Java复习七——Java常用类库
一、StringBuffer
StringBuffer是用来进行缓冲作用的,本身也是操作字符串,但是与String类不同,String类的内容一旦声明之后则不可改变,改变的只是其内存地址的指向,而StringBuffer中的内容是可以改变。对于StringBuffer而言,本身就是一个具体的操作类,不能像String采用直接赋值的方式进行对象的实例化,必须通过构造方法完成。
当一个字符串的内容需要被经常改变时,就要使用StringBuffer,在StringBuffer中使用append()方法,完成字符串的连接操作。StringBuffer属于java.lang
1.字符串的连接操作:append()方法
public class Demo1{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("Hello");
buf.append("World").append("!!!");
buf.append("\n");
buf.append("数字=").append(1).append("\n");
buf.append("字符=").append("C").append("\n");
buf.append("布尔=").append(true);
System.out.println(buf);
}
}public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("Hello");
fun(buf);
System.out.println(buf);
}
public static void fun(StringBuffer s) {
s.append("nihao").append("Java");
}
}
//结果:
HellonihaoJava
2.在任意处为StringBuffer添加内容insert()方法
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("World!");
buf.insert(0, "Hello");
System.out.println(buf);
buf.insert(buf.length(), "-Java");
System.out.println(buf);
}
}
//结果:
HelloWorld!
HelloWorld!-Java
3.字符串反转操作reverse()方法
直接使用reverse()方法就可以完成反转功能:
public StringBuffer reverse() public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("World!");
buf.insert(0, "Hello");
String str = buf.reverse().toString();//将内容反转成String类型
System.out.println(str);
}
}
//结果:
!dlroWolleH
4.替换制定范围的内容replace()方法
在StringBuffer类中也存在replace()方法,使用此方法可以对指定范围的内容进行替换
public StringBuff replace(int start,int end,String str){
}public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("Hello").append("World!");
buf.replace(6, 11, "Java是世界上最好的语言");
System.out.println("内容替换后的结果:"+buf);//输出内容
}
}
//结果
内容替换后的结果:HelloWJava是世界上最好的语言5.字符串截取subString()方法
substring()可以直接从StringBuffer中指定范围截取内容
public String substring(int strat,int end)public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("Hello").append("World!");
buf.replace(6, 11, "Java是世界上最好的语言");
String str = buf.substring(6,15);
System.out.println("内容替换后的结果:"+str);//输出内容
}
}6.字符串截取delet()方法
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("Hello").append("World!");
buf.replace(6, 11, "Java是世界上最好的语言");
String str = buf.delete(6,15).toString();
System.out.println("内容替换后的结果:"+str);//输出内容
}
}7.查找指定的内容是否存在indexOf()方法
此方法如果找到了内容则返回位置,否则返回-1
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("Hello").append("World!");
if(buf.indexOf("Hello")==-1) {
System.out.println("没有找到指定的内容");
}else {
System.out.println("可以查找到指定的内容");
}
}
}
//结果:
可以查找到指定的内容二、Runtime类
Runtime类在运行时,是一个封装了JVM进程的类。每一个Java程序实际上都只启动了一个JVM进程,那么每一个JVM进程都是对应这一个Runtime实例,此实例是由JVM为其实例化的。
使用public static Runtime getRuntime()直接使用此静态方法就可以取得Runtime类的实例。
得到JVM信息:
每一个Runtime对象都是由JVM进行实例化的,所以可以直接通过此类取得一些信息
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Runtime run = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println("JVM最大内存量"+run.maxMemory());//观察最大的内存
System.out.println("JVM空闲内存存量"+run.freeMemory());//取得程序运行的空闲内存
String str = "Hello"+"World!"+"\t"+"Welcome"+"to"+"Java世界";
System.out.println(str);
for(int x = 0 ; x < 1000; ++x) {
str += x;//循环修改内容,会产生多个垃圾
}
System.out.println("操作String之后,JVM空心内存量:"+run.freeMemory());
run.gc();//进行垃圾回收,释放空间
