状态机的描述方法案例分析(一段式、二段式、三段式)
上篇博文讲了:FPGA中有限状态机的状态编码采用格雷码还是独热码?
那篇博文讲了状态机的状态编码是用格雷码还是独热码的问题,以及两者之间的优劣。状态机的描述方式采用的是一段式描述方式,也就是将整个状态机全部写到一个always模块中去。
这篇博文仍用上篇博文的案例,说说状态机的描述方法。一段式的描述方法、二段式以及三段式,并比较三者之间的功能仿真情况,最后真心吐露这个案例的状态转移图的疑问?不能把有问题的地方回避,我想我不要做这样的人。
首先看看状态机的描述方法,和编码方式,这两段描述借鉴:基于Verilog HDL的有限状态机,人家说的不错,我也懒着码字了。
状态机的描述方法
状态机的描述方法多种多样,将整个状态机写到1个always 模块里,在该模块中既描述状态转移,又描述状态的输入和输出,这种写法一般被称为一段式FSM 描述方法;
还有一种写法是使用两个always模块,其中一个always 模块采用同步时序的方式描述状态转移,而另一个模块采用组合逻辑的方式判断状态转移条件,描述状态转移规律,这种写法被称为两段式FSM 描述方法;
还有一种写法是在两段式描述方法的基础上发展而来的,这种写法使用3 个always模块,一个always 模块采用同步时序的方式描述状态转移,一个采用组合逻辑的方式判断状态转移条件,描述状态转移规律,第三个always 模块使用同步时序电路描述每个状态的输出,这种写法称为三段式写法。
状态机的状态编码
二进制码(Binary)和格雷码(Gray)属于压缩状态编码,这种编码的优点是使用的状态向量最少,但是需要较多的逻辑资源用来状态译码。二进制码从一个状态转换到相邻状态时,可能有多个比特位发生变化,易产生中间状态转移问题,状态机的速度也要比采用其它编码方式慢。格雷码两个相邻的码值仅有一位就可区分,这将会减少电路中相邻物理信号线同时变化的情况,因而可以减少电路中的电噪声。Johnson码也有同样的特点,但是要用较多的位数。
独热码(One-hot)指对任意给定的状态,状态寄存器中只有l位为1,其余位都为0。n状态的有限状态机需要n个触发器,但这种有限状态机只需对寄存器中的一位进行译码,简化了译码逻辑电路,额外触发器占用的面积可用译码电路省下来的面积抵消。当设计中加入更多的状态时,译码逻辑没有变得更加复杂,有限状态机的速度仅取决于到某特定状态的转移数量,而其它类型有限状态机在状态增加时速度会明显下降。独热码还具有设计简单、修改灵活、易于综合和调试等优点。独热码相对于二进制码,速度快但占用面积大。
给出实际案例:
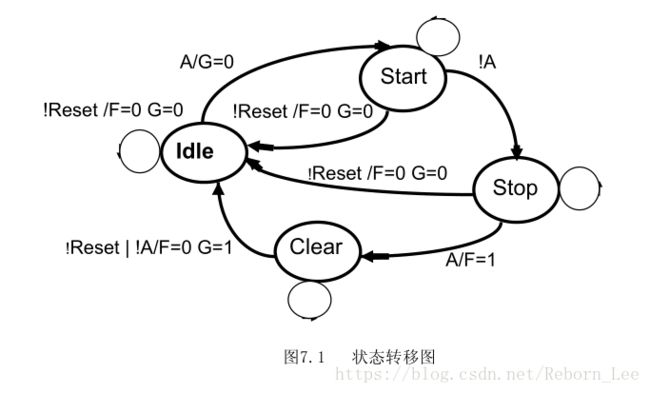
下面是一个状态转移图,我们接下来就这个状态转移图来用不同的描述方式来描述。
1)一段式描述方法:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 21:27:04 09/02/2018
// Design Name:
// Module Name: fsm
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
module fsm(
input Clock,
input rst_n,
input A,
output F,
output G
);
reg F, G;
reg [3:0] state;
parameter Idle = 4'b1000, Start = 4'b0100, Stop = 4'b0010, Clear = 4'b0001;
always @(posedge Clock) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
state <= Idle;
F <= 1'b0;
G <= 1'b0;
end
else
case(state)
Idle: begin
if(A) begin
state <= Start;
G <= 1'b0;
end
else
state <= Idle;
end
Start: begin
if(!A)
state <= Stop;
else
state <= Start;
end
Stop: begin
if(A) begin
state <= Clear;
F <= 1'b1;
end
else
state <= Stop;
end
Clear: begin
if(!A)begin
state <= Idle;
F <= 1'b0;
G <= 1'b1;
end
else
state <= Clear;
end
default: state <= Idle;
endcase
end
endmodule
给出测试文件,测试文件在这个案例中通用:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 23:39:28 09/02/2018
