从零开始之uboot、移植uboot2017.01(八、命令解析与实现)
终于到了最后的函数了
static int run_main_loop(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SANDBOX /* 没定义 */
sandbox_main_loop_init();
#endif
/* main_loop() can return to retry autoboot, if so just run it again */
for (;;)
main_loop();
return 0;
}
1.1、main_loop
void main_loop(void)
{
const char *s;
/* bootstage_mark_name函数调用了show_boot_progress,利用它显示启动进程(progress),
7 此处为空函数 */
bootstage_mark_name(BOOTSTAGE_ID_MAIN_LOOP, "main_loop");
#ifdef CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLE /* 没定义 */
setenv("ver", version_string); /* set version variable */
#endif /* CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLE */
/* cli_init用来初始化hush shell使用的一些变量。 */
cli_init();
/* 函数从环境变量中获取"preboot"的定义,*/
/* 该变量包含了一些预启动命令,一般环境变量中不包含该项配置。 */
run_preboot_environment_command();
#if defined(CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP) /* 网络相关的没定义 */
update_tftp(0UL, NULL, NULL);
#endif /* CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP */
/* bootdelay_process从环境变量中取出"bootdelay"和"bootcmd"的配置值 */
/* 将取出的"bootdelay"配置值转换成整数,赋值给全局变量stored_bootdelay */
/* 最后返回"bootcmd"的配置值 */
/* bootdelay为u-boot的启动延时计数值,计数期间内如无用户按键输入干预,那么将执行"bootcmd"配置中的命令 */
s = bootdelay_process();
if (cli_process_fdt(&s)) /* 环境变量里面有bootcmd,fdt如果有,fdt的会覆盖掉env里面的 */
cli_secure_boot_cmd(s);
/* autoboot_command,倒数计时实现,计时到-1前,没按键会指行bootcmd *
autoboot_command(s);
/* 进入 uboot 命令行中 */
cli_loop();
panic("No CLI available");
}
1.1.1、cli_init
void cli_init(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_HUSH_PARSER /* 定义了 */
u_boot_hush_start();
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_HUSH_INIT_VAR) /* 没定义 */
hush_init_var();
#endif
}
/* 初始化哈希表用到的参数 */
int u_boot_hush_start(void)
{
if (top_vars == NULL) {
top_vars = malloc(sizeof(struct variables));
top_vars->name = "HUSH_VERSION";
top_vars->value = "0.01";
top_vars->next = NULL;
top_vars->flg_export = 0;
top_vars->flg_read_only = 1;
#ifdef CONFIG_NEEDS_MANUAL_RELOC /* 没定义 */
u_boot_hush_reloc();
#endif
}
return 0;
}1.1.2、run_preboot_environment_command
static void run_preboot_environment_command(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_PREBOOT
char *p;
p = getenv("preboot");
if (p != NULL) {
# ifdef CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED
int prev = disable_ctrlc(1); /* disable Control C checking */
# endif
run_command_list(p, -1, 0);
# ifdef CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED
disable_ctrlc(prev); /* restore Control C checking */
# endif
}
#endif /* CONFIG_PREBOOT */
}1.1.2、bootdelay_process
默认是没配置CONFIG_AUTOBOOT
meke menuconfig配置添加这个宏,设置倒数时间,会出现开机倒数计时功能。
const char *bootdelay_process(void)
{
char *s;
int bootdelay;
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT /* 没定义 */
unsigned long bootcount = 0;
unsigned long bootlimit = 0;
#endif /* CONFIG_BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT */
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT /* 没定义 */
bootcount = bootcount_load();
bootcount++;
bootcount_store(bootcount);
setenv_ulong("bootcount", bootcount);
bootlimit = getenv_ulong("bootlimit", 10, 0);
#endif /* CONFIG_BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT */
s = getenv("bootdelay"); /* 这个是取得环境变量里的 */
bootdelay = s ? (int)simple_strtol(s, NULL, 10) : CONFIG_BOOTDELAY;
#ifdef CONFIG_OF_CONTROL /* 得到刚才配置的环境变量里的时间,并转化为整数,或覆盖前面的 */
bootdelay = fdtdec_get_config_int(gd->fdt_blob, "bootdelay",
bootdelay);
#endif
debug("### main_loop entered: bootdelay=%d\n\n", bootdelay);
#if defined(CONFIG_MENU_SHOW) /* 没定义 */
bootdelay = menu_show(bootdelay);
#endif
bootretry_init_cmd_timeout();
#ifdef CONFIG_POST /* 没定义 */
if (gd->flags & GD_FLG_POSTFAIL) {
s = getenv("failbootcmd");
} else
#endif /* CONFIG_POST */
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT /* 没定义 */
if (bootlimit && (bootcount > bootlimit)) {
printf("Warning: Bootlimit (%u) exceeded. Using altbootcmd.\n",
(unsigned)bootlimit);
s = getenv("altbootcmd");
} else
#endif /* CONFIG_BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT */
s = getenv("bootcmd"); /* 得到环境变量里的启动参数 */
process_fdt_options(gd->fdt_blob);
stored_bootdelay = bootdelay; /* 把bootdelay时间放到全局变量里面 */
return s;
}1.1.3、
void autoboot_command(const char *s)
{
debug("### main_loop: bootcmd=\"%s\"\n", s ? s : "");
/* 判断倒数计时 */
if (stored_bootdelay != -1 && s && !abortboot(stored_bootdelay)) {
#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)
int prev = disable_ctrlc(1); /* disable Control C checking bootdelay期间ctrl + C无效*/
#endif
/* 运行bootcmd */
run_command_list(s, -1, 0);
#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)
disable_ctrlc(prev); /* restore Control C checking */
