半同步/半反应堆模型(使用线程池)的TCP服务器例子
在半同步/半异步模式中“同步”和“异步”与I/O模型中同步、异步的概念不同:I/O模型中,同步和异步区分的是内核向应用程序通知的是何种I/O事件(是就绪事件还是完成事件),以及该由谁来完成I/O读写(是应用程序还是内核)。在并发模式中,“同步”指的是程序完全按照代码序列的顺序执行;“异步”指的是程序的执行需要由系统事件来驱动(常见的系统事件包括中断、信号)。
异步线程的执行的执行效率高,实时性强,但是编写以异步方式执行的程序相对复杂,难以调试和扩展,而且不适合大量的并发。而同步线程虽然效率相对较低,但是逻辑简单。对于服务器这种既要求较好的实时性,又要求能同时处理多个客户请求的应用程序,可以同时使用同步线程和异步线程实现。异步线程监听客户请求,将其封装成请求对象插入请求队列中。请求队列通知某个在同步模式下的工作线程来读取并处理该对象。最简单的选工作线程的是Round Robin算法,也可以使用条件变量或信号量。
如图是半同步/半异步的变形:“半同步/半反应堆模型”:
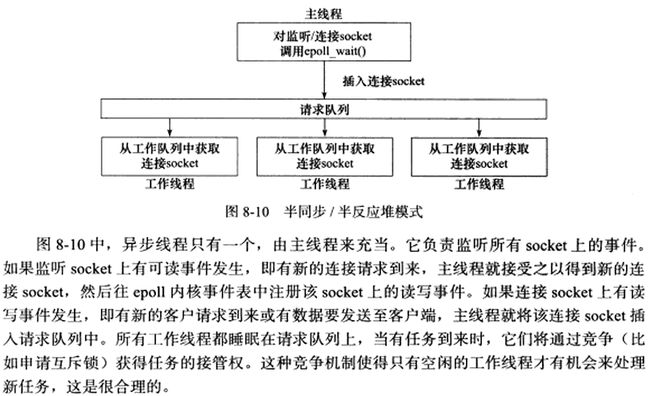
上图所示模型缺点:(1)主线程和工作线程共享请求队列。主线程添加任务和工作线程从队列取任务都要对请求队列加锁,消耗CPU时间。(2)每个工作线程在同一时间仅处理一个客户请求。如果客户数据多,而工作线程少,则请求队列中任务堆积,客户响应会越来越慢。可以通过增加工作线程来解决。
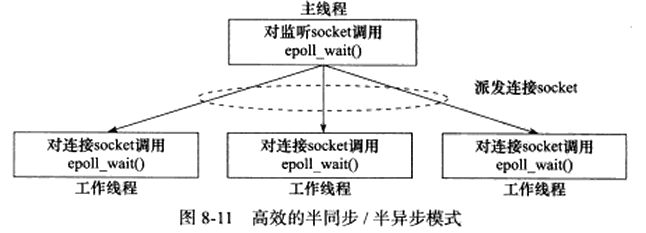
下图是相对高效的半同步半异步模式:
该模式的主线程只管理监听socket,连接socket由工作线程来管理。当有新的连接到来时,主线程就接受并将新返回的连接socket派发给某个工作线程,此后该新socket上的任何I/O操作都由被选中的线程来处理,直到客户关闭连接。上图的每个线程都维护自己的事件循环,它们各自独立监听不同事件。因此每个线程都是异步模式。
下面代码所示的服务器程序使用主线程来监听套接字并接收数据,将接收的数据存放在一个队列中(通过获取互斥锁来在队列中存放元素),在队列中存入数据后发送信号到条件变量信号,然后释放互斥锁,以允许线程池中某个线程为这个客户服务。线程池里的工作线程通过试图获取互斥锁,获取队列元素并对其进行处理(这里仅仅在控制台显示数据)。
//http_parse.cpp
#include "http_parse.h"
//错误处理函数
void err_exit(const char *info) {
perror(info);
exit(-1);
}
//设置描述符为非阻塞模式
int setnonblocking(int fd) {
int old_option = fcntl( fd, F_GETFL );
int new_option = old_option | O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl( fd, F_SETFL, new_option );
return old_option;
}
//向epoll中添加要监听的描述符
void addfd(int epollfd, int fd) {
epoll_event event;
event.data.fd = fd;
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
epoll_ctl( epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &event );
setnonblocking( fd );
}
//任务队列,主线程收到的数据队列,等待线程池线程处理
queue<char *> taskqueue;
//用于为任务队列加锁的互斥锁和通知的条件信号量
pthread_mutex_t clifd_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t clifd_cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
vector//http_parse.h
#ifndef HTTP_PARSE_H
#define HTTP_PARSE_H
#include 测试服务器的客户端是文章《unix网络编程》(15)poll函数以及使用poll的客户服务器程序中的客户端。
下图是服务端测试截图: