ClassLoader
类加载器,功能是负责读取Java字节码代码(.class文件),并转换成java.lang.Class类的一个实例(每个实例代表一个Java类)并加载到JVM中。
是抽象类
public abstract class ClassLoader {
双亲委派
先用父类加载器加载,如果加载不了,再用自己加载
类加载器这种父类优先加载的规则主要是为了保证类的唯一性,在Java中判断两个类是否相同(注意这里是类而不是类的实例),除了判断它们的全类名是否相同还有一点是加载它们的类加载器是否是一个,只有两个都相同,才认为两个类是相同的(可以将类加载器理解为类的命名空间)。
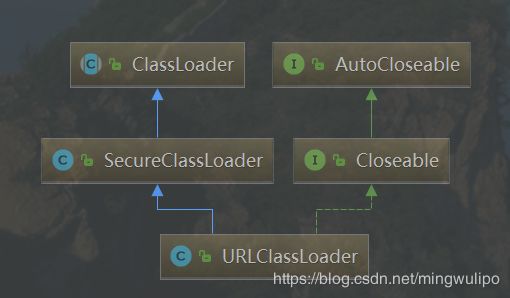
类继承关系。根加载器,扩展类加载器,系统类加载器,自定义类加载器

引导类加载器(bootstrapclass loader),用来加载Java的核心类库(通常从rt.jar加载),是虚拟机的一部分,通常使用C语言实现,与ClassLoader类无继承关系。
例如System.out.println(String.class.getClassLoader());//null
扩展类加载器(extensionsclass loader),用来加载Java的扩展库,这个扩展库专门指JDK的扩展库,从jre/lib/ext目录查找并加载类库,由Java语言实现。
例如System.out.println(EventID.class.getClassLoader());//sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@68e86f41
系统类加载器(systemclass loader),也称为应用类加载器,根据Java应用的类路径(ClassPath)来查找并加载Java类,由Java语言实现。
例如System.out.println(com.sun.javadoc.Doc.class.getClassLoader());//sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@68e86f41
加载引入的jar包,和自己写的代码
ClassLoader classLoader = LongToString.class.getClassLoader();
while(classLoader!=null) {
System.out.println("classLoader = " + classLoader.toString());
classLoader = classLoader.getParent();
}
classLoader = sun.misc.Launcher A p p C l a s s L o a d e r @ 18 b 4 a a c 2 c l a s s L o a d e r = s u n . m i s c . L a u n c h e r AppClassLoader@18b4aac2 classLoader = sun.misc.Launcher AppClassLoader@18b4aac2classLoader=sun.misc.LauncherExtClassLoader@2957fcb0
显式加载类
在代码中显式加载某个类,有三种方法:
this.getClass().getClassLoader().loadClass()
Class.forName()
MyClassLoader.findClass()
loadClass
/**
* Loads the class with the specified binary name.
* This method searches for classes in the same manner as the {@link
* #loadClass(String, boolean)} method. It is invoked by the Java virtual
* machine to resolve class references. Invoking this method is equivalent
* to invoking {@link #loadClass(String, boolean) loadClass(name,
* false)}.
*/
public Class loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(name, false);
}
/**
* Loads the class with the specified binary name. The
* default implementation of this method searches for classes in the
* following order:
*
*
*
* Invoke {@link #findLoadedClass(String)} to check if the class
* has already been loaded.
Invoke the {@link #loadClass(String) loadClass} method
* on the parent class loader. If the parent is null the class
* loader built-in to the virtual machine is used, instead.
Invoke the {@link #findClass(String)} method to find the
* class.
*
* If the class was found using the above steps, and the
* resolve flag is true, this method will then invoke the {@link
* #resolveClass(Class)} method on the resulting Class object.
*
*
Subclasses of ClassLoader are encouraged to override {@link
* #findClass(String)}, rather than this method.
*
* Unless overridden, this method synchronizes on the result of
* {@link #getClassLoadingLock getClassLoadingLock} method
* during the entire class loading process.
*/
protected Class loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
loadClass有3个步骤,findLoadedClass,调用根加载器加载或者父类加载器加载,findClass由子类实现,解析类resolveClass默认不执行
/**
* Returns the class with the given binary name if this
* loader has been recorded by the Java virtual machine as an initiating
* loader of a class with that binary name. Otherwise
* null is returned.
