Java集合类详解
集合类存放于java.util包下,主要有三种:Set(集),List(列表包含Queue),Map(映射)。
差异点:
Collections 这个类是集合的一个工具类(Arrays也是集合下的工具类),用于存放多个静态方法,供我们使用集合的时候直接调用。
1 collection接口:
colletion是集合List,Set,Queqe的最基本的接口。
collection接口依赖Iterator接口
1.1 List
List接口继承Collection接口
1.1.1 ArrayList
继承关系:
继承自AbstractList抽象类;实现List,RandomAccess(可随机访问),Cloneable,Serializable接口。
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return true (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//判断是否需要扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//添加新的元素
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
特征:
1,排列有序,可重复;
2,底层使用数组实现;
3,查询速度快,增删速度慢;
4,线程不安全;
5,当容量不足时,ArrayList是当前容量*1.5+1。Size为0的List的底层数组,在初始add元素的时候设置初始容量是10。
为什么线程不安全?
查看源码,在add添加元素的时候,其实是分两步执行的
1,调用ensureCapacityInternal()方法,来判断当前的数组是否需要扩容
2,新增元素
在多线程的程序中,多个线程同时操作某个数组,就可能会出现数组越界的情况。
1.1.2 Vector
继承关系:
继承自AbstractList抽象类;实现List,RandomAccess(可随机访问),Cloneable,Serializable接口。
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this Vector
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
特征:
1,排列有序,可重复;
2,底层使用数组实现;
3,查询速度快,增删速度慢;
4,线程安全,效率低;
5,当容量不足时,Vector是当前容量*2。Size为0的List的底层数组,在初始add元素的时候设置初始容量是10。
为什么Vector的线程是安全的?
通过分析源码,我们看到Vector在add新元素的时候,也是分两步 1,判断是否需要扩容;2,新增元素。只不过,它所有add元素,remove元素的的方法上都有 synchronized 关键字
1.1.3 LinkedList
继承关系:
继承自AbstractSequentialList抽象类;实现List,Deque(提供了操作队列的方法),Cloneable,Serializable接口。
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
特征:
1,排列有序,可重复;
2,基于双向链表实现(JDK1.7/8 之后取消了循环,修改为双向链表);
3,查询速度慢,增删快;
4,线程不安全。
1.2 SET
Set继承Collection接口
1.2.1 HashSet
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty linked hash set 构造新的空链接哈希集
* This package private constructor is only used by LinkedHashSet. 此包私有构造函数仅由LinkedHashSet使用
**/
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
继承关系:
继承自AbstractSet抽象类;实现Set,Cloneable,Serializable接口
特征:
1,排列无序,不可重复(对象是否重复,是自己定义的,重写equals和hashCode方法);
2,底层使用的是Hash表实现,内部是HashMap;
3,存储速度快;
4,一个 hashCode 位置上可以存放多个元素。
HashSet重写equals和hashcode方法
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description HashSet重写equals和hashcode方法
**/
class Student {
private Integer code;
private String name;
public Student(){}
public Student(Integer code, String name) {
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"code=" + code +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写equals方法
**/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(o==null){
return false;
}else if (this == o){//是否与当前对象相同
return true;
} else if(o instanceof Student){//是否与当前对象类相同
Student student = (Student) o;
if((student.getCode()).equals(code)){//code相同,认定为是同一对象
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写hashcode方法
**/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (code==null) ? 0 :code.hashCode();
}
}
1.2.2 TreeSet
interface NavigableMap<K,V> extends SortedMap<K,V>
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
继承关系:
继承AbstractSet抽象类;实现NavigableSet,Cloneable,Serializable接口
特征:
1,底层使用二叉树实现,内部是TreeMap;
2,不可重复(对象是否重复,是自己定义的,重写equals和hashCode方法);
3,排序存储;
4,需要保存的对象实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo方法;或者在对TreeSet进行实例化的时候,在构造函数中 通过匿名内部类 重写其中的compare方法。
TreeSet示例
/**
* @ClassName TreeSetTest
* @Description TreeSet排序测试
* @Author Johann
**/
public class TreeSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1,TreeSet使用1 对象没有实现Comparable接口,需要在TreeSet的构造函数中新增匿名内部类Comparator,重新compare方法
Set<Student> studentSet = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
if(o1.getCode() > o2.getCode()){
return 1;
}else if (o1.getCode() < o2.getCode()){
return -1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
});
studentSet.add(new Student(112,"zyh112"));
studentSet.add(new Student(112,"zyhcopy112"));
studentSet.add(new Student(111,"zyh111"));
studentSet.add(new Student(113,"zyh113"));
System.out.println(studentSet);
// 2,TreeSet使用2 对象实现了Comparable接口,重写compareTo方法。无需在TreeSet的构造函数中新增匿名内部类
Set<student2> student2Set = new TreeSet<student2>();
student2Set.add(new student2(312,"zyh312"));
student2Set.add(new student2(312,"zyhcopy312"));
student2Set.add(new student2(311,"zyh311"));
student2Set.add(new student2(313,"zyh313"));
