人工智能:用爬山法、模拟退火算法实现八皇后和八数码问题
这里简单介绍下局部搜索算法。
局部搜索算法是对一个或多个状态进行评价和修改,而不是系统地从初始状态开始的路径。这些算法适用于关注那些关注解状态而不是路径代价的问题。
局部搜索算法从单个当前节点出发,通常只移动到它的临近状态,一般保存搜索路径。
局部搜素不是系统化的,但有两个关键的优点。
1. 只用很少的内存——通常是常数
2. 经常能在系统化算法不适用的很大或无限的状态空间中找到合理的解。
爬山法(最陡上升版本)搜索,简单的循环过程,不断向值增加的方向持续移动。算法在到达一个“峰顶”时终止,邻接状态中没有比它值更高的。
爬山法伪代码如下所示:
以八皇后问题为例说明爬山法。局部搜索算法一般使用完整状态形式化,即每个状态都包括在棋盘上放置8个皇后,每行各一个。后继函数指移动某个皇后到这行的另一个可能方格中,因此有7*8=56个后继。启发式评估函数h是形成互相攻击的皇后对的数量,不管是直接还是间接。在每一步移动之前,先计算棋盘上所有后继状态的启发式评估函数值h。然后选择h最小的那个后继状态,这里也就是选出移动后棋盘上皇后对冲突总个数最少的一个后继状态。
爬山法有时被称为贪婪局部搜索,因为它只是选择邻居中状态最好的一个,而不考虑下一步该如何走。尽管贪婪是七宗罪之一,贪婪算法却很有效。爬山法很快朝着解的方向进展,因为它可以很容易地改善一个坏的状态。不幸的是,爬山法经常会陷入困境。
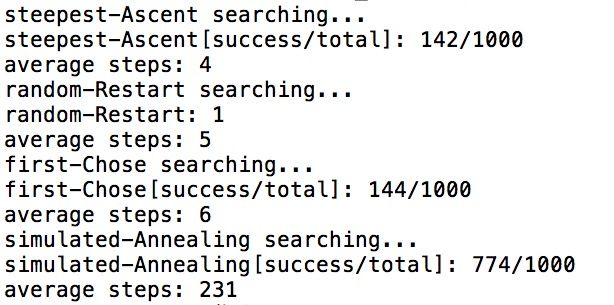
在每种情况下,爬山法都会到达无法再取得进展的地点。从随机生成的八皇后问题开始,最陡上升的爬山法86%的情况下会被卡住,只有14%的问题实例能求得解。算法求解的速度快,成功找到解的平均步数是4步,被卡住的平均步数是3步。(这是理论值,幸运的是,后面的运行结果可以发现与理论结果一致)
爬山法有很多变形。
随机爬山法在上山移动中随机地选择下一步,被选中的概率随着上山移动的陡峭程度不同而不同。这种算法通常比最陡上升算法的收敛速度慢不少。
首选爬山法实现了随机爬山法,随机地生成后继节点直到生成一个优于当前节点的后继。这个算法在后继节点很多的时候是个好策略。
随机重启爬山法通过随机生成初始状态来导引爬山法搜索,直到找到目标。这个算法完备的概率接近于1,因为它最终会生成一个目标状态作为初始状态。
现在再来讲下模拟退火搜索算法。
模拟退火算法的内层循环与爬山法类似,只是它没有选择最佳移动,而是随机移动。如果该移动使情况改善,该移动则被接收。否则,算法以某个小于1的概率接收该移动。如果移动导致状态“变坏”,概率则成指数级下降——评估值△E变坏。这个概率也随“温度”T降低而下降:开始T高的时候可能允许“坏的”移动,T越低则越不可能发生。如果调度让T下降得足够慢,算法找到最优解的概率逼近于1。
伪代码如下所示:
对于八数码问题,可以选择很多因素作为评估函数。这里我选取的是曼哈顿距离,每次移动都是往曼哈顿距离减少得最少的方向移动。
八数码代码实现如下:
#include 八皇后代码实现如下:
#include 八数码运行结果如下:
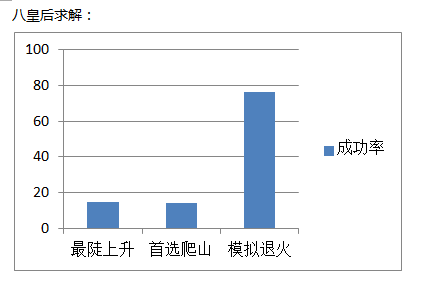
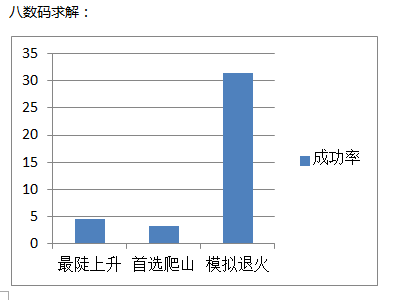
从实验运行结果看出,求解八数码和八皇后问题,用最陡上升爬山法和首选爬山法的查找成功率差不多大,八皇后的成功率为14~15%左右,八数码的成功率则为3~4%左右。
随机重启爬山法是遇到无解情况则重新开始初始状态直至找到有解,所以查找成功率几乎接近于1(理论上存在失败情况)。
而模拟退火搜索算法因为在选取下一状态的时候做了改进,所以无论是八皇后还是八数码,它的查找成功率是很高的。这里我的实现是八皇后77%,八数码30%。
在搜索代价方面, 这里仅显示了成功求解问题所需的平均移动步数。很明显,最陡上升爬山法、随机重启爬山法和首选爬山法的移动步数很少,几步之内就能很快求出解;模拟退火搜索算法虽然成功率高,但是移动步数却非常多,查找时间也比较长,代价也因此大了很多。