// Design Name: fsm
// Module Name: G:/modelsim_file/fsm01/fsm_tb.v
// Project Name: fsm01
// Target Device:
// Tool versions:
// Description:
//
// Verilog Test Fixture created by ISE for module: fsm
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
module fsm_tb;
// Inputs
reg Clock;
reg rst_n;
reg A;
// Outputs
wire F;
wire G;
// Instantiate the Unit Under Test (UUT)
fsm uut (
.Clock(Clock),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.A(A),
.F(F),
.G(G)
);
initial begin
// Initialize Inputs
rst_n = 0;
A = 0;
#30 A = 1;
rst_n = 1;
#30 A = 0;
#20 A = 1;
#20 A = 0;
// Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish
#100;
end
initial begin
Clock = 0;
forever #10 Clock = ~Clock;
end
endmodule
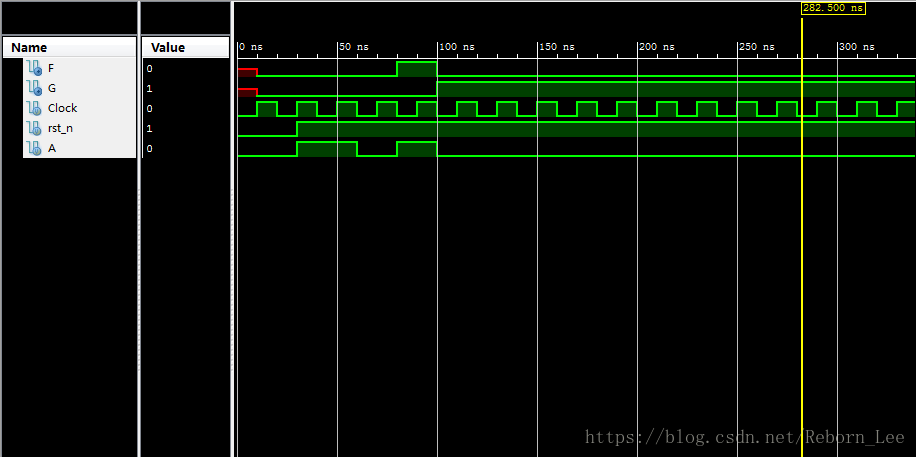
功能仿真:
两段式描述方法:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 21:27:04 09/02/2018
// Design Name:
// Module Name: fsm
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
module fsm(
input Clock,
input rst_n,
input A,
output F,
output G
);
reg F, G;
reg [3:0] pre_state;
reg [3:0] next_state;
parameter Idle = 4'b1000, Start = 4'b0100, Stop = 4'b0010, Clear = 4'b0001;
//第一个过程,同步时序always块,描述状态转移方程
always @(posedge Clock) begin
if(!rst_n)
pre_state <= Idle;
else
pre_state <= next_state;
end
//第二个过程,组合逻辑always块,描述激励方程以及输出方程
always @(pre_state or A or rst_n) begin
case(pre_state)
Idle:begin
if(!rst_n) begin
next_state = Idle;
F = 1'b0;
G = 1'b0;
end
else if(A) begin
next_state = Start;
G = 1'b0;
end
else begin
next_state = Idle;
end
end
Start: begin
if(!rst_n) begin
next_state = Idle;
F = 1'b0;
G = 1'b0;
end
else if(!A) begin
next_state = Stop;
end
else begin
next_state = Start;
end
end
Stop: begin
if(!rst_n) begin
next_state = Idle;
F = 1'b0;
G = 1'b0;
end
else if(A) begin
next_state = Clear;
F = 1'b1;
end
else begin
next_state = Stop;
end
end
Clear: begin
if(!rst_n) begin
next_state = Idle;
F = 1'b0;
G = 1'b0;
end
else if(!A) begin
next_state = Idle;
F = 0;
G = 1;
end
else begin
next_state = Clear;
end
end
default: begin
next_state = Idle;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
