2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> ![]()
本文简单分析一下JDK1.7的LinkedList源码,看一下其内部的结构以及典型方法的实现~
LinkedList内部结构
查看LinkedList的源码,发现其继承自AbstractSequentialList,实现了List,Deque,Cloneable以及Serializable接口,如:
public class LinkedList
extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
} 也就意味着:
- LinkedList 是一个继承于AbstractSequentialList的双向链表。它也可以被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作。
- LinkedList 实现 List 接口,能对它进行列表操作。
- LinkedList 实现 Deque 接口,即能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用。
- LinkedList 实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能克隆。
- LinkedList 实现java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着LinkedList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
public class LinkedList
extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node last;
} 从上述代码可以看出,LinkedList中有size,first以及last全局变量,其作用分别是:
size -- 存放当前链表有多少个节点。
first -- 指向链表的第一个节点的引用
last -- 指向链表的最后一个节点的引用
其中,Node是内部类,内容如下:
private static class Node {
E item;
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
} 从上述代码可以看出,
一个节点除了包含元素内容之外,同时包含前一个节点和后一个节点的引用~
各个节点通过指定前一个节点和后一个节点,最终形成了一个链表~
代码示例:
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList values = new LinkedList<>();
values.add(23);
values.add(3);
values.add(17);
values.add(9);
values.add(42);
System.out.println("LinkedList ==> " + values);
System.out.println("first ==> " + values.getFirst());
System.out.println("last ==> " + values.getLast());
}
} 输出结果:
LinkedList ==> [23, 3, 17, 9, 42]
first ==> 23
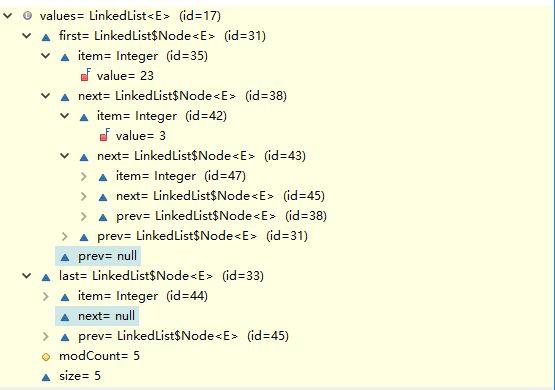
last ==> 42debug查看LinkedList的结构如下:
形成了一个链表
方法add的实现
源代码
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
add方法会调用linkLast方法,会在链表尾端添加节点~
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
} linkLast方法步骤
- 获取原来的last节点,然后创建一个新的节点,其prev为原来的last节点,其next节点为null
- 将last只想新的节点
- 如果原来的last节点为null,其实就是还没有元素,那么新的节点同样也是first节点;如果不为null,则原来的last节点的next就是新的节点
- 因为有新元素加入,size加1,且修改次数加1(modCount++)
方法addAll的实现
源代码
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if
* the specified collection is modified while the operation is in
* progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is
* this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
addAll在LinkedList内部其实就是调用了方法addAll(int index, Collection c)
方法addAll(int index, Collection c)
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element
* from the specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
} 方法addAll(int index, Collection c) 主要包含如下几个步骤:
- 检查指定index是否合理
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}index的有效位置是[0,size]
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an
* iterator or an add operation.
*/
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
- 定义pred和succ节点,并根据index的大小确定pred和succ节点
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
} - 对Collection转换成数组(Object[] a = c.toArray())的元素进行循环遍历,确定first、pred.next等节点信息
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
} - 检查succ是否为空,如果为null,则表示目前的pred节点就是最后一个了,将last节点指向pred;反之,如果不为null,则将prev的next节点指向succ,同时succ的prev节点指向pred。
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}- 最后修改size和modCount的值
size += numNew;
modCount++;上述是往指定位置添加多个元素,那么,往指定位置添加单个元素add(int index, E element) 就变得很简单了。
方法add(int index, E element)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}该方法包含如下两个步骤
检查指定index的值是否有效[0,size]
如果index == size 则使用linkLast添加在尾部;如果index != size, 则使用linkBefore将新元素添加在指定位置之前~
linkBefore方法如下
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node pred = succ.prev;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
} 本文上述已经讲述了linkLast,linkBefore的方法实现思路类似,这里就不再具体给出解释了。
此外,LinkedList还提供了addFirst以及addLast方法,分别用于将元素插在列表头部和尾部~
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
其中,linkFirst和linkLast方法如下:
/**
* Links e as first element.
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node f = first;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
} 方法remove的实现
LinkedList支持多种删除元素的方法~
一起来看看具体是怎么样的~
无参数remove方法
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}无参数的remove方法其实就是调用了removeFirst方法,也就是移除first元素~
removeFirst方法
/**
* Removes and returns the first element from this list.
*
* @return the first element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
} removeFirst使用了unlinkFirst方法来移除元素~
/**
* Unlinks non-null first node f.
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
} unlinkFirst方法处理主要包含如下几个步骤:
- 获取first元素值,然后获取first的next元素
- 将first节点指向next,同时原来的first节点的属性值置为null(包括item和next)
- 如果next节点(原first节点的nex节点)为null,则将last置为null值;如果不为null,则将next节点的prev属性置为null
- 然后修正元素个数以及修改次数(size和modCount)
同样,也存在移除尾节点的方法removeLast
removeLast方法
/**
* Removes and returns the last element from this list.
*
* @return the last element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
其使用了unlinkLast方法实现
/**
* Unlinks non-null last node l.
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
} unlinked方法的实现与unlinkedFirst的方法思路类似,就不在这里一一说明了~
方法remove(int index)
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}按照指定位置移除元素,主要包含如下几个部分:
- 检查index是否有效
- 通过node(index)查找index位置下的节点
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
} 从上述代码可以看出,方法node(int index)中
先判断index和中间点(size >>1)位置的大小。如果index < (size >> 1), 那么按下标从小到大查找;否则,按下标从大到小查找~
- 使用unlink(Node
x) 修改链表的连接关系,达到移除元素的效果
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node next = x.next;
final Node prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
} 方法remove(Object o)
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} 按照指定对象的移除,在代码中,区分删除的元素是否为null值,然后从first开始遍历链表,如果元素值和删除的值内容一致,则调用unlink方法移除元素~
方法indexOf的实现
源代码
// Search Operations
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i))),
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
} 从上述代码可以看出:
LinkedList的indexOf实现区分null和非null值。从first节点开始遍历,如果找到符合条件的元素,则返回元素所在的下标值。如果没有找到,则返回-1~
与之对应的还有lastIndexOf方法,该方法和indexOf的思路一致,区别就是,lastIndexOf是以last节点开始往前寻找~
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i))),
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
方法contains的实现
源代码
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this list contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that
* (o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e)).
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return {@code true} if this list contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}从上述代码可以看出,contains方法内调用了indexOf方法,然后采用获取的结果与-1比较,如果不相等表示有匹配的元素,否则表示没有符合条件的元素~
方法clear的实现
源代码
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list.
* The list will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
for (Node x = first; x != null; ) {
Node next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
} clear方法,从first开始遍历链表,将元素的item、prev和nex属性置为null值,然后将first和last置为null。同时将size置为0,修改次数加1(modCount+)
方法get的实现
LinkedList支持按索引查找以及获取first和last元素的操作~ 如:
方法get(int index)的实现
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}此方法包含两个步骤:
- 检查指定的index的值是否有效
- 调用node(index)获取节点,返回值node(index).item即可
方法getFirst
/**
* Returns the first element in this list.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
} 方法getFirst获取first节点的值item即可,得先判断first是否为空~
方法getLast
/**
* Returns the last element in this list.
*
* @return the last element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
} 方法getLast获取last节点的值item即可,得先判断last是否为空~
方法listIterator的实现
源代码
public ListIterator listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
} 其使用了内部类ListItr来实现,ListItr类内容如下:
private class ListItr implements ListIterator {
private Node lastReturned = null;
private Node next;
private int nextIndex;
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex > 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex - 1;
}
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e;
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);
else
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} listIterator接口继承自Iterator接口,具备更多的方法,如add,set,previous等等
ListIterator示例
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListIteratorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList values = new LinkedList<>();
values.add(23);
values.add(3);
values.add(17);
values.add(9);
values.add(42);
System.out.println("LinkedList ==> " + values);
System.out.println("listIterator~~");
Iterator iter = values.listIterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Integer ele = iter.next();
System.out.println(ele);
}
System.out.println("listIterator with index~~");
Iterator iterWithIndex = values.listIterator(2);
while(iterWithIndex.hasNext()) {
Integer ele = iterWithIndex.next();
System.out.println(ele);
}
}
} 输出结果:
LinkedList ==> [23, 3, 17, 9, 42]
listIterator~~
23
3
17
9
42
listIterator with index~~
17
9
42方法descendingIterator的实现
源代码
/**
* @since 1.6
*/
public Iterator descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
/**
* Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous
*/
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
} descendingIterator与Iterator的区别在于,Iterator是从first开始往后遍历;而descendingIterator是从last开始往前遍历;
Iterator和descendingIterator示例:
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListIteratorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList values = new LinkedList<>();
values.add(23);
values.add(3);
values.add(17);
values.add(9);
values.add(42);
System.out.println("LinkedList ==> " + values);
System.out.println("iterator~~");
Iterator iter = values.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Integer ele = iter.next();
System.out.println(ele);
}
System.out.println("descendingIter~~");
Iterator descendingIter = values.descendingIterator();
while(descendingIter.hasNext()) {
Integer ele = descendingIter.next();
System.out.println(ele);
}
}
} 输出结果:
LinkedList ==> [23, 3, 17, 9, 42]
iterator~~
23
3
17
9
42
descendingIter~~
42
9
17
3
23
方法toArray的实现
源代码
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
return result;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int i = 0;
Object[] result = a;
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
} 从first节点开始,依次遍历,然后得到一个数组对象~
其它的方法就不一一列举了。
本次LinkedList源码阅读分析就到这里,有兴趣的朋友可以实际去读一下,读源码,懂思想,还是很不错的~