Mybatis最全笔记--今日分享(参考狂神说)
一 CRUD(Mybatis)
1.namespace
namespace中的包名要和Dao/Mapper接口的包名一致。
2.select
选择,查询语句;
- id:就是对应的namespace中的方法名
- resultType:sql语句执行的返回值!
- parameterType:参数类型
1.编写接口
// 查询全部用户
List<User> selectUser();
2.编写对应的mapper中的sql语句
<select id="selectUser" resultType="com.Long.pojo.User">
SELECT * FROM mybatis.user
select>
3.测试
// 查询全部用户
@Test
public void test(){
// 通过工具类获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = utils.getSession();
// 执行sql(反射获得接口调用方法)
UserDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
List<User> userList = mapper.selectUser();
// 遍历数组
for (User user:userList
) {
System.out.println(user);
}
// 关闭sqlSession对象(避免内存泄漏)
sqlSession.close();
}
3.insert
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.Long.pojo.User" >
insert into mybatis.user (id,name,pwd) values (#{id},#{name},#{pwd});
insert>
4.update
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.Long.pojo.User" >
update mybatis.user set name=#{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id =#{id};
update>
5.delete
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="com.Long.pojo.User" >
delete from mybatis.user where id =#{id};
delete>
注意点:增删改需要提交事务
// 提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
6.模糊查询
方式一:(可能会产生sql注入)
@Test
public void test5(){
// 通过工具类获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = utils.getSession();
// 执行sql(反射获得接口调用方法)
UserDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
List<User> userList = mapper.getUserlike("飞");
for (User USER:userList
) {
System.out.println(USER);
}
// 关闭sqlSession对象(避免内存泄漏)
sqlSession.close();
}
<select id="getUserlike" parameterType="String" resultType="com.Long.pojo.User">
select * from mybatis.user where name like "%"#{value}"%";
select>
方式二:(推荐)
@Test
public void test5(){
// 通过工具类获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = utils.getSession();
// 执行sql(反射获得接口调用方法)
UserDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
List<User> userList = mapper.getUserlike("%飞%");
for (User USER:userList
) {
System.out.println(USER);
}
// 关闭sqlSession对象(避免内存泄漏)
sqlSession.close();
}
<select id="getUserlike" parameterType="String" resultType="com.Long.pojo.User">
select * from mybatis.user where name like #{value};
select>
二 配置解析
核心文件配置
- mybatis-config.xml
- Mybatis的配置文件包含了深深影响MyBatis行为的设置和属性信息。
- 属性优化
-
引入外部文件
<properties resource="mybatis.properties">properties> -
可以在其中增加一些属性配置
-
如果两个文件有同一字段,优先使用外部配置文件!
类型别名(typeAliases)
-
类型别名可为 Java 类型设置一个缩写名字。 它仅用于 XML 配置,意在降低冗余的全限定类名书写。
<typeAliases> <typeAlias type="com.Long.pojo.User" alias="user"/> typeAliases> -
也可以指定一个包名,MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean
<typeAliases> <package name="com.Long.pojo"/> typeAliases> -
每一个在包
com.Long中的 Java Bean,在没有注解的情况下,会使用 Bean 的首字母小写的非限定类名来作为它的别名。 比如com.Long.hello的别名为hello;若有注解,则别名为其注解值。
@Alias("hello")
<select id="selectUser" resultType="hello">
SELECT * FROM mybatis.user
select>
三 设置
mybatis极为重要的调整设置,他们会改变Mybatis的运行时行为
四 其他设置
- typeHandlers(类型处理器)
- objectFactory(对象工厂)
- plugins(插件)
- mybatis-generator-core
- mybatis-plus
- 通用mapper
五 映射器(mappers)
文档中提供4种,常用方式一
MapperRegistry:注册绑定我们的Mapper文件(类似于接口实现类)
方式一:
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/Long/dao/UserMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
方式二:
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.Long.dao.UserMapper"/>
mappers>
注意点:
- 接口和配置文件必须同名
- 接口和配置文件必须在同一包下
六 生命周期和作用域
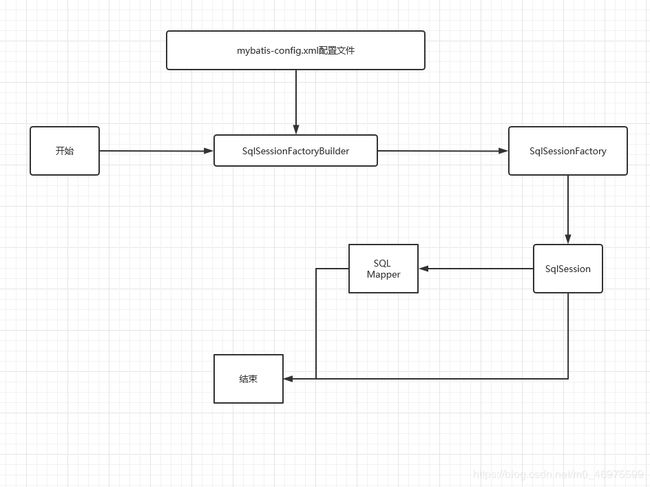
作用域和生命周期类别是至关重要的,因为错误的使用会导致非常严重的并发问题。
这里面的每一个Mapper,就代表一个具体的业务!
