spring系列(二)——AOP的两种实现方式(xml和注解)
资源链接
源码地址:https://code.csdn.net/luo4105/spring-aop.git
文章推荐:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-springaopcglib/
简介
AOP:面向切面编程,是作为面向对象编程的一种补充,专门用于处理系统中分布于各个模块中的交叉关注点的问题,在javaEE项目中,常用于处理一些具有横切性质的系统级服务,如事务管理、安全检查、缓存、对象池管理等。AOP的实现技术分为两大类,静态代理和动态代理,静态代理的实现时在java类编译时,生成 AOP 代理类;动态代理是在java内存中生成AOP代理类,AspectJ是静态代理,Spring AOP使用的是动态代理。
常用概念
1.Adivice(通知/增强处理):是指在特定连接点,AOP框架执行的操作,也就是上面说的相同代码段。
2.Joinpoint(连接点):程序执行过程中明确的点,如方法的调用或异常抛出,如方法1在方法2中的调用就是一个连接点。
3.Pointcut(切入点):一个通知将被引发的一系列连接点的集合。AOP框架必须允许开发者指定切入点,例如,使用正则表达式,通俗的理解是所有需要通知的目标的集合
4.Aspect(切面):通知和切入点共同组成了切面
5.Target(目标):即被通知的对象
6.(proxy)代理:参见设计模式里面的代理模式
7.weaving(织入):把切面应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程
Spring支持五种类型的通知,分别是before、after-returning、after-throwing、arround、introduction的使用,这里模拟一个需要使用事务和日志使用的场景,使用arround和after-returning。
AOP的实现
AOP是面向切面编程,理解这个需要多敲几次。
它采用动态代理的方式,实现在批量对方法进行前置操作、后置操作、环绕操作。
Aop的常用操作:before、around、after。
Java中AOP的常用实现是xml配置和使用@Aspect注解
xml配置
使用xml配置的方式需要导入spring-aop包,其maven为
4.3.7.RELEASE
UTF-8
1.8
org.springframework
spring-aop
${org.springframework-version}
org.springframework
spring-beans
${org.springframework-version}
org.springframework
spring-context
${org.springframework-version}
org.springframework
spring-core
${org.springframework-version}
org.springframework
spring-test
${org.springframework-version}
junit
junit
4.12
org.aspectj
aspectjweaver
1.8.4
编写AOP逻辑类
public class XmlAop {
public void before(JoinPoint point) {
System.out.println("方法之前");
System.out.println("参数: " + point.getArgs());
System.out.println("=====================");
}
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
System.out.println("围绕方法");
Object ret = point.proceed(point.getArgs());
System.out.println("返回结果:" + ret);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
return ret;
}
public void after(JoinPoint point) {
System.out.println("=====================");
System.out.println("方法之后");
}
}在spring配置文件中配置AOP
目标类
public class AopRun {
public Integer xmlAopTest(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
}测试类
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:spring/spring-config.xml"})
public class AopTest {
@Autowired
private AopRun aopRun;
@Test
public void AopRunTest() {
System.out.println(aopRun.xmlAopTest(1,2));
}
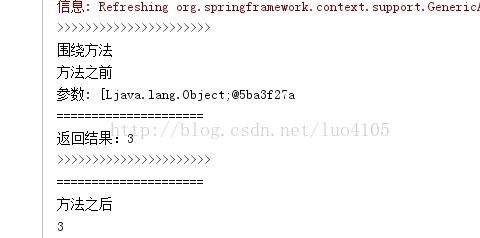
}结果
讲解
JoinPoint,在before和after的时候用JoinPoint接收切点。JoinPoint.getArgs()获得传入参数。
ProceedingJoinPoint,在around中使用ProceedingJoinPoint接收切点。around实际上是代理了,ProceedingJoinPoint.pross()就是调用代理方法,也可以在这里进行判断,是否调用。它可以修改参数,修改返回值。
注解方式
注解方式使用”@Aspect”注解,注解实际就是将spring中对AOP的配置一块以注解方式实现。
编写AOP逻辑类并注解AOP
@Component
@Aspect
public class AnnoAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.lc.RunAop.xmlAopTest(..))")
public void aspect() {
}
@Before("aspect()")
public void before(JoinPoint point) {
XmlAop xmlAop = new XmlAop();
xmlAop.before(point);
}
@Around("aspect()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
XmlAop xmlAop = new XmlAop();
return xmlAop.around(point);
}
@After("aspect()")
public void after(JoinPoint point) {
XmlAop xmlAop = new XmlAop();
xmlAop.after(point);
}
}实际上before的配置就改成了注解的@Before、@Around、@After。
Spring配置
测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:spring/spring-annoAop.xml"})
/*@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:spring/spring-xmlAop.xml"})*/
public class RunAopTest {
@Autowired
private RunAop runAop;
@Test
public void AopRunTest() {
System.out.println(runAop.xmlAopTest(1,2));
}
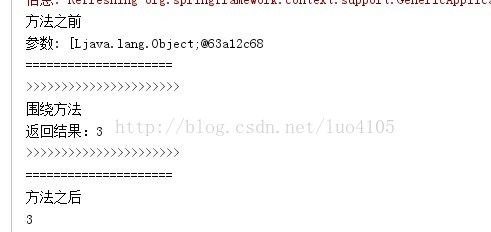
}结果