Prometheus部署(二)
Prometheus是最初在SoundCloud上构建的开源系统监视和警报工具包。自2012年成立以来,许多公司和组织都采用了Prometheus,该项目拥有非常活跃的开发人员和用户社区。Prometheus 于2016年加入了 Cloud Native Computing Foundation,这是继Kubernetes之后的第二个托管项目。
官网:https://prometheus.io 最新版本: 2.19.2
Exporter是一个采集监控数据并通过Prometheus监控规范对外提供数据的组件,能为Prometheus提供监控的接口。
Exporter将监控数据采集的端点通过HTTP服务的形式暴露给Prometheus Server,Prometheus Server通过访问该Exporter提供的Endpoint端点,即可获取到需要采集的监控数据。不同的Exporter负责不同的业务。
Prometheus 开源的系统监控和报警框架,灵感源自Google的Borgmon监控系统
AlertManager 处理由客户端应用程序(如Prometheus server)发送的警报。它负责将重复数据删除,分组和路由到正确的接收者集成,还负责沉默和抑制警报
Node_Exporter 用来监控各节点的资源信息的exporter,应部署到prometheus监控的所有节点
PushGateway 推送网关,用于接收各节点推送的数据并暴露给Prometheus server
文档:https://prometheus.io/docs/introduction/overview/
下载prometheus各组件:
https://prometheus.io/download/
环境准备
- 主机说明:
| 系统 | ip | 角色 | cpu | 内存 | hostname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CentOS 7.8 | 192.168.30.135 | prometheus、node1 | >=2 | >=2G | prometheus |
| CentOS 7.8 | 192.168.30.136 | altermanager、node2 | >=2 | >=2G | altermanager |
| CentOS 7.8 | 192.168.30.137 | grafana、node3 | >=2 | >=2G | grafana |
- 全部关闭防火墙和selinux:
systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld
sed -i 's/=enforcing/=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config && setenforce 0
PromQL介绍
PromQL (Prometheus Query Language) 是 Prometheus 自己开发的数据查询 DSL 语言,语言表现力非常丰富,内置函数很多,在日常数据可视化以及rules 告警中都会使用到它。
- 表达式数据类型:
在prometheus的表达式中,一个表达式或子表达式可以分为以下四种类型之一:
即时向量(Instant vector):一组时间序列,每个时间序列包含一个样本,所有样本共享相同的时间戳
范围向量(Range vector):一组时间序列,其中包含每个时间序列随时间变化的一系列数据点
标量(Scalar):一个简单的数字浮点值
字符串(String):一个简单的字符串值,目前未使用
- 查询条件:
prometheus 存储的是时序数据,而它的时序是由metric名称和一组标签构成的,其实metric名称也可以写出标签的形式,例如prometheus_http_requests_total等价于{name="prometheus_http_requests_total"}。
一个简单的查询相当于是对各种标签的筛选,例如:
