置教程
智驾
汽车电子软件stm32vscode单片机编译环境
文章目录1.背景2.配置步骤2.1.vscode插件安装2.2.新建工程2.3.配置编译环境2.3.1.芯片支持2.3.2.编译器选择2.3.3.CPU类型2.3.4.硬件浮点选项2.3.5.使用自定义的链接脚本2.3.6.RAM/FLASH布局2.3.7.构建器选项2.4.编译3.问题汇总3.1.浮点编译开关3.2.MicroLIB编译参考:1.背景想在vscode中开发STM32,本文主要描述
- Python_线性插值
胡小记
python
1、语法解释线性插值主要用到的是numpy中的interp函数interp(x,xp,fp,left=None,right=None,period=None)其中x为要插值点的横坐标,xp为x的坐标值(必须是递增),fp为y的坐标值left是可选择参数,如果x小于xp,则会默认返回xp[0]对应的fp值,right同理。period可设定横坐标的周期,该选项打开时,则忽略left和right。具体
- Hadoop 常用命令
ZenPower
hadoop大数据分布式
查看指定目录下的文件及文件夹hadoopfs-ls/user/hive/warehouse/查看指定目录下的文件及文件夹大小#文件大小(单位Byte)hadoopfs-du/user/hive/warehouse#文件大小(单位人性化)hadoopfs-du-h/user/hive/warehouse#文件大小(只显示汇总)hadoopfs-du-s/user/hive/warehouse删除指定
- hadoop常用命令汇总
m0_67402026
javajava后端
1、查看目录下的文件列表:hadoopfs–ls[文件目录]hadoopfs-ls-h/lance2、将本机文件夹存储至hadoop上:hadoopfs–put[本机目录][hadoop目录]hadoopfs-putlance/3、在hadoop指定目录内创建新目录:hadoopfs–mkdir[目录]hadoopfs-mkdir/lance4、在hadoop指定目录下新建一个文件,使用touch
- eclipse maven
IXHONG
eclipse
eclipse中使用maven插件的时候,运行run as maven build的时候报错
-Dmaven.multiModuleProjectDirectory system propery is not set. Check $M2_HOME environment variable and mvn script match.
可以设一个环境变量M2_HOME指
- timer cancel方法的一个小实例
alleni123
多线程timer
package com.lj.timer;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class MyTimer extends TimerTask
{
private int a;
private Timer timer;
pub
- MySQL数据库在Linux下的安装
ducklsl
mysql
1.建好一个专门放置MySQL的目录
/mysql/db数据库目录
/mysql/data数据库数据文件目录
2.配置用户,添加专门的MySQL管理用户
>groupadd mysql ----添加用户组
>useradd -g mysql mysql ----在mysql用户组中添加一个mysql用户
3.配置,生成并安装MySQL
>cmake -D
- spring------>>cvc-elt.1: Cannot find the declaration of element
Array_06
springbean
将--------
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3
- maven发布第三方jar的一些问题
cugfy
maven
maven中发布 第三方jar到nexus仓库使用的是 deploy:deploy-file命令
有许多参数,具体可查看
http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-deploy-plugin/deploy-file-mojo.html
以下是一个例子:
mvn deploy:deploy-file -DgroupId=xpp3
- MYSQL下载及安装
357029540
mysql
好久没有去安装过MYSQL,今天自己在安装完MYSQL过后用navicat for mysql去厕测试链接的时候出现了10061的问题,因为的的MYSQL是最新版本为5.6.24,所以下载的文件夹里没有my.ini文件,所以在网上找了很多方法还是没有找到怎么解决问题,最后看到了一篇百度经验里有这个的介绍,按照其步骤也完成了安装,在这里给大家分享下这个链接的地址
- ios TableView cell的布局
张亚雄
tableview
cell.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:[imageArray objectAtIndex:[indexPath row]]];
CGSize itemSize = CGSizeMake(60, 50);
&nbs
- Java编码转义
adminjun
java编码转义
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
/**
* 转换字符串的编码
*/
public class ChangeCharset {
/** 7位ASCII字符,也叫作ISO646-US、Unicode字符集的基本拉丁块 */
public static final Strin
- Tomcat 配置和spring
aijuans
spring
简介
Tomcat启动时,先找系统变量CATALINA_BASE,如果没有,则找CATALINA_HOME。然后找这个变量所指的目录下的conf文件夹,从中读取配置文件。最重要的配置文件:server.xml 。要配置tomcat,基本上了解server.xml,context.xml和web.xml。
Server.xml -- tomcat主
- Java打印当前目录下的所有子目录和文件
ayaoxinchao
递归File
其实这个没啥技术含量,大湿们不要操笑哦,只是做一个简单的记录,简单用了一下递归算法。
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author Perlin
* @date 2014-6-30
*/
public class PrintDirectory {
public static void printDirectory(File f
- linux安装mysql出现libs报冲突解决
BigBird2012
linux
linux安装mysql出现libs报冲突解决
安装mysql出现
file /usr/share/mysql/ukrainian/errmsg.sys from install of MySQL-server-5.5.33-1.linux2.6.i386 conflicts with file from package mysql-libs-5.1.61-4.el6.i686
- jedis连接池使用实例
bijian1013
redisjedis连接池jedis
实例代码:
package com.bijian.study;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoo
- 关于朋友
bingyingao
朋友兴趣爱好维持
成为朋友的必要条件:
志相同,道不合,可以成为朋友。譬如马云、周星驰一个是商人,一个是影星,可谓道不同,但都很有梦想,都要在各自领域里做到最好,当他们遇到一起,互相欣赏,可以畅谈两个小时。
志不同,道相合,也可以成为朋友。譬如有时候看到两个一个成绩很好每次考试争做第一,一个成绩很差的同学是好朋友。他们志向不相同,但他
- 【Spark七十九】Spark RDD API一
bit1129
spark
aggregate
package spark.examples.rddapi
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
//测试RDD的aggregate方法
object AggregateTest {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val conf = new Spar
- ktap 0.1 released
bookjovi
kerneltracing
Dear,
I'm pleased to announce that ktap release v0.1, this is the first official
release of ktap project, it is expected that this release is not fully
functional or very stable and we welcome bu
- 能保存Properties文件注释的Properties工具类
BrokenDreams
properties
今天遇到一个小需求:由于java.util.Properties读取属性文件时会忽略注释,当写回去的时候,注释都没了。恰好一个项目中的配置文件会在部署后被某个Java程序修改一下,但修改了之后注释全没了,可能会给以后的参数调整带来困难。所以要解决这个问题。
&nb
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-外观模式-Facade
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
/*
* 百度百科的定义:
* Facade(外观)模式为子系统中的各类(或结构与方法)提供一个简明一致的界面,
* 隐藏子系统的复杂性,使子系统更加容易使用。他是为子系统中的一组接口所提供的一个一致的界面
*
* 可简单地
- After Effects教程收集
cherishLC
After Effects
1、中文入门
http://study.163.com/course/courseMain.htm?courseId=730009
2、videocopilot英文入门教程(中文字幕)
http://www.youku.com/playlist_show/id_17893193.html
英文原址:
http://www.videocopilot.net/basic/
素
- Linux Apache 安装过程
crabdave
apache
Linux Apache 安装过程
下载新版本:
apr-1.4.2.tar.gz(下载网站:http://apr.apache.org/download.cgi)
apr-util-1.3.9.tar.gz(下载网站:http://apr.apache.org/download.cgi)
httpd-2.2.15.tar.gz(下载网站:http://httpd.apac
- Shell学习 之 变量赋值和引用
daizj
shell变量引用赋值
本文转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/papam/articles/1548679.html
Shell编程中,使用变量无需事先声明,同时变量名的命名须遵循如下规则:
首个字符必须为字母(a-z,A-Z)
中间不能有空格,可以使用下划线(_)
不能使用标点符号
不能使用bash里的关键字(可用help命令查看保留关键字)
需要给变量赋值时,可以这么写:
- Java SE 第一讲(Java SE入门、JDK的下载与安装、第一个Java程序、Java程序的编译与执行)
dcj3sjt126com
javajdk
Java SE 第一讲:
Java SE:Java Standard Edition
Java ME: Java Mobile Edition
Java EE:Java Enterprise Edition
Java是由Sun公司推出的(今年初被Oracle公司收购)。
收购价格:74亿美金
J2SE、J2ME、J2EE
JDK:Java Development
- YII给用户登录加上验证码
dcj3sjt126com
yii
1、在SiteController中添加如下代码:
/**
* Declares class-based actions.
