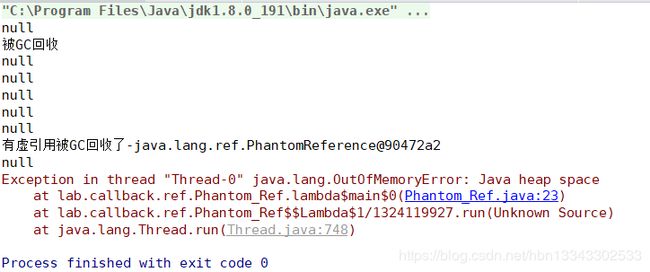
Java的四种引用——强软弱虚
强软弱虚
java中的数据被类型分为了两类,它们分别是基本类型和引用类型。一般我们new出来的对象都属于引用类型的范畴。我们知道java是有垃圾回收机制的一种语言,根据垃圾回收时的策略,java将对于堆对象的引用又进行了细分,引用被分为了强引用,软引用,弱引用和虚引用。
强引用
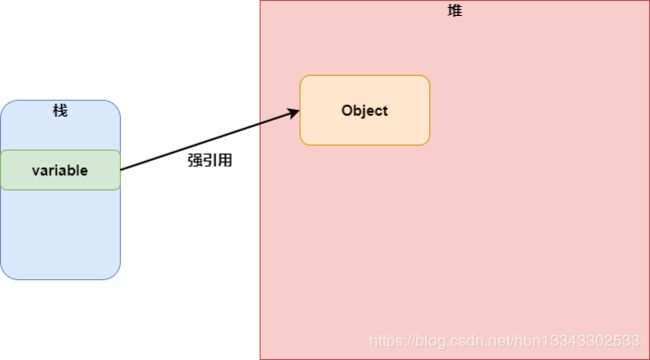
强引用又称普通引用,它是最常见的一种引用类型,一般我们通过new关键字创建对象时,变量对于堆对象的引用就是强引用。
强引用的特点:
- 如果堆中的一个对象被强引用指向,那么这个变量将不会被GC回收。
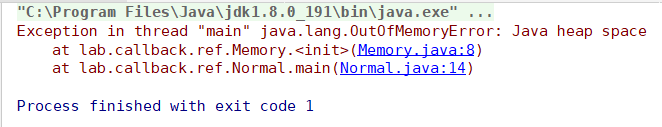
- 在堆内存不够用的情况下,被强引用指向的对象也不会被回收。(宁可抛出OOM异常)
- 被强引用指向的对象,只有在引用消失后才会被GC回收。
测试代码-1:
/* 这个类用于申请堆内存 */
public class Memory {
private byte[] alloc;
public Memory(int size) { this.alloc = new byte[size]; }
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
super.finalize();
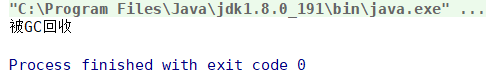
System.out.println("被GC回收");
}
}
public class Normal {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/* 栈变量m对new出来的Memory对象的引用为强引用 */
Memory m = new Memory(1024 * 1024 * 20);
/* 现在堆中的对象没有引用指向它,它要被GC回收 */
m = null;
System.gc(); /* 显式GC */
/*
* 当我们启动java程序时,默认会有两个线程,一个是我们的主线程,另一个便是GC线程。
* 通常GC线程的优先级比较低,并且GC线程默认为守护线程,即它会在主线程退出的同
* 时退出。
*
* 为了观察到GC的效果,我们让主线程休眠1s
*/
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
public class Normal {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/* 我们设定JVM参数,设置堆内存大小为25MB */
/* 栈变量m1对new出来的Memory对象的引用为强引用 */
/* 申请了20MB的内存,实际会大于20MB,因为我们的byte[]被Memory对象wrapper */