*/
protected final Class findLoadedClass(String name) {
if (!checkName(name))
return null;
return findLoadedClass0(name);
}
private native final Class findLoadedClass0(String name);
用根加载器加载,或者父类加载器加载
/**
* Returns a class loaded by the bootstrap class loader;
* or return null if not found.
*/
private Class findBootstrapClassOrNull(String name)
{
if (!checkName(name)) return null;
return findBootstrapClass(name);
}
// return null if not found
private native Class findBootstrapClass(String name);
findClass由子类实现
/**
* Finds the class with the specified binary name.
* This method should be overridden by class loader implementations that
* follow the delegation model for loading classes, and will be invoked by
* the {@link #loadClass loadClass} method after checking the
* parent class loader for the requested class. The default implementation
* throws a ClassNotFoundException.
*/
protected Class findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
解析类resolveClass
/**
* Links the specified class. This (misleadingly named) method may be
* used by a class loader to link a class. If the class c has
* already been linked, then this method simply returns. Otherwise, the
* class is linked as described in the "Execution" chapter of
* The Java™ Language Specification.
*/
protected final void resolveClass(Class c) {
resolveClass0(c);
}
private native void resolveClass0(Class c);
URLClassLoader实现findClass()
public class URLClassLoader extends SecureClassLoader implements Closeable {
/**
* Finds and loads the class with the specified name from the URL search
* path. Any URLs referring to JAR files are loaded and opened as needed
* until the class is found.
*
* @param name the name of the class
* @return the resulting class
* @exception ClassNotFoundException if the class could not be found,
* or if the loader is closed.
* @exception NullPointerException if {@code name} is {@code null}.
*/
protected Class findClass(final String name)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
final Class result;
try {
result = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction>() {
public Class run() throws ClassNotFoundException {
String path = name.replace('.', '/').concat(".class");
Resource res = ucp.getResource(path, false);
if (res != null) {
try {
return defineClass(name, res);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name, e);
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
}, acc);
} catch (java.security.PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw (ClassNotFoundException) pae.getException();
}
if (result == null) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
return result;
}
/*
* Defines a Class using the class bytes obtained from the specified
* Resource. The resulting Class must be resolved before it can be
* used.
*/
private Class defineClass(String name, Resource res) throws IOException {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
int i = name.lastIndexOf('.');
URL url = res.getCodeSourceURL();
if (i != -1) {
String pkgname = name.substring(0, i);
// Check if package already loaded.
Manifest man = res.getManifest();
definePackageInternal(pkgname, man, url);
}
// Now read the class bytes and define the class
java.nio.ByteBuffer bb = res.getByteBuffer();
if (bb != null) {
// Use (direct) ByteBuffer:
CodeSigner[] signers = res.getCodeSigners();
CodeSource cs = new CodeSource(url, signers);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getReadClassBytesTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t0);
return defineClass(name, bb, cs);
} else {
byte[] b = res.getBytes();
// must read certificates AFTER reading bytes.
CodeSigner[] signers = res.getCodeSigners();
CodeSource cs = new CodeSource(url, signers);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getReadClassBytesTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t0);
return defineClass(name, b, 0, b.length, cs);
}
}
}
SecureClassLoader
/**
* Converts a {@link java.nio.ByteBuffer ByteBuffer}
* into an instance of class {@code Class}, with an optional CodeSource.
* Before the class can be used it must be resolved.
*
* If a non-null CodeSource is supplied a ProtectionDomain is
* constructed and associated with the class being defined.
*
*/
protected final Class defineClass(String name, java.nio.ByteBuffer b,
CodeSource cs)
{
return defineClass(name, b, getProtectionDomain(cs));
}
ClassLoader
/**
* Converts a {@link java.nio.ByteBuffer ByteBuffer}
* into an instance of class Class,
* with an optional ProtectionDomain. If the domain is
* null, then a default domain will be assigned to the class as
* specified in the documentation for {@link #defineClass(String, byte[],
* int, int)}. Before the class can be used it must be resolved.
*
* The rules about the first class defined in a package determining the
* set of certificates for the package, and the restrictions on class names
* are identical to those specified in the documentation for {@link
* #defineClass(String, byte[], int, int, ProtectionDomain)}.
*
*
An invocation of this method of the form
* cl.defineClass(name,
* bBuffer, pd) yields exactly the same
* result as the statements
*
*
* ...
