1.前言
- 最近一直在看 《Android进阶解密》 的一本书,这本书编写逻辑、流程都非常好,而且很容易看懂,非常推荐大家去看看(没有收广告费,单纯觉得作者写的很好)。
- 上一篇简单的介绍了Android进阶(四):Activity启动过程(最详细&最简单)。
- 今天就介绍Service 2种启动方式中:startService启动 (基于Android 8.0 系统)。
- 本文提供一种看源码的思路,因此bindService启动流程就没有再本文展开(与startService流程类似)。
- 文章中实例 linhaojian的Github
2.Context继承关系
-
在讲解Service启动过程前,先了解一下它的继承关系,便于后续的源码理解:
- 从图中,可以发现:
- Activity,Service,Application都是ContextWrapper的子类;
- ContextWrapper里面引用着一个ContextImpl实例;
- ContextWrapper里所有的方法都是通过调用ContextImpl进行实现;
- 通过上述3点可以发现,其他就是
[装饰者模式](https://www.jianshu.com/p/16e946f42ce1)
2.Service启动过程的时序图
3.源码分析
3.1 startService()启动分析
3.1.1 ContextImpl:
class ContextImpl extends Context {
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, false, mUser);// 1
}
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, boolean requireForeground,
UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
ComponentName cn = ActivityManager.getService().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), requireForeground,
getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());// 2
// ....
return cn;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
- 注释1:startService最终也是调用startServiceCommon函数;
- 注释2:ActivityManager.getService()其实就是ActivityManagerService,调用ActivityManagerService类里面的startService方法;
3.1.2 ActivityManagerService:
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//.....
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res;
try {
res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid,
requireForeground, callingPackage, userId);// 1
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return res;
}
}
- 注释1:调用ActiveServices的startServiceLocked();
3.1.3 ActiveServices:
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//.....
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, false, false);// 1
if (res == null) {
return null;
}
if (res.record == null) {
return new ComponentName("!", res.permission != null
? res.permission : "private to package");
}
ServiceRecord r = res.record;
if (!mAm.mUserController.exists(r.userId)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Trying to start service with non-existent user! " + r.userId);
return null;
}
//.....
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);// 2
return cmp;
}
- 注释1:创建 & 封装启动Service的相关数据;
- 注释2:调用自身的startServiceInnerLocked();
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
ServiceState stracker = r.getTracker();
if (stracker != null) {
stracker.setStarted(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(), r.lastActivity);
}
r.callStart = false;
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startRunningLocked();
}
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false, false); // 3
if (error != null) {
return new ComponentName("!!", error);
}
//.....
return r.name;
}
- 注释3:调用自身的bringUpServiceLocked();
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// ....
final boolean isolated = (r.serviceInfo.flags&ServiceInfo.FLAG_ISOLATED_PROCESS) != 0;
final String procName = r.processName;
String hostingType = "service";
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid
+ " app=" + app);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.longVersionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);// 4
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
}
} else {
app = r.isolatedProc;
if (WebViewZygote.isMultiprocessEnabled()
&& r.serviceInfo.packageName.equals(WebViewZygote.getPackageName())) {
hostingType = "webview_service";
}
}
//.....
}
- 注释4:调用自身的realStartServiceLocked();
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
//.....
boolean created = false;
try {
if (LOG_SERVICE_START_STOP) {
String nameTerm;
int lastPeriod = r.shortName.lastIndexOf('.');
nameTerm = lastPeriod >= 0 ? r.shortName.substring(lastPeriod) : r.shortName;
EventLogTags.writeAmCreateService(
r.userId, System.identityHashCode(r), nameTerm, r.app.uid, r.app.pid);
}
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startLaunchedLocked();
}
mAm.notifyPackageUse(r.serviceInfo.packageName,
PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_SERVICE);
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);// 5
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application dead when creating service " + r);
mAm.appDiedLocked(app);
throw e;
} finally {
//...
}
// 通知ActivityThread调用Service的onStartCommand方法
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);// 6
//.....
}
- 注释5:通知ActivityThread,真正的创建Service;
- 注释6:调用自身的sendServiceArgsLocked()启动Service的其他生命周期方法,下面会介绍;
3.1.4 ActivityThread:
- scheduleCreateService()其实就是通过Handler机制进行线程切换,最后会调用handleCreateService();
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);// 1
Service service = null;
try {
// 通过类加载器,创建Service实例
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();// 2
service = packageInfo.getAppFactory()
.instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);// 3
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//向Service对象中初始化基本设置
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());// 4
//调用service的onCreate生命周期函数
service.onCreate();// 5
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
- 注释1:获取LoadedApk对象,负责解析manifest文件;
- 注释2:获取ClassLoader类加载器,负责创建Service实例;
- 注释3:通过AppComponentFactory,创建Service对象;
- 注释4:设置Service基础参数;
- 注释5:调用Service的onCreate方法;
3.1.5 AppComponentFactory:
public class AppComponentFactory {
public @NonNull Service instantiateService(@NonNull ClassLoader cl,
@NonNull String className, @Nullable Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (Service) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();// 1
}
}
- 注释1:通过类加载器,创建Service实例;
3.1.6 ActiveServices的sendServiceArgsLocked()函数:
private final void sendServiceArgsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg,
boolean oomAdjusted) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
Exception caughtException = null;
try {
r.app.thread.scheduleServiceArgs(r, slice);// 1
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Transaction too large for " + args.size()
+ " args, first: " + args.get(0).args);
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed delivering service starts", e);
caughtException = e;
}
//....
}
- 注释1:调用ActivityThread的scheduleServiceArgs函数(在Service创建之后,会调用sendServiceArgsLocked(),实现其他的生命周期方法的调用);
3.1.7 ActivityThread的handleServiceArgs函数:
- scheduleServiceArgs()最终通过Handler机制切换线程 & 调用handleServiceArgs();
private void handleServiceArgs(ServiceArgsData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
if (data.args != null) {
data.args.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.args.prepareToEnterProcess();
}
int res;
if (!data.taskRemoved) {
res = s.onStartCommand(data.args, data.flags, data.startId);// 1
} else {
s.onTaskRemoved(data.args);
res = Service.START_TASK_REMOVED_COMPLETE;
}
//...
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...
}
}
}
- 注释1:调用Service的onStartCommand();
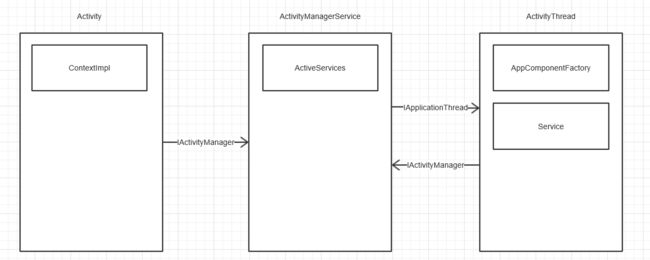
4.类关系
- 通过上图发现,Service启动过程就是AMS与ActivityThread不同的进程交互实现的。
5.总结
- 到此,
Service启动过程介绍完毕。 - 如果喜欢我的分享,可以点击 关注 或者 赞,你们支持是我分享的最大动力 。
- linhaojian的Github
欢迎关注linhaojian_CSDN博客或者linhaojian_!
不定期分享关于安卓开发的干货。
写技术文章初心
- 技术知识积累
- 技术知识巩固
- 技术知识分享
- 技术知识交流