PAT(甲级)2019年冬季考试——题解+总结
PAT(甲级)2019年冬季考试
总结写在前头:
- 考了字符串、链表(伪链表)、图、树。考点比较均衡。
- 本次考试难度还行,需要较扎实的数据结构底子,对于字符串处理的技巧有一定的要求。
说句题外话,字符串是个重点,主要因为很多人会忽视字符串。2018-2019年的GPLT(团体程序设计天梯赛)的l1最后一题就是一道字符串处理,当时卡住了不知道多少人,但其实稍微做做字符串的题目之后就会发现,那题不过如此。这次PAT甲级的第一题也是不过如此,但很可惜,我当时也忽视了字符串的处理,错失甲满。。。
Good in C (20分)
When your interviewer asks you to write “Hello World” using C, can you do as the following figure shows?
![]()
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first part gives the 26 capital English letters A-Z, each in a 7×5 matrix of C's and .'s. Then a sentence is given in a line, ended by a return. The sentence is formed by several words (no more than 10 continuous capital English letters each), and the words are separated by any characters other than capital English letters.
It is guaranteed that there is at least one word given.
Output Specification:
For each word, print the matrix form of each of its letters in a line, and the letters must be separated by exactly one column of space. There must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the word.
Between two adjacent words, there must be a single empty line to separate them. There must be no extra line at the beginning or the end of the output.
Sample Input:
..C..
.C.C.
C...C
CCCCC
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
.CCC.
C...C
C....
C....
C....
C...C
.CCC.
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
CCCCC
C....
C....
CCCC.
C....
C....
CCCCC
CCCCC
C....
C....
CCCC.
C....
C....
C....
CCCC.
C...C
C....
C.CCC
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCCC
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCCC
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
CCCCC
CCCCC
....C
....C
....C
....C
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C..C.
C.C..
CC...
C.C..
C..C.
C...C
C....
C....
C....
C....
C....
C....
CCCCC
C...C
C...C
CC.CC
C.C.C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
CC..C
C.C.C
C..CC
C...C
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.CCC.
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C....
C....
C....
.CCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C.C.C
C..CC
.CCC.
CCCC.
C...C
CCCC.
CC...
C.C..
C..C.
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C....
.CCC.
....C
C...C
.CCC.
CCCCC
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.C.C.
..C..
C...C
C...C
C...C
C.C.C
CC.CC
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.C.C.
..C..
.C.C.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.C.C.
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
CCCCC
....C
...C.
..C..
.C...
C....
CCCCC
HELLO~WORLD!
Sample Output:
C...C CCCCC C.... C.... .CCC.
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
CCCCC CCCC. C.... C.... C...C
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
C...C CCCCC CCCCC CCCCC .CCC.
C...C .CCC. CCCC. C.... CCCC.
C...C C...C C...C C.... C...C
C...C C...C CCCC. C.... C...C
C.C.C C...C CC... C.... C...C
CC.CC C...C C.C.. C.... C...C
C...C C...C C..C. C.... C...C
C...C .CCC. C...C CCCCC CCCC.
没啥好说的,直接按照题目要求来,用c++的string比纯c的string.h方便。
注意一些细节:
- 单词中间可能会用空格隔开,所以不要使用cin读入,要用getline(这个点卡了我40分钟 ; ( )
代码:
#includeBlock Reversing (25分)
Given a singly linked list L. Let us consider every K nodes as a block (if there are less than K nodes at the end of the list, the rest of the nodes are still considered as a block). Your job is to reverse all the blocks in L. For example, given L as 1→2→3→4→5→6→7→8 and K as 3, your output must be 7→8→4→5→6→1→2→3.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains the address of the first node, a positive N (≤105) which is the total number of nodes, and a positive K (≤N) which is the size of a block. The address of a node is a 5-digit nonnegative integer, and NULL is represented by −1.
Then N lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
Address Data Next
where Address is the position of the node, Data is an integer, and Next is the position of the next node.