*/
public function actions() {
return array(
// captcha action renders the CAPTCHA image displ
- Lucene使用说明
dyy_gusi
Lucenesearch分词器
Lucene使用说明
1、lucene简介
1.1、什么是lucene
Lucene是一个全文搜索框架,而不是应用产品。因此它并不像baidu或者googleDesktop那种拿来就能用,它只是提供了一种工具让你能实现这些产品和功能。
1.2、lucene能做什么
要回答这个问题,先要了解lucene的本质。实际
- 学习编程并不难,做到以下几点即可!
gcq511120594
数据结构编程算法
不论你是想自己设计游戏,还是开发iPhone或安卓手机上的应用,还是仅仅为了娱乐,学习编程语言都是一条必经之路。编程语言种类繁多,用途各 异,然而一旦掌握其中之一,其他的也就迎刃而解。作为初学者,你可能要先从Java或HTML开始学,一旦掌握了一门编程语言,你就发挥无穷的想象,开发 各种神奇的软件啦。
1、确定目标
学习编程语言既充满乐趣,又充满挑战。有些花费多年时间学习一门编程语言的大学生到
- Java面试十问之三:Java与C++内存回收机制的差别
HNUlanwei
javaC++finalize()堆栈内存回收
大家知道, Java 除了那 8 种基本类型以外,其他都是对象类型(又称为引用类型)的数据。 JVM 会把程序创建的对象存放在堆空间中,那什么又是堆空间呢?其实,堆( Heap)是一个运行时的数据存储区,从它可以分配大小各异的空间。一般,运行时的数据存储区有堆( Heap)和堆栈( Stack),所以要先看它们里面可以分配哪些类型的对象实体,然后才知道如何均衡使用这两种存储区。一般来说,栈中存放的
- 第二章 Nginx+Lua开发入门
jinnianshilongnian
nginxlua
Nginx入门
本文目的是学习Nginx+Lua开发,对于Nginx基本知识可以参考如下文章:
nginx启动、关闭、重启
http://www.cnblogs.com/derekchen/archive/2011/02/17/1957209.html
agentzh 的 Nginx 教程
http://openresty.org/download/agentzh-nginx-tutor
- MongoDB windows安装 基本命令
liyonghui160com
windows安装
安装目录:
D:\MongoDB\
新建目录
D:\MongoDB\data\db
4.启动进城:
cd D:\MongoDB\bin
mongod -dbpath D:\MongoDB\data\db
&n
- Linux下通过源码编译安装程序
pda158
linux
一、程序的组成部分 Linux下程序大都是由以下几部分组成: 二进制文件:也就是可以运行的程序文件 库文件:就是通常我们见到的lib目录下的文件 配置文件:这个不必多说,都知道 帮助文档:通常是我们在linux下用man命令查看的命令的文档
二、linux下程序的存放目录 linux程序的存放目录大致有三个地方: /etc, /b
- WEB开发编程的职业生涯4个阶段
shw3588
编程Web工作生活
觉得自己什么都会
2007年从学校毕业,凭借自己原创的ASP毕业设计,以为自己很厉害似的,信心满满去东莞找工作,找面试成功率确实很高,只是工资不高,但依旧无法磨灭那过分的自信,那时候什么考勤系统、什么OA系统、什么ERP,什么都觉得有信心,这样的生涯大概持续了约一年。
根本不是自己想的那样
2008年开始接触很多工作相关的东西,发现太多东西自己根本不会,都需要去学,不管是asp还是js,
- 遭遇jsonp同域下变作post请求的坑
vb2005xu
jsonp同域post
今天迁移一个站点时遇到一个坑爹问题,同一个jsonp接口在跨域时都能调用成功,但是在同域下调用虽然成功,但是数据却有问题. 此处贴出我的后端代码片段
$mi_id = htmlspecialchars(trim($_GET['mi_id ']));
$mi_cv = htmlspecialchars(trim($_GET['mi_cv ']));
贴出我前端代码片段:
$.aj

 在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述