java8使用Lambda表达式编写并发
java8使用Lambda表达式编写并发
- 1.提倡使用非阻塞性IO
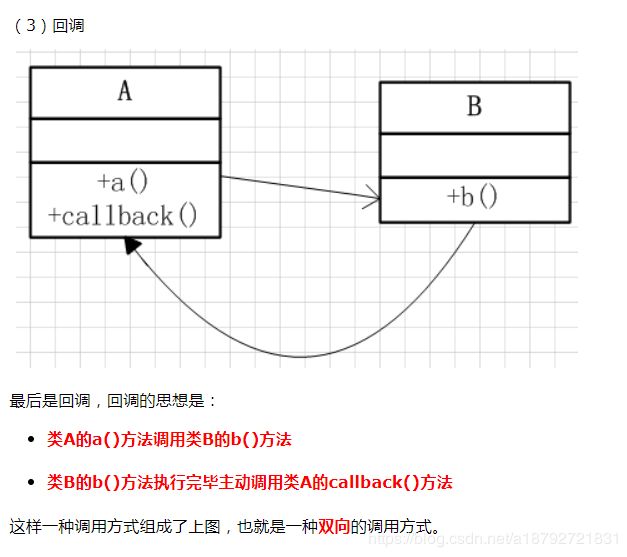
- 2.回调
- 3.Lambda化
- 4.末日金字塔
- 5.Future
- 6.CompletableFuture
- 7.supplyAsync
- 8.CompletableFuture一些常用方法
- 9.响应式编程
- 10.总结
1.提倡使用非阻塞性IO
阻塞性IO对于大量的数据的支持性并不是很好,如果有大量的IO操作等待执行,那么使用阻塞性IO就会降低整个程序的性能。
相反,使用非阻塞性IO就可以节省大量的时间。
通过名字就能明白,阻塞性IO就是在进行IO操作时,程序无法做其他的事情,只能等待IO完成后,在继续进行程序。
非阻塞行IO就是在进行IO操作的同时,软件可以做其他的事情。
2.回调
package intf;
public interface CallBack {
default void callBack(){
System.out.println("callBack default call back");
}
}
package intf;
public interface Student {
default void answer(CallBack callBack){
System.out.println("student default answer");
callBack.callBack();
}
}
package intf;
public interface Teacher extends CallBack{
default void question(Student student){
System.out.println("teacher default question");
student.answer(this);
}
}
package main;
import intf.CallBack;
import intf.Student;
import intf.Teacher;
import org.junit.Test;
public class Main {
@Test
public void test(){
new Teacher() {
@Override
public void question(Student student){
Teacher.super.question(student);
System.out.println("inner teacher");
}
@Override
public void callBack(){
Teacher.super.callBack();
System.out.println("inner callBack");
}
}.question(new Student() {
@Override
public void answer(CallBack callBack){
Student.super.answer(callBack);
System.out.println("inner student");
}
});
}
}
teacher default question
student default answer
callBack default call back
inner callBack
inner student
inner teacher
3.Lambda化
package intf;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CallBack {
// default void callBack(){
// System.out.println("callBack default call back");
// }
void callBack();
}
package intf;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Student {
// default void answer(CallBack callBack){
// System.out.println("student default answer");
// callBack.callBack();
// }
void answer(CallBack callBack);
}
package intf;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Teacher{
// default void question(Student student){
// System.out.println("teacher default question");
// student.answer(this);
// }
void question(Student student);
}
@Test
public void test(){
CallBack callBack = () -> System.out.println("callBack");
Teacher Wangteacher = (student) -> {
System.out.println("Wang teacher");
student.answer(callBack);
};
Student zhangStudent = (cal) -> {
System.out.println("Zhang student");
cal.callBack();
};
Wangteacher.question(zhangStudent);
}
Wang teacher
Zhang student
callBack
4.末日金字塔
可以看到未Lambda化的代码现在只是两层,如果有多层,那么随着缩进,代码都被挤到屏幕的右侧。
