PCL快速点特征直方图配准算法
已知点云P中有n个点,那么它的点特征直方图(PFH)的理论计算复杂度是O(nk^2) , 其中k是点云P中每个点p计算特征向量时考虑的邻域数量。对于实际应用中,密集点云的点特征直方图(PFH)的计算,是十分耗时的。本博文介绍一种快速快速点特征直方图FPFH(Fast Point Feature Histograms)算法。FPFH把算法的计算复杂度降低到了O(nk) ,但是任然保留了PFH大部分的识别特性。
理论基础
直方图特征计算步骤:
Step 1.计算了每个查询点Pq的一系列![]() 值,并把它叫做SPFH(Simplified Point Feature Histgram)
值,并把它叫做SPFH(Simplified Point Feature Histgram)
Step 2.重新确定每个点的k邻域,使用邻近的SPFH值来计算 的最终直方图(称为FPFH),如下所示:
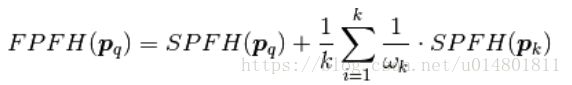
这里的Wk代表了两点的距离。权重(weight)的组合是非常重要的,下面的图显示了这一点:
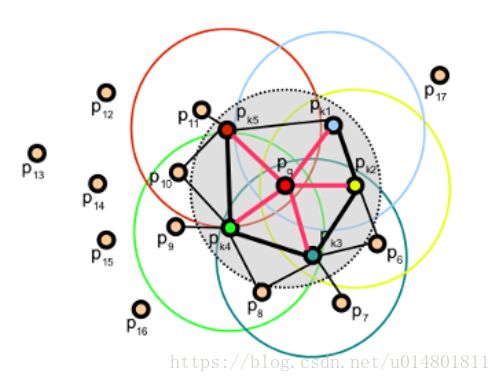
可以看到越近的权重越大,线越粗。
因此,给定一个点Pq,这个算法第一步评估了SPFH的值,通过创造它和它的近邻的匹配。这个过程将一直重复,通过近邻SPFH的值不停的改变权重,最终生成了Pq的FPFH。
PFH与FPFH之间的差异
1.FPFH没有和它所有的近邻有着联系,因此可能会丢失一些值的匹配。
2.PFH模型可以更精确的描述表面,而FPFH则包括了额外的点的配对在半径为r的圆的外面(最多不会超过2r)
3.因为权重的组合,FPFH结合了SPFH的值并且重新获取了一些点的近邻。
4.FPFH复杂度大大降低,计算更快。
FPFH的执行使用了11个分发的子区间,和一个非相关的组合(33位的数组),把它存在pcl::FPFHSignature33这个点类型里面。
下面看一段代码:
// Feature.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
// 用于特征提取学习
// NARF (Normal Aligned Radial Feature 法向径向特征对齐)
// FPFH (Fast Point Feature histograms 快速点特征直方图)
// SIFT (Scale-invariant Feature Transform 尺寸不变特征变换)
// BRIEF (Binary Robust Independent Elementary Features 二进制健壮的独立的基本特性)
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //FPFH
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //omp加速计算
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef pcl::PointCloud pointcloud;
typedef pcl::PointCloud pointnormal;
typedef pcl::PointCloud fpfhFeature;
//为了使用fpfh特征匹配,声明一个计算fpfh特征点的函数
fpfhFeature::Ptr compute_fpfh_feature(pointcloud::Ptr input_cloud, pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
clock_t start, end; //long
start = clock();//开始时间
pointcloud::Ptr source(new pointcloud);
pointcloud::Ptr target(new pointcloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("bunny_target.pcd", *target);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("bunny_source.pcd", *source);
cout << target->size() << endl;
//精简
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr target_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr source_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud());
pcl::VoxelGrid sor;
sor.setInputCloud(target);
sor.setLeafSize(0.005, 0.005, 0.005);
sor.filter(*target_filtered);
pcl::VoxelGrid sor1;
sor1.setInputCloud(source);
sor1.setLeafSize(0.005, 0.005, 0.005);
sor1.filter(*source_filtered);
cout << source_filtered->size() << " " << target_filtered->size() << endl;
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree());//创建搜索树
fpfhFeature::Ptr source_fpfh = compute_fpfh_feature(source_filtered, tree);//计算点云点特征直方图
fpfhFeature::Ptr target_fpfh = compute_fpfh_feature(target_filtered, tree);
//对齐 //输入参数 ①源点云+源点特征直方图 ②目标点云+目标点特征直方图
pcl::SampleConsensusInitialAlignment sac_ia;
sac_ia.setInputSource(source_filtered);
sac_ia.setSourceFeatures(source_fpfh);
sac_ia.setInputTarget(target_filtered);
sac_ia.setTargetFeatures(target_fpfh);
pointcloud::Ptr final(new pointcloud);//
//对齐参数设置
sac_ia.setNumberOfSamples(20);
sac_ia.setCorrespondenceRandomness(6);//设置计算协方差时选择多少近邻点,该值越大,协防差越精确,但是计算效率越低.(可省)
//sac_ia.setMaximumIterations(100);