System.out.println("垃圾回收之后,JVM空闲内存量:"+run.freeMemory());
}
}
//结果:
JVM最大内存量764411904
JVM空闲内存存量51280400
HelloWorld! WelcometoJava世界
45471600
51865760
Runtime与Process类
可以使用Runtime类运行本机的可执行程序,例如调用记事本
public Process exec(String command)throws IOExceptionpublic class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Runtime run = Runtime.getRuntime();
try {
run.exec("notepad.exe");//调用本机程序,此方法需要异常方法
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();//打印异常信息
}
}
}exec()方法的返回值是Process,表示一个进程的操作类,可以通过destroy()方法销毁掉一个进程。
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Runtime run = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process p = null;//定义进程变量
try {
p=run.exec("notepad.exe");//调用本机程序,此方法需要异常方法
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();//打印异常信息
}
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
p.destroy();
}
}三、国际化程序
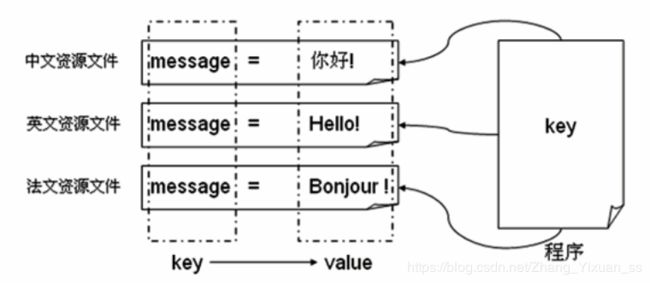
国际化操作就是指一个程序可以同时适应多门语言,即:如果现在程序的使用者是中国人,则会显示中文,如果是英国人使用,则显示英文。程序不会有任何变化,只是操作的语言根据使用者的语言发生改变。
国际化程序的实现思路
国际化实现的支持类
如果要想实现Java程序的国际化操作必须通过以下三个类完成:
- java.util.Locale:用于标识一个国家的语言类
- java.util.ResourceBundle:用于访问资源文件
- java.text.MessageFormat:格式化资源文件的占位字符串
Locale类:
Locale表示的是本地,实际上使用的是一个ISO编码的封装类,对于各个国家来说都存在一个唯一的编码,那么这种编码就称ISO编码,使用locale可以指定一个具体的国家编码。
例如:
中国编码:zh-CN
英语-美国的编码:en-US
法语的编码:fr-FR
ResourceBundle类:
此类专门完成属性文件读取操作,读取的时候直接指定文件名称,可以根据locale所指定的区域来自动选择所需要的资源文件。
public static final ResourceBundle getBundle(String baseName,Locale locale),此方法也是指定操作的资源文件,并传入Locale对象。
public final String getString(String key)根据key取得对应的value
在src文件夹下创建一个Message.properties,其中的内容为info=Hello
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("Message");
System.out.println("内容:"+rb.getString("info"));
}
}import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Locale zhLoc = new Locale("zh","CN");
Locale enLoc = new Locale("en","US");
Locale frLoc = new Locale("fr","FR");
ResourceBundle zhrb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("Message",zhLoc);
ResourceBundle enrb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("Message",enLoc);
ResourceBundle frrb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("Message",frLoc);
System.out.println("中文"+zhrb.getString("info"));
System.out.println("英文"+enrb.getString("info"));
System.out.println("法文"+frrb.getString("info"));
}
}处理动态文本省略
三、System类基本使用
System类是一些与系统相关的属性和方法的集合在System类中所有的属性都是静态的,要想引用这些属性和方法,直接使用System类调用即可。
利用System.currentTimeMillis()方法取得一个程序的运行时间
代码如下:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//取得程序开始时间
int sum = 0 ;
for(int i = 0 ; i<30000000;++i) {
sum +=i;
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//取得计算之后的时间
System.out.println("计算所花费的时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");
}
}四、垃圾对象的回收
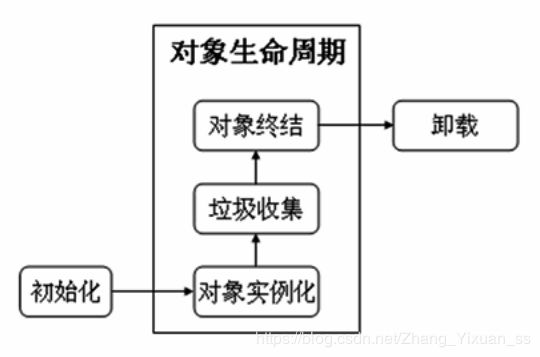
一个对象如果不适用,则肯定要进行垃圾回收,垃圾回收可手动也可以自动,手动调用时使用System.gc()和Runtime.getRuntime.gc()方法。System.gc()属于强制性垃圾回收。
对象的声明周期:
五、日期类
Date类
Date的使用格式:Date date = new Date();
例子:
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println("当前时间"+date);
}
}Calendar类
如果想要按照自己的格式显示时间以及使时间精确到毫秒可以使用Calendar类
calendar类是一个抽象方法,无法直接使用,因此需要利用对象多态性概念,通过向上转型关系使对象实例化。
