求矩阵最大和最小路径的动态规划程序(Path in Matrix)
(1)Largest sum of any of the paths starting from any cell of row 0 to any cell of row N-1.
Given a N X N matrix Matrix[N][N] of positive integers. There are only three possible moves from a cell Matrix[r][c].
1. Matrix[r+1][c]
2. Matrix[r+1][c-1]
3. Matrix[r+1][c+1]
Starting from any column in row 0, return the largest sum of any of the paths up to row N-1.
Input:
The first line of the input contains an integer T denoting the number of test cases. The description of T test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer N denoting the order of matrix. Next line contains N*N integers denoting the elements of the matrix in row-major form.
Output:
Output the largest sum of any of the paths starting from any cell of row 0 to any cell of row N-1. Print the output of each test case in a new line.
Constraints:
1<=T<=20
2<=N<=20
1<=Matrix[i][j]<=1000 (for all 1<=i<=N && 1<=j<=N)
Example:
Input:
1
2
348 391 618 193
Output:
1009
Explanation: In the sample test case, the path leading to maximum possible sum is 391->618. (391 + 618 = 1009)
#code
import math
T = int(input())
for _ in range(T):
n = int(input())
arr = list(map(int, input().split()))
arrlist = []
for i in range(0, len(arr), n):
arrlist.append([arr[j] for j in range(i,i+n)])
dp = [[0]* n for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
dp[0][i]=arrlist[0][i]
for i in range(1, n):
for j in range(n):
if j==0:
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j+1])+arrlist[i][j]
elif j==n-1:
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-1])+arrlist[i][j]
else:
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],max(dp[i-1][j+1],dp[i-1][j-1]))+arrlist[i][j]
res=-float('inf')
for i in range(n):
res=max(res,dp[n-1][i])
print(res)(2)Min Cost Path
Given a cost matrix cost[][] and a position (m, n) in cost[][], write a function that returns cost of minimum cost path to reach (m, n) from (0, 0). Each cell of the matrix represents a cost to traverse through that cell. Total cost of a path to reach (m, n) is sum of all the costs on that path (including both source and destination). You can only traverse down, right and diagonally lower cells from a given cell, i.e., from a given cell (i, j), cells (i+1, j), (i, j+1) and (i+1, j+1) can be traversed. You may assume that all costs are positive integers.
For example, in the following figure, what is the minimum cost path to (2, 2)?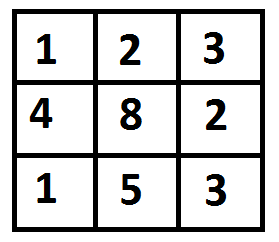
The path with minimum cost is highlighted in the following figure. The path is (0, 0) –> (0, 1) –> (1, 2) –> (2, 2). The cost of the path is 8 (1 + 2 + 2 + 3).
# Dynamic Programming Python implementation of Min Cost Path problem
R = 3
C = 3
def minCost(cost, m, n):
# Instead of following line, we can use int tc[m+1][n+1] or
# dynamically allocate memoery to save space. The following
# line is used to keep te program simple and make it working
# on all compilers.
tc = [[0 for x in range(C)] for x in range(R)]
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0]
# Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array
for i in range(1, m+1):
tc[i][0] = tc[i-1][0] + cost[i][0]
# Initialize first row of tc array
for j in range(1, n+1):
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j-1] + cost[0][j]
# Construct rest of the tc array
for i in range(1, m+1):
for j in range(1, n+1):
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i-1][j-1], tc[i-1][j], tc[i][j-1]) + cost[i][j]
return tc[m][n]
# Driver program to test above functions
cost = [[1, 2, 3],
[4, 8, 2],
[1, 5, 3]]
print(minCost(cost, 2, 2))