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:
- 一旦创建了 SqlSessionFactory,就不再需要它了
- 局部变量
SqlSessionFactory:
- 可以想象为数据库连接池
- SqlSessionFactory 一旦被创建就应该在应用的运行期间一直存在,没有任何理由丢弃它或重新创建另一个实例。
- 因此 SqlSessionFactory 的最佳作用域是应用作用域。
- 最简单的就是使用单例模式或者静态单例模式。
SqlSession:
- 连接到连接池的一个请求!
- SqlSession 的实例不是线程安全的,因此是不能被共享的,所以它的最佳的作用域是请求或方法作用域。
- 用完赶快关闭,否则资源被占用。
七 日志
如果一个数据库操作,出现了异常,那么日志是最好的排错助手!
主要:
-
STDOUT_LOGGING
-
lo4j
-
导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>log4jgroupId> <artifactId>log4jartifactId> <version>1.2.17version> dependency> -
写配置文件
-
配置log4j为日志的实现
-
log4j的使用
简单使用
- 在要使用的log4j类中,导入import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
- 日志对象,参数为当前类的class
- 日志级别
- info
- debug
- error
-
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
settings>
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-KOfQhzH7-1589118905499)(D:\前锋教育\自创学习资料\image\2020-05-09_091633.png)]
八 解决属性名和字段名不一致的问题
-
select
id name pwd ---> 数据库column
id name password ---> 实体类property
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="user">
<result column="pwd" property="password">result>
resultMap>
-
update,delete,insert
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="user" > insert into mybatis.user (id,name,pwd) values (#{id},#{name},#{password}); insert>
九 分页
用处:减少数据的处理量
// limit实现分页查询
@Test
public void test6(){
// 通过工具类获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = utils.getSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("startIndex",0);
map.put("pageSize",2);
List<User> userList = mapper.getlimit(map);
for (User USER:userList
) {
System.out.println(USER);
}
// 关闭sqlSession对象(避免内存泄漏)
sqlSession.close();
}
十 注解开发
本质:反射机制实现
底层:动态代理
使用
- 注解在接口上实现
- 需要在核心配置文件中绑定接口
- 测试
十一 MyBatis源码分析
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-qf6srHhz-1589118905501)(D:\前锋教育\自创学习资料\image\mybatis源码分析 (1)].png)
十二 lombok的使用
第一步:导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.12version>
dependency>
第二步:安装插件
第三步:测试
十三 多对一处理(association)
创建student表与teacher表;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `teacher`(
`id` INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
INSERT INTO `teacher` (`id`,`name`) VALUES (1,"韩老师");
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS student(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
tid INT DEFAULT NULL,
KEY `fktid`(tid),
CONSTRAINT `fiktid` FOREIGN KEY (tid) REFERENCES teacher (id)
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO student (id,`name`,tid) VALUES (5,'小齐',1);
注意 resources里不识别com.Long.dao,
解决办法:一个个创建。
方式一:按照查询嵌套处理:
<mapper namespace="com.Long.dao.StudentMapper">
<select id="selectTeacher" resultMap="StudentTeacher">
SELECT * FROM student;
select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="student">
<association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="Teacher" select="getTeacher">association>
resultMap>
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="Teacher">
select * from teacher where id =#{id};
select>
mapper>
方式二:按照结果嵌套处理:
<select id="SelectTeacher" resultMap="student_teacher">
SELECT t.id tid,s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname
FROM student s,teacher t
WHERE s.tid=t.id;
select>
<resultMap id="student_teacher" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="sid">result>
<result property="name" column="sname">result>
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher">
<result property="name" column="tname">result>
<result property="id" column="tid">result>
association>
resultMap>
类似于Mysql联表查询,子查询!