import java.util.*;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Calendar calendar = new GregorianCalendar();//实例化Calendar类对象
System.out.println("Year"+calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.println("Month"+calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1);//注意这里需要加1
System.out.println("Day_of_Month"+calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println("Hour_of_Day"+calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY));
System.out.println("Minute"+calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println("Second"+calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND));
System.out.println("Millisecond"+calendar.get(Calendar.MILLISECOND));
}
}DateFormat类
通过此类可以将date类获取的当前时间合理的格式化,可以通过Locale对象指明要显示的地区。其中有两个方法,getDateInstance()和getDateTimeInstance()
例子:
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
DateFormat df1 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.YEAR_FIELD,new Locale("zh","CN"));
DateFormat df2 = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.YEAR_FIELD,DateFormat.ERA_FIELD,new Locale("zh","CN"));
System.out.println("DATE:"+df1.format(new Date()));
System.out.println("DateTime:"+df2.format(new Date()));
}
}SimpleDateFormat类
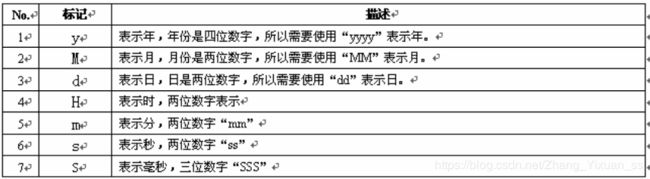
此类完成日期的格式转化,在生活中我们有时会将时间格式:年月日写成日月年。
构造方法:public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern)
转换:public Date parse(String source) throws ParseException
格式化:public final String format(Date date)六、Math和Random类
Math类表示数学操作:Math类中方法都是静态方法,直接使用“类.方法名称()”的形式调用即可
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("求平方根"+Math.sqrt(9.0));
System.out.println("求两数的最大值"+Math.max(10,30));
System.out.println("求两数的最小值"+Math.min(10,30));
System.out.println("2的3次方"+Math.pow(2, 3));
System.out.println("四舍五入"+Math.round(33.4));
}
}Random类
Random类的主要功能是产生随机数,可以产生一个指定范围的随机数。Random类是定义java.util包中的类。
import java.util.Random;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Random r = new Random();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
System.out.println(r.nextInt(100)+"\t");
}
}
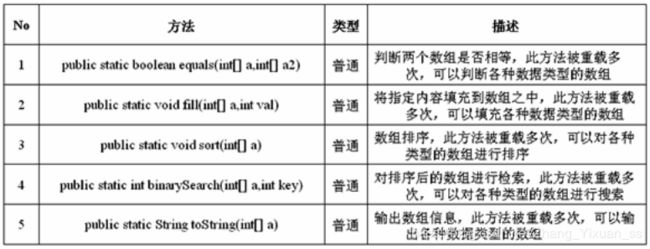
}七、Arrays类
Arrays表示数组的操作类,是直接定义在java.util包中的,主要功能是实现数组元素的查找,数组内容的填充,排序等
import java.util.*;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
int temp[] = {3,4,5,2,4,6,9};
Arrays.sort(temp);
System.out.println("输出排序后的语句:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp));//以字符串的形式输出数组
int point = Arrays.binarySearch(temp, 3);
System.out.println(point);
}
}
//结果:
输出排序后的语句:
[2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 9]
1
其他方法,例如比较器等内容放到数据结构中总结
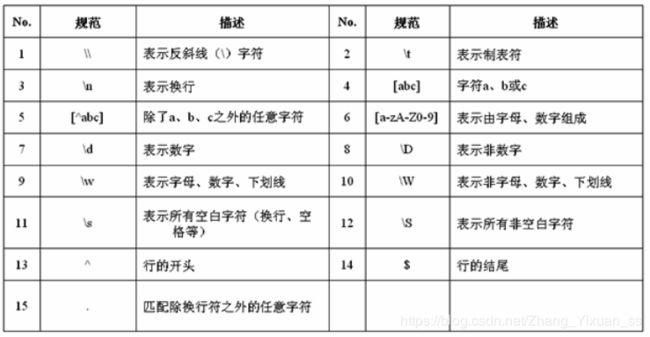
八、正则表达式
正则表达式可以方便的对数据进行匹配,可以执行更加复杂的字符串验证,拆分,替换功能。
例如:现在要求判断一个字符串是否由数字组成,则可以使用正则表达式
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "123456789";
if(Pattern.compile("[0-9]+").matcher(str).matches()) {
System.out.println("是数字组成");
}else {
System.out.println("不是数字组成");
}
}
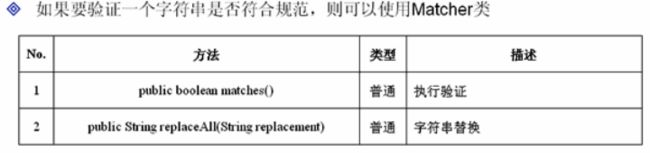
}在Java中使用正则表达式,必须依靠Pattern和Matcher类,这两个类都在java.util.regex包中定义。Pattern主要是进行正则规范的编写,而Matcher类主要是执行规范,验证一个字符串是否符合其规范。
Pattern类常用方法:
Matcher类常用方法:
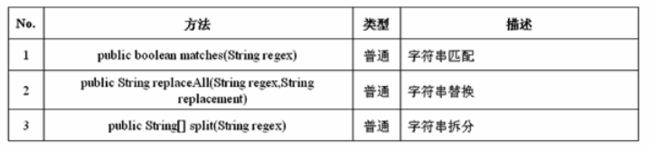
String类对正则的支持: