关于Scikit-Learn,你不一定知道的10件事
点击上方“AI公园”,关注公众号,选择加“星标“或“置顶”
作者:Rebecca Vickery
编译:ronghuaiyang
导读
Scikit-learn中有很多方便的功能,你不一定知道。
Scikit-learn是使用最广泛的Python机器学习库之一。它有一个标准化和简单的接口用来预处理数据和进行模型的训练,优化和评估。
该项目最初是由David Cournapeau开发的谷歌Summer of Code项目,并在2010年首次公开发布。自创建以来,这库已经发展成为一个丰富的生态系统,用于开发机器学习模型。
随着时间的推移,该项目开发了许多方便的功能,增强了其易用性。在本文中,我将介绍10个你可能不知道的最有用的特性。
1. Scikit-learn 有内置的数据集
Scikit-learn API有多种内置的toy和现实世界数据集。只需一行代码就可以访问这些函数,如果你正在学习或只是想快速尝试一些新功能,那么它们非常有用。
你还可以使用生成器方便地为回归make_regression()、聚类make_blobs()以及分类make_classification()生成合成数据集。
所有的加载工具都提供了返回已经分割成X(特征)和y(目标)的数据的选项,这样就可以直接使用它们来训练模型。
# Toy regression data set loading
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
X,y = load_boston(return_X_y = True)
# Synthetic regresion data set loading
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
X,y = make_regression(n_samples=10000, noise=100, random_state=0)
2. 第三方公开数据集获取也很方便
如果你想通过Scikit-learn直接访问更多公开可用的数据集,有一个方便的函数可以让你直接从openml.org网站导入数据。这个网站包含超过21,000种不同的数据集,用于机器学习项目。
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
X,y = fetch_openml("wine", version=1, as_frame=True, return_X_y=True)
3. 有现成的分类器来训练基线模型
在开发机器学习模型时,明智的做法是首先创建一个基线模型。这个模型本质上应该是一个“伪”模型,比如总是预测最经常出现的类。这为你的“智能”模型提供了一个基准,这样你就可以确保它比随机结果表现得更好。
Scikit-learn中包含用于分类任务的 DummyClassifier()和用于回归问题的DummyRegressor()。
from sklearn.dummy import DummyClassifier
# Fit the model on the wine dataset and return the model score
dummy_clf = DummyClassifier(strategy="most_frequent", random_state=0)
dummy_clf.fit(X, y)
dummy_clf.score(X, y)
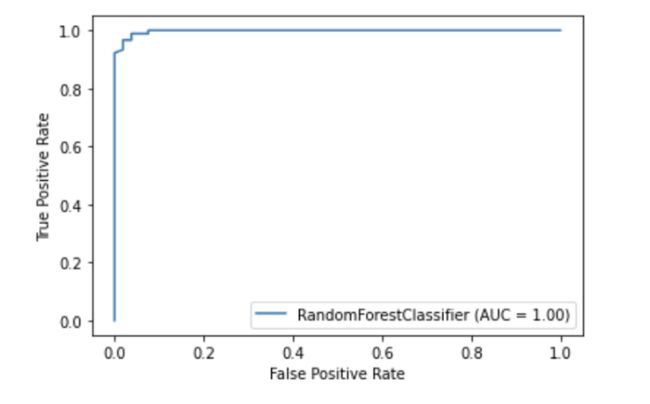
4. Scikit-learn 有自己的绘图 API
Scikit-learn有一个内置的绘图API,它允许你在不导入任何其他库的情况下可视化模型性能。包括下列绘图功能:部分依赖图、混淆矩阵、精确度召回率曲线和ROC曲线。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import metrics, model_selection
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
X,y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y = True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
clf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=0)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
metrics.plot_roc_curve(clf, X_test, y_test)
plt.show()
5. Scikit-learn 具有内置的特征选择方法
提高模型性能的一种方法是只使用最好的特征集来训练模型,或者去除冗余的特征。这个过程称为特征选择。
Scikit-learn有许多函数来进行feature selection。其中一个是SelectPercentile()。该方法根据所选择的统计方法选择表现最好的X百分位特征进行评分。
from sklearn import model_selection
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectPercentile, chi2
X,y = load_wine(return_X_y = True)
X_trasformed = SelectPercentile(chi2, percentile=60).fit_transform(X, y)
6. Pipelines 可以让你把所有的机器学习工作流串到一起
除了为机器学习提供广泛的算法,Scikit-learn也有一系列的预处理和数据变换的功能。为了便于机器学习工作流的重现性和简单性,Scikit-learn创建了**pipeline **,它允许你将大量的预处理步骤与模型训练阶段链接在一起。
pipeline将工作流中的所有步骤存储为单个实体,可以通过fit和predict方法调用。在pipeline对象上调用fit方法时,将自动执行预处理步骤和模型训练。
from sklearn import model_selection
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
X,y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y = True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
# Chain together scaling the variables with the model
pipe = Pipeline([('scaler', StandardScaler()), ('rf', RandomForestClassifier())])
pipe.fit(X_train, y_train)
pipe.score(X_test, y_test)
7. 使用ColumnTransformer,你可以对不同的特征应用不同的预处理
在许多数据集中,你将拥有不同类型的特征,需要应用不同的预处理步骤。例如,数据集中可能混合有分类数据和数值数据,你可能希望通过独热编码将分类数据转换为数值数据并缩放数值变量。
Scikit-learn pipeline中有一个函数ColumnTransformer,可以让你非常容易地通过索引或通过指定的列名来指定哪些列应用最合适的预处理。
from sklearn import model_selection
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, OneHotEncoder
# Load auto93 data set which contains both categorical and numeric features
X,y = fetch_openml("auto93", version=1, as_frame=True, return_X_y=True)
# Create lists of numeric and categorical features
numeric_features = X.select_dtypes(include=['int64', 'float64']).columns
categorical_features = X.select_dtypes(include=['object']).columns
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
# Create a numeric and categorical transformer to perform preprocessing steps
numeric_transformer = Pipeline(steps=[
('imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy='median')),
('scaler', StandardScaler())])
categorical_transformer = Pipeline(steps=[
('imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy='constant', fill_value='missing')),
('onehot', OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown='ignore'))])
# Use the ColumnTransformer to apply to the correct features
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
transformers=[
('num', numeric_transformer, numeric_features),
('cat', categorical_transformer, categorical_features)])
# Append regressor to the preprocessor
lr = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor),
('classifier', LinearRegression())])
# Fit the complete pipeline
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("model score: %.3f" % lr.score(X_test, y_test))
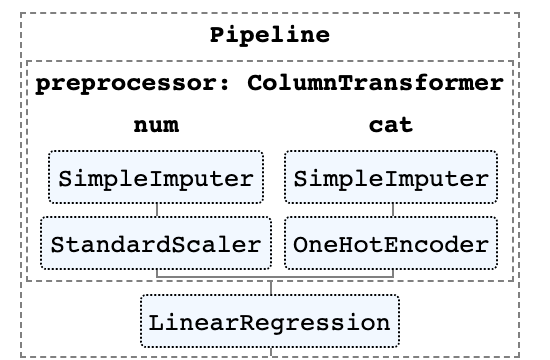
8. 你可以简单的输出一个HTML来表示你的pipeline
pipeline通常非常复杂,特别是在处理真实数据时。因此,Scikit-learn提供了一个方法来输出pipeline中步骤的HTML图,这非常方便。
from sklearn import set_config
set_config(display='diagram')
lr
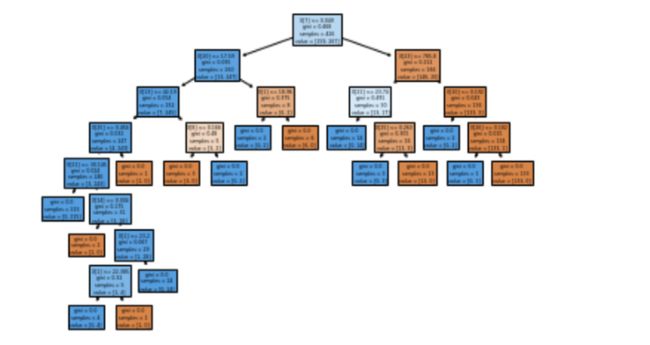
9. 有一个绘图函数来可视化决策树
plot_tree()函数允许你创建一个决策树模型中的步骤图。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import metrics, model_selection
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, plot_tree
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
X,y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y = True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
plot_tree(clf, filled=True)
plt.show()
10. 有许多第三方的库可以扩展Scikit-learn的功能
许多第三方库都可以使用Scikit-learn并扩展其功能。其中两个例子包括category-encoders库,它为分类特征提供了更广泛的预处理方法,以及ELI5库,用于更好的模型可解释性。
这两个包也可以直接在Scikit-learn pipeline中使用。
![]()
—END—
英文原文:https://towardsdatascience.com/10-things-you-didnt-know-about-scikit-learn-cccc94c50e4f
![]()
请长按或扫描二维码关注本公众号
喜欢的话,请给我个好看吧!![]()