prometheus_http_requests_total{code="200"} #表示查询metric名称为 prometheus_http_requests_total,code 为 "200" 的数据
查询条件支持正则匹配,例如:
prometheus_http_requests_total{code!="200"} #表示查询 code 不为 "200" 的数据
prometheus_http_requests_total{code=~"2.."} #表示查询 code 为 "2xx" 的数据
prometheus_http_requests_total{code!~"2.."} #表示查询 code 不为 "2xx" 的数据
- 操作符:
prometheus 查询语句中,支持常见的各种表达式操作符,例如:
算术运算符:+、-、*、/、%、^ ,比如 prometheus_http_requests_total * 2 表示将 prometheus_http_requests_total 所有数据乘以2
比较运算符:==、!=、>、<、>=、<= ,比如 prometheus_http_requests_total > 100 表示 prometheus_http_requests_total 结果中大于 100 的数据
逻辑运算符:and、or、unless ,比如 prometheus_http_requests_total == 5 or prometheus_http_requests_total == 2 表示 prometheus_http_requests_total 结果中等于 5 或者 2 的数据
聚合运算符:sum、min、max、avg、stddev、stdvar、count、count_values、bottomk、topk、quantile,比如 max(prometheus_http_requests_total) 表示 prometheus_http_requests_total 结果中最大的数据
注意,运算符也有优先级,它们遵从(^)> (*, /, %) > (+, -) > (==, !=, <=, <, >=, >) > (and, unless) > (or) 的原则。
- 内置函数:
prometheus 内置不少函数,方便查询以及数据格式化,例如将结果由浮点数转为整数的 floor 和 ceil,
floor(avg(prometheus_http_requests_total{code="200"}))
ceil(avg(prometheus_http_requests_total{code="200"}))
查看 prometheus_http_requests_total 5分钟内平均每秒的数据,
rate(prometheus_http_requests_total[5m])
常用内置函数:
abs(v instant-vector) 返回所有样本值均转换为绝对值的输入即时向量v
absent(v instant-vector) 如果传递给它的即时向量v有任何元素,则返回一个空向量;如果传递给它的即时向量v没有元素,则返回值为1的单元素向量
absent_over_time(v range-vector) 如果传递给它的范围向量v有任何元素,则返回一个空向量;如果传递给它的范围向量v没有元素,则返回值为1的单元素向量
avg_over_time(range-vector) 指定时间间隔内范围向量所有元素样本值的平均值
ceil(v instant-vector) 将即时向量v中所有元素的样本值向上取整到最接近的整数
changes(v range-vector) 对于范围向量v中的时间序列,返回其值在提供的时间范围内变化的次数作为一个即时向量
clamp_max(v instant-vector, max scalar) 将即时向量v中所有元素的样本值锁定上限为标量max
clamp_min(v instant-vector, min scalar) 将即时向量v中所有元素的样本值锁定下限为标量min
count_over_time(range-vector) 指定时间间隔内范围向量所有元素样本值的计数
day_of_month(v=vector(time()) instant-vector) 返回UTC中每个给定时间的月份。返回值是1到31