#endif
}
#ifdef CONFIG_MENUKEY /* 没定义 */
if (menukey == CONFIG_MENUKEY) {
s = getenv("menucmd");
if (s)
run_command_list(s, -1, 0);
}
#endif /* CONFIG_MENUKEY */
}
static int abortboot(int bootdelay)
{
int abort = 0;
if (bootdelay >= 0) /* bootdelay大于0,就要实现倒数计时 */
abort = __abortboot(bootdelay);
#ifdef CONFIG_SILENT_CONSOLE /* 没定义 */
if (abort)
gd->flags &= ~GD_FLG_SILENT;
#endif
return abort;
}
static int __abortboot(int bootdelay)
{
int abort = 0;
unsigned long ts;
#ifdef CONFIG_MENUPROMPT /* 没定义 */
printf(CONFIG_MENUPROMPT);
#else
printf("Hit any key to stop autoboot: %2d ", bootdelay); /* 时间打印提示信息,2d是以两位数打印 */
#endif
/*
* Check if key already pressed
*/
if (tstc()) { /* we got a key press,判断串口是否有按键,有按键则终止 auto boot */
(void) getc(); /* consume input */
puts("\b\b\b 0");
abort = 1; /* don't auto boot */
}
while ((bootdelay > 0) && (!abort)) {
--bootdelay;
/* delay 1000 ms */
ts = get_timer(0);
do {
if (tstc()) { /* we got a key press */
abort = 1; /* don't auto boot */
bootdelay = 0; /* no more delay */
# ifdef CONFIG_MENUKEY
menukey = getc();
# else
(void) getc(); /* consume input */
# endif
break;
}
udelay(10000); //10000us = 10 ms延时
} while (!abort && get_timer(ts) < 1000); /* 有按键或超过1s则退出 */
printf("\b\b\b%2d ", bootdelay); /* 覆盖掉之前的显示,并显示新的时间 */
}
putc('\n');
return abort; /* 0表示没按键要执行bootcmd,1表示有按键 */
}
/* 执行命令行参数,和传进来的cmd有关 */
int run_command_list(const char *cmd, int len, int flag)
{
int need_buff = 1;
char *buff = (char *)cmd; /* cast away const */
int rcode = 0;
if (len == -1) {
len = strlen(cmd);
#ifdef CONFIG_HUSH_PARSER /* 我们使用哈希表 */
/* hush will never change our string */
need_buff = 0;
#else
/* the built-in parser will change our string if it sees \n */
need_buff = strchr(cmd, '\n') != NULL;
#endif
}
if (need_buff) {
buff = malloc(len + 1);
if (!buff)
return 1;
memcpy(buff, cmd, len);
buff[len] = '\0';
}
#ifdef CONFIG_HUSH_PARSER /* 解析字符串,在哈希表中找到对应的函数 */
rcode = parse_string_outer(buff, FLAG_PARSE_SEMICOLON);
#else
/*
* This function will overwrite any \n it sees with a \0, which
* is why it can't work with a const char *. Here we are making
* using of internal knowledge of this function, to avoid always
* doing a malloc() which is actually required only in a case that
* is pretty rare.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_CMDLINE
rcode = cli_simple_run_command_list(buff, flag); /* 这个函数我放在后面分析 */
#else
rcode = board_run_command(buff);
#endif
#endif
if (need_buff)
free(buff);
return rcode;
}
最终的函数
void cli_loop(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_HUSH_PARSER /* 一种是哈希表的文件结构分析命令行 */
parse_file_outer();
/* This point is never reached */
for (;;);
#elif defined(CONFIG_CMDLINE) /* 一种是循环扫描方式 */
cli_simple_loop();
#else
printf("## U-Boot command line is disabled. Please enable CONFIG_CMDLINE\n");
#endif /*CONFIG_HUSH_PARSER*/
}
哈希表的主要是一些算法上的,因为篇幅所限,这里就先跳过
static int parse_file_outer(FILE *f)
#else
int parse_file_outer(void)
#endif
{
int rcode;
struct in_str input;
#ifndef __U_BOOT__
setup_file_in_str(&input, f);
#else
setup_file_in_str(&input);
#endif
rcode = parse_stream_outer(&input, FLAG_PARSE_SEMICOLON);
return rcode;
}
我们简单分析一下循环命令行方式的
#define CONFIG_SYS_CBSIZE 256 //smdkv210.h文件定义,命令行的最大长度
void cli_simple_loop(void)
{
static char lastcommand[CONFIG_SYS_CBSIZE + 1] = { 0, };
int len;
int flag;
int rc = 1;
for (;;) {
if (rc >= 0) {
/* Saw enough of a valid command to
* restart the timeout. 命令行的rimeout主要是比如输入了一半命令好久没继续输入,则会把timeout超时提示重新输入,对主流程无关
*/
bootretry_reset_cmd_timeout();
}
/* 读取命令,比较重要,这个下面分析,传入参数CONFIG_SYS_PROMPT是我们在smdkv210_defconfig里面定义的"SMDKV210 #",也就是命令行提示符 */
len = cli_readline(CONFIG_SYS_PROMPT);
flag = 0; /* assume no special flags for now */
if (len > 0)
strlcpy(lastcommand, console_buffer, //把读到的命令拷贝到局部变量数组
CONFIG_SYS_CBSIZE + 1);
else if (len == 0)
flag |= CMD_FLAG_REPEAT;
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOT_RETRY_TIME //没定义
else if (len == -2) {
/* -2 means timed out, retry autoboot
*/
puts("\nTimed out waiting for command\n");
# ifdef CONFIG_RESET_TO_RETRY
/* Reinit board to run initialization code again */
do_reset(NULL, 0, 0, NULL);
# else
return; /* retry autoboot */
# endif
}
#endif
if (len == -1) /* -1是一些特殊的ctrl + c之类的特殊按键 */
puts("\n");
else
rc = run_command_repeatable(lastcommand, flag); /* 运行命令 */
if (rc <= 0) {
/* invalid command or not repeatable, forget it */
lastcommand[0] = 0;
}
}
} 读字符串
//全局变量
char console_buffer[CONFIG_SYS_CBSIZE + 1]; /* console I/O buffer */
int cli_readline(const char *const prompt)
{
/*
* If console_buffer isn't 0-length the user will be prompted to modify
* it instead of entering it from scratch as desired.
