Python爬虫(九)——京东比价定向爬虫
文章目录
- Python爬虫(九)——京东比价定向爬虫
- 判断可行性
- 查看链接
- 查看robots协议
- 程序的设计
- 步骤
- 方法
- def getHTMLText(url)
- parsePage(ilt, html)
- printGoodLists(ilt)
- 完整代码
Python爬虫(九)——京东比价定向爬虫
- 目标:获取京东搜索页面的信息,提取其中的商品名称和价格。
- 要求:京东的搜索接口 翻页的处理
- 技术路线:requests-re
判断可行性
查看链接
第一页:
https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=相机&enc=utf-8&page=1
第二页:
https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=相机&enc=utf-8&page=3
第三页:
https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=相机&enc=utf-8&page=5
由上我们可以猜测最后的s变量和页码有关。
查看robots协议
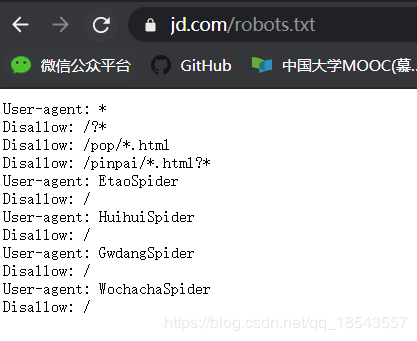
打开京东的robots.txt。发现:
结果我们发现它不允许我们爬取。不过我们如果行为就像人类的行为,没有过度消耗服务器的资源仅仅是用于学习和探索那是没有问题的。
程序的设计
步骤
- 提交上屏搜索请求,循环获取页面
- 对于每个页面,提取商品名称和价格信息
- 将信息输出到屏幕上
方法
def getHTMLText(url)
def getHTMLText(url):
try: # 利用前面的代码框架返回页面的text
r=requests.get(url,timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding=r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return ''
这时我们发现无法得到结果,查看后发现界面跳转到了登录界面,于是我们加入cookies参数来解决这个问题。
那么如何得到cookie呢?我们打开这个网页,按下f12打开开发者模式:
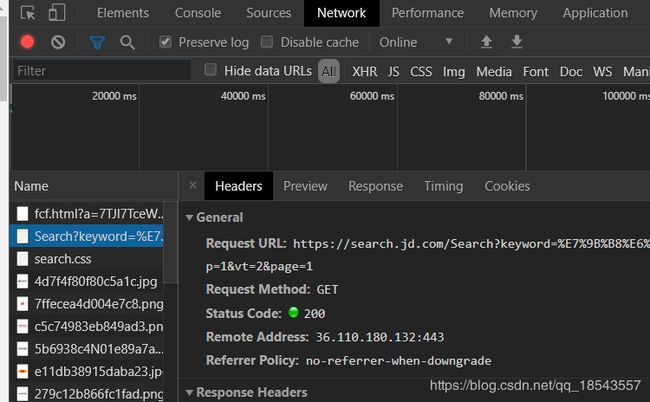
然后选中network刷新一下界面,在最上面找到Search?keyword=这个包:
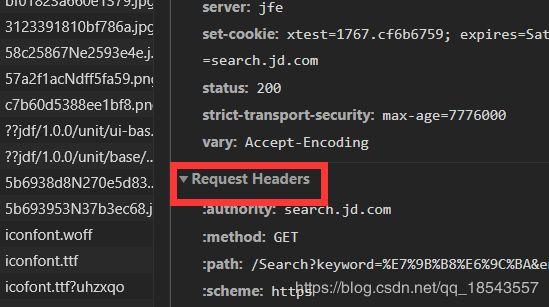
然后我们在右边的Request Hearders中就能找到自己的cookie:
代码:
def getHTMLText(url):
try: # 利用前面的代码框架返回页面的text
r = requests.get(url, timeout=30, headers={'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/79.0.3945.130 Safari/537.36'}, cookies={
'cookie': '你的cookie'})
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return ''
parsePage(ilt, html)
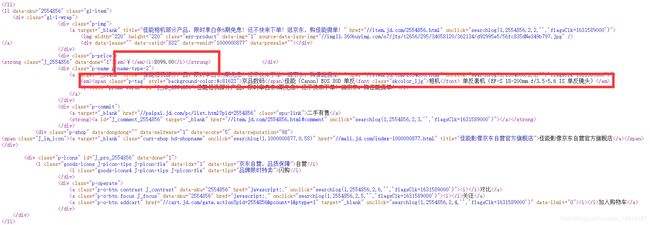
我们首先打开网页的源代码找到商品的信息。
我们发现淘宝商品的名字在标签em中且都有相机,而价格在标签i中且都是由数字.数字组成,于是利用以下两个正则表达式表示:
#价格
r'\[\d]*\.[\d]*\<\/i\>'
#商品名称
r'\.*相机.*\<\/em\>'
那么方法的代码为:
def parsePage(ilt, html):
try:
# 商品价格由数字和小数点组成所以用[\d.]*\.[\d]*来表示
plt = re.findall(r'\[\d]*\.[\d]*\<\/i\>' , html)
tlt = re.findall(r'\.*相机.*\<\/em\>' , html)
for i in range(len(plt)):
price = plt[i][3:-4] # 直接利用python字符串特性得到价格
if re.findall(r'.*京品数码.*', tlt[i]) or re.findall(r'.*京东国际.*', tlt[i]) or re.findall(r'.*京东超市.*', tlt[i]):