System.out.println(student2Set);
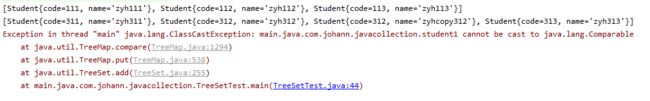
//3, TreeSet不能使用实现Comparator接口的对象。报异常:student1 cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable
Set<student1> student1Set = new TreeSet<student1>();
student1Set.add(new student1(212,"zyh212"));
student1Set.add(new student1(212,"zyhcpoy212"));
student1Set.add(new student1(211,"zyh211"));
student1Set.add(new student1(213,"zyh213"));
System.out.println(student1Set);
}
}
/**
* 待使用的普通对象
*/
class Student {
private Integer code;
private String name;
public Student(){}
public Student(Integer code, String name) {
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"code=" + code +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写equals方法
**/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(o==null){
return false;
}else if (this == o){//是否与当前对象相同
return true;
} else if(o instanceof Student){//是否与当前对象类相同
Student student = (Student) o;
if((student.getCode()).equals(code)){//code相同,认定为是同一对象
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写hashcode方法
**/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (code==null) ? 0 :code.hashCode();
}
}
/**
* 实现Comparator接口的对象
*/
class student1 implements Comparator<student1> {
private Integer code;
private String name;
public student1(){}
public student1(Integer code, String name) {
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"code=" + code +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写equals方法
**/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(o==null){
return false;
}else if (this == o){//是否与当前对象相同
return true;
} else if(o instanceof Student){//是否与当前对象类相同
Student student = (Student) o;
if((student.getCode()).equals(code)){//code相同,认定为是同一对象
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写hashcode方法
**/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (code==null) ? 0 :code.hashCode();
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写compare方法
**/
@Override
public int compare(student1 o1, student1 o2) {
if(o1.getCode() > o2.getCode()){
return 1;
}else if (o1.getCode() < o2.getCode()){
return -1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
}
/**
* 实现Comparable接口的对象
*/
class student2 implements Comparable<student2>{
private Integer code;
private String name;
public student2(){}
public student2(Integer code, String name) {
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"code=" + code +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写equals方法
**/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(o==null){
return false;
}else if (this == o){//是否与当前对象相同
return true;
} else if(o instanceof Student){//是否与当前对象类相同
Student student = (Student) o;
if((student.getCode()).equals(code)){//code相同,认定为是同一对象
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写hashcode方法
**/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (code==null) ? 0 :code.hashCode();
}
/**
* @Author Johann
* @Description 重写compareTo方法
**/
@Override
public int compareTo(student2 o) {
if(code > o.getCode()){
return 1;
}else if (code < o.getCode()){
return -1;
}else {
//return 0;
return name.compareTo(o.name);
}
}
}
通过上述TreeSet示例,我们可以发现以下几点:
1,TreeSet需要保存的对象实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo方法,而不能保存实现Comparator接口的对象。
2,我们发现,即使student2重写了hashcode和equals方法,但是在TreeSet中,依然加入了重复元素。
为什么呢?
请注意student2类重写的compareTo方法:如果code相同,则继续比较name。在使用TreeSet的时候,要注意重写的compareTo方法是否与重写的hashcode,equals方法不一致。
1.2.3 LinkedHashSet
public LinkedHashSet() {
super(16, .75f, true);
}
/**
* LinkedHashSet继承自HashSet,该方法即使HashSet中,LinkedHashSet的专用构造函数。
* Constructs a new, empty linked hash set 构造新的空链哈希Set
* This package private constructor is only used by LinkedHashSet. 此包私有构造函数仅由LinkedHashSet使用
**/
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
继承关系:
继承自HashSet类;实现Set,Cloneable,Serializable接口
特征:
1,采用Hash表存储,不可重复。保证元素的唯一(哈希表),哈希表是真正存储数据的地方;
2,存储有序(底层有一个链接表),链表记录着存储数据的顺序(插入顺序);
3,线程不安全,效率高;
理解区分TreeSet和LinkedHashSet的“有序”
1,TreeSet是根据重写的compareTo方法,对Set内部的集合进行排序,来实现Set“有序”。
2,LinkedHashSet是根据内部链表记录插入顺序,来实现Set“有序”
1.3 Queue
队列,与List和Set同级别,都继承自Collection接口。
1,什么是队列?