day_of_week(v=vector(time()) instant-vector) 返回UTC中每个给定时间的星期几。返回值是从0到6,其中0表示星期日
days_in_month(v=vector(time()) instant-vector) 返回UTC中每个给定时间的月份中的天数。返回值是28到31
delta(v range-vector) 计算范围向量v中每个时间序列元素的第一个值与最后一个值之间的差,并返回具有给定增量和相同标签的即时向量。delta 应仅与Gauge一起使用
deriv(v range-vector) 使用简单的线性回归来计算范围向量v中时间序列的每秒导数。deriv 应仅与Gauge一起使用
exp(v instant-vector) 计算即时向量v中的所有元素的指数函数。特殊情况是:Exp(+Inf) = +Inf、Exp(NaN) = NaN
floor(v instant-vector) 将即时向量v中所有元素的样本值向下取整到最接近的整数
hour(v=vector(time()) instant-vector) 返回UTC中每个给定时间的一天中的小时。返回值是从0到23
idelta(v range-vector) 计算范围向量v中最后两个样本之间的差,并返回具有给定增量和相同标签的即时向量。idelta 应仅与Gauge一起使用
increase(v range-vector) 计算范围向量v中时间序列的增加。单调性中断(例如由于目标重新启动而导致的计数器重置)会自动进行调整。increase 应仅与Counter一起使用
irate(v range-vector) 计算范围向量v中时间序列的每秒瞬时增加率。单调性中断(例如由于目标重新启动而导致的计数器重置)会自动进行调整
label_join(v instant-vector, dst_label string, separator string, src_label_1 string, src_label_2 string, ...) 对于即时向量v中的每个时间序列,使用分隔符separator将所有源标签src_labels的值连接在一起,并返回带有标签值的目的标签dst_label的时间序列。src_labels可以有任意多个
label_replace(v instant-vector, dst_label string, replacement string, src_label string, regex string) 对于即时向量v中的每个时间序列,使用正则表达式regex匹配标签 src_label。如果匹配,则返回时间序列,并将标签dst_label替换为replacement的扩展。$1用第一个匹配的子组替换,$2再用第二个匹配的子组替换。如果正则表达式不匹配,则时间序列不变
max_over_time(range-vector) 指定时间间隔内范围向量所有元素样本值的最大值
min_over_time(range-vector) 指定时间间隔内范围向量所有元素样本值的最小值
minute(v=vector(time()) instant-vector) 返回UTC中每个给定时间的小时分钟。返回值是从0到59
month(v=vector(time()) instant-vector) 返回UTC中每个给定时间的一年中的月份。返回值是从1到12,其中1表示一月
rate(v range-vector) 计算范围向量v中时间序列的每秒平均增长率。单调性中断(例如由于目标重新启动而导致的计数器重置)会自动进行调整
resets(v range-vector) 对于范围向量v中的每个时间序列,将提供的时间范围内的计数器重置次数作为即时向量返回,两个连续样本之间值的任何下降都被视为计数器重置。resets 应仅与Counter一起使用
round(v instant-vector, to_nearest=1 scalar) 将即时向量v中所有元素的样本值四舍五入为最接近的整数
scalar(v instant-vector) 给定一个单元素即时向量v,返回该单个元素的样本值作为标量。如果即时向量v不是单元素向量,scalar则将返回NaN