*/
console_buffer[0] = '\0'; /* 先初始化为0 */
/* 三个参数分别是 "SMDKV210 #", 空字符串, 0 */
return cli_readline_into_buffer(prompt, console_buffer, 0);
}
int cli_readline_into_buffer(const char *const prompt, char *buffer,
int timeout)
{
char *p = buffer;
/* 这个宏的作用是在使用终端时可以使用上下键,读取历史命令 */
#ifdef CONFIG_CMDLINE_EDITING
unsigned int len = CONFIG_SYS_CBSIZE;
int rc;
static int initted;
/*
* History uses a global array which is not
* writable until after relocation to RAM.
* Revert to non-history version if still
* running from flash.
*/
if (gd->flags & GD_FLG_RELOC) {
if (!initted) {
hist_init(); /* 初始化一些全局变量 */
initted = 1;
}
if (prompt)
puts(prompt); /* 打印命令行提示符 "SMDKV210 # */
rc = cread_line(prompt, p, &len, timeout); /* 读取命令行到上面传来的全局变量数组里(历史命令) */
return rc < 0 ? rc : len;
} else {
#endif /* CONFIG_CMDLINE_EDITING */
char *p_buf = p;
int n = 0; /* buffer index */
int plen = 0; /* prompt length */
int col; /* output column cnt */
char c;
/* print prompt */
if (prompt) {
plen = strlen(prompt); /* 打印命令行提示符 "SMDKV210 # */
puts(prompt);
}
col = plen;
for (;;) {
if (bootretry_tstc_timeout())
return -2; /* timed out */
WATCHDOG_RESET(); /* Trigger watchdog, if needed */
#ifdef CONFIG_SHOW_ACTIVITY
while (!tstc()) {
show_activity(0);
WATCHDOG_RESET();
}
#endif
c = getc();
/*
* Special character handling
*/
switch (c) {
case '\r': /* Enter */
case '\n':
*p = '\0';
puts("\r\n");
return p - p_buf;
case '\0': /* nul */
continue;
case 0x03: /* ^C - break */
p_buf[0] = '\0'; /* discard input */
return -1;
case 0x15: /* ^U - erase line */
while (col > plen) {
puts(erase_seq);
--col;
}
p = p_buf;
n = 0;
continue;
case 0x17: /* ^W - erase word */
p = delete_char(p_buf, p, &col, &n, plen);
while ((n > 0) && (*p != ' '))
p = delete_char(p_buf, p, &col, &n, plen);
continue;
case 0x08: /* ^H - backspace */
case 0x7F: /* DEL - backspace */
p = delete_char(p_buf, p, &col, &n, plen);
continue;
default:
/*
* Must be a normal character then
*/
if (n < CONFIG_SYS_CBSIZE-2) {
if (c == '\t') { /* expand TABs */
#ifdef CONFIG_AUTO_COMPLETE
/*
* if auto completion triggered just
* continue
*/
*p = '\0';
if (cmd_auto_complete(prompt,
console_buffer,
&n, &col)) {
p = p_buf + n; /* reset */
continue;
}
#endif
puts(tab_seq + (col & 07));
col += 8 - (col & 07);
} else {
char __maybe_unused buf[2];
/*
* Echo input using puts() to force an
* LCD flush if we are using an LCD
*/
++col;
buf[0] = c;
buf[1] = '\0';
puts(buf);
}
*p++ = c;
++n;
} else { /* Buffer full */
putc('\a');
}
}
}
#ifdef CONFIG_CMDLINE_EDITING
}
#endif
}
static int cread_line(const char *const prompt, char *buf, unsigned int *len,
int timeout)
{
unsigned long num = 0;
unsigned long eol_num = 0;
unsigned long wlen;
char ichar;
int insert = 1;
int esc_len = 0;
char esc_save[8];
int init_len = strlen(buf);
int first = 1;
if (init_len) /* 历史命令相关的 */
cread_add_str(buf, init_len, 1, &num, &eol_num, buf, *len);
while (1) {
if (bootretry_tstc_timeout())
return -2; /* timed out */
if (first && timeout) {
uint64_t etime = endtick(timeout);
while (!tstc()) { /* while no incoming data,反复的读命令,退出表明读到了字符输入 */
if (get_ticks() >= etime)
return -2; /* timed out */
WATCHDOG_RESET();
}
first = 0;
}
ichar = getcmd_getch(); // getcmd_getch == getc
/* 如果输入的是回车换行则退出break */
if ((ichar == '\n') || (ichar == '\r')) {
putc('\n');
break;
}
/*
* handle standard linux xterm esc sequences for arrow key, etc.