队列与栈是相对的一种数据结构。只允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表。栈的特点是后进先出,而队列的特点是先进先出。
2,Queue的实现
2.1,没有实现的阻塞接口的:
实现了java.util.Queue接口和java.util.AbstractQueue接口
内置的不阻塞队列: PriorityQueue 和 ConcurrentLinkedQueue
PriorityQueue 和 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 类在 Collection Framework 中加入两个具体集合实现。
2.1.1,PriorityQueue又叫做优先级队列,保存队列元素的顺序不是按照及加入队列的顺序,而是按照队列元素的大小进行重新排序。
加入到 Queue 中的元素根据它们的天然排序(通过其 java.util.Comparable实现)或者根据传递给构造函数的 java.util.Comparator 实现来定位。
2.1.2,ConcurrentLinkedQueue 是基于链接节点的、线程安全的队列。并发访问不需要同步。因为它在队列的尾部添加元素并从头部删除它们,所以只要不需要知道队列的大小,
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 对公共集合的共享访问就可以工作得很好。收集关于队列大小的信息会很慢,需要遍历队列。
2.2,实现阻塞接口的:
java.util.concurrent 中加入了 BlockingQueue 接口和五个阻塞队列类。它实质上就是一种带有一点扭曲的 FIFO 数据结构。不是立即从队列中添加或者删除元素,
线程执行操作阻塞,直到有空间或者元素可用。
2.2.1,ArrayBlockingQueue :一个由数组支持的有界队列。
2.2.2,LinkedBlockingQueue :一个由链接节点支持的可选有界队列。
2.2.3,PriorityBlockingQueue :一个由优先级堆支持的无界优先级队列。
2.2.4,DelayQueue :一个由优先级堆支持的、基于时间的调度队列。
2.2.5,SynchronousQueue :一个利用 BlockingQueue 接口的简单聚集(rendezvous)机制。
3,总结:
当 Deque 当做 Queue队列使用时(FIFO),添加元素是添加到队尾,删除时删除的是头部元素
Deque 也能当Stack栈用(LIFO)。这时入栈、出栈元素都是在双端队列的头部进行。
插一嘴:Stack过于古老,并且实现地非常不好,因此现在基本已经不用了,可以直接用Deque来代替Stack进行栈操作。
ArrayDeque不是线程安全的。 当作为栈使用时,性能比Stack好;当作为队列使用时,性能比LinkedList好。
使用阻塞队列实现一个生产者消费者模式
/**
* 使用阻塞队列实现一个生产者消费者模式
*/
public class BlockingQueueTest {
/**
定义装苹果的篮子
*/
public static class Basket{
// 篮子,能够容纳3个苹果
BlockingQueue<String> basket = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(3);
// 生产苹果,放入篮子
public void produce() throws InterruptedException{
// put方法放入一个苹果,若basket满了,等到basket有位置
basket.put("An apple");
}
// 消费苹果,从篮子中取走
public String consume() throws InterruptedException{
// get方法取出一个苹果,若basket为空,等到basket有苹果为止
String apple = basket.take();
return apple;
}
public int getAppleNumber(){
return basket.size();
}
}
// 测试方法
public static void testBasket() {
// 建立一个装苹果的篮子
final Basket basket = new Basket();
// 定义苹果生产者
class Producer implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
// 生产苹果
System.out.println("生产者准备生产苹果:"
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
basket.produce();
System.out.println("生产者生产苹果完毕:"
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("生产完后有苹果:"+basket.getAppleNumber()+"个");
// 休眠300ms
Thread.sleep(300);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
}
}
}
// 定义苹果消费者
class Consumer implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
// 消费苹果
System.out.println("消费者准备消费苹果:"
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
basket.consume();
System.out.println("消费者消费苹果完毕:"
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("消费完后有苹果:"+basket.getAppleNumber()+"个");
// 休眠1000ms
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
}
}
}
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Producer producer = new Producer();
Consumer consumer = new Consumer();
service.submit(producer);
service.submit(consumer);
// 程序运行10s后,所有任务停止
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
service.shutdownNow();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueueTest.testBasket();
}
}
2 Map
映射表的基础接口;依赖Collection接口
2.1 HashMap
继承关系:
继承AbstractMap类;实现Map,Cloneable,Serializable接口
为什么HashMap的key允许为null ?????