* byte[] temp = new byte[bBuffer.{@link
* java.nio.ByteBuffer#remaining remaining}()];
* bBuffer.{@link java.nio.ByteBuffer#get(byte[])
* get}(temp);
* return {@link #defineClass(String, byte[], int, int, ProtectionDomain)
* cl.defineClass}(name, temp, 0,
* temp.length, pd);
*
*/
protected final Class defineClass(String name, java.nio.ByteBuffer b,
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain)
throws ClassFormatError
{
int len = b.remaining();
// Use byte[] if not a direct ByteBufer:
if (!b.isDirect()) {
if (b.hasArray()) {
return defineClass(name, b.array(),
b.position() + b.arrayOffset(), len,
protectionDomain);
} else {
// no array, or read-only array
byte[] tb = new byte[len];
b.get(tb); // get bytes out of byte buffer.
return defineClass(name, tb, 0, len, protectionDomain);
}
}
protectionDomain = preDefineClass(name, protectionDomain);
String source = defineClassSourceLocation(protectionDomain);
Class c = defineClass2(name, b, b.position(), len, protectionDomain, source);
postDefineClass(c, protectionDomain);
return c;
}
protected final Class defineClass(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len,
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain)
throws ClassFormatError
{
protectionDomain = preDefineClass(name, protectionDomain);
String source = defineClassSourceLocation(protectionDomain);
Class c = defineClass1(name, b, off, len, protectionDomain, source);
postDefineClass(c, protectionDomain);
return c;
}
private native Class defineClass1(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len,
ProtectionDomain pd, String source);
ClassLoader.resolveClass()
loadClass只是加载到内存,后面还有链接,初始化。
/**
* Links the specified class. This (misleadingly named) method may be
* used by a class loader to link a class. If the class c has
* already been linked, then this method simply returns. Otherwise, the
* class is linked as described in the "Execution" chapter of
* The Java™ Language Specification.
*/
protected final void resolveClass(Class c) {
resolveClass0(c);
}
private native void resolveClass0(Class c);
自定义类加载器
默认父加载器是系统类加载器,即Launcher.getLauncher().getClassLoader()
public class MyClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyClassLoader mcl = new MyClassLoader();
System.out.println(mcl.getParent());//sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
}
}
ClassLoader
protected ClassLoader() {
this(checkCreateClassLoader(), getSystemClassLoader());
}
public static ClassLoader getSystemClassLoader() {
initSystemClassLoader();
if (scl == null) {
return null;
}
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkClassLoaderPermission(scl, Reflection.getCallerClass());
}
return scl;
}
private static synchronized void initSystemClassLoader() {
if (!sclSet) {
if (scl != null)
throw new IllegalStateException("recursive invocation");
sun.misc.Launcher l = sun.misc.Launcher.getLauncher();
if (l != null) {
Throwable oops = null;
scl = l.getClassLoader();
try {
scl = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new SystemClassLoaderAction(scl));
} catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
oops = pae.getCause();
if (oops instanceof InvocationTargetException) {
oops = oops.getCause();
}
}
if (oops != null) {
if (oops instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) oops;
} else {
// wrap the exception
throw new Error(oops);
}
}
}
sclSet = true;
}
}
重写loadClass,打破双亲委派
public class MyClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
@Override
public Class loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyClassLoader mcl = new MyClassLoader();
Class aClass = mcl.loadClass("com.dtdream.cma.svc.User");
ClassLoader cl = Launcher.getLauncher().getClassLoader();
Class aClass2 = cl.loadClass("com.dtdream.cma.svc.User");
System.out.println(aClass);
System.out.println(aClass2);
System.out.println(aClass == aClass2);
}
}
null
class com.dtdream.cma.svc.User
false
不重写loadClass,就还是双亲委派
public class MyClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
@Override
public Class loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return super.loadClass(name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyClassLoader mcl = new MyClassLoader();
Class aClass = mcl.loadClass("com.dtdream.cma.svc.User");
ClassLoader cl = Launcher.getLauncher().getClassLoader();
Class aClass2 = cl.loadClass("com.dtdream.cma.svc.User");
System.out.println(aClass);
System.out.println(aClass2);
System.out.println(aClass == aClass2);
}
}
class com.dtdream.cma.svc.User
class com.dtdream.cma.svc.User
true