* 兼容linux的 xterm的关系不大
*/
if (esc_len != 0) {
enum { ESC_REJECT, ESC_SAVE, ESC_CONVERTED } act = ESC_REJECT;
if (esc_len == 1) {
if (ichar == '[' || ichar == 'O')
act = ESC_SAVE;
} else if (esc_len == 2) {
switch (ichar) {
case 'D': /* <- key */
ichar = CTL_CH('b');
act = ESC_CONVERTED;
break; /* pass off to ^B handler */
case 'C': /* -> key */
ichar = CTL_CH('f');
act = ESC_CONVERTED;
break; /* pass off to ^F handler */
case 'H': /* Home key */
ichar = CTL_CH('a');
act = ESC_CONVERTED;
break; /* pass off to ^A handler */
case 'F': /* End key */
ichar = CTL_CH('e');
act = ESC_CONVERTED;
break; /* pass off to ^E handler */
case 'A': /* up arrow */
ichar = CTL_CH('p');
act = ESC_CONVERTED;
break; /* pass off to ^P handler */
case 'B': /* down arrow */
ichar = CTL_CH('n');
act = ESC_CONVERTED;
break; /* pass off to ^N handler */
case '1':
case '3':
case '4':
case '7':
case '8':
if (esc_save[1] == '[') {
/* see if next character is ~ */
act = ESC_SAVE;
}
break;
}
} else if (esc_len == 3) {
if (ichar == '~') {
switch (esc_save[2]) {
case '3': /* Delete key */
ichar = CTL_CH('d');
act = ESC_CONVERTED;
break; /* pass to ^D handler */
case '1': /* Home key */
case '7':
ichar = CTL_CH('a');
act = ESC_CONVERTED;
break; /* pass to ^A handler */
case '4': /* End key */
case '8':
ichar = CTL_CH('e');
act = ESC_CONVERTED;
break; /* pass to ^E handler */
}
}
}
switch (act) {
case ESC_SAVE:
esc_save[esc_len++] = ichar;
continue;
case ESC_REJECT:
esc_save[esc_len++] = ichar;
cread_add_str(esc_save, esc_len, insert,
&num, &eol_num, buf, *len);
esc_len = 0;
continue;
case ESC_CONVERTED:
esc_len = 0;
break;
}
}
/* 输入的是特殊测什么ctrl +c,退格,ctrl+v之类,特殊处理*/
switch (ichar) {
case 0x1b:
if (esc_len == 0) {
esc_save[esc_len] = ichar;
esc_len = 1;
} else {
puts("impossible condition #876\n");
esc_len = 0;
}
break;
case CTL_CH('a'):
BEGINNING_OF_LINE();
break;
case CTL_CH('c'): /* ^C - break */
*buf = '\0'; /* discard input */
return -1;
case CTL_CH('f'):
if (num < eol_num) {
getcmd_putch(buf[num]);
num++;
}
break;
case CTL_CH('b'):
if (num) {
getcmd_putch(CTL_BACKSPACE);
num--;
}
break;
case CTL_CH('d'):
if (num < eol_num) {
wlen = eol_num - num - 1;
if (wlen) {
memmove(&buf[num], &buf[num+1], wlen);
putnstr(buf + num, wlen);
}
getcmd_putch(' ');
do {
getcmd_putch(CTL_BACKSPACE);
} while (wlen--);
eol_num--;
}
break;
case CTL_CH('k'):
ERASE_TO_EOL();
break;
case CTL_CH('e'):
REFRESH_TO_EOL();
break;
case CTL_CH('o'):
insert = !insert;
break;
case CTL_CH('x'):
case CTL_CH('u'):
BEGINNING_OF_LINE();
ERASE_TO_EOL();
break;
case DEL:
case DEL7:
case 8:
if (num) {
wlen = eol_num - num;
num--;
memmove(&buf[num], &buf[num+1], wlen);
getcmd_putch(CTL_BACKSPACE);
putnstr(buf + num, wlen);
getcmd_putch(' ');
do {
getcmd_putch(CTL_BACKSPACE);
} while (wlen--);
eol_num--;
}
break;
case CTL_CH('p'):
case CTL_CH('n'):
{
char *hline;
esc_len = 0;
if (ichar == CTL_CH('p'))
hline = hist_prev();
else
hline = hist_next();
if (!hline) {
getcmd_cbeep();
continue;
}
/* nuke the current line */
/* first, go home */
BEGINNING_OF_LINE();
/* erase to end of line */
ERASE_TO_EOL();
/* copy new line into place and display */
strcpy(buf, hline);
eol_num = strlen(buf);
REFRESH_TO_EOL();
continue;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_AUTO_COMPLETE
case '\t': {
int num2, col;
/* do not autocomplete when in the middle */
if (num < eol_num) {
getcmd_cbeep();
break;
}
buf[num] = '\0';
col = strlen(prompt) + eol_num;
num2 = num;
if (cmd_auto_complete(prompt, buf, &num2, &col)) {
col = num2 - num;
num += col;
eol_num += col;
}
break;
}
#endif
default:
/* 把字符放到buf数组里面去 */
cread_add_char(ichar, insert, &num, &eol_num, buf,
*len);
break; //
}
}
*len = eol_num;
buf[eol_num] = '\0'; /* lose the newline */
/* 保存参数 */
if (buf[0] && buf[0] != CREAD_HIST_CHAR)
cread_add_to_hist(buf);
hist_cur = hist_add_idx;
return 0;
}
运行命令
int run_command_repeatable(const char *cmd, int flag) //flag = 0
{
#ifndef CONFIG_HUSH_PARSER
return cli_simple_run_command(cmd, flag); /* 分析写个,不分析哈希的 */
#else
/*
* parse_string_outer() returns 1 for failure, so clean up
* its result.