//为什么HashMap的key允许为null
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
//计算key的hashcode值
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
/**
* 我们可以看到,HashMap在计算hashcode值的时候,会判断Key是否为空,如果为空则将hashcode值置为 0
* 所以HashMap的Key允许为空。
**/
HashMap内部实现
内部实现:
1,在JDK1.7中,HashMap的数据结构是,外层是一个数组,数组中每个元素是一个单项链表(Map.Entry)。
capacity:当前数组的容量,始终保持2^n,可以扩容,扩容后数组大小为当前的2倍。初始默认是 16 (1>>4)
loadFactor:负载因子,默认是 0.75f
threshold:扩容的阈值,等于capacity*loadFactor。即超过这个值,就会对数组进行扩容。
resize()方法,是一个十分消耗性能的方法,因为要重构hash表。
2,在JDK1.8中,Hash的内部结构是由 数组+链表+红黑树 组成。在JDK7中,查找的时候,根据hash值我们可以快速定位到数组的具体下标,但是之后,
需要顺着链表一个个比较下去才能找到我们需要的,时间复杂度取决于链表的长度为O(n)。
为了降低这部分的开销,在java1.8中,当链表中的元素达到 8 个时,会将链表转换为红黑树,在这些位置进行查找的时候,可以降低时间复杂度为O(logN)。
当外层数组index节点的元素个数减少 6 时,会把红黑数再转换为链表。
特征:
1,Key不可重复(只允许存在一个null),Value允许为null;
2,底层为数组+链表+红黑树(红黑树1.8新增);
3,线程不安全,具有很快的访问速度。
2.2 Hashtable
继承关系:
继承Dictionary类;实现Map,Cloneable,Serializable接口
为什么Hashtable的Key和Value都不允许为null ?????
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
/**
* 通过以上源码我们可以看到,如果value为null,则抛出异常。计算key的hashcode值的时候,没有包装方法,
* 而是直接使用的key.hashcode()方法,如果key为null,也会报空指针异常。
**/
特征:
1,hashtable是一个过时的类,不再推荐使用;
2,Key不允许为null,Value不允许为null;
3,继承自Dictionary类;
4,线程安全
2.3 TreeMap
继承关系:
继承AbstractMap类;实现NavigableMap,Cloneable,Serializable接口
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
/**
* 如果key为空,则直接抛出异常
**/
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
特征:
1,Key不允许为null,Value允许为null;
2,TreeMap 实现 SortedMap 接口,能够把它保存的记录根据键排序,默认是按键值的升序排序;
3,在使用 TreeMap 时,key 必须实现 Comparable 接口或者在构造 TreeMap 传入自定义的Comparator,否则会在运行时抛出 java.lang.ClassCastException 类型的异常
2.4 LinkedHashMap
继承关系:
继承HashMap类;实现Map接口
特征:
LinkedHashMap 是 HashMap 的一个子类,保存了记录的插入顺序,在用 Iterator 遍历
LinkedHashMap 时,先得到的记录肯定是先插入的,也可以在构造时带参数,按照访问次序排序。
2.5 ConcurrentHashMap
继承关系:
继承AbstractMap类;实现ConcurrentMap,Serializable接口
ConcurrentHashMap内部实现
1,JDK1.5中的实现
ConcurrentHashMap使用的是分段锁技术,将ConcurrentHashMap将锁一段一段的存储,然后给每一段数据配一把锁(segment),
当一个线程占用一把锁(segment)访问其中一段数据的时候,其他段的数据也能被其它的线程访问,默认分配16个segment。默认比Hashtable效率提高16倍。
2,JDK1.8中的实现
ConcurrentHashMap取消了segment分段锁,而采用CAS和synchronized来保证并发安全。数据结构跟HashMap1.8的结构一样,数组+链表/红黑二叉树。
synchronized只锁定当前链表或红黑二叉树的首节点,这样只要hash不冲突,就不会产生并发,效率又提升N倍。
源码分析
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
//ConcurrentHashMap 不允许插入null键,HashMap允许插入一个null键
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//计算key的hash值
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
//for循环的作用:因为更新元素是使用CAS机制更新,需要不断的失败重试,直到成功为止。
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
// f:链表或红黑二叉树头结点,向链表中添加元素时,需要synchronized获取f的锁。
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
//判断Node[]数组是否初始化,没有则进行初始化操作
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
//通过hash定位Node[]数组的索引坐标,是否有Node节点,如果没有则使用CAS进行添加(链表的头结点),添加失败则进入下次循环。
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
//检查到内部正在移动元素(Node[] 数组扩容)
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
//帮助它扩容
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
//锁住链表或红黑二叉树的头结点
synchronized (f) {
//判断f是否是链表的头结点
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
//如果fh>=0 是链表节点
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
//遍历链表所有节点
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
//如果节点存在,则更新value
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
//不存在则在链表尾部添加新节点。
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
//TreeBin是红黑二叉树节点
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
//添加树节点
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
//如果链表长度已经达到临界值8 就需要把链表转换为树结构
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
//将当前ConcurrentHashMap的size数量+1
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
特征:
1,Key不允许为null,Value不允许为null;
2,线程安全,且效率比较高(锁分段技术)