Memory m1 = new Memory(1024 * 1024 * 20);
System.gc();
Thread.sleep(1000);
/* 再申请10MB堆内存 */
Memory m2 = new Memory(1024 * 1024 * 10);
}
}
软引用
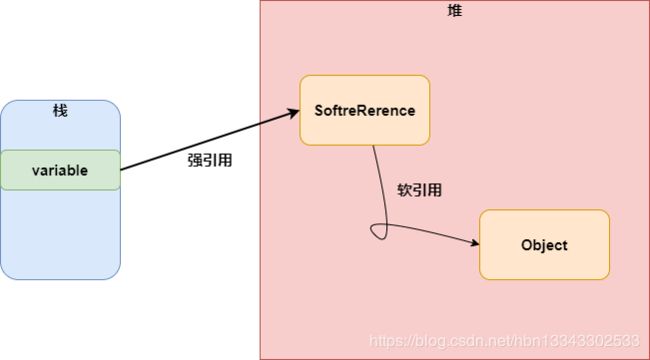
软引用的创建需要借助jdk中java.lang.ref.SoftReference这个类来创建。也就是说,我们的变量是先引用到SoftReference这个对象,SofReference这个对象再去引用我们想要设置为软引用的对象。
软引用的特点
- 当堆内存够用时,被软引用指向的对象不会被GC回收。
- 当堆内存不够用时,被软引用指向的对象自动的被GC回收。
测试代码-3
public class Soft_Ref {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/* 堆内存大小为50MB */
/* 申请30MB */
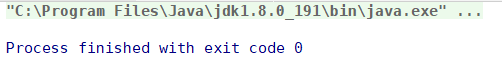
SoftReference<Memory> m1 = new SoftReference<>(new Memory(1024 * 1024 * 30));
System.gc(); /* 显示调用GC */
/* 此时内存够用,所以结果可以预见性的为GC不会回收被软引用指向的对象 */
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
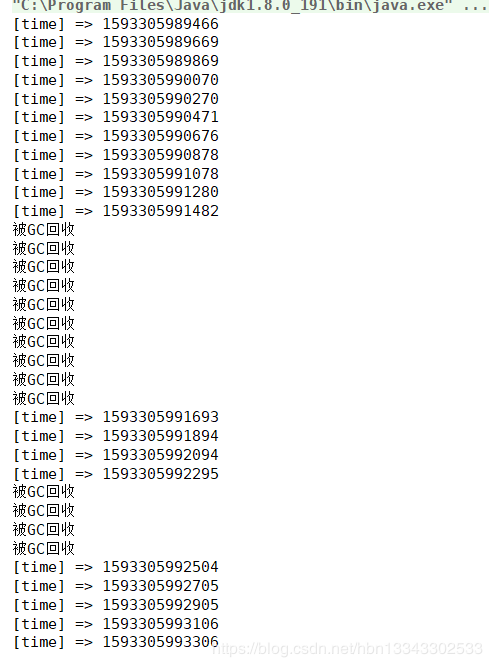
public class Soft_Ref {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/* 堆内存大小为50MB */
/* 申请30MB */
SoftReference<Memory> m1 = new SoftReference<>(new Memory(1024 * 1024 * 30));
/* 申请20MB */
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {
System.out.println("[time] => " + System.currentTimeMillis());
SoftReference<Memory> ma = new SoftReference<>(new Memory(1024 * 1024));
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}
}
从测试结果可以看出,当内存不够用或者将要不够用时,会触发GC,GC会自动的回收那些软引用指向对象。
一定要注意,软引用指向对象的回收是在触发GC的条件下才会被回收,如果内存够用,就算显式的调用GC,软引用指向的对象也不会被回收。
弱引用
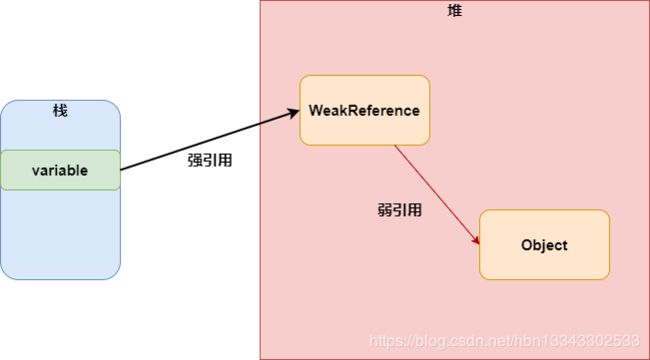