sort(v instant-vector) 将即时向量v中元素的样本值升序排列
sort_desc(v instant-vector) 与sort相同,但以降序排列
sum_over_time(range-vector) 指定时间间隔内范围向量所有元素样本值的总和
time() 返回自1970年1月1日UTC以来的秒数
timestamp(v instant-vector) 返回即时向量v的每个样本的时间戳,作为自1970年1月1日UTC以来的秒数
vector(s scalar) 返回标量s作为不带标签的向量
year(v=vector(time()) instant-vector) 返回UTC中每个给定时间的年份
- 查询示例:
返回metric名称是http_requests_total的所有时间序列
http_requests_total
返回所有metric名称是http_requests_total、job是apiserver、handler是/api/comments的时间序列
http_requests_total{job="apiserver", handler="/api/comments"}
返回5分钟内metric名称是http_requests_total、job是apiserver、handler是/api/comments的时间序列
http_requests_total{job="apiserver", handler="/api/comments"}[5m]
返回所有metric名称是http_requests_total、job以server结尾的时间序列
http_requests_total{job=~".*server"}
返回所有metric名称是http_requests_total、status不是4xx的时间序列
http_requests_total{status!~"4.."}
返回过去30分钟内metric名称是http_requests_total时间序列的5分钟速率,分辨率为1分钟
rate(http_requests_total[5m])[30m:1m]
返回所有metric名称是http_requests_total时间序列的每秒速率,以最近5分钟为单位
rate(http_requests_total[5m])
返回每个实例中未使用的内存,以MiB为单位
(instance_memory_limit_bytes - instance_memory_usage_bytes) / 1024 / 1024
根据app和proc求和,返回每个实例中未使用的内存的总和,以MiB为单位
sum by (app, proc) (
instance_memory_limit_bytes - instance_memory_usage_bytes
) / 1024 / 1024
查询演示
在简单了解了PromQL之后,可以在prometheus界面进行数据的查询,不断调试表达式,最终得到想要的数据并以此作为规则的表达式。
上文已经部署了prometheus、node_exporter、alertmanager,因此查询时可以选择的metric名称也只与三者相关。如果想要查询其它如mysql、redis的数据,需要安装对应的exporter。
表达式中要用到的job和实例名可以在prometheus.yml中自定义。
- 存活状态:
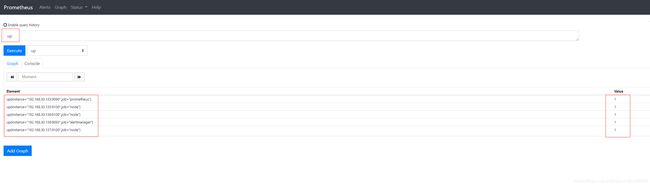
up #检查是否存活,存活返回1,否则返回0
访问ip:9090,输入up(或下拉框选择up),点击Execute,
可以看到,value都是1,这表明前面部署的组件都处于存活状态。
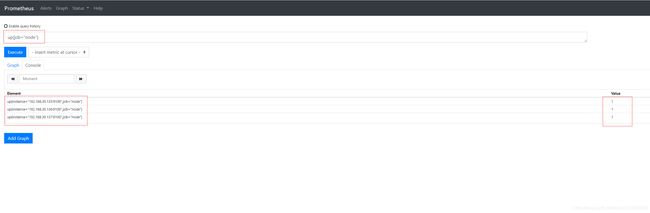
针对up返回的Element,可以自定义查询表达式,如根据job:
up{job="prometheus"} #仅查询prometheus的存活状态
up{job="node"} #仅查询node_exporter的存活状态
up{job="alertmanager"} #仅查询prometheus的存活状态
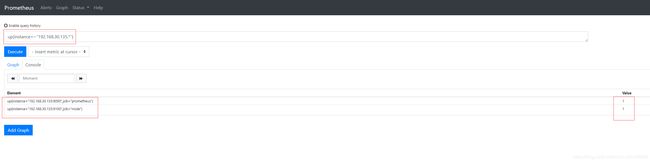
还可以根据实例名来查询某一实例的存活状态:
up{instance=~"192.168.30.135.*"} #仅查询192.168.30.135上组件的存活状态
up{instance=~"192.168.30.136.*"} #仅查询192.168.30.136上组件的存活状态
up{instance=~"192.168.30.137.*"} #仅查询192.168.30.137上组件的存活状态
up对于监控是否存活非常重要。
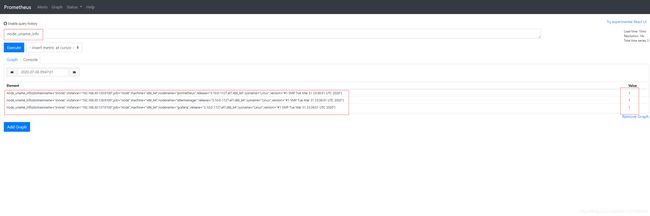
- 主机名:
node_uname_info #主机信息,包含主机名
count by (nodename) (node_uname_info) #主机名
在grafana中,可以添加变量hostname,并设置Query为label_values(node_uname_info{job=~"$job"}, nodename),筛选出主机名。
- 运行时间:
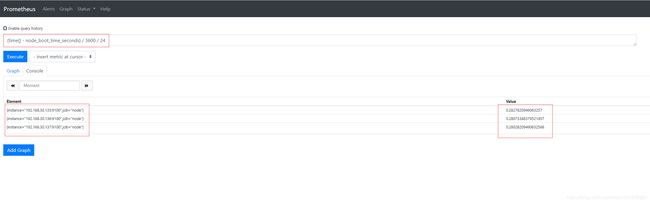
time() - node_boot_time_seconds #系统运行时间,单位是s
(time() - node_boot_time_seconds) / 3600 #系统运行时间,单位是h
(time() - node_boot_time_seconds) / 3600 / 24 #系统运行时间,单位是d
以192.168.30.135为例,针对单台主机查询:(time() - node_boot_time_seconds{instance=~"192.168.30.135.*"}) / 3600 / 24。
系统运行时间可以配置为记录规则,记录监控主机的运行时间。
- 平均负载:
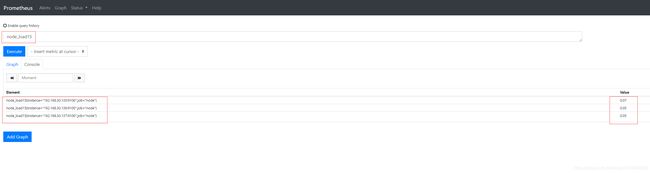
node_load1 #查看当前node_exporter所在节点1分钟的平均负载
node_load5 #查看当前node_exporter所在节点5分钟的平均负载
node_load15 #查看当前node_exporter所在节点15分钟的平均负载
平均负载也可以根据job或实例名来进行查询,如根据实例名:
node_load15{instance=~"192.168.30.135.*"} #仅查询192.168.30.135 15分钟的平均负载
node_load15{instance=~"192.168.30.136.*"} #仅查询192.168.30.136 15分钟的平均负载
node_load15{instance=~"192.168.30.137.*"} #仅查询192.168.30.137 15分钟的平均负载
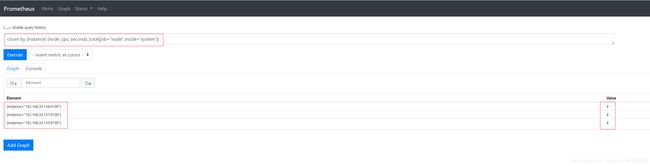
- cpu核数:
count by (instance) (node_cpu_seconds_total{job="node",mode='system'}) #cpu核数
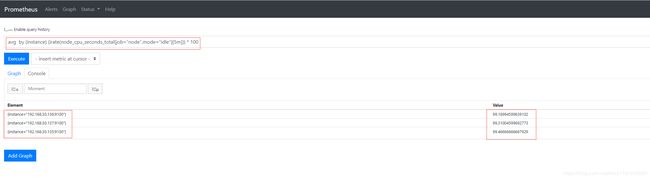
- cpu空闲率:
avg by (instance) (irate(node_cpu_seconds_total{job="node",mode="idle"}[5m])) * 100 #5分钟内cpu空闲率,单位是%
- cpu使用率:
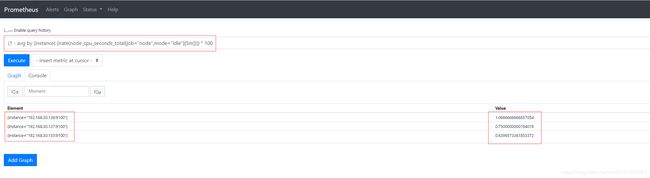
(1 - avg by (instance) (irate(node_cpu_seconds_total{job="node",mode="idle"}[5m]))) * 100 #5分钟内cpu使用率,单位是%
- 内存总大小:
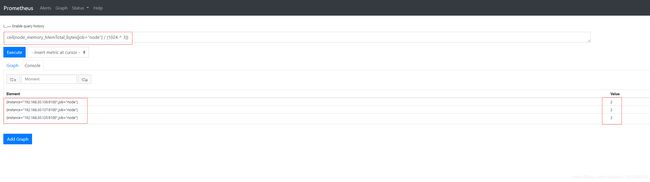
ceil(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes{job="node"} / (1024 ^ 3)) #内存总大小,单位是GiB
- 可用内存大小:
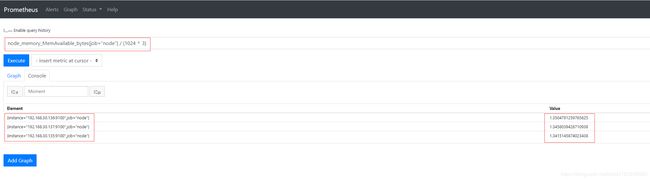
node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes{job="node"} / (1024 ^ 3) #可用内存大小,单位是GiB
- 内存使用率:
(1 - (node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes{job="node"} / node_memory_MemTotal_bytes{job="node"})) * 100 #内存使用率,单位是%
- 磁盘总大小:
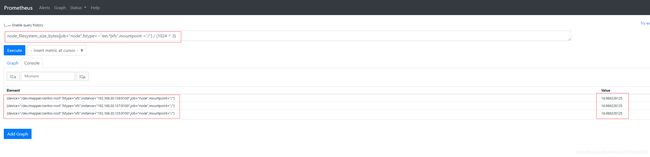
node_filesystem_size_bytes{job="node",fstype=~"ext.*|xfs",mountpoint ="/"} / (1024 ^ 3) # / 分区磁盘大小,单位是GiB
node_filesystem_size_bytes{job="node",fstype=~"ext.*|xfs",mountpoint ="/boot"} / (1024 ^ 3) # /boot 分区磁盘大小,单位是GiB
- 磁盘可用大小:
node_filesystem_avail_bytes{job="node",fstype=~"ext.*|xfs",mountpoint ="/"} / (1024 ^ 3) # / 分区磁盘可用大小,单位是GiB
node_filesystem_avail_bytes{job="node",fstype=~"ext.*|xfs",mountpoint ="/boot"} / (1024 ^ 3) # /boot 分区磁盘可用大小,单位是GiB
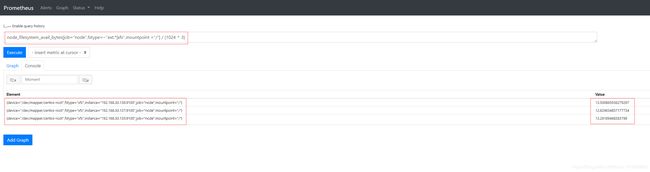
- 磁盘使用率:
(1 - node_filesystem_avail_bytes{job="node",fstype=~"ext.*|xfs",mountpoint ="/"} / node_filesystem_size_bytes{job="node",fstype=~"ext.*|xfs",mountpoint ="/"}) * 100 # / 分区磁盘使用率,单位是%
(1 - node_filesystem_avail_bytes{job="node",fstype=~"ext.*|xfs",mountpoint ="/boot"} / node_filesystem_size_bytes{job="node",fstype=~"ext.*|xfs",mountpoint ="/boot"}) * 100 # /boot 分区磁盘使用率,单位是%
- 磁盘设备最大读取速率:
max by (instance) (irate(node_disk_read_bytes_total{job="node"}[5m])) #5分钟内磁盘设备的最大读取速率,单位是bytes/s
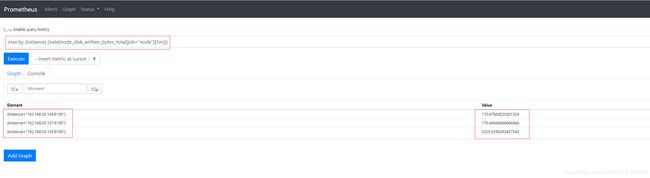
- 磁盘设备最大写入速率:
max by (instance) (irate(node_disk_written_bytes_total{job="node"}[5m])) #5分钟内磁盘设备的最大写入速率,单位是bytes/s
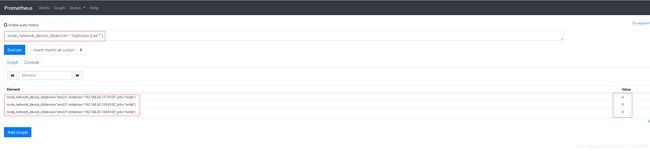
- 网卡名:
node_network_device_id{device!~"lo|docker.|cali.*"} #主机所有网卡名
- 网卡状态:
node_network_up{device!~"lo|docker.|cali.*"} #网卡存活状态
- 网络下载速率:
max by (instance) (irate(node_network_receive_bytes_total{job="node"}[5m]) * 8) #5分钟内网络最大下载速率,单位是bits/s
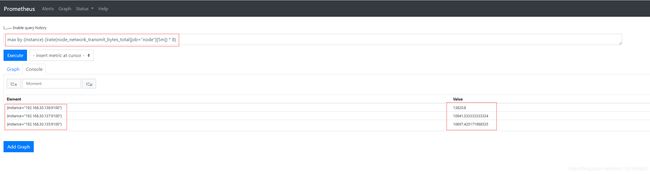
- 网络上传速率:
