Spring Boot 2 读取配置文件
开发环境:IntelliJ IDEA 2019.2.2
Spring Boot版本:2.1.8
新建一个名称为demo的Spring Boot项目。
一、默认配置文件
Spring Boot会读取名称application.properties(yml)的配置文件。
如果有多个同名文件,默认情况下,按照下面顺序读取:
(1)项目根目录的config目录
(2)项目根目录
(3)项目classpath下的config目录
(4)项目classpath根目录
如果同一个配置项出现在多份配置文件中,后面读取的值不会覆盖前面的。
测试:
在项目的4个位置各建立application.properties,内容如下:
(1)config/application.properties
test = config/application.properties
test1 = test1(2)application.properties
test = application.properties
test2 = test2(3)src/main/resources/config/application.properties
test = src/main/resources/config/application.properties
test3 = test3(4)src/main/resources/application.properties
test = src/main/resources/application.properties
test4 = test4修改默认生成的启动类 DemoApplication.java 代码:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String getProp(){
String test = env.getProperty("test");
String test1 = env.getProperty("test1");
String test2 = env.getProperty("test2");
String test3 = env.getProperty("test3");
String test4 = env.getProperty("test4");
return test + "," + test1 + "," + test2 + "," + test3 + "," + test4;
}
}访问 http://localhost:8080/
输出:config/application.properties,test1,test2,test3,test4
二、指定配置文件
读取指定的配置文件,不使用默认的application.properties。
测试:
(1)src/main/resources/application.properties 内容:
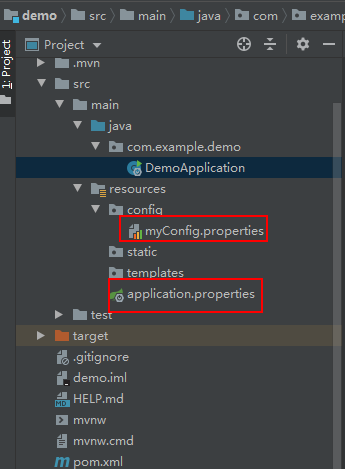
test1 = application.properties(2)在项目的src/main/resources新建目录config,新建配置文件myConfig.properties,内容:
test2= myConfig.properties修改默认生成的启动类 DemoApplication.java 代码:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
new SpringApplicationBuilder(DemoApplication.class).properties(
"spring.config.location=classpath:/config/myConfig.properties"
).run(args);
}
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String getProp(){
String test1 = env.getProperty("test1");
String test2 = env.getProperty("test2");
return test1 + "," + test2;
}
}访问 http://localhost:8080/
输出:null,myConfig.properties
可见application.properties已读取不到,成功读取到配置文件myConfig.properties。
也可以使用spring.config.name指定配置文件的名称,如下面代码指定了myConfig,Spring Boot会到classpath下寻找myConfig.properties(yml)。
public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
/*new SpringApplicationBuilder(DemoApplication.class).properties(
"spring.config.location=classpath:/config/myConfig.properties"
).run(args);*/
new SpringApplicationBuilder(DemoApplication.class).properties(
"spring.config.name=myConfig").run(args);
}三、使用profile指定配置
使用profile可以根据特定的环境来激活不同的配置。
src/main/resources/application.yml 内容如下:
spring:
profiles: mysql
jdbc:
driver:
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
---
spring:
profiles: oracle
jdbc:
driver:
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver修改默认生成的启动类 DemoApplication.java 代码:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Scanner;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String profile = scan.nextLine();
new SpringApplicationBuilder(DemoApplication.class).properties(
"spring.config.location=classpath:/application.yml"
).profiles(profile).run(args);
}
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String getProp(){
String res = env.getProperty("jdbc.driver");
return res;
}
}在IDEA中点击Run按钮后,在控制台先敲回车再输入oracle,
访问 http://localhost:8080/ 输出:oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
重新Run,在控制台先敲回车再输入mysql,
访问 http://localhost:8080/ 输出:com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
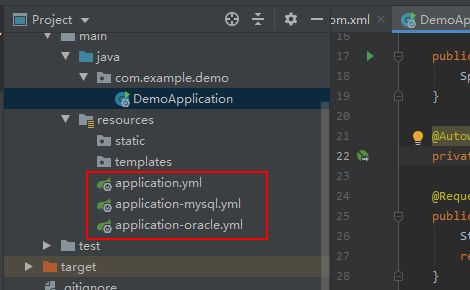
还可以通过不同配置文件的名称来设置profile,创建下面3个文件。
(1)src/main/resources/application.yml 内容:
spring:
profiles:
active: oracle(2)src/main/resources/application-mysql.yml 内容:
jdbc:
driver:
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver(3)src/main/resources/application-oracle.yml 内容:
jdbc:
driver:
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver修改默认生成的启动类 DemoApplication.java 代码:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Scanner;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String getProp(){
String res = env.getProperty("jdbc.driver");
return res;
}
}访问 http://localhost:8080/ 输出:oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver