TabActivity简介及实例使用
一、简介

1. TabActivity继承Activity,主要功能是实现多个activity或者view之间的切换和显示,要使用该类必须新建一个类来继承TabActivity,并且该类的xml配置文件中必须包含TabHost、TabWidget、FrameLayout三个视图(View),其中后面两个标签是前面一个标签的子标签,表示tab页的选项卡,相当于菜单页,表示显示内容的区域。实现标签页的功能,通过导航栏对各个页面进行管理,从而实现让同一界面容纳更多内容。
效果如下所示:
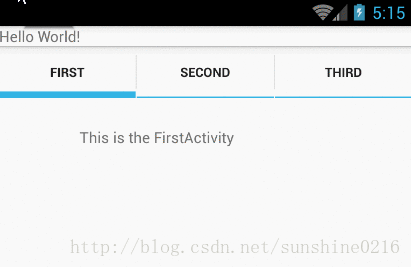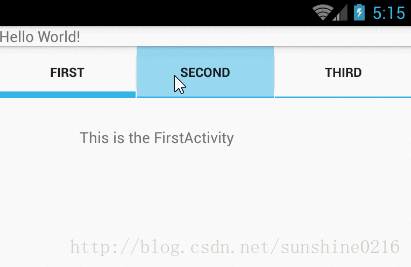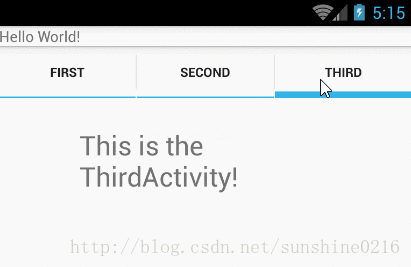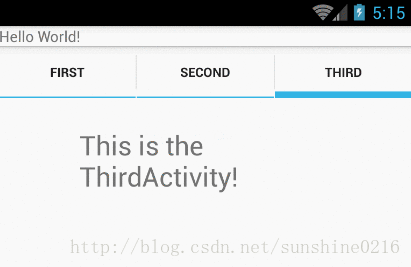
2. TabActivity里主要函数:
public TabHost getTabHost () //获得当前TabActivity的TabHost
public TabWidget getTabWidget () //获得当前TabActivity 的TabWidget
public void setDefaultTab (String tag) //这两个函数很易懂, 就是设置默认的Tab
public void setDefaultTab (int index) //通过tab名——tag或者index(从0开始)
protected void onRestoreInstanceState (Bundle state)
protected void onSaveInstanceState (Bundle outState)
//这两个函数的介绍可以参考 Activity的生命周期3. TabHost:TabHost是Tab的载体,用来管理Tab,3个内嵌类:1个类TabHost.TabSpec,2个接口 TabHost.TabContentFactory和TabHost.OnTabChangeListener。主要包括以下函数:
public void addTab (TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec) //添加 tab,参数TabHost.TabSpec通过下面的函数返回得到
public TabHost.TabSpec newTabSpec (String tag) //创 建TabHost.TabSpec
public void clearAllTabs () //remove所有的Tabs
public int getCurrentTab ()//得到当前的Tab
public String getCurrentTabTag ()//得到当前的TabTag
public View getCurrentTabView ()//得到当前的TabView
public View getCurrentView ()//得到当前的View
public FrameLayout getTabContentView () //返回Tab content的FrameLayout
public TabWidget getTabWidget ()
public void setCurrentTab (int index) //设置当前的Tab by index
public void setCurrentTabByTag (String tag) //设置当前的Tab by tag
public void setOnTabChangedListener (TabHost.OnTabChangeListener l) //设置TabChanged事件的响应处理TabHost.TabSpec用来管理以下三个函数:
public String getTag ()
public TabHost.TabSpec setContent
public TabHost.TabSpec setIndicatorIndicator可以
设置label : setIndicator (CharSequence label)
或者同时设置label和icon :setIndicator (CharSequence label, Drawable icon)
或者直接指定某个view : setIndicator (View view)
对于Content ,就是Tab里面的内容,可以
设置View的id : setContent(int viewId)
或者TabHost.TabContentFactory 的createTabContent(String tag)来处理:setContent(TabHost.TabContentFactory contentFactory)
或者用new Intent 来引入其他Activity的内容:setContent(Intent intent)
4.原理
一般Activity的启动,调用startActivty(Intent i)方法。然后这个方法会辗转调用到ams(ActivityManagerService)来启动目标activity.
