PCL 【点云分割】
一、平面模型分割
1、分割代码
//平面分割代码
#include //模型系数相关头文件
#include //模型定义头文件
#include //随机参数估计方法头文件
#include //基于采样一致性分割的类的头文件
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);//创建分割时所需要的模型系数对象coefficients以及存储内点的点索引集合对象
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices);
//创建分割对象
pcl::SACSegmentation seg;
//可选设置,设置模型系数需要优化
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);
//必须设置,设置分割的模型类型、所用的随机参数估计方法、距离阈值、输入点云
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.01);//距离阈值,包括0.01
seg.setInputCloud (cloud.makeShared ());
seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);//分割,存储分割结果到点集合inliers及存储平面模型的系数coefficients 2、完整代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //模型定义头文件
#include //随机参数估计方法头文件
#include //基于采样一致性分割的类的头文件
#include //可视化头文件
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PointCloud cloud;
//填充点云数据
cloud.width = 15;
cloud.height = 1;
cloud.points.resize (cloud.width * cloud.height);
//生成数据
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud.points.size (); ++i)
{
cloud.points[i].x = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud.points[i].y = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud.points[i].z = 1.0;
}
//设置几个局外点,使其偏离z=1的平面
cloud.points[0].z = 2.0;
cloud.points[3].z = -2.0;
cloud.points[6].z = 4.0;
cloud.points[7].z = 1.01;
cloud.points[8].z = 1.005;
std::cerr << "Point cloud data: " << cloud.points.size () <<" points" << std::endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud.points.size (); ++i)
std::cerr << " " << cloud.points[i].x << " "
<< cloud.points[i].y << " "
<< cloud.points[i].z << std::endl;
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);//创建分割时所需要的模型系数对象coefficients以及存储内点的点索引集合对象
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices);
//创建分割对象
pcl::SACSegmentation seg;
//可选设置,设置模型系数需要优化
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);
//必须设置,设置分割的模型类型、所用的随机参数估计方法、距离阈值、输入点云
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.01);//距离阈值,包括0.01
seg.setInputCloud (cloud.makeShared ());
seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);//分割,存储分割结果到点集合inliers及存储平面模型的系数coefficients
if (inliers->indices.size () == 0)
{
PCL_ERROR ("Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset.");
return (-1);
}
//输出平面模型的系数 a,b,c,d
std::cerr << "Model coefficients: " << coefficients->values[0] << " "
<values[1] << " "
<values[2] << " "
<values[3] <indices.size () << std::endl;
//输出点集合的坐标
for (size_t i = 0; i < inliers->indices.size (); ++i)
std::cerr << inliers->indices[i] << " " <indices[i]].x << " "
<indices[i]].y << " "
<indices[i]].z << std::endl;
//可视化
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3d viewer"));
//左边窗口显示输入的点云(待拟合)
int v1(0);
viewer->createViewPort(0,0,0.5,1,v1);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0,0,0,v1);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom color_in(cloud.makeShared(),255,0,0);
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud.makeShared(),color_in,"cloud_in",v1);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE,9,"cloud_in",v1);
//右边的窗口显示拟合之后的点云
int v2(0);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_out(new pcl::PointCloud);//存放最后拟合好的平面
cloud_out->width = inliers->indices.size();
cloud_out->height = 1;
cloud_out->is_dense = false;
cloud_out->resize(cloud_out->height * cloud_out->width);
for(size_t i=0;iindices.size();i++)
{
cloud_out->points[i].x = cloud.points[inliers->indices[i]].x;
cloud_out->points[i].y = cloud.points[inliers->indices[i]].y;
cloud_out->points[i].z = cloud.points[inliers->indices[i]].z;
}
std::cout<<"convert succeed!"<createViewPort(0.5,0,1,1,v2);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(255,255,255,v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud_out,"cloud_out",v2);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR,0,255,0,"cloud_out",v2);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE,9,"cloud_out",v2);
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
{
viewer->spinOnce();
}
return (0);
}
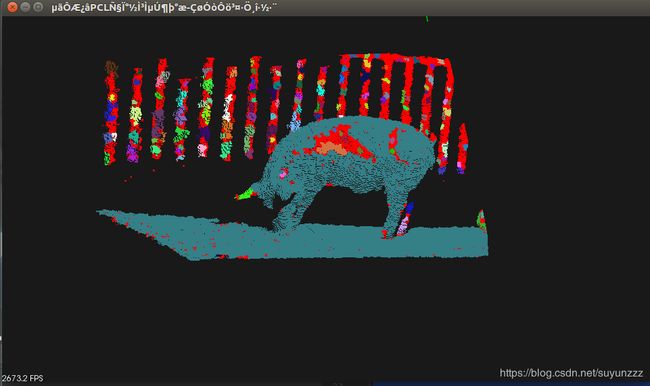
3、可视化
二、圆柱体模型分割提取
1、完整代码(不太懂,和之前的从点云中提取一个子集流程基本相同)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //可视化相关头文件
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