*/
if (parse_string_outer(cmd,
FLAG_PARSE_SEMICOLON | FLAG_EXIT_FROM_LOOP))
return -1;
return 0;
#endif
}
int cli_simple_run_command(const char *cmd, int flag)
{
char cmdbuf[CONFIG_SYS_CBSIZE]; /* working copy of cmd */
char *token; /* start of token in cmdbuf */
char *sep; /* end of token (separator) in cmdbuf */
char finaltoken[CONFIG_SYS_CBSIZE];
char *str = cmdbuf;
char *argv[CONFIG_SYS_MAXARGS + 1]; /* NULL terminated */
int argc, inquotes;
int repeatable = 1;
int rc = 0;
debug_parser("[RUN_COMMAND] cmd[%p]=\"", cmd);
if (DEBUG_PARSER) {
/* use puts - string may be loooong */
puts(cmd ? cmd : "NULL");
puts("\"\n");
}
clear_ctrlc(); /* forget any previous Control C, */
if (!cmd || !*cmd) //错误判断
return -1; /* empty command */
if (strlen(cmd) >= CONFIG_SYS_CBSIZE) { //错误判断
puts("## Command too long!\n");
return -1;
}
strcpy(cmdbuf, cmd); /* 拷贝一份局部的cmd,这样可以随意修改 */
/* Process separators and check for invalid
* repeatable commands
*/
debug_parser("[PROCESS_SEPARATORS] %s\n", cmd);
while (*str) {
/*
* Find separator, or string end
* Allow simple escape of ';' by writing "\;
* 可以通过';'间隔,一次执行多条命令,这里是解析开如果有';'就解析成多条命令
*/
for (inquotes = 0, sep = str; *sep; sep++) {
if ((*sep == '\'') &&
(*(sep - 1) != '\\'))
inquotes = !inquotes;
if (!inquotes &&
(*sep == ';') && /* separator */
(sep != str) && /* past string start */
(*(sep - 1) != '\\')) /* and NOT escaped */
break;
}
/*
* Limit the token to data between separators
*
*/
token = str;
if (*sep) {
str = sep + 1; /* start of command for next pass */
*sep = '\0';
} else {
str = sep; /* no more commands for next pass */
}
debug_parser("token: \"%s\"\n", token);
/* find macros in this token and replace them,里面各种解析,主要是解析一些宏,比如uboot,kernel之类要解析成对应的地址等,通过finaltoken返回 */
cli_simple_process_macros(token, finaltoken);
/* Extract arguments,分解finaltoken,里面的命令行带的参数,分解成argc和argv类型 */
argc = cli_simple_parse_line(finaltoken, argv);
if (argc == 0) {
rc = -1; /* no command at all */
continue;
}
/* 真正的执行命令和前面解析好的参数 */
if (cmd_process(flag, argc, argv, &repeatable, NULL))
rc = -1;
/* Did the user stop this? */
if (had_ctrlc())
return -1; /* if stopped then not repeatable */
}
return rc ? rc : repeatable;
}
下面要用到的一些数据结构
enum command_ret_t {
CMD_RET_SUCCESS, /* 0 = Success */
CMD_RET_FAILURE, /* 1 = Failure */
CMD_RET_USAGE = -1, /* Failure, please report 'usage' error */
};
/* uboot中的所有命令都是采用这种形式,所以这个结构体很重要 */
struct cmd_tbl_s {
char *name; /* Command Name,比如bootcmd,help之类*/
int maxargs; /* maximum number of arguments,每个命令都有最大参数限制 */
int repeatable; /* autorepeat allowed? ,是否支持可重复,即按回车键会再次执行 */
/* Implementation function,正真的处理命令的函数 */
int (*cmd)(struct cmd_tbl_s *, int, int, char * const []);
char *usage; /* Usage message (short) ,短帮助信息*/
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP
char *help; /* Help message (long) 长帮助信息 */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_AUTO_COMPLETE
/* do auto completion on the arguments ,命令自动补全,目前我们是没定义的,可以在smdkv210.h中定义 */
int (*complete)(int argc, char * const argv[], char last_char, int maxv, char *cmdv[]);
#endif
};
typedef struct cmd_tbl_s cmd_tbl_t;
enum command_ret_t cmd_process(int flag, int argc, char * const argv[],
int *repeatable, ulong *ticks)
{
enum command_ret_t rc = CMD_RET_SUCCESS;
cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp;
/* Look up command in command table */
cmdtp = find_cmd(argv[0]); /* argv[0],就是命令本身,这里通过这个字符串找到对应的cmd_tbl_t */
if (cmdtp == NULL) { /* NULL表示没找到 */
printf("Unknown command '%s' - try 'help'\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
/* found - check max args */
if (argc > cmdtp->maxargs) /* 检查参数个数 */
rc = CMD_RET_USAGE;
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_BOOTD)
/* avoid "bootd" recursion */
else if (cmdtp->cmd == do_bootd) { /* 如果定义这个命令的话,则执行bootm命令 */
if (flag & CMD_FLAG_BOOTD) {
puts("'bootd' recursion detected\n");
rc = CMD_RET_FAILURE; /* 执行bootm是不会返回的,返回就说明错了 */
} else {
flag |= CMD_FLAG_BOOTD;
}
}
#endif
/* If OK so far, then do the command */
if (!rc) {
if (ticks)
*ticks = get_timer(0);
rc = cmd_call(cmdtp, flag, argc, argv); /* 执行找到的命令,并把上面解析好的参数传给它 */
if (ticks)
*ticks = get_timer(*ticks);
*repeatable &= cmdtp->repeatable; /* 执行完上一条命令,则把上一条命令的repet置位给大循环里面传过来的 */
}
if (rc == CMD_RET_USAGE)
rc = cmd_usage(cmdtp);
return rc;
}
查找到命令
cmd_tbl_t *find_cmd(const char *cmd)
{
cmd_tbl_t *start = ll_entry_start(cmd_tbl_t, cmd);
const int len = ll_entry_count(cmd_tbl_t, cmd);