所以,TabActivity实现的要点有两个:
a. 找到一个入口,这个入口可以访问到ActivityThread类(这个类是隐藏的,应用程序是访问不到的),然后调用ActivityThread里面的启动activity方法
b. 绕开ams,就是我们TabActivity加载的FirstActivity和SecondActivity是不能让ams知道的。
所以,一个新的类诞生了 —- LocalActivityManager , 它的作用如下:
1. 这个类和ActivityThread处于一个包内,所以它有访问ActivityThread的权限。
2. 这个类提供了类似Ams管理Activity的方法,比如调用activity的onCreate方法,onResume()等等,维护了activity生命周期
运行的进程和它管理的Activity是在一个进程里面。
二、实例使用
实例一(实现上图效果)
1、创建Android项目,MainActivity继承TabActivity;
1、修改XML文件,将TabWidget、FrameLayout放到一个LinearLayout中垂直分布
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.hmh.tabactivity.MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello World!" />
<TabHost
android:id="@android:id/tabhost"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TabWidget
android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">TabWidget>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">FrameLayout>
TabHost>
LinearLayout>
3、创建三个Activity,编写MainActivity代码
FirstActivity.java
public class FirstActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TextView textView=new TextView(this);
textView.setPadding(150,150,150,150);
textView.setText("This is the FirstActivity");
setContentView(textView);
}
}SecondActivity.java
public class SecondActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TextView textView=new TextView(this);
textView.setText("This is the SecondActivity");
textView.setPadding(150,150,150,150);
setContentView(textView);
Intent intent=getIntent();
String str=intent.getStringExtra("name");
textView.setText(textView.getText()+"\n\n"+str);
}
}
ThirdActivity.java
public class ThirdActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TextView textView = new TextView(this);
textView.setText("This is the ThirdActivity!");
setContentView(textView);
textView.setTextSize(25);
textView.setPadding(150,150,150,150);
textView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
MainActivity.mTabHost.setCurrentTabByTag("firstActivity");
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if(keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK && event.getRepeatCount() == 0) {
MainActivity.mTabHost.setCurrentTabByTag("secondActivity");
return true;
}
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
}MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends TabActivity {
public static MainActivity mainActivity;
public static TabHost mTabHost;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Resources res=getResources();
mainActivity=this;
mTabHost=this.getTabHost();
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(this,FirstActivity.class);
TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec=mTabHost.newTabSpec("First").setIndicator("First",res.getDrawable(R.drawable.blue1)).setContent(intent);
mTabHost.addTab(tabSpec);
intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("name","value");
tabSpec=mTabHost.newTabSpec("Second").setIndicator("Second",res.getDrawable(R.drawable.blue1)).setContent(intent);
mTabHost.addTab(tabSpec);
intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(this, ThirdActivity.class);
tabSpec = MainActivity.mTabHost.newTabSpec("third").
setIndicator("third", res.getDrawable(android.R.drawable.ic_media_next)).setContent(intent);
MainActivity.mTabHost.addTab(tabSpec);
mTabHost.setCurrentTabByTag("firstActivity");
}
}
实例二:
*MainActivity.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.TabActivity;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.widget.TabHost;
public class MainActivity extends TabActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//获得当前TabActivity的TabHost
TabHost tabHost = getTabHost();
LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.activity_main, tabHost.getTabContentView(), true);
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1")
.setIndicator("米蓝")
.setContent(R.id.view1));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab2")
.setIndicator("米红")
.setContent(R.id.view2));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3")
.setIndicator("米绿")
.setContent(R.id.view3));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab4")
.setIndicator("米紫")
.setContent(R.id.view4));
}
}
XML
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
id="@+id/view1"
android:background="@drawable/blue1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="米蓝"
android:textSize="25dp"/>
id="@+id/view2"
android:background="@drawable/red1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="米红"
android:textSize="25dp"/>
id="@+id/view3"
android:background="@drawable/green1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="米绿"
android:textSize="25dp"/>
id="@+id/view4"
android:background="@drawable/purple1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="米紫"
android:textSize="25dp"
/>
本人菜鸟,请多多指教
API参考链接