// All the objects needed
pcl::PCDReader reader;//点云读入对象
pcl::PassThrough pass;//直通滤波器对象
pcl::NormalEstimation ne;//法线估计对象
pcl::SACSegmentationFromNormals seg; //分割对象
pcl::PCDWriter writer;//写对象
pcl::ExtractIndices extract;//点提取对象
pcl::ExtractIndices extract_normals;//法线提取对象
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree ());//搜索方式对象
// Datasets
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_normals (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered2 (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_normals2 (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients_plane (new pcl::ModelCoefficients), coefficients_cylinder (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers_plane (new pcl::PointIndices), inliers_cylinder (new pcl::PointIndices);//一个指向索引的指针
// Read in the cloud data
reader.read ("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd", *cloud);
std::cerr << "PointCloud has: " << cloud->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
// Build a passthrough filter to remove spurious NaNs
//对cloud的z fields进行滤波,剔除0~1.5之外的点
pass.setInputCloud (cloud);//设置输入点云
pass.setFilterFieldName ("z");//设置滤波的field
pass.setFilterLimits (0, 1.5);//滤波范围
pass.filter (*cloud_filtered);//滤波结果存放
std::cerr << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
// Estimate point normals
ne.setSearchMethod (tree);//搜索方式
ne.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);//输入点云为直通滤波器的结果
ne.setKSearch (50);//选择最近邻的50个点进行法线估计
ne.compute (*cloud_normals);//法线的计算结果存放至cloud_normals
// Create the segmentation object for the planar model and set all the parameters
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);//选择是否优化系数
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE);
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight (0.1);
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations (100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.03);
seg.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);//输入的点云
seg.setInputNormals (cloud_normals);//输入的法线
// Obtain the plane inliers and coefficients
seg.segment (*inliers_plane, *coefficients_plane);//得到平面内点和平面的4个系数
std::cerr << "Plane coefficients: " << *coefficients_plane << std::endl;
// Extract the planar inliers from the input cloud
//提取出平面内点
extract.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices (inliers_plane);
extract.setNegative (false);
// Write the planar inliers to disk
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_plane (new pcl::PointCloud ());
extract.filter (*cloud_plane);//将平面点提取至clodu_plane
std::cerr << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
writer.write ("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_plane.pcd", *cloud_plane, false);
// Remove the planar inliers, extract the rest
extract.setNegative (true);//提取平面点之外的点,继续处理
extract.filter (*cloud_filtered2);//平面点
extract_normals.setNegative (true);
extract_normals.setInputCloud (cloud_normals);
extract_normals.setIndices (inliers_plane);
extract_normals.filter (*cloud_normals2);
// Create the segmentation object for cylinder segmentation and set all the parameters
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_CYLINDER);
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight (0.1);
seg.setMaxIterations (10000);
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.05);
seg.setRadiusLimits (0, 0.1);
seg.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered2);//提取平面之后剩余的点云
seg.setInputNormals (cloud_normals2);//剩余点云的法向量
// Obtain the cylinder inliers and coefficients
seg.segment (*inliers_cylinder, *coefficients_cylinder);//得到点的索引和圆柱体系数
std::cerr << "Cylinder coefficients: " << *coefficients_cylinder << std::endl;
// Write the cylinder inliers to disk
extract.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered2);
extract.setIndices (inliers_cylinder);
extract.setNegative (false);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_cylinder (new pcl::PointCloud ());
extract.filter (*cloud_cylinder);//按照圆柱体的索引将圆柱体的点提取至cloud_cylinder
if (cloud_cylinder->points.empty ())
std::cerr << "Can't find the cylindrical component." << std::endl;
else
{
std::cerr << "PointCloud representing the cylindrical component: " << cloud_cylinder->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