这种随着调用关系的增加,代码有规律的右移现象被称为末日金字塔(不知道是谁起的这个名字)
末日金字塔是良好代码风格的一个反例,在if语句,匿名内部类等情况下比较多见,特别是if语句中,如果if的层数大于2层,很容易发生末日金字塔的情况。
所以开发时尽可能的避免出现末日金字塔问题。
如果现在的代码已经出现末日金字塔的问题,那么尽快进行重构是一个非常明智的选择。
5.Future
Future像一张欠条,方法返回不是一个值,而是返回一个Future对象。
方法一开始执行的时候,返回一个欠条,等待一段时间后,可以使用欠条换钱。
需要注意:
Future对象的get方法会阻塞当前线程进行阻塞性获取值。
源码
public interface Future<V> {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
6.CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture结合了回调和Future的思想:
使用CompletableFuture与使用Stream类似,拥有许多的方法可以调用。
CompletableFuture最常用的情景之一是异步执行一段代码,然后返回执行结果。
7.supplyAsync
有一个工厂方法,用来创建异步的CompletableFuture实例。
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,
Executor executor) {
return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier);
}
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> asyncSupplyStage(Executor e,
Supplier<U> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture<U> d = new CompletableFuture<U>();
e.execute(new AsyncSupply<U>(d, f));
return d;
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
static final class AsyncSupply<T> extends ForkJoinTask<Void>
implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask {
CompletableFuture<T> dep; Supplier<T> fn;
AsyncSupply(CompletableFuture<T> dep, Supplier<T> fn) {
this.dep = dep; this.fn = fn;
}
public final Void getRawResult() { return null; }
public final void setRawResult(Void v) {}
public final boolean exec() { run(); return true; }
public void run() {
CompletableFuture<T> d; Supplier<T> f;
if ((d = dep) != null && (f = fn) != null) {
dep = null; fn = null;
if (d.result == null) {
try {
d.completeValue(f.get());
} catch (Throwable ex) {
d.completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
d.postComplete();
}
}
}
很明显的看出这个工厂方法执行的操作:
1.返回一个CompletableFuture实例
2.使用传入的Executor执行
3.使用内部类定义的方式进行许多费时的操作,但是因为使用了CompletableFuture的实例,所以初始化的线程与当前线程不是同一个线程。
需要注意的问题:
CompletableFuture实例并不是保证完成的。在线程执行的过程中发生异常,可能会导致线程异常,最后得不到返回值。
那么这个欠条就是坏账了。。
8.CompletableFuture一些常用方法
- 在链的末端执行一些代码不返回任何值:thenAccepy,thenRun
- 转换CompletableFuture的值,类似Stream的map方法:thenApply
- 当CompletableFuture出现异常时,可以使用exceptionally方法恢复,接受函数,返回替代值
- 存在一个map,既包含正常情况的结果,又包括异常情况的结果:handle
- 当CompletableFuture存在异常时,需要调试到底是什么问题:isDone,isCompleted,Exceptionally
9.响应式编程
RxJava类库
响应式编程:发膜护发的返回值从单一的返回值推广到数据流。
响应式编程实际是一种声明式编程。
举个例子:
在excel表格中,在某个单元格写下=B1+5.
这个时候就定义了这个单元格的值的运算规则。当B1格子填入数据后,这个格子的数据也就自动填充了,而且B1的值发生改变时,这个格子的值也会发生改变。
10.总结
时间驱动和响应式应用正在变得越来月流行,而且经常是最好的问题建模的方式之一。
相比阻塞式设计,这两种情况特别适合使用响应式或者时间驱动的方式思考。
- 1.业务逻辑本身就是使用事件来描述。Twitter,图形化。。。
- 2.需要同时处理大量的IO操作。阻塞式IO需要同时使用大量线程,会导致大量锁之间的竞争和太多的上下文切换。所以使用非阻塞性IO是一个更好的选择。
java8相关的源码: