Flink ProcessFunction onTimer 延迟处理数据
ProcessFunction和CoProcessFunction
说明
DataStream与KeyedStreamd都有Process方法,
DataStream接收的是ProcessFunction,而KeyedStream接收的是KeyedProcessFunction(原本也支持ProcessFunction,现在已被废弃)
0.AbstractRichFunction介绍
1.ProcessFunction对flink更精细的操作
<1> Events(流中的事件)
<2> State(容错,一致性,仅仅用于keyed stream)
<3> Timers(事件时间和处理时间,仅仅适用于keyed stream)
ProcessFunction可以视为是FlatMapFunction,但是它可以获取keyed state和timers。每次有事件流入processFunction算子就会触发处理。
为了容错,ProcessFunction可以使用RuntimeContext访问flink内部的keyed state。
timer允许应用程序对处理时间和事件时间的变化做出反应。每次有事件到达都会调用函数processElement(...),该函数有参数,也就是Context对象,该对象可以访问元素的事件时间戳和TimerService,还有侧输出。
TimerService可用于注册为后续处理事件或者事件时间的回调。当达到计时器的特定时间时,将调用onTimer(...)方法。在该调用期间,所有状态再次限定为创建计时器的key,允许计时器操纵keyed状态。
2.CoProcessFunction 实现底层join
<1> 实现底层join操作典型模板就是:
- 为一个或者两个输入创建一个状态对象
- 根据输入的事件更新状态
- 根据从另一个流接受的元素,更新状态并且产生joined结果
3.KeyedProcessFunction
keyedProcessFunction是ProcessFunction的扩展,可以在onTimer获取timer的key (通过context.getCurrentKey方法)
4.Timer类型
1.两种类型(事件时间和处理时间)的timer都是由TimerService维护并且以队列的形式执行。
TimerService会使用key和timestamp对timer进行去重,也即是对于每一对key和timestamp仅仅会存在一个timer。如果同一个timestamp注册了多个timers,onTimer()函数仅仅会调用一次。
对于onTimer()和processElement()方法flink是做了同步的,所以不需要关系并发问题。
image.png
image.png
5.ProcessFunction与状态的结合使用案例
WordCount,如果某一个key一分钟(事件时间)没有更新,就直接输出。
基本思路:
// 1.ValueState内部包含了计数、key和最后修改时间
// 2.对于每一个输入的记录,ProcessFunction都会增加计数,并且修改时间戳
// 3.该函数会在事件时间的后续1min调度回调函数
// 4.然后根据每次回调函数,就去检查回调事件时间戳和保存的时间戳,如果匹配就将数据发出
public class ProcessFunctionExample {
// 1.ValueState内部包含了计数、key和最后修改时间
// 2.对于每一个输入的记录,ProcessFunction都会增加计数,并且修改时间戳
// 3.该函数会在事件时间的后续1min调度回调函数
// 4.然后根据每次回调函数,就去检查回调事件时间戳和保存的时间戳,如果匹配就将数据发出
private static class StreamDataSource extends RichParallelSourceFunction> {
private volatile boolean running = true;
@Override
public void run(SourceContext> sourceContext) throws Exception {
Tuple3[] elements = new Tuple3[]{
Tuple3.of("a", 1L, 1000000050000L),
Tuple3.of("a", 1L, 1000000054000L),
Tuple3.of("a", 1L, 1000000079900L),
Tuple3.of("a", 1L, 1000000115000L),
Tuple3.of("b", 1L, 1000000100000L),
Tuple3.of("b", 1L, 1000000108000L)
};
int count = 0;
while (running && count < elements.length) {
sourceContext.collect(new Tuple3<>((String) elements[count].f0, (Long) elements[count].f1, (Long) elements[count].f2));
count++;
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
running = false;
}
}
/**
* 存储在状态中的对象
*/
public static class CountWithTimestamp {
//单词
public String key;
//单词计数
public long count;
//最近更新时间
public long lastModified;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CountWithTimestamp{" +
"key='" + key + '\'' +
", count=" + count +
", lastModified=" + new Date(lastModified) +
'}';
}
}
/**
* ProcessFunction有两个泛型类,一个输入一个输出
*/
public static class CountWithTimeoutFunction extends ProcessFunction, Tuple2> {
private ValueState state;
//最先调用
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
//根据上下文获取状态
state = getRuntimeContext().getState(new ValueStateDescriptor("myState", CountWithTimestamp.class));
}
@Override
public void processElement(Tuple2 input, Context context, Collector> output) throws Exception {
CountWithTimestamp current = state.value();
if (current == null) {
current = new CountWithTimestamp();
current.key = input.f0;
}
//更新ValueState
current.count++;
//这里面的context可以获取时间戳
//todo 此时这里的时间戳可能为null,如果设置的时间为ProcessingTime
current.lastModified = context.timestamp();
System.out.println("元素"+input.f0+"进入事件时间为:" + new Date(current.lastModified));
state.update(current);
//注册ProcessTimer,更新一次就会有一个ProcessTimer
context.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer(current.lastModified + 9000);
System.out.println("定时触发时间为:"+new Date(current.lastModified + 9000));
}
//EventTimer被触发后产生的行为
//todo 这里的timestamp是触发时间
@Override
public void onTimer(long timestamp, OnTimerContext ctx, Collector> out) throws Exception {
//获取上次时间,与参数中的timestamp相比,如果相差等于60s 就会输出
CountWithTimestamp res = state.value();
System.out.println("当前时间为:"+new Date(timestamp)+res);
if (timestamp >= res.lastModified + 9000) {
System.out.println("定时器被触发:"+"当前时间为"+new Date(timestamp)+" 最近修改时间为"+new Date(res.lastModified));
out.collect(new Tuple2(res.key, res.count));
}
}
}
//执行主类
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream> data = env.addSource(new StreamDataSource()).setParallelism(1)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor>(Time.milliseconds(0)) {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple3 input) {
return input.f2;
}
}).map(new MapFunction, Tuple2>() {
@Override
public Tuple2 map(Tuple3 input) throws Exception {
return new Tuple2<>(input.f0, input.f1);
}
});
data.keyBy(0).process(new CountWithTimeoutFunction()).print();
env.execute();
}
}
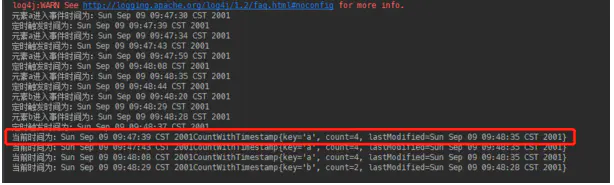
这一步的结果是:
image.png
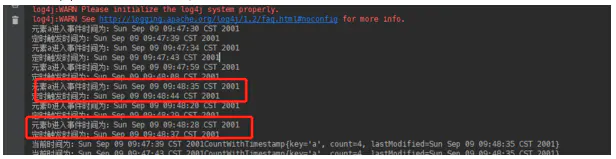
发现共有四个OnTimer被执行,其中没有执行OnTimer的两条元素是
image.png
这两条消息定时器预计执行时间都超过了09:48:35,因为这个案例采用的是事件时间,而这六条元素最大的事件时间为09:48:35,所以默认到09:48:35就停止了
注意:看代码可以发现这里发送的元素之间是每隔10秒发送,因为以为会影响结果,实际是我们使用的是EventTime,所以OnTimer被执行的时间,是看事件时间。
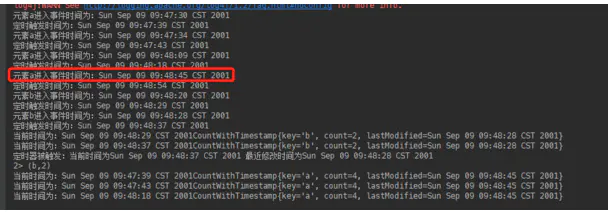
如果将最大事件时间改一下,改成
image.png
结果就是除了他自身,其余onTimer全部被执行了,因为它的事件时间,超过了其余5个元素的定时器触发时间。
并且我们发现有一条消息满足了其中的条件。
这里有一个疑问就是:为什么a的所有最近修改时间都是09:48:45 ,a的最大事件时间????
