TransmittableThreadLocal 解决 线程池线程复用 无法复制 InheritableThreadLocal 的问题
ThreadLoacl,InheritableThreadLocal,原理,以及配合线程池使用的一些坑
TransmittableThreadLocal 原理
之前为了能让InheritableThreadLocal 正确传递,不得不每次
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(>=[任务线程数]); 或者直接new Thread. 这样不仅引起性能损耗,并且如果并发上来了,会造成不必要的上下文切换.还必须用信号量做并发控制. 偶然发现 阿里开源 TransmittableThreadLocal 可以解决此问题. 以下来实验一下
![]()
/**
* User: laizhenwei
* Date: 2018-04-12 Time: 10:07
* Description:
*/
public class Ttl {
static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//子线程每次new 所以会复制线程的InheritableThreadLocal,结果正确
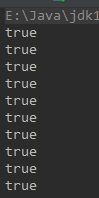
// withoutThreadPool(10);
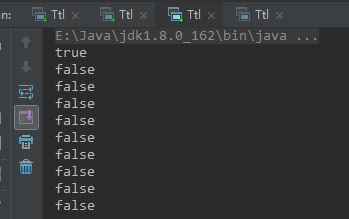
//因线程池复用线程,不会每次new 所以不会更新父线程InheritableThreadLocal 的值,导致结果错误
withThreadPool(10);
}
public static void withoutThreadPool(int c){
for(int i=0;iassert1(var1,var2)).start();
}
public static void threadPoolExecute(Integer var1,Integer var2){
executorService.execute(()->assert1(var1,var2));
}
public static void assert1(Integer var1,Integer var2){
System.out.println(MyContextHolder.get()*var2==var1*var2);
}
public static class MyContextHolder{
private static ThreadLocal stringThreadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
public static void set(Integer data) {
stringThreadLocal.set(data);
}
public static Integer get() {
return stringThreadLocal.get();
}
}
}
![]()
withoutThreadPool(10)输出结果
withThreadPool(10); 输出结果
解决方式
pom引入
![]()
com.alibaba
transmittable-thread-local
2.2.0
![]()
修改MyContextHolder
![]()
public static class MyContextHolder{
private static ThreadLocal stringThreadLocal = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();
// private static ThreadLocal stringThreadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
public static void set(Integer data) {
stringThreadLocal.set(data);
}
public static Integer get() {
return stringThreadLocal.get();
}
}
![]()
修改threadPoolExecute
public static void threadPoolExecute(Integer var1,Integer var2){
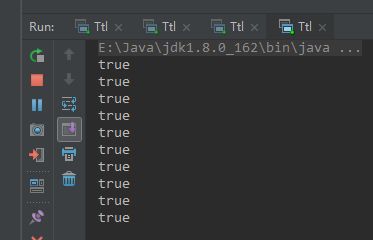
//使用TransmittableThreadLocal 解决
executorService.execute(TtlRunnable.get(()->assert1(var1,var2)) );
// executorService.execute(()->assert1(var1,var2));
}
运行 withThreadPool(10); 结果