Spring Boot学习(二十七):Spring Boot Actuator让你轻松监控你的Spring Boot应用
Spring Boot Actuator
Spring Boot Actuator可以帮助你监控和管理Spring Boot应用,比如健康检查、审计、统计和HTTP追踪等。所有的这些特性可以通过JMX或者HTTP endpoints来获得。
Actuator同时还可以与外部应用监控系统整合,比如 Prometheus, Graphite, DataDog, Influx, Wavefront, New Relic等。这些系统提供了非常好的仪表盘、图标、分析和告警等功能,使得你可以通过统一的接口轻松的监控和管理你的应用。
Spring Boot还有一个用于监控基于 Spring Boot 的应用:Spring Boot Admin,它是在 Spring Boot Actuator 的基础上提供简洁的可视化 WEB UI。Spring Boot Admin会在下一篇文章进行讲解
集成Spring Boot Actuator
Spring Boot 集成Spring Boot Actuator很简单,只需要添加一个actuator依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
Spring Boot Actuator使用
当我们将Spring Actuator Dependencies添加到我们的Spring启动项目时,它就会自动启用执行器端点。
Actuator 的核心是端点(endpoints),我们通过端点可以获取应用的一些监控信息或者通过端点来改变系统的一些状态。
当你运行应用程序时,你将看到执行器端点映射到日志中。
//在基本路径“/actuator'”下暴露2个端点
Exposing 2 endpoint(s) beneath base path '/actuator'
执行器端点(endpoints)可用于监控应用及与应用进行交互,Spring Boot包含很多内置的端点,你也可以添加自己的。下面是Spring Boot内置的端点
| 项目 | Value |
|---|---|
| 电脑 | $1600 |
| 手机 | $12 |
| 导管 | $1 |
| ID | 描述 |
|---|---|
| auditevents | 公开当前应用程序的审核事件信息。 |
| beans | 显示应用程序中所有Spring bean的完整列表。 |
| caches | 暴露可用的缓存。 |
| conditions | 显示在配置和自动配置类上评估的条件以及它们匹配或不匹配的原因。 |
| configprops | 显示所有的整理列表@ConfigurationProperties,查看配置属性,包括默认配置 |
| env | 露出Spring的属性的各种环境变量,后面可跟/{name}查看具体的值 |
| flyway | 显示已应用的任何Flyway数据库迁移。 |
| health | 显示应用健康信息,在spring boot2.0以后需要在配置里show-details打开所有健康信息 |
| httptrace | 显示HTTP跟踪信息(默认情况下,最后100个HTTP请求 - 响应交换),2.0以后需要手动打开 |
| info | 显示任意应用信息,是在配置文件里自己定义的 |
| integrationgraph | 显示Spring Integration图。 |
| loggers | 显示和修改应用程序中记录器的配置。 |
| liquibase | 显示已应用的任何Liquibase数据库迁移。 |
| metrics | 显示当前应用程序的“指标”信息,比如内存用量和HTTP请求计数,后可跟/{name}查看具体值 |
| mappings | 显示所有@RequestMapping路径的整理列表。 |
| scheduledtasks | 显示应用程序中的计划任务。 |
| sessions | 允许从Spring Session支持的会话存储中检索和删除用户会话。使用Spring Session对响应式Web应用程序的支持时不可用 |
| shutdown | 允许应用以优雅的方式关闭(默认情况下不启用)。 默认关闭 |
| threaddump | 执行线程转储。 |
注意事项:
在spring boot 2.0以后,actuator默认只公开了info和health两个端点,要想使用其他的端点,需要在application.yml中打开:
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include:"*"
注意:
在这里include: “*” ,这个"“双引号在YML中是必须要,在application.properties是不需要”"双引号的,application.properties中是这样的:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
而且所有的端点都以默认的路径http://localhost:8080/actuator 开始;
如我们查看health端点的信息就是访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/health
默认health端点只显示一些简单的信息
显示所有健康状态,需要加配置
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
如下,是我访问health的所有信息。因为我的rabbitmq服务下掉了,所以状态变成了DOWN
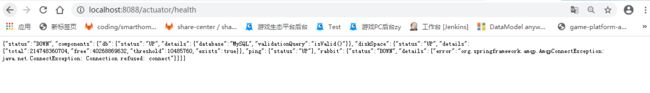
端点的路径
默认情况下,端点通过使用端点的ID在/actuator路径下的HTTP上公开。例如,beans端点暴露在/actuator/beans下。如果要将端点映射到其他路径,则可以使用management.endpoints.web.path-mapping属性。另外,如果您想更改基本路径,则可以使用management.endpoints.web.base-path。
以下示例将/actuator/health重新映射到/healthcheck:
#修改基本路径为/,即将/actuator改为/
management.endpoints.web.base-path=/
#修改health端点的路径,即将/health改为/healthcheck
management.endpoints.web.path-mapping.health=healthcheck
启用端点
但是如果你只想打开某个端点,我们是这样的配置的,同样式在application.yml中:
management:
endpoint:
端点名称:
enabled: true
默认情况下,除shutdown以外的所有端点均已启用。要配置单个端点的启用,请使用management.endpoint..enabled属性。以下示例启用shutdown端点:
management.endpoint.shutdown.enabled=true
暴露端点
要更改公开哪些端点,请使用以下技术特定的include和exclude属性:
| Property | Default |
|---|---|
| management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.exclude | * |
| management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.include | * |
| management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude | * |
| management.endpoints.web.exposure.include | info, health |
include属性列出了公开的端点的ID,exclude属性列出了不应该公开的端点的ID
exclude属性优先于include属性。包含和排除属性都可以使用端点ID列表进行配置。
注意:这里的优先级是指同一端点ID,同时出现在include属性表和exclude属性表里,exclude属性优先于include属性,即此端点没有暴露
配置端点缓存时间
对于不带任何参数的读取操作,端点自动缓存对其响应。要配置端点缓存响应的时间,请使用cache.time-live属性。以下示例将beans端点缓存的生存时间设置为10秒:
management.endpoint.beans.cache.time-to-live=10s
注意:在进行经过验证的HTTP请求时,Principal将被视为端点的输入,因此不会缓存响应。
Actuator Endpoints安全
我们可以使用Spring Security来保证Actuator Endpoints安全:
1、在pom.xml中添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、添加配置类,拦截所有actuator请求
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//对actuator监控所用的访问全部需要认证
http.formLogin().and().authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/actuator/*").authenticated();
}
}
3、在application.yml中配置帐号密码:这里是在spring boot2.0以后的版本中,在2.0之前不是这样的,稍微有差别:
# http安全机制
spring:
security:
user:
name: m
password: 123
roles: ADMIN
properties:
#http安全机制
spring.security.user.name=m
spring.security.user.password=123
spring.security.user.roles=ADMIN