Output Specification:
For each case, output the resulting ordered linked list. Each node occupies a line, and is printed in the same format as in the input.
Sample Input:
00100 8 3
71120 7 88666
00000 4 99999
00100 1 12309
68237 6 71120
33218 3 00000
99999 5 68237
88666 8 -1
12309 2 33218
Sample Output:
71120 7 88666
88666 8 00000
00000 4 99999
99999 5 68237
68237 6 00100
00100 1 12309
12309 2 33218
33218 3 -1
没有什么太难的点,
可以直接使用reverse函数,或者手写,我一开始手写的,但是最后一个测试点一直卡住了,不知道是什么情况。。。后来换成了reverse()就ac了,唉,人间未解之谜。。。
代码:
#includeSummit (25分)
A summit (峰会) is a meeting of heads of state or government. Arranging the rest areas for the summit is not a simple job. The ideal arrangement of one area is to invite those heads so that everyone is a direct friend of everyone.
Now given a set of tentative arrangements, your job is to tell the organizers whether or not each area is all set.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives two positive integers N (≤ 200), the number of heads in the summit, and M, the number of friendship relations. Then M lines follow, each gives a pair of indices of the heads who are friends to each other. The heads are indexed from 1 to N.
Then there is another positive integer K (≤ 100), and K lines of tentative arrangement of rest areas follow, each first gives a positive number L (≤ N), then followed by a sequence of L distinct indices of the heads. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each of the K areas, print in a line your advice in the following format:
- if in this area everyone is a direct friend of everyone, and no friend is missing (that is, no one else is a direct friend of everyone in this area), print
Area X is OK.. - if in this area everyone is a direct friend of everyone, yet there are some other heads who may also be invited without breaking the ideal arrangement, print
Area X may invite more people, such as H.whereHis the smallest index of the head who may be invited. - if in this area the arrangement is not an ideal one, then print
Area X needs help.so the host can provide some special service to help the heads get to know each other.
Here X is the index of an area, starting from 1 to K.
Sample Input:
8 10
5 6
7 8
6 4
3 6
4 5
2 3
8 2
2 7
5 3
3 4
6
4 5 4 3 6
3 2 8 7
2 2 3
1 1
2 4 6
3 3 2 1
Sample Output:
Area 1 is OK.
Area 2 is OK.
Area 3 is OK.
Area 4 is OK.
Area 5 may invite more people, such as 3.
Area 6 needs help.
这题嘛,算是考了一些图方面的知识点,比较基础,直接暴力就好了,也不卡你暴力的时间,直接按照题目的判断要求一个一个来,for循环耍起来!
代码:
#includeCartesian Tree (30分)
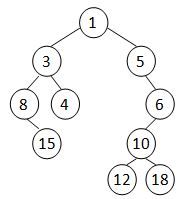
A Cartesian tree is a binary tree constructed from a sequence of distinct numbers. The tree is heap-ordered, and an inorder traversal returns the original sequence. For example, given the sequence { 8, 15, 3, 4, 1, 5, 12, 10, 18, 6 }, the min-heap Cartesian tree is shown by the figure.
Your job is to output the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts from giving a positive integer N (≤30), and then N distinct numbers in the next line, separated by a space. All the numbers are in the range of int.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
Sample Input:
10
8 15 3 4 1 5 12 10 18 6
Sample Output:
1 3 5 8 4 6 15 10 12 18
这题考树,也不难,我简单说一下题目意思和思路:
题意:给你一串数字,让你以这个为二叉树的中序遍历结果去建立一个符合最小堆的树。
思路:既然要符合最小堆,还给了中序遍历这个限制条件,好嘛,那已经很明显了,一组数字中最小的那个值肯定是当前的根节点(符合最小堆)根据这个思路递归建树就好了。
ps:你可以用指针去做,也可以直接用数组去解,我觉得本题用数组足够了
代码:
#include