writer.write ("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_cylinder.pcd", *cloud_cylinder, false);
}
//将原点云、平面cloud_plane、圆柱体cloud_cylinder可视化
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3d viewer"));
//第一个窗口显示输入点云
int v1(0);
viewer->createViewPort(0,0,0.33,1,v1);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0,0,0,v1);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom color(cloud,255,255,255);
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud,color,"cloud",v1);
//第二个窗口显示分割的平面
int v2(0);
viewer->createViewPort(0.33,0,0.66,1,v2);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0,0,0,v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud_plane,color,"cloud_plane",v2);
//第三个窗口显示分割的圆柱
int v3(0);
viewer->createViewPort(0.66,0,1,1,v3);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0,0,0,v3);
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud_cylinder,color,"cloud_cylinder",v3);
viewer->addCoordinateSystem();//显示坐标系
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
{
viewer->spinOnce();
}
return (0);
}
2、可视化
提取桌子(平面分割)、提取杯子(圆柱体分割提取)
三、欧式聚类分割
1、API思路
对输入点云进行欧式聚类提取,将聚类结果保存至一个vector
2、欧式聚类提取代码
// Creating the KdTree object for the search method of the extraction
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree);
tree->setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);//将无法提取平面的点云作为cloud_filtered
std::vector cluster_indices;//保存每一种聚类,每一种聚类下还有具体的聚类的点
pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction ec;//实例化一个欧式聚类提取对象
ec.setClusterTolerance (0.02); // 近邻搜索的搜索半径为2cm,重要参数
ec.setMinClusterSize (100);//设置一个聚类需要的最少点数目为100
ec.setMaxClusterSize (25000);//一个聚类最大点数目为25000
ec.setSearchMethod (tree);//设置点云的搜索机制
ec.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);//设置输入点云
ec.extract (cluster_indices);//将聚类结果保存至cluster_indices中
//迭代访问点云索引cluster_indices,直到分割出所有聚类,一个循环提取出一类点云
int j = 0;
for (std::vector::const_iterator it = cluster_indices.begin (); it != cluster_indices.end (); ++it)
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_cluster (new pcl::PointCloud);
//创建新的点云数据集cloud_cluster,直到分割出所有聚类
for (std::vector::const_iterator pit = it->indices.begin (); pit != it->indices.end (); pit++)
cloud_cluster->points.push_back (cloud_filtered->points[*pit]); //*
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size ();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the Cluster: " << cloud_cluster->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "cloud_cluster_" << j << ".pcd";
writer.write (ss.str (), *cloud_cluster, false); //*
j++;
}
3、完整代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //可视化相关头文件
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
// Read in the cloud data
pcl::PCDReader reader;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud), cloud_f (new pcl::PointCloud);
reader.read ("table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud);
std::cout << "PointCloud before voxel filtering has: " << cloud->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl; //*
// Create the filtering object: downsample the dataset using a leaf size of 1cm
pcl::VoxelGrid vg;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud);
vg.setInputCloud (cloud);
vg.setLeafSize (0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f);
vg.filter (*cloud_filtered);
std::cout << "PointCloud after voxel filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl; //*
// Create the segmentation object for the planar model and set all the parameters
pcl::SACSegmentation seg;//实例化一个分割对象
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices);//实例化一个索引
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);//实例化模型参数
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_plane (new pcl::PointCloud ());//提取到的平面保存至cloud_plane
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);//参数优化
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);//模型类型:平面
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);//参数估计方法
seg.setMaxIterations (100);//最大迭代次数
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.02);//设置内点到模型的距离允许最大值
int i=0, nr_points = (int) cloud_filtered->points.size ();//计数变量i,记下提取的平面的个数