max by (instance) (irate(node_network_transmit_bytes_total{job="node"}[5m]) * 8) #5分钟内网络最大上传速率,单位是bits/s
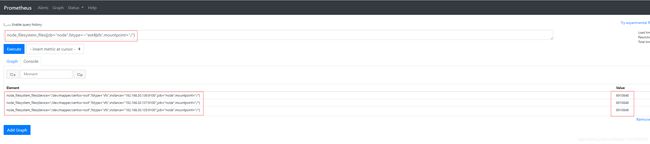
- inode总数:
node_filesystem_files{job="node",fstype=~"ext4|xfs",mountpoint="/"} # / 分区磁盘inode总数
node_filesystem_files{job="node",fstype=~"ext4|xfs",mountpoint="/boot"} # /boot 分区磁盘inode总数
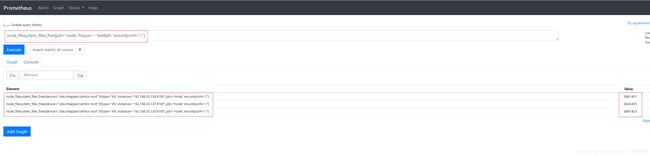
- inode可用数:
node_filesystem_files_free{job="node",fstype=~"ext4|xfs",mountpoint="/"} # / 分区磁盘inode可用数
node_filesystem_files_free{job="node",fstype=~"ext4|xfs",mountpoint="/boot"} # /boot 分区磁盘inode可用数
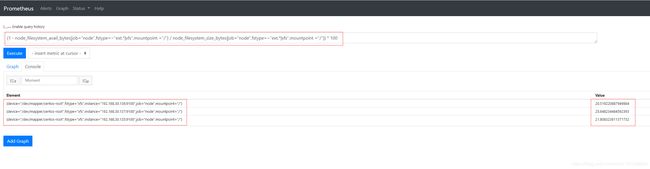
- inode使用率:
(1 - node_filesystem_files_free{job="node",fstype=~"ext4|xfs",mountpoint="/"} / node_filesystem_files{job="node",fstype=~"ext4|xfs",mountpoint="/"}) * 100 # / 分区磁盘inode使用率,单位是%
(1 - node_filesystem_files_free{job="node",fstype=~"ext4|xfs",mountpoint="/boot"} / node_filesystem_files{job="node",fstype=~"ext4|xfs",mountpoint="/boot"}) * 100 # /boot 分区磁盘inode使用率,单位是%
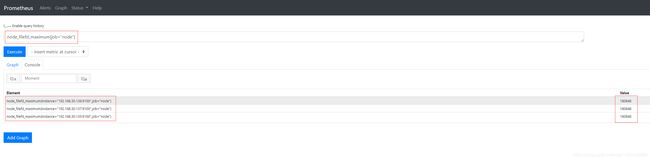
- 最大文件描述符:
node_filefd_maximum{job="node"} #系统最大文件描述符
- 打开文件描述符数:
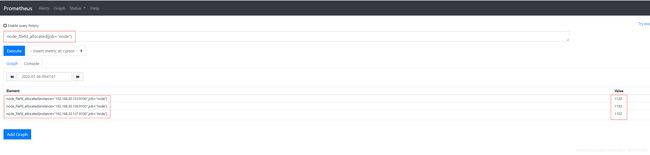
node_filefd_allocated{job="node"} #打开的文件描述符数
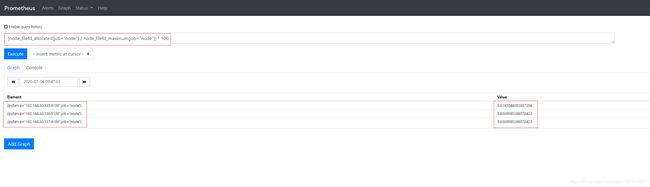
- 文件描述符使用率:
(node_filefd_allocated{job="node"} / node_filefd_maximum{job="node"}) * 100 #文件描述符使用率,单位是%
- tcp相关:
node_netstat_Tcp_ActiveOpens #从 CLOSED 状态直接转换到 SYN-SENT 状态的 TCP 连接数
node_netstat_Tcp_CurrEstab #当前状态为 ESTABLISHED 或 CLOSE-WAIT 的 TCP 连接数
node_netstat_Tcp_InErrs #TCP 接收的错误报文数
node_netstat_Tcp_InSegs #TCP 接收的报文数
node_netstat_Tcp_OutSegs #TCP 发送的报文数
node_netstat_Tcp_PassiveOpens #从 LISTEN 状态直接转换到 SYN-RCVD 状态的 TCP 连接数
node_netstat_Tcp_RetransSegs #TCP 重传报文数
node_sockstat_TCP_tw #等待关闭的TCP连接数
node_sockstat_sockets_used #已使用的所有协议套接字总量
node_sockstat_TCP_alloc #已分配(已建立、已申请到sk_buff)的TCP套接字数量