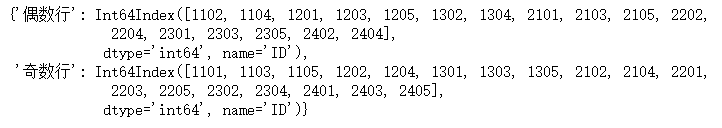数据分析之Pandas分组操作总结
↑↑↑关注后"星标"Datawhale
每日干货 & 每月组队学习,不错过
Datawhale干货
作者:耿远昊,Datawhale成员
Pandas做分析数据,可以分为索引、分组、变形及合并四种操作。之前介绍过索引操作,现在接着对Pandas中的分组操作进行介绍:主要包含SAC含义、groupby函数、聚合、过滤和变换、apply函数。文章的最后,根据今天的知识介绍,给出了6个问题与2个练习,供大家学习实践。
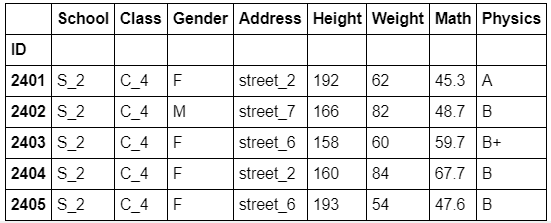
在详细讲解每个模块之前,首先读入数据:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
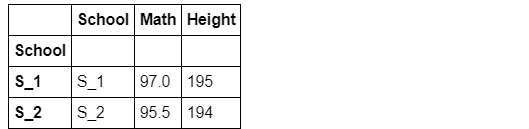
df = pd.read_csv('data/table.csv',index_col='ID')
df.head()
SAC过程
1. 内涵
SAC指的是分组操作中的split-apply-combine过程。其中split指基于某一些规则,将数据拆成若干组;apply是指对每一组独立地使用函数;combine指将每一组的结果组合成某一类数据结构。
2. apply过程
在apply过程中,我们实际往往会遇到四类问题:
整合(Aggregation):即分组计算统计量(如求均值、求每组元素个数);
变换(Transformation):即分组对每个单元的数据进行操作(如元素标准化);
过滤(Filtration):即按照某些规则筛选出一些组(如选出组内某一指标小于50的组);
综合问题:即前面提及的三种问题的混合。
groupby函数
经过groupby后会生成一个groupby对象,该对象本身不会返回任何内容,只有当相应的方法被调用才会起作用。
1. 分组函数的基本内容:
根据某一列分组
根据某几列分组
组容量与组数
组的遍历
level参数(用于多级索引)和axis参数
a). 根据某一列分组
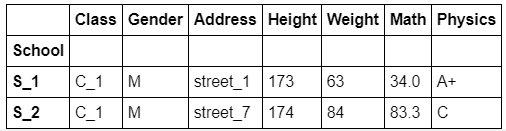
grouped_single = df.groupby('School')
经过groupby后会生成一个groupby对象,该对象本身不会返回任何东西,只有当相应的方法被调用才会起作用。例如取出某一个组:
grouped_single.get_group('S_1').head()
b). 根据某几列分组
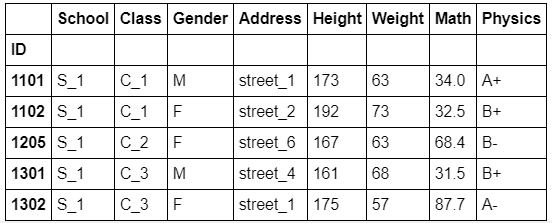
grouped_mul = df.groupby(['School','Class'])
grouped_mul.get_group(('S_2','C_4'))
c). 组容量与组数
调用的时候最好先根据size看下里面的内容,不然在get_group的时候可能会出错。
grouped_single.size()
grouped_mul.size()
grouped_single.ngroups
grouped_mul.ngroups
d). 组的遍历
for name,group in grouped_single:
print(name)
display(group.head())
e). level参数(用于多级索引)和axis参数
df.set_index(['Gender','School']).groupby(level=1,axis=0).get_group('S_1').head()
2. groupby对象的特点:
查看所有可调用的方法
分组对象的head 和first
分组依据
groupby的[]操作
连续型变量分组
a). 查看所有可调用的方法
由此可见,groupby对象可以使用相当多的函数,灵活程度很高
print([attr for attr in dir(grouped_single) if not attr.startswith('_')])
b). 分组对象的head和first
对分组对象使用head函数,返回的是每个组的前几行,而不是数据集前几行
grouped_single.head(2)
first显示的是以分组为索引的每组的第一个分组信息
grouped_single.first()
c). 分组依据
对于groupby函数而言,分组的依据是非常自由的,只要是与数据框长度相同的列表即可,同时支持函数型分组。
df.groupby(np.random.choice(['a','b','c'],df.shape[0])).get_group('a').head()
# 相当于将np.random.choice(['a','b','c'],df.shape[0])当做新的一列进行分组
从原理上说,我们可以看到利用函数时,传入的对象就是索引,因此根据这一特性可以做一些复杂的操作。