while (cloud_filtered->points.size () > 0.3 * nr_points)
{
// Segment the largest planar component from the remaining cloud
seg.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);//设置要分割的点云
seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);//输出平面点的索引和参数
if (inliers->indices.size () == 0)//如果平面点索引的数量为0
{
std::cout << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << std::endl;
break;
}
// Extract the planar inliers from the input cloud
pcl::ExtractIndices extract;//实例化一个提取对象
extract.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);//设置要提取的点云
extract.setIndices (inliers);//根据分割得到的平面的索引提取平面
extract.setNegative (false);//提取内点
// Write the planar inliers to disk
extract.filter (*cloud_plane);//保存提取到的平面
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
//存写指针的参数
cloud_plane->width = cloud_plane->points.size();
cloud_plane->height = 1;
cloud_plane->resize(cloud_plane->width);
cloud_plane->is_dense = false;
//依次将该指针(cloud_plane)保存至一个专门存放平面的文件(未设置点云格式)、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
std::stringstream s_plane;
s_plane << "cloud_plane_"<< i <<".pcd";
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII(s_plane.str(),*cloud_plane);
std::cout<::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree);
tree->setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);//将无法提取平面的点云作为cloud_filtered
std::vector cluster_indices;//保存每一种聚类,每一种聚类下还有具体的聚类的点
pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction ec;//实例化一个欧式聚类提取对象
ec.setClusterTolerance (0.02); // 近邻搜索的搜索半径为2cm,重要参数
ec.setMinClusterSize (100);//设置一个聚类需要的最少点数目为100
ec.setMaxClusterSize (25000);//一个聚类最大点数目为25000
ec.setSearchMethod (tree);//设置点云的搜索机制
ec.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);//设置输入点云
ec.extract (cluster_indices);//将聚类结果保存至cluster_indices中
//迭代访问点云索引cluster_indices,直到分割出所有聚类,一个循环提取出一类点云
int j = 0;
for (std::vector::const_iterator it = cluster_indices.begin (); it != cluster_indices.end (); ++it)
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_cluster (new pcl::PointCloud);
//创建新的点云数据集cloud_cluster,直到分割出所有聚类
for (std::vector::const_iterator pit = it->indices.begin (); pit != it->indices.end (); pit++)
cloud_cluster->points.push_back (cloud_filtered->points[*pit]); //*
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size ();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the Cluster: " << cloud_cluster->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "cloud_cluster_" << j << ".pcd";
writer.write (ss.str (), *cloud_cluster, false); //*
j++;
}
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3d viewer"));
int v1(0);
viewer->createViewPort(0,0,0.5,1,v1);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0,0,0,v1);
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud,"cloud",v1);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR,255,0,0,"cloud",v1);
//第二个视口,显示分割聚类后的点云
//读入每一个点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr view0(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr view1(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr view2(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr view3(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr view4(new pcl::PointCloud);
//读取两个平面的指针
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr view_plane1(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr view_plane2(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("cloud_cluster_0.pcd",*view0);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("cloud_cluster_1.pcd",*view1);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("cloud_cluster_2.pcd",*view2);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("cloud_cluster_3.pcd",*view3);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("cloud_cluster_4.pcd",*view4);
//读取两个平面
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("cloud_plane_0.pcd",*view_plane1);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("cloud_plane_1.pcd",*view_plane2);
std::cerr<<"cloud_plane read"<createViewPort(0.5,0,1,1,v2);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(1,1,1,v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(view0,"view0",v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(view1,"view1",v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(view2,"view2",v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(view3,"view3",v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(view4,"view4",v2);