return find_cmd_tbl(cmd, start, len);
}
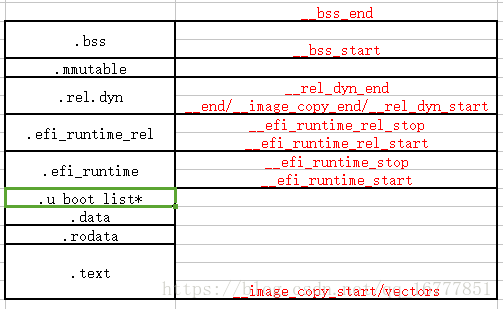
在分析这命令之前,我们先看一下uboot的链接脚本布局
这里有个u_boot_list*段
我们分析一个简单的uboot的命令实现
const char __weak version_string[] = U_BOOT_VERSION_STRING;
/* 真正的函数,所有的函数格式都是cmd_tbl_t里面的函数指针一样 */
static int do_version(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char * const argv[])
{
printf("\n%s\n", version_string);
#ifdef CC_VERSION_STRING
puts(CC_VERSION_STRING "\n");
#endif
#ifdef LD_VERSION_STRING
puts(LD_VERSION_STRING "\n");
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_COREBOOT
printf("coreboot-%s (%s)\n", lib_sysinfo.version, lib_sysinfo.build);
#endif
return 0;
}
/* 这句是真正的定义uboot的一个命令,U_BOOT_CMD是一个宏下面我们一次把这个version命令展开 */
U_BOOT_CMD(
version, 1, 1, do_version,
"print monitor, compiler and linker version",
""
);
看起来很负责的样子,我们一步一步来展开
#define U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, \
_usage, _help, _comp) \
{ #_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, \
_CMD_HELP(_help) _CMD_COMPLETE(_comp) }
#define ll_entry_declare(_type, _name, _list) \
_type _u_boot_list_2_##_list##_2_##_name __aligned(4) \
__attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_"#_list"_2_"#_name)))
#define U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help, _comp) \
ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, _name, cmd) = \
U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, \
_usage, _help, _comp);
#define U_BOOT_CMD(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help) \
U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help, NULL)第一步
U_BOOT_CMD(
version, 1, 1, do_version,
"print monitor, compiler and linker version",
""
);
#define U_BOOT_CMD(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help) \
U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help, NULL)
展开后
#define U_BOOT_CMD(version, 1, 1, do_version,"print monitor, compiler and linker version", "") \
U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(version, 1, 1, do_version, "print monitor, compiler and linker version", "", NULL)
第二步
U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(version, 1, 1, do_version, "print monitor, compiler and linker version", "", NULL)
#define U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help, _comp) \
ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, _name, cmd) = \
U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, \
_usage, _help, _comp);
展开后
#define U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(version, 1, 1, do_version, "print monitor, compiler and linker version", "", NULL) \
ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, version, cmd) = \
U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(version, 1, 1, do_version, \
"print monitor, compiler and linker version", "", NULL);
第三步
ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, version, cmd) = \
U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(version, 1, 1, do_version, \
"print monitor, compiler and linker version", "", NULL);
#define ll_entry_declare(_type, _name, _list) \
_type _u_boot_list_2_##_list##_2_##_name __aligned(4) \
__attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_"#_list"_2_"#_name)))
#define U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, \
_usage, _help, _comp) \
{ #_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, \
_CMD_HELP(_help) _CMD_COMPLETE(_comp) }
这里面有量个宏,我们分两次分别展开
第一个
ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, version, cmd)
#define ll_entry_declare(_type, _name, _list) \
_type _u_boot_list_2_##_list##_2_##_name __aligned(4) \
__attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_"#_list"_2_"#_name)))
#define ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, version, cmd) \
cmd_tbl_t _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version __aligned(4) \
__attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version")))
第二个
U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(version, 1, 1, do_version, \
"print monitor, compiler and linker version", "", NULL);
#define U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, \
_usage, _help, _comp) \
{ #_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, \
_CMD_HELP(_help) _CMD_COMPLETE(_comp) }
#define U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(version, 1, 1, do_version, \
"print monitor, compiler and linker version", "", NULL) \
