对手写体Mnist数据集中10个字符 (0-9)的分类识别
目录
1、理解“查准率”、“查全率”、“F1-Score”、“ROC”、“混淆矩阵”的定义。
2、Jupyter编程完成对手写体Mnist数据集中10个字符 (0-9)的分类识别。
1、理解“查准率”、“查全率”、“F1-Score”、“ROC”、“混淆矩阵”的定义。
a、查准率与查全率
查准率(精度)是衡量某一检索系统的信号噪声比的一种指标,即检出的相关文献量与检出的文献总量的百分比。
查全率(召回率),是衡量某一检索系统从文献集合中检出相关文献成功度的一项指标,即检出的相关文献量与检索系统中相关文献总量的百分比。

查准率和查全率是一对矛盾的度量,查全率越高,查准率往往越低。因为查全需要的数量大,但数量大之后,所需目标数的数量所占百分比就越低;而查准需要所需的目标数越大,所以只会选择有把握的对象,这样就会漏掉许多的目标数,查全率就很低。
b、F1-Score
F1分数(F1 Score),是统计学中用来衡量二分类模型精确度的一种指标。它同时兼顾了分类模型的精确率和召回率。F1分数可以看作是模型精确率和召回率的一种调和平均,它的最大值是1,最小值是0。
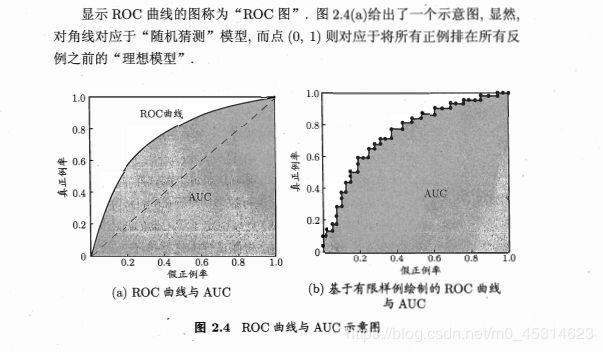
c、ROC
在信号检测理论中,接收者操作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,或者叫ROC曲线)是坐标图式的分析工具,用于 (1) 选择最佳的信号侦测模型、舍弃次佳的模型。 (2) 在同一模型中设定最佳阈值。
d、混淆矩阵
混淆矩阵也称误差矩阵,是表示精度评价的一种标准格式,用n行n列的矩阵形式来表示。具体评价指标有总体精度、制图精度、用户精度等,这些精度指标从不同的侧面反映了图像分类的精度。 [1] 在人工智能中,混淆矩阵(confusion matrix)是可视化工具,特别用于监督学习,在无监督学习一般叫做匹配矩阵。在图像精度评价中,主要用于比较分类结果和实际测得值,可以把分类结果的精度显示在一个混淆矩阵里面。混淆矩阵是通过将每个实测像元的位置和分类与分类图像中的相应位置和分类相比较计算的。
2、Jupyter编程完成对手写体Mnist数据集中10个字符 (0-9)的分类识别。
使用sklearn的函数来获取MNIST数据集
# 使用sklearn的函数来获取MNIST数据集
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
import numpy as np
import os
import datetime
# to make this notebook's output stable across runs
np.random.seed(42)
# To plot pretty figures
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
mpl.rc('axes', labelsize=14)
mpl.rc('xtick', labelsize=12)
mpl.rc('ytick', labelsize=12)
# 为了显示中文
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = [u'SimHei']
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 耗时巨大
def sort_by_target(mnist):
reorder_train=np.array(sorted([(target,i) for i, target in enumerate(mnist.target[:60000])]))[:,1]
reorder_test=np.array(sorted([(target,i) for i, target in enumerate(mnist.target[60000:])]))[:,1]
mnist.data[:60000]=mnist.data[reorder_train]
mnist.target[:60000]=mnist.target[reorder_train]
mnist.data[60000:]=mnist.data[reorder_test+60000]
mnist.target[60000:]=mnist.target[reorder_test+60000]
sklearn获取数据集所需的时间:
starttime=datetime.datetime.now()
mnist=fetch_openml('mnist_784',version=1,cache=True)
mnist.target=mnist.target.astype(np.int8)
sort_by_target(mnist)
endtime=datetime.datetime.now()
print("运行时间:",endtime-starttime)
mnist["data"], mnist["target"]
查看数据集维度
X,y=mnist["data"],mnist["target"]
X.shape
展示图片
# 展示图片
def plot_digit(data):
image = data.reshape(28, 28)
plt.imshow(image, cmap = mpl.cm.binary,
interpolation="nearest")
plt.axis("off")
some_digit = X[36000]
plot_digit(X[36000].reshape(28,28))
完成对手写体Mnist数据集中10个字符 (0-9)的分类识别
# 更好看的图片展示
def plot_digits(instances,images_per_row=10,**options):
size=28
# 每一行有一个
image_pre_row=min(len(instances),images_per_row)
images=[instances.reshape(size,size) for instances in instances]
# 有几行
n_rows=(len(instances)-1) // image_pre_row+1
row_images=[]
n_empty=n_rows*image_pre_row-len(instances)
images.append(np.zeros((size,size*n_empty)))
for row in range(n_rows):
# 每一次添加一行
rimages=images[row*image_pre_row:(row+1)*image_pre_row]
# 对添加的每一行的额图片左右连接
row_images.append(np.concatenate(rimages,axis=1))
# 对添加的每一列图片 上下连接
image=np.concatenate(row_images,axis=0)
plt.imshow(image,cmap=mpl.cm.binary,**options)
plt.axis("off")
plt.figure(figsize=(9,9))
example_images=np.r_[X[:12000:600],X[13000:30600:600],X[30600:60000:590]]
plot_digits(example_images,images_per_row=10)
plt.show()
3、参考文献
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42585108/article/details/105779031