JUnit4 参数化测试( Parameterized tests)
@RunWith
当类被@RunWith注解修饰,或者类继承了一个被该注解修饰的类,JUnit将会使用这个注解所指明的运行器(runner)来运行测试,而不使用JUnit默认的运行器。
要进行参数化测试,需要在类上面指定如下的运行器:
@RunWith (Parameterized.class)
然后,在提供数据的方法上加上一个@Parameters注解,这个方法必须是静态static的,并且返回一个集合Collection。
Junit4 中通过 Parameterized 运行器实现参数化测试。
当执行参数化测试类时,实例的测试方法和测试数据元素将在测试示例创建时交叉连接到一起。
下面是测试菲波那切数的测试方法:
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class FibonacciTest {
@Parameters
public static Collection data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 2, 1 }, { 3, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 5 }, { 6, 8 }
});
}
private int fInput;
private int fExpected;
public FibonacciTest(int input, int expected) {
fInput= input;
fExpected= expected;
}
@Test
public void test() {
assertEquals(fExpected, Fibonacci.compute(fInput));
}
} public class Fibonacci {
public static int compute(int n) {
int result = 0;
if (n <= 1) {
result = n;
} else {
result = compute(n - 1) + compute(n - 2);
}
return result;
}
}每个FibonacciTest类的示例都将通过两个参数的构造器来创建。而这两个参数将通过带有@Parameters注解的方法来获取。
除了构造器注入之外,@Parameters注解支持属性注入
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameter;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class FibonacciTest {
@Parameters
public static Collection data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 2, 1 }, { 3, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 5 }, { 6, 8 }
});
}
@Parameter // first data value (0) is default
public /* 不能为 private */ int fInput;
@Parameter(1)
public /* 不能为 private */ int fExpected;
@Test
public void test() {
assertEquals(fExpected, Fibonacci.compute(fInput));
}
}
public class Fibonacci {
...
} 单个参数的测试
如果你的测试只需要单个参数,则不需要将其包装成数组。这种情况下可以提供一个迭代器或对象数组。
@Parameters
public static Iterable data() {
return Arrays.asList("first test", "second test");
}或
@Parameters
public static Object[] data() {
return new Object[] { "first test", "second test" };
}识别每个测试用例
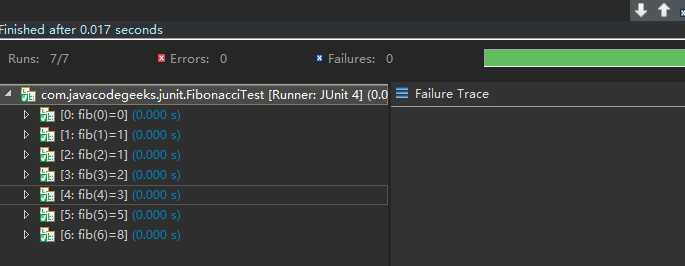
为了更容易地区分参数化测试中每个测试用例,你可以在@Parameters 注解上提供一个名称。
此名称可以包含占位符,该占位符在运行时将会被替换。
{index}: 当前参数的索引{0}, {1}, …: 第一个参数,第二个参数等,参数值. 注意:单引号'应该被转义成两个单引号''.
例子
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class FibonacciTest {
@Parameters(name = "{index}: fib({0})={1}")
public static Iterable data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 2, 1 }, { 3, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 5 }, { 6, 8 }
});
}
private int input;
private int expected;
public FibonacciTest(int input, int expected) {
this.input = input;
this.expected = expected;
}
@Test
public void test() {
assertEquals(expected, Fibonacci.compute(input));
}
}
public class Fibonacci {
...
} 上面这个例子,参数化 运行器 创建如 [3: fib(3)=2] 这种名称。如果你没有指定名称,默认使用当前参数的索引。
原文:https://github.com/junit-team/junit4/wiki/Parameterized-tests