df[:5].groupby(lambda x:print(x)).head(0)
根据奇偶行分组。
df.groupby(lambda x:'奇数行' if not df.index.get_loc(x)%2==1 else '偶数行').groups
如果是多层索引,那么lambda表达式中的输入就是元组,下面实现的功能为查看两所学校中男女生分别均分是否及格。注意:此处只是演示groupby的用法,实际操作不会这样写。
math_score = df.set_index(['Gender','School'])['Math'].sort_index()
grouped_score = df.set_index(['Gender','School']).sort_index().\
groupby(lambda x:(x,'均分及格' if math_score[x].mean()>=60 else '均分不及格'))
for name,_ in grouped_score:print(name)
d). groupby的[]操作
可以用[]选出groupby对象的某个或者某几个列,上面的均分比较可以如下简洁地写出:
df.groupby(['Gender','School'])['Math'].mean()>=60
用列表可选出多个属性列:
df.groupby(['Gender','School'])[['Math','Height']].mean()
e). 连续型变量分组
例如利用cut函数对数学成绩分组:
bins = [0,40,60,80,90,100]
cuts = pd.cut(df['Math'],bins=bins) #可选label添加自定义标签
df.groupby(cuts)['Math'].count()
聚合、过滤和变换
1. 聚合
常用聚合函数
同时使用多个聚合函数
使用自定义函数
利用NameAgg函数
带参数的聚合函数
a). 常用聚合函数
所谓聚合就是把一堆数,变成一个标量,因此mean/sum/size/count/std/var/sem/describe/first/last/nth/min/max都是聚合函数。为了熟悉操作,不妨验证标准误sem函数,它的计算公式是:组内标准差/组容量,下面进行验证:
group_m = grouped_single['Math']
group_m.std().values/np.sqrt(group_m.count().values)== group_m.sem().values
![]()
b). 同时使用多个聚合函数
group_m.agg(['sum','mean','std'])
利用元组进行重命名
group_m.agg([('rename_sum','sum'),('rename_mean','mean')])
指定哪些函数作用哪些列
grouped_mul.agg({'Math':['mean','max'],'Height':'var'})
c). 使用自定义函数
grouped_single['Math'].agg(lambda x:print(x.head(),'间隔'))
#可以发现,agg函数的传入是分组逐列进行的,有了这个特性就可以做许多事情
官方没有提供极差计算的函数,但通过agg可以容易地实现组内极差计算
grouped_single['Math'].agg(lambda x:x.max()-x.min())
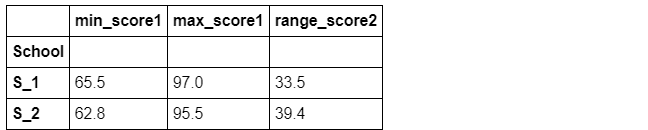
d). 利用NamedAgg函数进行多个聚合
注意:不支持lambda函数,但是可以使用外置的def函数
def R1(x):
return x.max()-x.min()
def R2(x):
return x.max()-x.median()
grouped_single['Math'].agg(min_score1=pd.NamedAgg(column='col1', aggfunc=R1),
max_score1=pd.NamedAgg(column='col2', aggfunc='max'),
range_score2=pd.NamedAgg(column='col3', aggfunc=R2)).head()
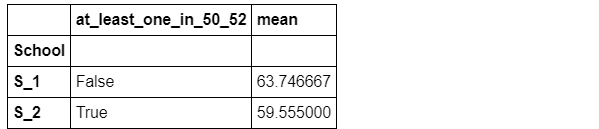
e). 带参数的聚合函数
判断是否组内数学分数至少有一个值在50-52之间:
def f(s,low,high):
return s.between(low,high).max()
grouped_single['Math'].agg(f,50,52)
如果需要使用多个函数,并且其中至少有一个带参数,则使用wrap技巧:
