java中ThreadLoacl解析
一:ThreadLocal变量的解释
ThreadLocal类型是一个线程变量,其并不是用来像lock/sychronized一样解决java多线程中变量共享的安全性问题的,并且使用ThreadLocal类型变量并不一定能保证共享对象上的安全并发(放入Thread类的变量ThreadLocalMap threadLocals中的对象即value值,必须是在当前线程方法中所创建的局部变量,或者是在其他地方正确发布的线程安全对象。否则,若放入的对象为多个线程所共享的非线程安全对象,那么就会造成并发问题)。
ThreadLocal类型变量最大的用途是用来存储线程内部的变量,使得在线程的方法调用栈上的任何方法中,都可以通过ThreadLocal变量的get方法得到该ThreadLocal类型为key对应的value值。
在Thread类中,定义有
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;`即,每个运行的线程都会有一个名字为threadLocals的map,其中存放的是key=声明的ThreadLocal类型的变量引用,value=放入的线程变量值/初始化值/null(一般该对象会在线程方法中创建,即为线程的局部变量,为线程封闭对象)。
并不是有些地方所说的key=当前线程,value=要获得的值(如果是key=当前线程的话,那么岂不是这个map中仅仅只存放 了一个Entry对象)。
若在程序中声明有多个ThreadLocal类型的对象引用,那么在线程的threadLocals所引用的map中就会有多个Entry对象,其key值就为声明的ThreadLocal对象的引用。
二:ThreadLocal变量在框架中的应用
在Spring中大量使用带该技术。其就相当于是一个线程局部变量,被封装在线程Stack中,仅被当前线程所使用。并且该线程终结之前,在该线程方法调用链的任何一个方法中都可以通过get()方法获得该变量值。
在MVC构架的Web项目中:
某些变量若不使用ThradLocal处理,则,需要在该线程的方法链中,将局部变量一直传递下去。
但如果使用ThreadLocal处理,就可以在任何一层通过get方法获得给变量。
在基于SSH构架的MVC结构的javaWeb项目中,从接受请求到响应,都属于是一个线程。
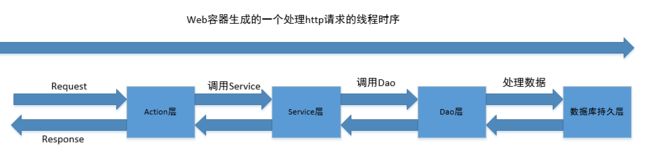
那么,如果在Action层创建一个ThreadLocal变量,这在Service层和Dao层都可以通过get方法获得该变量。
三:线程使用ThreadLocal对象创建线程内部变量时的调用顺序:
- 第一次调用ThreadLocal类型对象的set或者get方法时,会根据当前线程所拥有的ThreadLocal类型对象作为key,null或者若重写initialValue()方法自定义初始值为value,创建一个ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal key,Object value)类型的map对象,并赋值给当前线程的threadLocals变量。
- 后续每次对get或者set方法的调用都会直接获得当前线程的threadLocals变量,即第一步初始化的ThreadLocalMap类型的map。然后根据当前调用对象this(即声明的ThreadLocal类型变量的引用)作为key,去找到对应的value值返回。
通过下面的例子,描述ThreadLocal的调用顺序:
SequenceNumber 为一个计数类,内部有一个ThreadLocal类型变量,并重写其initialValue方法。
public class SequenceNumber {
// ①覆盖ThreadLocal的initialValue()方法,指定初始值
private static ThreadLocal seqNum = new ThreadLocal() {
public Integer initialValue() {
return 0;
}
};
// ②获取下一个序列值
public int getNextNum() {
seqNum.set(seqNum.get() + 1);
return seqNum.get();
}
} A,当线程A第一次调用getNextNum()方法时,会调用seqNum(ThreadLocal类型对象)的get()方法,jdk中源代码如下:
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null)
return (T)e.value;
}
return setInitialValue();
}
/**
* Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @return the map
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}- 获得当前线程A。
- 获得当前线程A的threadLocals变量,为ThreadLocalMap类型,jdk中Thread类中源码如下。
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;3.此时,线程A中的threadLocals变量还没有初始化,故为null,即会运行return setInitialValue();
/**
* Variant of set() to establish initialValue. Used instead
* of set() in case user has overridden the set() method.
*
* @return the initial value
*/
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}- 获得value值,会调用SequenceNumber类中定义的initialValue()方法,返回value=0;
- 获得当前线程A
- 获得当前线程A的threadLocals变量,此时还为null
- 故运行createMap(t, value)方法;其中t为当前线程A,value=0
/**
* Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map
* @param map the map to store.