//显示两个平面
viewer->addPointCloud(view_plane1,"view_plane1",v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(view_plane2,"view_plane2",v2);
std::cout<<"added!"<setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR,255,0,0,"view0",v2);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR,0,255,0,"view1",v2);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR,0,0,255,"view2",v2);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR,126,123,0,"view3",v2);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR,0,0,0,"view4",v2);
//设置两个平面的颜色
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR,100,0,60,"view_plane1",v2);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR,0,255,60,"view_plane2",v2);
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
{
viewer->spinOnce();
}
return (0);
}
注:点云保存,读取,可视化部分没有利用循环,有点蠢,跑完例程之后回头解决这个问题
4、可视化
注:两个平面是使用平面分割提取出来的,其余部分是使用欧式聚类提取得到的结果
四、基于区域生长的分割
1、概述
本例程学习如何用pcl::RegionGrowing类实现区域生长分割。算法的输出是一个聚类的集合,每个聚类集合被认为是同一光滑表面的一部分。
该算法思想:首先依据点的曲率值对点进行排序,之所以排序,是因为区域生长算法是从曲率最小的点开始生长的,这个点就是初始种子点,初始种子点所在的区域即为最平滑的区域,一般场景中平面区域较大,这样从最平滑的区域开始生长即可减少分割区域的总数,提高效率等。
算法的流程:设置一空的聚类区域Ç和空的种子点序列Q,选好初始种子点,将其加入种子点序列,并搜索该种子点的领域点,计算每一个领域点法线与种子点法线之间的夹角,小于设定的平滑阀值时,将领域点加入到ç中,同时判断该领域点的曲率值是否小于曲率阀值,将小于曲率阔值的领域点加入种子点序列Q中,在Q中重新选择新的种子点重复上述步骤,直到Q中序列为空,算法结束。
2、基于区域生长的分割部分代码
基于法线
#include
// 区域生长算法的5个参数
pcl::RegionGrowing reg;//创建区域生长分割对象
reg.setMinClusterSize (50);//设置一个聚类需要的最小点数
reg.setMaxClusterSize (1000000);//设置一个聚类需要的最大点数
reg.setSearchMethod (tree);//设置搜索方法
reg.setNumberOfNeighbours (30);//设置搜索的临近点数目
reg.setInputCloud (cloud);//设置输入点云
if(Bool_Cuting)reg.setIndices (indices);//通过输入参数设置,确定是否输入点云索引.如果需要直通滤波,就设置输入点云的索引
reg.setInputNormals (normals);//设置输入点云的法向量
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold (SmoothnessThreshold / 180.0 * M_PI);//设置平滑阈值
reg.setCurvatureThreshold (CurvatureThreshold);//设置曲率阈值
std::vector clusters;//保存每一种聚类,每一种聚类下面还有具体的点
reg.extract (clusters);//获取聚类的结果,分割结果保存在点云索引的向量中。
end = time(0);
diff[2] = difftime (end, start)-diff[0]-diff[1]; //区域生长分割算法花费的时间
PCL_INFO ("\tRegion growing takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[2]);
std::cout << "Number of clusters is equal to " << clusters.size () << std::endl;//输出聚类的数量,有几类
std::cout << "First cluster has " << clusters[0].indices.size () << " points." << endl;//输出第一个聚类中点的数量
/***
std::cout << "These are the indices of the points of the initial" <<
std::endl << "cloud that belong to the first cluster:" << std::endl;
int counter = 0;
while (counter < clusters[0].indices.size ())
{
std::cout << clusters[0].indices[counter] << ", ";
counter++;
if (counter % 10 == 0)
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
***/
//保存第一个分割
//vector和迭代器 理解不到位
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_seg1(new pcl::PointCloud);
for (std::vector::const_iterator pit = clusters[0].indices.begin();pit !=clusters[0].indices.end();pit++)//创建一个迭代器pit以访问第一个聚类的每一个点
{
cloud_seg1->points.push_back(cloud->points[*pit]);//迭代器pit类似于一个指针,将第一个聚类分割中的每一个点进行强制类型转换,并放置在points中
}
cloud_seg1->width = cloud_seg1->points.size();
cloud_seg1->height = 1;
cloud_seg1->is_dense = false;
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("cloud_seg1.pcd",*cloud_seg1);
std::cerr<<"cloud_seg1 saved!!! poins: "<size()< 3、完整代码
//该算法(区域生长分割)同欧式聚类分割类似,也是最后将聚类分割的结果存放至一个点云索引的向量vector中
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//#include
#include
//#include
/***
void PrintMemoryInfo( )
{
HANDLE hProcess;
PROCESS_MEMORY_COUNTERS pmc;
hProcess=GetCurrentProcess();
printf( "\nProcess ID: %u\n", hProcess );
// Print information about the memory usage of the process.
//输出进程使用的内存信息
if (NULL == hProcess)
return;
if ( GetProcessMemoryInfo( hProcess, &pmc, sizeof(pmc)) )
{
printf( "\tPageFaultCount: 0x%08X\n", pmc.PageFaultCount );
printf( "\tPeakWorkingSetSize: 0x%08X\n",
pmc.PeakWorkingSetSize );
printf( "\tWorkingSetSize: 0x%08X\n", pmc.WorkingSetSize );
printf( "\tQuotaPeakPagedPoolUsage: 0x%08X\n",
pmc.QuotaPeakPagedPoolUsage );
printf( "\tQuotaPagedPoolUsage: 0x%08X\n",
pmc.QuotaPagedPoolUsage );