三段式描述:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 21:27:04 09/02/2018
// Design Name:
// Module Name: fsm
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
module fsm(
input Clock,
input rst_n,
input A,
output F,
output G
);
reg F, G;
reg [3:0] pre_state;
reg [3:0] next_state;
parameter Idle = 4'b1000, Start = 4'b0100, Stop = 4'b0010, Clear = 4'b0001;
//第一个过程,同步时序always块,描述状态转移方程
always @(posedge Clock) begin
if(!rst_n)
pre_state <= Idle;
else
pre_state <= next_state;
end
//第二个过程,组合逻辑always块,描述激励方程
always @(pre_state or A or rst_n) begin
case(pre_state)
Idle: begin
if(!rst_n) next_state = Idle;
else if(A) next_state = Start;
else next_state = Idle;
end
Start: begin
if(!rst_n) next_state = Idle;
else if(!A) next_state = Stop;
else next_state = Start;
end
Stop: begin
if(!rst_n) next_state = Idle;
else if(A) next_state = Clear;
else next_state = Stop;
end
Clear: begin
if(!rst_n) next_state = Idle;
else if(!A) next_state = Idle;
else next_state = Clear;
end
default: next_state = Idle;
endcase
end
//第三个always块,描述输出方程
always @(pre_state or A or rst_n) begin
case(pre_state)
Idle:begin
if(!rst_n) begin
F = 1'b0;
G = 1'b0;
end
else if(A) begin
G = 1'b0;
end
else begin
;
end
end
Start: begin
if(!rst_n) begin
F = 1'b0;
G = 1'b0;
end
else if(!A) begin
;
end
else begin
;
end
end
Stop: begin
if(!rst_n) begin
F = 1'b0;
G = 1'b0;
end
else if(A) begin
F = 1'b1;
end
else begin
;
end
end
Clear: begin
if(!rst_n) begin
F = 1'b0;
G = 1'b0;
end
else if(!A) begin
F = 0;
G = 1;
end
else begin
;
end
end
default: begin
;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
功能仿真:
可见,三种描述方式的仿真图都是一样的,说明了完成同样的功能。
但是从代码的简洁度来看,就这个小状态转移图来说,无疑,一段式的描述方式是最为简单的。但是随着项目的复杂度增高,这种描述方式不便于维护和阅读。
所以呢?要综合来看,不能说哪一种一定好,哪一种一定坏,要根据实际情况而定。
最后我要提出的问题,就是Clear这个状态向Idle这个状态转移的条件:从状态图上看,注意图中的状态图的复位我用rst_n代替,这样更人性化!继续:从状态图上看,是!rst_n或!A有效时,向Idle状态转移,并且输出是F = 0 ,且 G =1;
但是从原作者的一段式代码中,我们可以看出,复位信号rst_n的优先级别要高,如果复位了,那么状态肯定转向Idle,且此时,输出F=0且G=0.这明显和状态转移图中的意思不一样啊,我们推测状态转移图写法有误,所以这里我个人默认复位信号有限,其次是输入A和当前状态决定输出。也就是说,如果复位信号无效时,当前状态为Clear且 !A有效,那么输出就是F = 0 ,且 G =1,并且状态转向Idle.