def f_test(s,low,high):
return s.between(low,high).max()
def agg_f(f_mul,name,*args,**kwargs):
def wrapper(x):
return f_mul(x,*args,**kwargs)
wrapper.__name__ = name
return wrapper
new_f = agg_f(f_test,'at_least_one_in_50_52',50,52)
grouped_single['Math'].agg([new_f,'mean']).head()
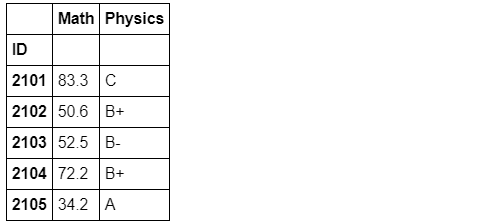
2. 过滤 Filteration
filter函数是用来筛选某些组的(务必记住结果是组的全体),因此传入的值应当是布尔标量。
grouped_single[['Math','Physics']].filter(lambda x:(x['Math']>32).all()).head()
3. 变换 Transformation
传入对象
利用变换方法进行组内标准化
利用变换方法进行组内缺失值的均值填充
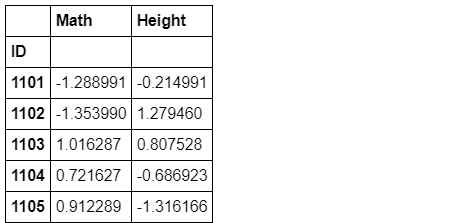
a). 传入对象
transform函数中传入的对象是组内的列,并且返回值需要与列长完全一致
grouped_single[['Math','Height']].transform(lambda x:x-x.min()).head()
如果返回了标量值,那么组内的所有元素会被广播为这个值
grouped_single[['Math','Height']].transform(lambda x:x.mean()).head()
b). 利用变换方法进行组内标准化
grouped_single[['Math','Height']].transform(lambda x:(x-x.mean())/x.std()).head()
c). 利用变换方法进行组内缺失值的均值填充
df_nan = df[['Math','School']].copy().reset_index()
df_nan.loc[np.random.randint(0,df.shape[0],25),['Math']]=np.nan
df_nan.head()
df_nan.groupby('School').transform(lambda x: x.fillna(x.mean())).join(df.reset_index()['School']).head()
apply函数
1. apply函数的灵活性
标量返回值
列表返回值
数据框返回值
可能在所有的分组函数中,apply是应用最为广泛的,这得益于它的灵活性:对于传入值而言,从下面的打印内容可以看到是以分组的表传入apply中。
df.groupby('School').apply(lambda x:print(x.head(1)))
apply函数的灵活性很大程度来源于其返回值的多样性:
a). 标量返回值
df[['School','Math','Height']].groupby('School').apply(lambda x:x.max())
b). 列表返回值
df[['School','Math','Height']].groupby('School').apply(lambda x:x-x.min()).head()
c). 数据框返回值
df[['School','Math','Height']].groupby('School')\
.apply(lambda x:pd.DataFrame({'col1':x['Math']-x['Math'].max(),
'col2':x['Math']-x['Math'].min(),
'col3':x['Height']-x['Height'].max(),
'col4':x['Height']-x['Height'].min()})).head()
2. 用apply同时统计多个指标
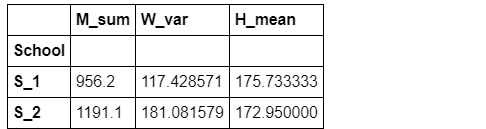
此处可以借助OrderedDict工具进行快捷的统计:
from collections import OrderedDict
def f(df):
data = OrderedDict()
data['M_sum'] = df['Math'].sum()
data['W_var'] = df['Weight'].var()
data['H_mean'] = df['Height'].mean()
return pd.Series(data)
grouped_single.apply(f)
问题与练习
问题
问题1. 什么是fillna的前向/后向填充,如何实现?