printf( "\tQuotaPeakNonPagedPoolUsage: 0x%08X\n",
pmc.QuotaPeakNonPagedPoolUsage );
printf( "\tQuotaNonPagedPoolUsage: 0x%08X\n",
pmc.QuotaNonPagedPoolUsage );
printf( "\tPagefileUsage: 0x%08X\n", pmc.PagefileUsage );
printf( "\tPeakPagefileUsage: 0x%08X\n",
pmc.PeakPagefileUsage );
}
CloseHandle( hProcess );
}
****/
using namespace pcl::console;
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
if(argc<2)
{
std::cout<<".exe xx.pcd -kn 50 -bc 0 -fc 10.0 -nc 0 -st 30 -ct 0.05"<::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);
if ( pcl::io::loadPCDFile (argv[1], *cloud) == -1)
{
std::cout << "Cloud reading failed." << std::endl;
return (-1);
}// 加载输入点云数据
end = time(0);
diff[0] = difftime (end, start);
PCL_INFO ("\tLoading pcd file takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[0]);
//Noraml estimation step(1 parameter)
//创建一个tree对象
pcl::search::Search::Ptr tree = boost::shared_ptr > (new pcl::search::KdTree);//创建一个指向kd树搜索对象的共享指针
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr normals (new pcl::PointCloud );
pcl::NormalEstimation normal_estimator;//创建法线估计对象
normal_estimator.setSearchMethod (tree);//设置搜索方法
normal_estimator.setInputCloud (cloud);//设置法线估计对象输入点集
normal_estimator.setKSearch (KN_normal);// 设置用于法向量估计的k近邻数目
normal_estimator.compute (*normals);//计算并输出法向量
end = time(0);
diff[1] = difftime (end, start)-diff[0];
PCL_INFO ("\tEstimating normal takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[1]);//输出法线估计这一步用了多久时间
//optional step: cutting the part are far from the orignal point in Z direction.2 parameters
pcl::IndicesPtr indices (new std::vector );//创建一组索引
if(Bool_Cuting)//判断是否需要直通滤波
{
pcl::PassThrough pass;//设置直通滤波器对象
pass.setInputCloud (cloud);//设置输入点云
pass.setFilterFieldName ("z");//设置指定过滤的维度
pass.setFilterLimits (near_cuting, far_cuting);//设置指定纬度过滤的范围
pass.filter (*indices);//执行滤波,保存滤波结果在上述索引中
}
// 区域生长算法的5个参数
pcl::RegionGrowing reg;//创建区域生长分割对象
reg.setMinClusterSize (50);//设置一个聚类需要的最小点数
reg.setMaxClusterSize (1000000);//设置一个聚类需要的最大点数
reg.setSearchMethod (tree);//设置搜索方法
reg.setNumberOfNeighbours (30);//设置搜索的临近点数目
reg.setInputCloud (cloud);//设置输入点云
if(Bool_Cuting)reg.setIndices (indices);//通过输入参数设置,确定是否输入点云索引.如果需要直通滤波,就设置输入点云的索引
reg.setInputNormals (normals);//设置输入点云的法向量
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold (SmoothnessThreshold / 180.0 * M_PI);//设置平滑阈值
reg.setCurvatureThreshold (CurvatureThreshold);//设置曲率阈值
std::vector clusters;//保存每一种聚类,每一种聚类下面还有具体的点
reg.extract (clusters);//获取聚类的结果,分割结果保存在点云索引的向量中。
end = time(0);
diff[2] = difftime (end, start)-diff[0]-diff[1]; //区域生长分割算法花费的时间
PCL_INFO ("\tRegion growing takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[2]);
std::cout << "Number of clusters is equal to " << clusters.size () << std::endl;//输出聚类的数量,有几类
std::cout << "First cluster has " << clusters[0].indices.size () << " points." << endl;//输出第一个聚类中点的数量
/***
std::cout << "These are the indices of the points of the initial" <<
std::endl << "cloud that belong to the first cluster:" << std::endl;
int counter = 0;
while (counter < clusters[0].indices.size ())
{
std::cout << clusters[0].indices[counter] << ", ";
counter++;
if (counter % 10 == 0)
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
***/
//保存第一个分割
//vector和迭代器 理解不到位
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_seg1(new pcl::PointCloud);
for (std::vector::const_iterator pit = clusters[0].indices.begin();pit !=clusters[0].indices.end();pit++)//创建一个迭代器pit以访问第一个聚类的每一个点
{
cloud_seg1->points.push_back(cloud->points[*pit]);//迭代器pit类似于一个指针,将第一个聚类分割中的每一个点进行强制类型转换,并放置在points中
}
cloud_seg1->width = cloud_seg1->points.size();
cloud_seg1->height = 1;
cloud_seg1->is_dense = false;
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("cloud_seg1.pcd",*cloud_seg1);
std::cerr<<"cloud_seg1 saved!!! poins: "<size()<::const_iterator it = clusters.begin (); it != clusters.end (); ++it)
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud);
//创建新的点云数据集cloud_cluster,直到分割出所有聚类
for (std::vector::const_iterator pit = it->indices.begin(); pit != it->indices.end(); pit++)
cloud_cluster->points.push_back(cloud_seg1->points[*pit]);
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the Cluster: " << cloud_cluster->points.size() << " data points."
<< std::endl;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "cloud_cluster_" << j << ".pcd";
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII(ss.str(),*cloud_cluster);
j++;
}
**/
//PrintMemoryInfo();
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr colored_cloud = reg.getColoredCloud ();//如果点云分割成功,该函数返回有色点云,相同的分割有相同的颜色,但是该函数不保证不同的分割一定会有不同的颜色,即不同的分割也可能会有相同的颜色
pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer ("点云库PCL学习教程第二版-区域增长分割方法");
viewer.showCloud(colored_cloud);
while (!viewer.wasStopped ())
{
}//进行可视化
return (0);
} 4、可视化
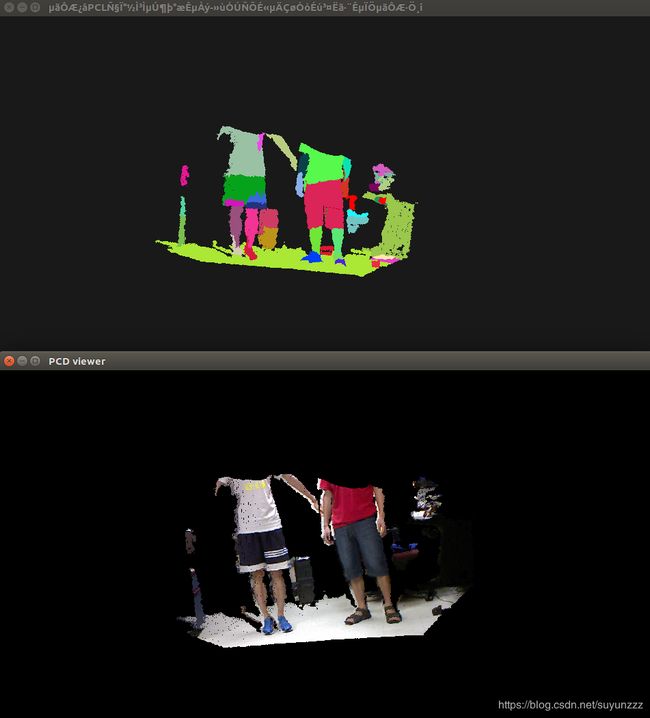
五、基于颜色的区域生长分割
1、 概述
该算法与区域生长算法一样,是基于同一策略之上的,其基本思想可参考区域生长算法相关章节。与区域生长算法相比,该算法主要有两个不同之处。第一,该算法用颜色测试代替了法线测试。第二,利用合并算法来控制过分割和欠分割。分割过程中,若两个相邻聚类的平均颜色相差较少,则将这两个聚类合并。然后进行第二步合并,在此步骤中,检查每一个聚类所包含的点的数量,如果这个数量小于用户定义的值,则当前这个聚类与其最近聚类合并在一起。
注意:输入的点云数据必须带有颜色
2、基于颜色的区域生长分割代码
// Region growing RGB
pcl::RegionGrowingRGB reg;//实例化一个区域生长对象
reg.setInputCloud (cloud);//设置输入点云
if(Bool_Cuting)reg.setIndices (indices);//如果刚才启动了直通滤波就设置点的索引
reg.setSearchMethod (tree);//设置搜索方式
reg.setDistanceThreshold (DistanceThreshold);//设置距离阈值,用于判断点云中的两点是否是相邻点,若小于此阈值则认为两点是相邻的
reg.setPointColorThreshold (ColorThreshold);//设置点之间颜色阈值,若颜色差距不超过这个阈值则认为两点是同一区聚类
reg.setRegionColorThreshold (RegionColorThreshold);//设置聚类间的颜色阈值,若小于此阈值则将两个聚类合并
reg.setMinClusterSize (MinClusterSize);//设置聚类最少点的数目
if(b_n)//控制是否同时使用颜色测试和法线测试两种测试手段
{
reg.setSmoothModeFlag(true);//设置平滑??????
reg.setCurvatureTestFlag(true);//设置曲率????
reg.setInputNormals (normals);//输入点云法向量
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold (SmoothnessThreshold / 180.0 * M_PI);//平滑阈值
reg.setCurvatureThreshold (CurvatureThreshold);//曲率阈值
}
std::vector clusters;//保存每一种聚类,每种聚类下还有点
reg.extract (clusters);//保存聚类结果至clusters
end = time(0);
diff[2] = difftime (end, start)-diff[0]-diff[1];
PCL_INFO ("\tRGB region growing takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[2]);//输出基于颜色的区域生长分割花费的时间
//输出聚类的数目
std::cout<<"number of cluster : "< 3、完整代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //基于颜色的区域生长分割
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace pcl::console;
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
if(argc<2)
{
std::cout<<".exe xx.pcd -b_n 0 -kn 50 -st_n 30 -ct_n 0.05 -bc 0 -fc 10 -nc 0 -dt 10 -ct 6 -rt 5 -mt 600" <::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);//读入点云,注意点云数据必须带颜色
if ( pcl::io::loadPCDFile (argv[1], *cloud) == -1)
{
std::cout << "Cloud reading failed." << std::endl;
return (-1);
}
end = time(0);
diff[0] = difftime (end, start);
PCL_INFO ("\tLoading pcd file takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[0]);//读入点云所需时间
pcl::search::Search ::Ptr tree = boost::shared_ptr > (new pcl::search::KdTree);//实例化一个KdTree对象
//Noraml estimation step(1 parameter)
pcl::search::Search::Ptr tree1 = boost::shared_ptr > (new pcl::search::KdTree);
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr normals (new pcl::PointCloud );
pcl::NormalEstimation normal_estimator;//实例化一个法线估计对象
normal_estimator.setSearchMethod (tree);//设置搜索方式
normal_estimator.setInputCloud (cloud);//输入点云
normal_estimator.setKSearch (KN_normal);//法线估计的K近邻数目
normal_estimator.compute (*normals);//法线估计结果保存至normals
end = time(0);
diff[1] = difftime (end, start)-diff[0];
PCL_INFO ("\tEstimating normal takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[1]);//输出法线估计花费时间
//Optional step: cutting away the clutter scene too far away from camera
pcl::IndicesPtr indices (new std::vector );
if(Bool_Cuting)//是否通过z轴范围对待处理数据进行裁剪
{
pcl::PassThrough pass;
pass.setInputCloud (cloud);
pass.setFilterFieldName ("z");
pass.setFilterLimits (near_cuting, far_cuting);
pass.filter (*indices);//直通滤波结果保存
}
// Region growing RGB
pcl::RegionGrowingRGB reg;//实例化一个区域生长对象
reg.setInputCloud (cloud);//设置输入点云
if(Bool_Cuting)reg.setIndices (indices);//如果刚才启动了直通滤波就设置点的索引
reg.setSearchMethod (tree);//设置搜索方式
reg.setDistanceThreshold (DistanceThreshold);//设置距离阈值,用于判断点云中的两点是否是相邻点,若小于此阈值则认为两点是相邻的
reg.setPointColorThreshold (ColorThreshold);//设置点之间颜色阈值,若颜色差距不超过这个阈值则认为两点是同一区聚类
reg.setRegionColorThreshold (RegionColorThreshold);//设置聚类间的颜色阈值,若小于此阈值则将两个聚类合并
reg.setMinClusterSize (MinClusterSize);//设置聚类最少点的数目
if(b_n)//控制是否同时使用颜色测试和法线测试两种测试手段
{
reg.setSmoothModeFlag(true);//设置平滑??????
reg.setCurvatureTestFlag(true);//设置曲率????
reg.setInputNormals (normals);//输入点云法向量
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold (SmoothnessThreshold / 180.0 * M_PI);//平滑阈值
reg.setCurvatureThreshold (CurvatureThreshold);//曲率阈值
}
std::vector clusters;//保存每一种聚类,每种聚类下还有点
reg.extract (clusters);//保存聚类结果至clusters
end = time(0);
diff[2] = difftime (end, start)-diff[0]-diff[1];
PCL_INFO ("\tRGB region growing takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[2]);//输出基于颜色的区域生长分割花费的时间
//输出聚类的数目
std::cout<<"number of cluster : "<::Ptr colored_cloud = reg.getColoredCloud ();//如果分割成功则返回有色点云
pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer ("点云库PCL学习教程第二版实例-基于颜色的区域生长算法实现点云分割");
viewer.showCloud (colored_cloud);
while (!viewer.wasStopped ())
{
boost::this_thread::sleep (boost::posix_time::microseconds (100));
}
return (0);
} 4、可视化
下面的均为输入点云,上面的是基于颜色的区域生长分割的结果