手把手教物体检测——yolov3
目录
训练
下载算法
下载.weights结尾的预训练模型,并将weight文件转为h5文件
修改类别。
Labelme标注的数据集转为yolov3训练的数据集。
执行Kmeans.py文件计算anchors。
修改train.py文件。
测试
修改yolo.py
修改yolo_video.py
摘要
YOLOv3是YOLO (You Only Look Once)系列目标检测算法中的第三版,相比之前的算法,尤其是针对小目标,精度有显著提升。在Pascal Titan X上处理608x608图像速度达到20FPS,在 COCO test-dev 上 [email protected] 达到 57.9%,与RetinaNet(FocalLoss论文所提出的单阶段网络)的结果相近,并且速度快4倍。
相比YOLOV2,YOLOV3的改进之处主要有两点:
- 多尺度预测 (类FPN)
- 更好的基础分类网络(类ResNet)和分类器
关于YOLOV3 的理解可以参照这两篇文章:
1、yolo系列之yolo v3【深度解析】
https://blog.csdn.net/leviopku/article/details/82660381。
YOLOV3的整体结构
2、目标检测网络之 YOLOv3
https://www.cnblogs.com/makefile/p/YOLOv3.html
训练
本地环境:TensorFlow 1.15.3
Python 3.7
Keras 2.1.5
下载算法
yolo v3 的算法版本比较多,我建议大家选用是qqwweee的keras版本,复现比较容易,代码相对来说比较容易理解。
github地址:https://github.com/qqwweee/keras-yolo3
下载.weights结尾的预训练模型,并将weight文件转为h5文件
下载地址:https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights。
新建weight文件夹,将下载的模型放进去。然后修改convert.py文件
将config_path、weightsPath和output_path这个三个参数删除。如下图:
修改main函数中的路径。
def _main(args):
config_path = "yolov3.cfg"
weights_path = "weight/yolov3.weights"
assert config_path.endswith('.cfg'), '{} is not a .cfg file'.format(
config_path)
assert weights_path.endswith(
'.weights'), '{} is not a .weights file'.format(weights_path)
output_path = "weight/yolov3.h5"修改完成后点击运行。
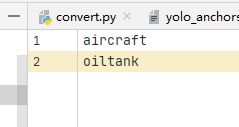
修改类别。
yolo默认使用的类别文件是coco_classes.txt,所以我们需要将此文件的类别修改为数据集的类别。本例使用的数据集有两个类别,分别是aircraft和oiltank。
Labelme标注的数据集转为yolov3训练的数据集。
增加labelme2txt.py文件
from os import getcwd
import os
import json
import glob
wd = getcwd()
"labelme标注的json 数据集转为keras 版yolov3的训练集"
classes = ["aircraft","oiltank"]
image_ids = glob.glob(r"LabelmeData/*jpg")
print(image_ids)
list_file = open('train.txt', 'w')
def convert_annotation(image_id, list_file):
jsonfile=open('%s.json' % (image_id))
in_file = json.load(jsonfile)
for i in range(0,len(in_file["shapes"])):
object=in_file["shapes"][i]
cls=object["label"]
points=object["points"]
xmin=int(points[0][0])
ymin=int(points[0][1])
xmax=int(points[1][0])
ymax=int(points[1][1])
if cls not in classes:
print("cls not in classes")
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
b = (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
list_file.write(" " + ",".join([str(a) for a in b]) + ',' + str(cls_id))
jsonfile.close()
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write('%s.jpg' % (image_id.split('.')[0]))
convert_annotation(image_id.split('.')[0], list_file)
list_file.write('\n')
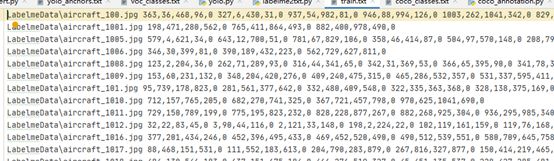
list_file.close()生成的train.txt内容如下:
每张图片是x1,y1,x2,y2 class 组成的字符串。
执行Kmeans.py文件计算anchors。
打开Kmeans.py文件,修改self.filename = "train.txt",然后运行,计算的结果会直接覆盖到yolo_anchors.txt
修改train.py文件。
annotation_path = 'train.txt'
classes_path = 'model_data/coco_classes.txt'
anchors_path = 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'model = create_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes,
freeze_body=2, weights_path='weight/yolov3.h5')这几个文件的路径按照上面文件的存放位置和名称修改。注意57行和76行的batch_size按照电脑的配置去修改。完成上面的步骤就可以开始训练了,点击run,开始训练。
测试
修改yolo.py
mode_path 修改为最终模型的路径:
"model_path": 'logs/000/trained_weights_final.h5',修改yolo_video.py
删除以下参数
parser.add_argument(
'--model', type=str,
help='path to model weight file, default ' + YOLO.get_defaults("model_path")
)
parser.add_argument(
'--anchors', type=str,
help='path to anchor definitions, default ' + YOLO.get_defaults("anchors_path")
)
parser.add_argument(
'--classes', type=str,
help='path to class definitions, default ' + YOLO.get_defaults("classes_path")
)
parser.add_argument(
'--gpu_num', type=int,
help='Number of GPU to use, default ' + str(YOLO.get_defaults("gpu_num"))
)将image参数改为true
parser.add_argument(
'--image', default=True, action="store_true",
help='Image detection mode, will ignore all positional arguments'
)修改detect_img的img路径
def detect_img(yolo):
while True:
img ="D:\keras-yolo3-master\LabelmeData/aircraft_4.jpg"测试结果