十四 一对多处理(collection)
方式二:按照结果嵌套处理:
<select id="selectTEACHER" resultMap="stuTeacher">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname,t.id tid
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid=t.id and t.id= #{tid}
select>
<resultMap id="stuTeacher" type="Teacher">
<result property="id" column="tid">result>
<result property="name" column="tname">result>
<collection property="students" ofType="Student">
<result property="name" column="sname">result>
<result property="id" column="sid">result>
<result property="tid" column="tid">result>
collection>
resultMap>
注意点:
- 保证sql的可读性
- 注意属性和字段名的问题
- 如果问题不好排错,用日志。
- oftype:用来指定实体类中属性的类型
- javatype:用来指定映射到List或者集合中的pojo类型,泛型中的约束类型。
十五:动态sql
根据不同的条件生成不同的sql语句
环境搭建:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS blog(
id VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY COMMENT '博客id',
title VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '博客标题',
author VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT '博客作者',
create_time DATETIME NOT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
views INT NOT NULL COMMENT '浏览量'
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
插入数据:
// 插入数据
@Test
public void insert(){
SqlSession session = utils.getSession();
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setId(IDutils.getid());
blog.setAuthor("韩海龙");
blog.setCreateTime(new Date());
blog.setViews(9999);
blog.setTitle("Mvbatis如此简单!");
mapper.addBlog(blog);
blog.setId(IDutils.getid());
blog.setTitle("Spring如此简单!");
mapper.addBlog(blog);
blog.setId(IDutils.getid());
blog.setTitle("Java如此简单!");
mapper.addBlog(blog);
blog.setId(IDutils.getid());
blog.setTitle("python如此简单!");
mapper.addBlog(blog);
blog.setId(IDutils.getid());
blog.setTitle("c++如此简单!");
mapper.addBlog(blog);
session.commit();
session.close();
}
动态sql就是在sql语句中加入逻辑判断
注意:开启事务自动提交:
public static SqlSession getSession() {
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
}
set标签(去除,)
<update id="updateBlog" parameterType="map" >
update mybatis.blog
<set>
<if test="title != null">
title=#{title},
if>
<if test="author != null">
author =#{author},
if>
set>
where id =#{id}
update>
where 标签(去除 and|or)
<select id="queryBlog" resultType="Blog" parameterType="map">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
title=#{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null ">
and author=#{author}
</when>
<otherwise>
and views={views}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
sql片段
有的时候,我们可能会将一些功能的部分抽取出来,方便复用!
1.使用sql标签抽取公共部分
<sql id="if-title-author">
<if test="title != null">
title=#{title},
if>
<if test="author != null">
author =#{author},
if>
sql>
2.在需要使用的地方使用include标签引用即可
注意事项:
- 最好基于单表来定义sql片段
- 不要存在where标签
foreach
动态 SQL 的另一个常见使用场景是对集合进行遍历(尤其是在构建 IN 条件语句的时候)。它允许你指定一个集合,声明可以在元素体内使用的集合项(item)和索引(index)变量。它也允许你指定开头与结尾的字符串以及集合项迭代之间的分隔符。
<select id="selectPostIn" resultType="blog" parameterType="map">
SELECT *
FROM blog b
WHERE id in
<foreach item="id" index="index" collection="strings"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
foreach>
select>
@Test
public void test4(){
SqlSession session = utils.getSession();
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
ArrayList<String> strings = new ArrayList<String>();
strings.add("613a27070e674889acd30063bf41d854");
strings.add("99cfdb02879847f89c0b21a64ce37da5");
map.put("strings",strings);
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.selectPostIn(map);
for (Blog blog:blogs
) {
System.out.println(blog);
}
session.close();
}
动态sql就是在拼接sql语句,我们只要保证sql的正确性,按照sql的格式,去排列组合就可以了。
@Test
public void test4(){
SqlSession session = utils.getSession();
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
ArrayList<String> strings = new ArrayList<String>();
strings.add("613a27070e674889acd30063bf41d854");
strings.add("99cfdb02879847f89c0b21a64ce37da5");
map.put("strings",strings);
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.selectPostIn(map);
for (Blog blog:blogs
) {
System.out.println(blog);
}
session.close();
}
动态sql就是在拼接sql语句,我们只要保证sql的正确性,按照sql的格式,去排列组合就可以了。
- 现在MySQL中写出完整的SQL,在对应的去修改成为动态的sql实现通用即可!