弱引用的创建方式与软引用类似,需要借助于jdk中java.lang.ref.WeakReference类去创建。
弱引用的特点:
- 不管什么情况,遇到GC就会回收被弱引用指向的对象。
测试代码-5
public class Weak_Ref {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/* 堆内存没有设置大小,为默认状态 */
WeakReference<Memory> m = new WeakReference<>(new Memory(1024 * 1024 * 10));
System.gc(); /* 调用GC */
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
虚引用
虚引用是一种十分特殊的引用,它主要用在堆外内存的管理,虚引用可以指向堆中的对象,但是没有实际的意义。
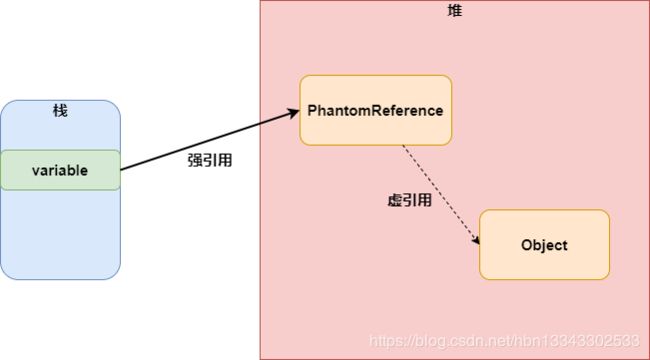
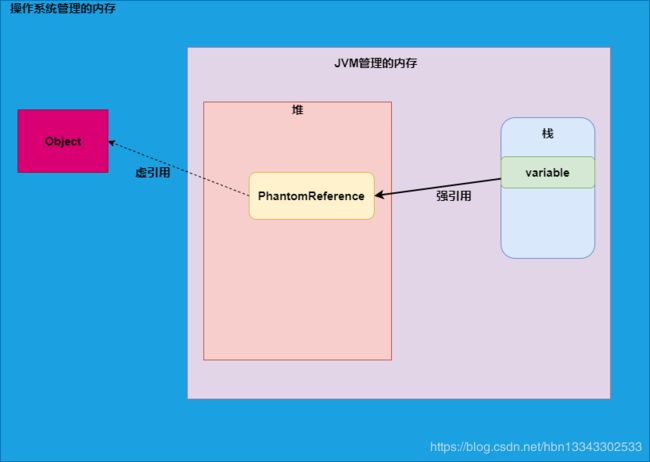
虚引用的特点:
- 无法获取虚引用指向的对象的值。
- 虚引用在被GC回收时会有通知。
- 虚引用在遇到GC时,不管是否还有对象引用它,它都会被GC回收。
测试代码-6
public class Phantom_Ref {
static final ArrayList<byte[]> LIST = new ArrayList<>();
static final ReferenceQueue<Memory> QUEUE = new ReferenceQueue<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
PhantomReference<Memory> m = new PhantomReference<>(new Memory(1024 * 1024 * 10), QUEUE);
new Thread(()->{
while (true) {
LIST.add(new byte[1024 * 1024 ]);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
System.out.println(m.get()); /* 虚引用指向的值永远无法被获取 */
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
while (true) {
Reference<? extends Memory> poll = QUEUE.poll();
if (poll != null) {
/* 虚引用在对象回收时,会进行通知 */
System.out.println("有虚引用被GC回收了-" + poll);
break;
}
}
}).start();
}
}
Reference
本文章参考自马士兵老师对于引用的讲解视频,在此感谢马士兵老师的讲解。