sac_ia.setEuclideanFitnessEpsilon(0.001);
sac_ia.setTransformationEpsilon(1e-10);
sac_ia.setRANSACIterations(30);
sac_ia.align(*final);
cout <<"has converged:"<< sac_ia.hasConverged() <<"score"< view(new
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("fpfh test"));
int v1 = 0;
int v2 = 1;
view->createViewPort(0, 0, 0.5, 1, v1);
view->createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1, 1, v2);
view->setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0, v1);
view->setBackgroundColor(0.05, 0, 0, v2);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom source_cloud_color(source_filtered, 255, 0, 0);
view->addPointCloud(source_filtered, source_cloud_color, "sources_cloud_v1", v1);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom target_cloud_color(target_filtered, 0, 255, 0);
view->addPointCloud(target_filtered, target_cloud_color, "target_cloud_v1", v1);
view->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "sources_cloud_v1", v1);
//
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom aligend_cloud_color(final, 255, 0, 0);
view->addPointCloud(final, aligend_cloud_color, "aligend_cloud_v2", v2);
view->addPointCloud(target_filtered, target_cloud_color, "target_cloud_v2", v2);
view->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "aligend_cloud_v2");
view->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "target_cloud_v2");
//对应关系可视化
pcl::registration::CorrespondenceEstimation crude_cor_est;
boost::shared_ptr cru_correspondences(new pcl::Correspondences);
crude_cor_est.setInputSource(source_fpfh);
crude_cor_est.setInputTarget(target_fpfh);
//crude_cor_est.determineCorrespondences(*cru_correspondences);
crude_cor_est.determineReciprocalCorrespondences(*cru_correspondences);
cout << "crude size is " << cru_correspondences->size() << endl;
view->addCorrespondences(source, target, *cru_correspondences,"correspondence", v1);
view->initCameraParameters();
while (!view->wasStopped())
{
view->spinOnce(100);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100000));
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
fpfhFeature::Ptr compute_fpfh_feature(pointcloud::Ptr input_cloud, pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree)
{
//法向量
pointnormal::Ptr point_normal(new pointnormal);
pcl::NormalEstimation est_normal;
est_normal.setInputCloud(input_cloud);
est_normal.setSearchMethod(tree);
est_normal.setKSearch(10);
//est_normal.setSearchSurface();
est_normal.compute(*point_normal);
//fpfh估计
fpfhFeature::Ptr fpfh(new fpfhFeature);
//pcl::FPFHEstimation est_target_fpfh;
pcl::FPFHEstimationOMP est_fpfh;
est_fpfh.setNumberOfThreads(4);//指定4核计算
est_fpfh.setInputCloud(input_cloud);
est_fpfh.setInputNormals(point_normal);
est_fpfh.setSearchMethod(tree);
est_fpfh.setKSearch(10);
est_fpfh.compute(*fpfh);
return fpfh;
}
References:
[1].https://blog.csdn.net/qq_25491201/article/details/51105826
[2].https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000007703156
[3].http://www.pclcn.org/study/shownews.php?lang=cn&id=96
[4].http://pointclouds.org/documentation/tutorials/fpfh_estimation.php#fpfh-estimation