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('data/table.csv',index_col='ID')
df.head(3)
df_nan = df[['Math','School']].copy().reset_index()
df_nan.loc[np.random.randint(0,df.shape[0],25),['Math']]=np.nan
df_nan.head()
fillna 的method方法可以控制参数的填充方式,是向上填充:将缺失值填充为该列中它上一个未缺失值;向下填充相反
method : {‘backfill', ‘bfill', ‘pad', ‘ffill', None}, default None
pad / ffill: 向下自动填充
backfill / bfill: 向上自动填充
df_nan.Math=df_nan.Math.fillna(method='pad')
df_nan.head()
问题2. 下面的代码实现了什么功能?请仿照设计一个它的groupby版本。
s = pd.Series ([0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0])
s1 = s.cumsum()
result = s.mul(s1).diff().where(lambda x: x < 0).ffill().add(s1,fill_value =0)
s1:将s序列求累加和 [0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5]
s.mul(s1):s 与s1累乘 [0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 4, 5, 0]
.diff() 求一阶差分 [nan, 1.0, 1.0, -2.0, 3.0, 1.0, 1.0, -5.0]
.where(lambda x: x < 0) 值是否小于0:[nan, nan, nan, -2.0, nan, nan, nan, -5.0]
.ffill():向下填充 [nan, nan, nan, -2.0, -2.0, -2.0, -2.0, -5.0]
.add(s1,fill_value =0) 缺失值补0后与s1求和:[0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 0.0]
list(s.mul(s1).diff().where(lambda x: x < 0).ffill().add(s1,fill_value =0))
gp =df.groupby('School')
gp.apply(lambda x:x['Math'].mul(x['Math'].cumsum()).diff().where(lambda m: m < 0).ffill().add(x['Math'].cumsum(),fill_value =0)
问题3. 如何计算组内0.25分位数与0.75分位数?要求显示在同一张表上。
gp.apply(lambda x:pd.DataFrame({'q25':x.quantile(0.25),
'q75':x.quantile(0.75)
}))
问题4. 既然索引已经能够选出某些符合条件的子集,那么filter函数的设计有什么意义?
答:filter函数是用来筛选组的,结果是组的全体。
问题5. 整合、变换、过滤三者在输入输出和功能上有何异同?
整合(Aggregation)分组计算统计量:输入的是每组数据,输出是每组的统计量,在列维度上是标量。
变换(Transformation):即分组对每个单元的数据进行操作(如元素标准化):输入的是每组数据,输出是每组数据经过某种规则变换后的数据,不改变数据的维度。
过滤(Filtration):即按照某些规则筛选出一些组:输入的是每组数据,输出的是满足要求的组的所有数据。
问题6. 在带参数的多函数聚合时,有办法能够绕过wrap技巧实现同样功能吗?
def f_test(s,low=50,high=52):
return s.between(low,high).max()
grouped_single['Math'].agg([f_test,'mean']).head()
#这里需要理解的是,agg除了传入字符形式的np函数外,其他传入对象也应当是一个函数
练习
练习1 :现有一份关于diamonds的数据集,列分别记录了克拉数、颜色、开采深度、价格,请解决下列问题:
df=pd.read_csv('data/Diamonds.csv')
df.head(3)
(a). 在所有重量超过1克拉的钻石中,价格的极差是多少?
df.groupby(lambda x : '>1克拉' if df.loc[x,'carat']>1.0 else '<=1克拉').price.agg(lambda x:x.max()-x.min()
(b). 若以开采深度的0.2\0.4\0.6\0.8分位数为分组依据,每一组中钻石颜色最多的是哪一种?该种颜色是组内平均而言单位重量最贵的吗?
bins=[df.depth.quantile(i) for i in [0,0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8,1]]
df['cuts']=pd.cut(df.depth,bins=bins)
df['unit_price']=df['price']/df['carat']df.groupby(['cuts','color'])['unit_price'].agg(['count','mean']).reset_index().groupby('cuts')\
.apply(lambda x:pd.DataFrame({'cuts':x['cuts'],'color':x['color']
,'count':x['count'],'count_diff':x['count']-x['count'].max()
, 'mean':x['mean'], 'mean_diff':x['mean']-x['mean'].max()})).sort_values(by='count_diff',ascending=False)
##有些是单位质量最贵的,有些不是(当count_diff与mean_diff同为0时,则是)
(c). 以重量分组(0-0.5,0.5-1,1-1.5,1.5-2,2+),按递增的深度为索引排序,求每组中连续的严格递增价格序列长度的最大值。
bins=[0,0.5,1,1.5,2,6]
df['carat_cuts']=pd.cut(df.carat,bins=bins)
sorted_df=df.groupby('carat_cuts').apply(lambda x:x.sort_values('depth')).reset_index(drop=True)
#再求价格递增
tp=sorted_df.groupby('carat_cuts').apply(lambda x: pd.DataFrame({'carat_cuts':x['carat_cuts'],'price':x['price'],'is_f':x['price'].diff()>0,'continuous':((x['price'].diff()>0)!=(x['price'].diff()>0).shift()).cumsum()} ))
tp.loc[tp.is_f==True,:].groupby(['carat_cuts','continuous']).price.agg(['count']).reset_index().groupby('carat_cuts').max()
##因为没有计算序列第一个值。严格递增最大序列长度在max的基础上+1,结果如下.
#(0.0, 0.5] 8
#(0.5, 1.0] 8
#(1.0, 1.5] 7
#(1.5, 2.0] 11
#(2.0, 6.0] 7
(d). 请按颜色分组,分别计算价格关于克拉数的回归系数。(单变量的简单线性回归,并只使用Pandas和Numpy完成)
df['ones']=1
colors=['G','E','F','H','D','I','J']
for c in colors:
X=np.matrix( df.loc[ df.color==c, ['carat','ones']].values)
Y=np.matrix( df.loc[ df.color==c, ['price']].values)
params=np.linalg.inv(X.T@X)@X.T@Y
print('color {}的 参数为k={},b={}'.format(c,params[0],params[1]) )
# color G的 参数为k=[[8525.34577932]],b=[[-2575.52764286]]
# color E的 参数为k=[[8296.21278346]],b=[[-2381.04960038]]
# color F的 参数为k=[[8676.65834379]],b=[[-2665.80619085]]
# color H的 参数为k=[[7619.0983199]],b=[[-2460.41804636]]
# color D的 参数为k=[[8408.35312588]],b=[[-2361.01715228]]
# color I的 参数为k=[[7761.04116881]],b=[[-2878.15035558]]
# color J的 参数为k=[[7094.19209226]],b=[[-2920.60333719]]
练习2:有一份关于美国10年至17年的非法药物数据集,列分别记录了年份、州(5个)、县、药物类型、报告数量,请解决下列问题:
pd.read_csv('data/Drugs.csv').head()
(a). 按照年份统计,哪个县在哪年的报告数量最多?这个县所属的州在当年也是报告数最多的吗?
答:按照年份统计,HAMILTON在2017年报告数量最多,该县所属的州PA在当年不是报告数最多的。
df_ex2.groupby(['YYYY', 'COUNTY'])['DrugReports'].sum().sort_values(ascending = False
df_ex2['State'][df_ex2['COUNTY'] == 'HAMILTON'].unique()
array(['PA'], dtype=object)
df_ex2.loc[df_ex2['YYYY'] == 2017, :].groupby('State')['DrugReports'].sum().sort_values(ascending = False)
(b). 从14年到15年,Heroin的数量增加最多的是哪一个州?它在这个州是所有药物中增幅最大的吗?若不是,请找出符合该条件的药物。
答:从14年到15年,Heroin的数量增加最多的是OH,它在这个州是所有药物中增幅最大。
方法一
df_ex2_b_1 = df_ex2.loc[((df_ex2['YYYY'] == 2014) | (df_ex2['YYYY'] == 2015)) & (df_ex2['SubstanceName'] == 'Heroin'), :]
df_ex2_b_2 = df_ex2_b_1.groupby(['YYYY', 'State'])['DrugReports'].sum().to_frame().unstack(level=0)
(df_ex2_b_2[('DrugReports', 2015)] - df_ex2_b_2[('DrugReports', 2014)]).sort_values(ascending = False)
方法二
df_ex2_b_1 = df_ex2.loc[((df_ex2['YYYY'] == 2014) | (df_ex2['YYYY'] == 2015)) & (df_ex2['SubstanceName'] == 'Heroin'), :]
df_ex2_b_3 = df_ex2_b_1.groupby(['YYYY', 'State'])['DrugReports'].sum().to_frame()
df_ex2_b_3.groupby('State').apply(lambda x:x.loc[2015, :] - x.loc[2014, :]).sort_values(by = 'DrugReports', ascending = False)
df_ex2_b_1 = df_ex2.loc[((df_ex2['YYYY'] == 2014) | (df_ex2['YYYY'] == 2015)), :]
df_ex2_b_2 = df_ex2_b_1.groupby(['YYYY', 'State', 'SubstanceName'])['DrugReports'].sum().to_frame().unstack(level=0)
(df_ex2_b_2[('DrugReports', 2015)] - df_ex2_b_2[('DrugReports', 2014)]).sort_values(ascending = False)
本文电子版 后台回复 Pandas分组 获取
![]()
“在看,为沉迷学习点赞↓