print('here')
# 通过最小匹配来得到第一个<之前的内容
title = re.findall(r'span\>.*?\<', tlt[i])[0][5:-1]+'相机'
else:
# 同样的方法获得其他类型商品名称
title = re.findall(r'em\>.*?\<', tlt[i])[0][3:-1]+'相机'
ilt.append([price, title])
except:
print("")
printGoodLists(ilt)
最后将结果打印出来,这里我也遇到了一些问题:无法打印出界面中所有的商品,我用BeautifulSoup+re分析也是同样的结果,如果你知道问题的所在希望能够给我留言或者私信我。
def printGoodLists(ilt):
tplt = "{:4}\t{:8}\t{:16}" # 给出打印模板,第一个长度为4,第二个长度为8,最后一个长度为16
print(tplt.format("序号", "价格", "商品名称"))
count = 0
for goods in ilt:
count += 1
print(tplt.format(count, goods[0], goods[1]))
print("")
完整代码
#encoding='utf-8
import requests
import re
def getHTMLText(url):
try: # 利用前面的代码框架返回页面的text
r = requests.get(url, timeout=30, headers={'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/79.0.3945.130 Safari/537.36'}, cookies={
'cookie': '你的cookie'})
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return ''
def parsePage(ilt, html):
try:
# 商品价格由数字和小数点组成所以用[\d.]*\.[\d]*来表示
plt = re.findall(r'\[\d]*\.[\d]*\<\/i\>' , html)
tlt = re.findall(r'\.*相机.*\<\/em\>' , html)
for i in range(len(plt)):
price = plt[i][3:-4] # 直接利用python字符串特性得到价格
if re.findall(r'.*京品数码.*', tlt[i]) or re.findall(r'.*京东国际.*', tlt[i]) or re.findall(r'.*京东超市.*', tlt[i]):
# 通过最小匹配来得到第一个<之前的内容
title = re.findall(r'span\>.*?\<', tlt[i])[0][5:-1]+'相机'
else:
# 同样的方法获得其他类型商品名称
title = re.findall(r'em\>.*?\<', tlt[i])[0][3:-1]+'相机'
ilt.append([price, title])
except:
print("")
def printGoodLists(ilt):
tplt = "{:4}\t{:8}\t{:16}" # 给出打印模板,第一个长度为4,第二个长度为8,最后一个长度为16
print(tplt.format("序号", "价格", "商品名称"))
count = 0
for goods in ilt:
count += 1
print(tplt.format(count, goods[0], goods[1]))
print("")
goods = '相机'
depth = 3
startUrl = 'https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword='+goods+'&enc=utf-8'
infoList = []
for i in range(depth): # 这里通过循环来查询多个页面并保存再infoList中
try:
page = i*2+1
url = startUrl+'&page='+str(page) # 利用之前观察的页面url来设定每个页面的url
html = getHTMLText(url)
parsePage(infoList, html)
except:
continue
printGoodLists(infoList)
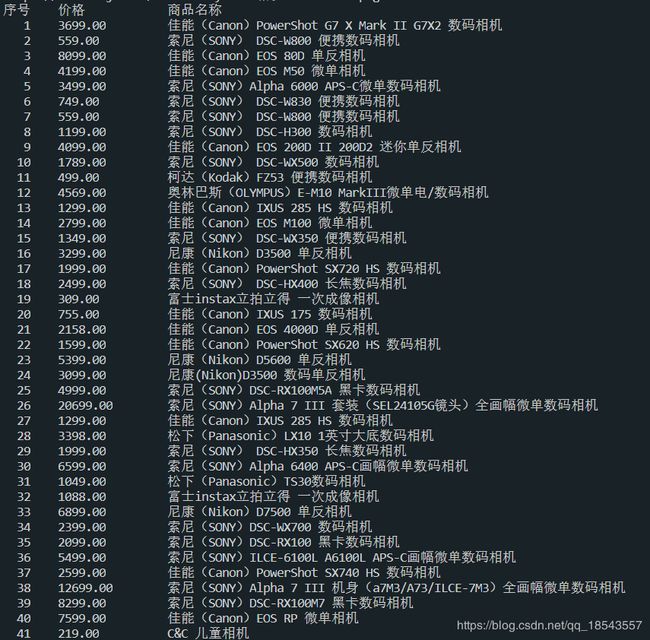
运行结果: