SynchronousQueue中分为TransferQueue(公平模式)和TransferStack(非公平模式)
下面我们先分析一下TransferQueue
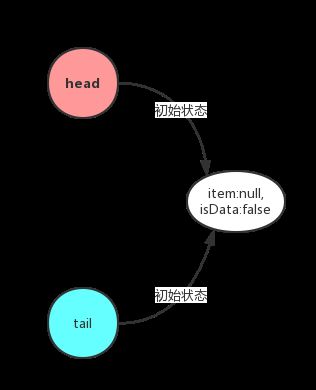
当新建一个TransferQueue时
1 TransferQueue() { 2 QNode h = new QNode(null, false); // initialize to dummy node. 3 head = h; 4 tail = h; 5 }
如下
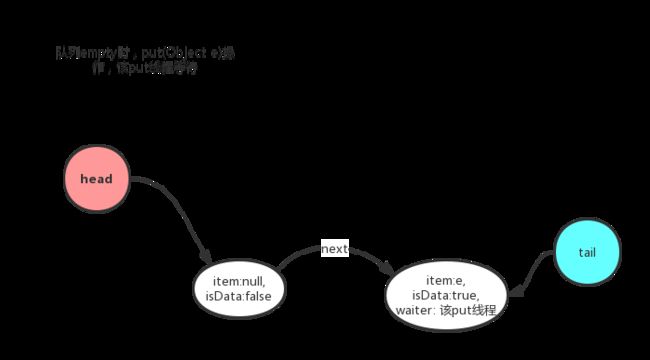
通过put或者take调用最终调用transfer()方法
1 /** 2 * Puts or takes an item. 3 */ 4 Object transfer(Object e, boolean timed, long nanos) { 5 /* Basic algorithm is to loop trying to take either of 6 * two actions: 7 * 8 * 1. If queue apparently empty or holding same-mode nodes, 9 * try to add node to queue of waiters, wait to be 10 * fulfilled (or cancelled) and return matching item. 11 * 12 * 2. If queue apparently contains waiting items, and this 13 * call is of complementary mode, try to fulfill by CAS'ing 14 * item field of waiting node and dequeuing it, and then 15 * returning matching item. 16 * 17 * In each case, along the way, check for and try to help 18 * advance head and tail on behalf of other stalled/slow 19 * threads. 20 * 21 * The loop starts off with a null check guarding against 22 * seeing uninitialized head or tail values. This never 23 * happens in current SynchronousQueue, but could if 24 * callers held non-volatile/final ref to the 25 * transferer. The check is here anyway because it places 26 * null checks at top of loop, which is usually faster 27 * than having them implicitly interspersed. 28 */ 29 30 QNode s = null; // constructed/reused as needed 31 boolean isData = (e != null); 32 33 for (;;) { 34 QNode t = tail; 35 QNode h = head; 36 if (t == null || h == null) // saw uninitialized value 37 continue; // spin 38 39 if (h == t || t.isData == isData) { // empty or same-mode 40 QNode tn = t.next; 41 if (t != tail) // inconsistent read 42 continue; 43 if (tn != null) { // lagging tail 44 advanceTail(t, tn); 45 continue; 46 } 47 if (timed && nanos <= 0) // can't wait 48 return null; 49 if (s == null) 50 s = new QNode(e, isData); 51 if (!t.casNext(null, s)) // failed to link in 52 continue; 53 54 advanceTail(t, s); // swing tail and wait 55 Object x = awaitFulfill(s, e, timed, nanos); 56 if (x == s) { // wait was cancelled 57 clean(t, s); 58 return null; 59 } 60 61 if (!s.isOffList()) { // not already unlinked 62 advanceHead(t, s); // unlink if head 63 if (x != null) // and forget fields 64 s.item = s; 65 s.waiter = null; 66 } 67 return (x != null) ? x : e; 68 69 } else { // complementary-mode 70 QNode m = h.next; // node to fulfill 71 if (t != tail || m == null || h != head) 72 continue; // inconsistent read 73 74 Object x = m.item; 75 if (isData == (x != null) || // m already fulfilled 76 x == m || // m cancelled 77 !m.casItem(x, e)) { // lost CAS 78 advanceHead(h, m); // dequeue and retry 79 continue; 80 } 81 82 advanceHead(h, m); // successfully fulfilled 83 LockSupport.unpark(m.waiter); 84 return (x != null) ? x : e; 85 } 86 } 87 }
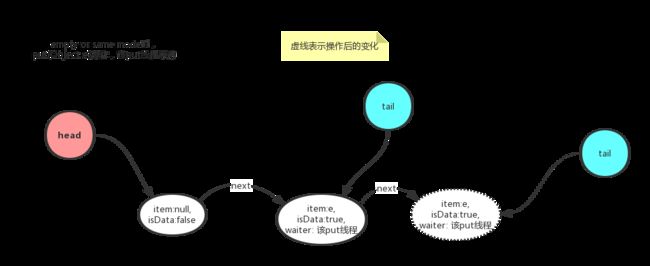
在empty或者same mode模式下时,从tail入队Qnode元素,tail指向最尾部
empty put
same mode put
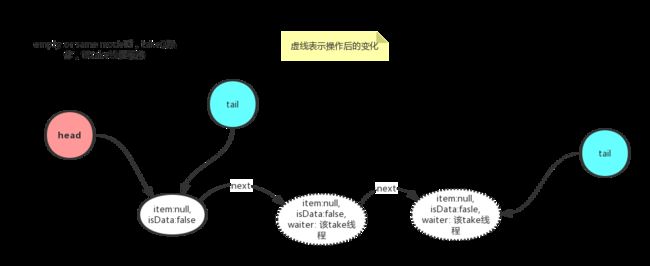
take
该操作线程会阻塞,直到其它线程走complementary-mode,unpark该线程
在complementary-mode,从head出队,head指向next节点
put
take
其它操作如offer,poll等,与put、take相比,
相同点:都是调用transfer()方法,
不同点:入参boolean timed, long nanos 不同
如调用offer(e)时,same mode模式下时,入队不成功,直接返回null
complementary mode下与put一致
1 public boolean offer(E e) { 2 if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 3 return transferer.transfer(e, true, 0) != null; 4 }
1 Object transfer(Object e, boolean timed, long nanos) { 2 3 QNode s = null; // constructed/reused as needed 4 boolean isData = (e != null); 5 6 for (;;) { 7 QNode t = tail; 8 QNode h = head; 9 if (t == null || h == null) // saw uninitialized value 10 continue; // spin 11 12 if (h == t || t.isData == isData) { // empty or same-mode 13 QNode tn = t.next; 14 if (t != tail) // inconsistent read 15 continue; 16 if (tn != null) { // lagging tail 17 advanceTail(t, tn); 18 continue; 19 } 20 if (timed && nanos <= 0) // can't wait 21 return null; 22 if (s == null) 23 s = new QNode(e, isData); 24 if (!t.casNext(null, s)) // failed to link in 25 continue; 26 27 advanceTail(t, s); // swing tail and wait 28 Object x = awaitFulfill(s, e, timed, nanos); 29 if (x == s) { // wait was cancelled 30 clean(t, s); 31 return null; 32 } 33 34 if (!s.isOffList()) { // not already unlinked 35 advanceHead(t, s); // unlink if head 36 if (x != null) // and forget fields 37 s.item = s; 38 s.waiter = null; 39 } 40 return (x != null) ? x : e; 41 42 } else { // complementary-mode 43 QNode m = h.next; // node to fulfill 44 if (t != tail || m == null || h != head) 45 continue; // inconsistent read 46 47 Object x = m.item; 48 if (isData == (x != null) || // m already fulfilled 49 x == m || // m cancelled 50 !m.casItem(x, e)) { // lost CAS 51 advanceHead(h, m); // dequeue and retry 52 continue; 53 } 54 55 advanceHead(h, m); // successfully fulfilled 56 LockSupport.unpark(m.waiter); 57 return (x != null) ? x : e; 58 } 59 } 60 }