{ "version", 1, 1, do_version, "print monitor, compiler and linker version", \
_CMD_HELP("") _CMD_COMPLETE(NULL) }
第四步、合并上一步的两个
#define ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, version, cmd) \
cmd_tbl_t _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version __aligned(4) \
__attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version")))
#define U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(version, 1, 1, do_version, \
"print monitor, compiler and linker version", "", NULL) \
{ "version", 1, 1, do_version, "print monitor, compiler and linker version", \
_CMD_HELP("") _CMD_COMPLETE(NULL) }
合并后
cmd_tbl_t _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version __aligned(4) __attribute__ ((unused,section(".u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version")))
{
"version",
1,
1,
do_version,
"print monitor, compiler and linker version",
_CMD_HELP("") _CMD_COMPLETE(NULL)
}第五步
#ifdef CONFIG_AUTO_COMPLETE /* 假设都定义了 */
# define _CMD_COMPLETE(x) x,
#else
# define _CMD_COMPLETE(x)
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP
# define _CMD_HELP(x) x,
#else
# define _CMD_HELP(x)
#endif
cmd_tbl_t _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version __aligned(4) __attribute__ ((unused,section(".u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version")))
{
"version",
1,
1,
do_version,
"print monitor, compiler and linker version",
_CMD_HELP("") _CMD_COMPLETE(NULL)
}
展开后
cmd_tbl_t _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version __aligned(4) __attribute__ ((unused,section(".u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_version")))
{
"version",
1,
1,
do_version,
"print monitor, compiler and linker version",
"",
NULL, /* 自动命令补全 */
}
通过上面的五步分析可以看到,每个命令结构体都会被__sttribute__定义在一个新的段里面,这里可以看到每个命令的段都是不同的,那怎么统一管理呢?
看一下连接脚本就懂了
用*,只要前面的u_boot_list段相同,后面的不同用*则忽略,这样吧所有的命令都定义在了这个段里面了。
下面要用到一个宏在这里就一块分析了
#define ll_entry_count(_type, _list) \
({ \
_type *start = ll_entry_start(_type, _list); \
_type *end = ll_entry_end(_type, _list); \
unsigned int _ll_result = end - start; \
_ll_result; \
})
假设传给它的还是cmd_tbl_t 和version
#define ll_entry_count(cmd_tbl_t , version) \
({ \
cmd_tbl_t *start = ll_entry_start(cmd_tbl_t , version); \
cmd_tbl_t *end = ll_entry_end(cmd_tbl_t , version); \
unsigned int _ll_result = end - version; \
_ll_result; \
})
#define ll_entry_start(_type, _list) \
({ \
static char start[0] __aligned(4) __attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_"#_list"_1"))); \
(_type *)&start; \
})
替换后
#define ll_entry_start(cmd_tbl_t , version) \
({ \
static char start[0] __aligned(4) __attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_version_1"))); \
(cmd_tbl_t *)&start; \
})
继续
static char start[0] __aligned(4) __attribute__ ((unused,section(".u_boot_list_2_version_1")));
(cmd_tbl_t *)&start;
#define ll_entry_end(_type, _list) \
({ \
static char end[0] __aligned(4) __attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_"#_list"_3"))); \
(_type *)&end; \
})
替换
#define ll_entry_end(cmd_tbl_t , version) \
({ \
static char end[0] __aligned(4) __attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_version_3"))); \
(cmd_tbl_t *)&end; \
})
继续 定义一个指针,用来存放 该段的地址
static char end[0] __aligned(4) __attribute__ ((unused, section(".u_boot_list_2_version_3")));
(cmd_tbl_t *)&end;
#define ll_entry_count(cmd_tbl_t , version) \
({ \
cmd_tbl_t *start = ll_entry_start(cmd_tbl_t , version); \
cmd_tbl_t *end = ll_entry_end(cmd_tbl_t , version); \
unsigned int _ll_result = end - version; \
_ll_result; \
})
整体替换
#define ll_entry_count(cmd_tbl_t , version) \
({ \
cmd_tbl_t *start = &u_boot_list_2_version_1; \
cmd_tbl_t *end = &u_boot_list_2_version_3; \
unsigned int _ll_result = end - version; \
_ll_result; \
})
为什么一个boot_list要定义这么多的1、2、3这么多的段,看一下官方的举例解释
/**
* A linker list is constructed by grouping together linker input
* sections, each containing one entry of the list. Each input section
* contains a constant initialized variable which holds the entry's
* content. Linker list input sections are constructed from the list
* and entry names, plus a prefix which allows grouping all lists
* together. Assuming _list and _entry are the list and entry names,
* then the corresponding input section name is
*
* .u_boot_list_ + 2_ + @_list + _2_ + @_entry
*
* and the C variable name is
*
* _u_boot_list + _2_ + @_list + _2_ + @_entry
*
* This ensures uniqueness for both input section and C variable name.
*
* Note that the names differ only in the first character, "." for the
* section and "_" for the variable, so that the linker cannot confuse
* section and symbol names. From now on, both names will be referred
* to as
*
* %u_boot_list_ + 2_ + @_list + _2_ + @_entry
*
* Entry variables need never be referred to directly.
*
* The naming scheme for input sections allows grouping all linker lists
* into a single linker output section and grouping all entries for a
* single list.
*
* Note the two '_2_' constant components in the names: their presence
* allows putting a start and end symbols around a list, by mapping
* these symbols to sections names with components "1" (before) and
* "3" (after) instead of "2" (within).
* Start and end symbols for a list can generally be defined as
*
* %u_boot_list_2_ + @_list + _1_...
* %u_boot_list_2_ + @_list + _3_...
*
* Start and end symbols for the whole of the linker lists area can be
* defined as
*
* %u_boot_list_1_...
* %u_boot_list_3_...
*
* Here is an example of the sorted sections which result from a list
* "array" made up of three entries : "first", "second" and "third",
* iterated at least once.
*
* .u_boot_list_2_array_1
* .u_boot_list_2_array_2_first
* .u_boot_list_2_array_2_second
* .u_boot_list_2_array_2_third
* .u_boot_list_2_array_3
*
* If lists must be divided into sublists (e.g. for iterating only on
* part of a list), one can simply give the list a name of the form
* 'outer_2_inner', where 'outer' is the global list name and 'inner'
* is the sub-list name. Iterators for the whole list should use the
* global list name ("outer"); iterators for only a sub-list should use
* the full sub-list name ("outer_2_inner").
*
* Here is an example of the sections generated from a global list
* named "drivers", two sub-lists named "i2c" and "pci", and iterators
* defined for the whole list and each sub-list:
*
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_1
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_i2c_1
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_i2c_2_first
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_i2c_2_first
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_i2c_2_second
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_i2c_2_third
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_i2c_3
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_pci_1
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_pci_2_first
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_pci_2_second
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_pci_2_third
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_2_pci_3
* %u_boot_list_2_drivers_3
*/哇,还来2可以实现很多个。好吧,我们还是分析点简单的。
下面再分析find_cmd就会简单有一些
cmd_tbl_t *find_cmd(const char *cmd)
{
/* 可以看到上面ll_entry_start/ll_entry_start这个宏解析后就是一个和命令名称相关的唯一的段 */
cmd_tbl_t *start = ll_entry_start(cmd_tbl_t, cmd);
const int len = ll_entry_count(cmd_tbl_t, cmd); /* 假设我们的长度就1个命令 */
return find_cmd_tbl(cmd, start, len); /* 命令的地址和长度都有了,接下来就直接搜索就可以 */
}
find_cmd_tbl
/* find command table entry for a command */
cmd_tbl_t *find_cmd_tbl(const char *cmd, cmd_tbl_t *table, int table_len)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_CMDLINE
cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp;
cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp_temp = table; /* Init value */
const char *p;
int len;
int n_found = 0;
if (!cmd) /* 检查参数有效 */
return NULL;
/*
* Some commands allow length modifiers (like "cp.b");
* compare command name only until first dot.
* 上面注释说的比较明白了,一些命令会有多个命令既,比如cp.b cp.w cp.l,命令集每个的后缀和命令名用.间隔
*/
/* 如果是命令集,只要.前面命令的长度 */
len = ((p = strchr(cmd, '.')) == NULL) ? strlen (cmd) : (p - cmd);
/* 循环搜索,看命令集(1个命令也可以这样称呼)中的名字能否匹配上 */
for (cmdtp = table; cmdtp != table + table_len; cmdtp++) {
if (strncmp(cmd, cmdtp->name, len) == 0) {
if (len == strlen(cmdtp->name)) /* 命令集中的名字长度和这个一致 */
return cmdtp; /* full match,正确返回这个命令结构体的地址 */
cmdtp_temp = cmdtp; /* abbreviated command ? */
n_found++;
}
}
if (n_found == 1) { /* exactly one match */
return cmdtp_temp;
}
#endif /* CONFIG_CMDLINE */
return NULL; /* not found or ambiguous command,没找到则返回NULL */
}通过查找,如果找到命令了,则就要执行命令了
static int cmd_call(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char * const argv[])
{
int result;
/* 执行函数命令很简单,直接一个指针函数调用,具体函数在命令实现中 */
result = (cmdtp->cmd)(cmdtp, flag, argc, argv); /* 正常命令执行返回0 */
if (result)
debug("Command failed, result=%d\n", result);
return result;