分析可能是构造的数据源的原因。这里模拟的是将优先数据源作为无限数据源使用
解决问题:
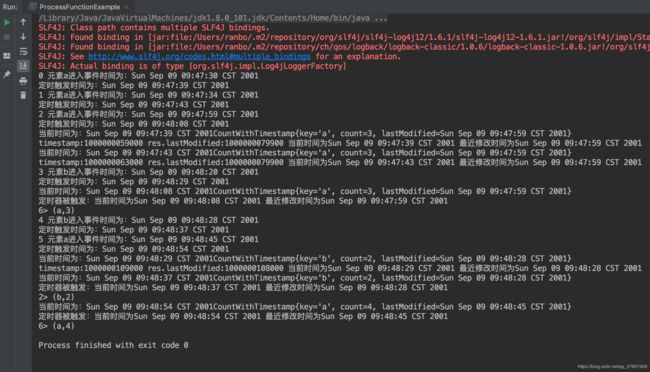
一开始没有设置为EventTime,所以在处理的时候还是以Process Time来处理的。
改完之后的效果:
分析问题产生的原因:因为一开始未指定时间类型为EventTime,所以默认是以Process Time来处理,而一般来说使用ProcessTime,就不需要指定Watermark了(Watermark只是与EventTime配合使用),但是代码中偏偏还是使用了assign...方法,所以会在数据加载完了,使用最近的元素的时间,生成一个Watermark,这时候有了Watermark才会执行onTimer方法,所以才会出现数据全部加载完,才执行onTimer方法;
而当指定为EventTime时,来一个元素就会生成一个Watermark,当Watermark大于某个元素的触发时间,OnTimer就会执行,而不是等数据全部加载完之后才会生成
所以上面一开始对某些onTimer没有执行的理解是错误的,应该按照上面没有指定EventTime的方式去理解
最终代码为:
package com.meituan.flink.example;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple3;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimeCharacteristic;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.ProcessFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.RichParallelSourceFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.timestamps.BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author ranbo
* @version V1.0
* @Title:
* @Package local.example
* @Description:
* @date 2020-04-06 19:39
*/
public class ProcessFunctionExample {
// 1.ValueState内部包含了计数、key和最后修改时间
// 2.对于每一个输入的记录,ProcessFunction都会增加计数,并且修改时间戳
// 3.该函数会在事件时间的后续1min调度回调函数
// 4.然后根据每次回调函数,就去检查回调事件时间戳和保存的时间戳,如果匹配就将数据发出
private static class StreamDataSource extends
RichParallelSourceFunction> {
private volatile boolean running = true;
@Override
public void run(SourceContext> sourceContext) throws Exception {
Tuple3[] elements = new Tuple3[]{
Tuple3.of("a", 1L, 1000000050000L), // 09:47:30
Tuple3.of("a", 1L, 1000000054000L), // 09:47:34
Tuple3.of("a", 1L, 1000000079900L), // 09:47:59
// Tuple3.of("a", 1L, 1000000115000L), // 09:48:35
Tuple3.of("b", 1L, 1000000100000L), // 09:48:20
Tuple3.of("b", 1L, 1000000108000L), // 09:48:28
Tuple3.of("a", 1L, 1000000125000L) // 09:48:45
};
int count = 0;
while (running && count < elements.length) {
sourceContext.collect(new Tuple3<>((String) elements[count].f0, (Long) elements[count].f1, (Long) elements[count].f2));
count++;
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
running = false;
}
}
/**
* 存储在状态中的对象
*/
public static class CountWithTimestamp {
//单词
public String key;
//单词计数
public long count;
//最近更新时间
public long lastModified;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CountWithTimestamp{" +
"key='" + key + '\'' +
", count=" + count +
", lastModified=" + new Date(lastModified) +
'}';
}
}
/**
* ProcessFunction有两个泛型类,一个输入一个输出
*/
public static class CountWithTimeoutFunction extends
ProcessFunction, Tuple2> {
private ValueState state;
private static int cnt = 0;
//最先调用
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
//根据上下文获取状态
state = getRuntimeContext().getState(new ValueStateDescriptor("myState", CountWithTimestamp.class));
}
@Override
public void processElement(Tuple2 input, Context context, Collector> output) throws Exception {
CountWithTimestamp current = state.value();
if (current == null) {
current = new CountWithTimestamp();
current.key = input.f0;
}
//更新ValueState
current.count++;
//这里面的context可以获取时间戳
//todo 此时这里的时间戳可能为null,如果设置的时间为ProcessingTime
current.lastModified = context.timestamp();
System.out.println(cnt + " 元素"+input.f0+"进入事件时间为:" + new Date(current.lastModified));
cnt++;
state.update(current);
//注册ProcessTimer,更新一次就会有一个ProcessTimer
context.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer(current.lastModified + 9000);
System.out.println("定时触发时间为:"+new Date(current.lastModified + 9000));
}
//EventTimer被触发后产生的行为
//todo 这里的timestamp是触发时间
@Override
public void onTimer(long timestamp, OnTimerContext ctx, Collector> out) throws Exception {
//获取上次时间,与参数中的timestamp相比,如果相差等于60s 就会输出
CountWithTimestamp res = state.value();
System.out.println("当前时间为:"+new Date(timestamp)+res);
if (timestamp == res.lastModified + 9000) {
// if (timestamp >= res.lastModified + 9000) {
System.out.println("定时器被触发:"+"当前时间为"+new Date(timestamp)+" 最近修改时间为"+new Date(res.lastModified));
out.collect(new Tuple2(res.key, res.count));
} else {
System.out.println("timestamp:" + timestamp + " res.lastModified:" + res.lastModified +" 当前时间为"+new Date(timestamp)+" 最近修改时间为"+new Date(res.lastModified));
}
}
}
//执行主类
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime);
DataStream> data = env.addSource(new StreamDataSource()).setParallelism(1)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor>(
Time.milliseconds(0)) {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple3 input) {
return input.f2;
}
}).map(new MapFunction, Tuple2>() {
@Override
public Tuple2 map(Tuple3 input) throws Exception {
return new Tuple2<>(input.f0, input.f1);
}
});
data.keyBy(0).process(new CountWithTimeoutFunction()).print();
env.execute();
}
}