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}- 这里会根据形参t即是线程A。创建ThreadLocalMap对象,并将其赋给线程A的threadLocals变量。
- 这里的this为当前线程中的TheadLocal类型的对象,即为SequenceNumber类中的seqNum对象。
/**
* Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue).
* ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create
* one when we have at least one entry to put in it.
*/
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}- 初始化map中的桶数组table;
- 根据firstkey=SequenceNumbe.seqNum对象的hash值,定位到数组中的位置;
- key=ThreadLocal对象,value=0创建Entry对象;
- map初始化完毕。
B,第一次调用get方法时,返回初始值0,然后再调用set方法:
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}- 首先获得当前线程A;
- 获得线程A的threadLocals变量,即为上述一中说创建的ThreadLocalMap类型的map;
此时threadLocals不为null,调用map.set(this, value)方法,其中this=SequenceNumbe.seqNum对象,value=1;即定位到的Entry还是第一次调用get方法初始化时的那个Entry对象,这个threadLocals(ThreadLocalMap类型的map)中就存放了一个Entry对象,其key=SequenceNumbe.seqNum,value=1;
C,到此,若线程A运行完毕那么就会清除线程A中的threadLocals变量;
/**
* This method is called by the system to give a Thread
* a chance to clean up before it actually exits.
*/
private void exit() {
if (group != null) {
group.threadTerminated(this);
group = null;
}
/* Aggressively null out all reference fields: see bug 4006245 */
target = null;
/* Speed the release of some of these resources */
threadLocals = null;
inheritableThreadLocals = null;
inheritedAccessControlContext = null;
blocker = null;
uncaughtExceptionHandler = null;
}- 将thradLocals变量置为null;
那么到此,线程A对于ThreadLocal类的使用就结束了。
PS:简单的说,ThreadLocal变量就是Thread类中(ThreadLocalMap)threadLocals的key,而value就是需要使用到的线程局部变量.。关于value值的设置有两个途径:
- 初始化的时候设置。默认为null,或者是自己重写初始化方法。
在线程的方法中调用ThreadLocal变量的set方法。
那么在该线程栈之后的方法中,都可以通过get方法来获得ThreaadLocal变量对应的线程局部变量,该变量封闭在该线程中,其他线程无法获得。但是,在上述两个途径中设置线程局部变量时,必须注意该对象的来源:一般是在线程方法中创建的对象或者基本数据类型(自动转换成包装类)。这样,在每个线程中都是自己的私有数据,而不会被其他线程获得。
- 若该对象本身为共享的对象,那么使用ThreadLocal并不能解决并发问题,这样会使每个线程通过ThreadLocal变量拿到的还是同一个共享对象,与将该共享对象设置为static效果一样。并且根本就没有必要将共享的对象放入到ThreadLocal线程本地变量中,直接设置为static即可。
PS:一篇关于ThreadLocal讲解的还不错的文章:http://www.iteye.com/topic/103804
其中也提到ThreadLocalMap类型的map中并不简单是存放的对象的拷贝/复制。而是在线程方法中创建的线程封闭的局部变量,不管是基本类型变量还是对象。并且该map是以ThreadLocal类型对象引用为key值,每个线程各自一个ThreadLocalMap类型的map。
ps:后续还有一篇关于ThreadLocal变量使用的注意事项,使用ThreadLocal变量并不能一定保证线程安全。
附:上述分析的源代码
package thread;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import java.util.Random;
import org.junit.Test;
public class SequenceNumber {
// ①覆盖ThreadLocal的initialValue()方法,指定初始值
private static ThreadLocal seqNum = new ThreadLocal() {
public Integer initialValue() {
return 0;
}
};
// ②获取下一个序列值
public int getNextNum() {
seqNum.set(seqNum.get() + 1);
return seqNum.get();
}
//创建第二个threadLocal类型的变量
private static ThreadLocal name = new ThreadLocal(){
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "lecky";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args){
SequenceNumber sn = new SequenceNumber();
System.out.println(sn);
// ③ 3个线程共享sn,各自产生序列号
TestClient t1 = new TestClient(sn);
TestClient t2 = new TestClient(sn);
TestClient t3 = new TestClient(sn);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
private static class TestClient extends Thread {
private SequenceNumber sn;
public TestClient(SequenceNumber sn) {
this.sn = sn;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("初始化值为="+name.get());
name.set(Thread.currentThread().getName());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {// ④每个线程打出3个序列值
System.out.println("当前线程="+name.get());
System.out.println("thread[" + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "] sn[" + sn.getNextNum() + "]");
}
}
}
}