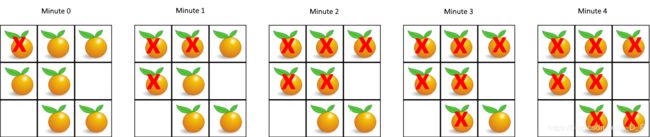
LeetCode-994-腐烂的橘子
题意描述:
在给定的网格中,每个单元格可以有以下三个值之一:
- 值 0 代表空单元格;
- 值 1 代表新鲜橘子;
- 值 2 代表腐烂的橘子。
每分钟,任何与腐烂的橘子(在 4 个正方向上)相邻的新鲜橘子都会腐烂。
返回直到单元格中没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数。如果不可能,返回 -1。
提示:
- 1 <= grid.length <= 10
- 1 <= grid[0].length <= 10
- grid[i][j] 仅为 0、1 或 2
示例:
输入:[[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
输出:4
二:
输入:[[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]]
输出:-1
解释:左下角的橘子(第 2 行, 第 0 列)永远不会腐烂,因为腐烂只会发生在 4 个正向上。
三:
输入:[[0,2]]
输出:0
解释:因为 0 分钟时已经没有新鲜橘子了,所以答案就是 0
解题思路:
Alice: 这就是模拟题吗 ?
Bob: 可以当成模拟题去做。
Alice: 有点BFS的样子,用队列的话应该能减少重复计算的。
Bob: 对对。
代码:
Java 方法一: 模拟, 多次遍历二维数组。
class Solution {
private int rotedCnt = 0;
private int orangeCnt = 0;
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
// 统计共有多少橘子
for(int i=0; i<grid.length; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<grid[i].length; ++j){
if(grid[i][j] > 0){
orangeCnt += 1;
}
}
}
//System.out.println("oranges " + orangeCnt);
// rotting(grid) 返回这一分钟有多少橘子会腐败
int minutes = 0;
while(rotting(grid) > 0){
minutes ++;
}
//System.out.println("minutes " + minutes);
//System.out.println("rotedCnt " + rotedCnt);
// 腐败过程结束,查看结果
if(rotedCnt == orangeCnt){
return minutes;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public int rotting(int[][] grid){
int rottingCnt = 0;
rotedCnt = 0;
// 这一秒钟腐败的
int[][] directions = {{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
for(int i=0; i<grid.length; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<grid[i].length; ++j){
if(grid[i][j] == 2){
rotedCnt += 1;
for(int[] direction : directions){
int xx = i + direction[0];
int yy = j + direction[1];
if(xx >=0 && xx < grid.length && yy >= 0 && yy < grid[i].length && grid[xx][yy] == 1){
grid[xx][yy] = 3; // 把这一分钟要腐败的先标记为 3 防止与之前已经腐败的混淆
rottingCnt ++;
}
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<grid.length; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<grid[i].length; ++j){
if(grid[i][j] == 3){
grid[i][j] = 2;
}
}
}
// 这一分钟的腐败过程结束,标记重置为2
return rottingCnt;
}
}
Python 方法一:
class Solution:
def orangesRotting(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# 统计橘子总数
self.orangeCnt = 0
for row in grid:
for cell in row:
if cell > 0:
self.orangeCnt += 1
# 模拟腐烂过程
self.rottedCnt = 0
minute = 0
while self.helper(grid) > 0:
minute += 1
# 返回结果
if self.orangeCnt == self.rottedCnt:
return minute
else:
return -1
def helper(self, grid):
self.rottedCnt = 0 # 置零,重新累加
rotting = 0 # 本次腐败的橘子数量
directions = [[1,0],[-1,0],[0,1],[0,-1]]
for x in range(len(grid)):
for y in range(len(grid[x])):
if grid[x][y] == 2:
self.rottedCnt += 1
for direction in directions:
xx = x + direction[0]
yy = y + direction[1]
if xx >= 0 and xx < len(grid) and yy >= 0 and yy < len(grid[xx]) and grid[xx][yy] == 1:
grid[xx][yy] = 3
rotting += 1
for x in range(len(grid)):
for y in range(len(grid[x])):
if grid[x][y] == 3:
grid[x][y] = 2
return rotting
Python 方法二: 优化内存使用
class Solution:
def orangesRotting(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
self.orangeCnt = 0
rotting = []
for x in range(len(grid)):
for y in range(len(grid[x])):
if grid[x][y] > 0:
self.orangeCnt += 1
if grid[x][y] == 2:
rotting.append([x, y])
self.rotted = 0
minute = 0
rottingCnt, rotting = self.helper(grid, rotting)
while rottingCnt > 0:
minute += 1
rottingCnt, rotting = self.helper(grid, rotting)
if self.rotted == self.orangeCnt:
return minute
else:
return -1
def helper(self, grid, rotting):
directions = [[1,0],[-1,0],[0,1],[0,-1]]
rottingCnt = 0
rottingOne = []
for coor in rotting:
self.rotted += 1
for direction in directions:
xx = coor[0] + direction[0]
yy = coor[1] + direction[1]
if xx>=0 and xx<len(grid) and yy>=0 and yy<len(grid[xx]) and grid[xx][yy] == 1:
rottingCnt += 1
grid[xx][yy] = 2
rottingOne.append([xx, yy])
return rottingCnt, rottingOne
易错点:
- 每一分钟只能 “BFS” 走一步,这一分钟即将腐烂的橘子不应该和上一分钟已经腐烂的橘子混淆,前者在这一分钟还不具备传播腐败的能力。
总结