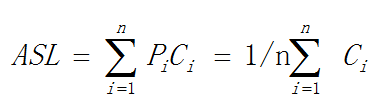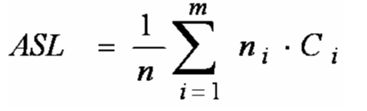数据结构与算法10——字典与检索(C语言代码)
数据结构与算法整理10——字典与检索(C语言)
目录
数据结构与算法整理10——字典与检索(C语言)
1、字典与检索相关相关概念
2、查找方法
2.1静态查找
2.2动态查找
3、散列法
3.1散列表的定义
3.2 冲突(碰撞)及负载因子
3.3设计散列函数需要考虑的因素
3.4 散列表解决冲突的方法
4、AVL树的生成过程与ASL的计算
4.1 AVL树即平衡二叉树
4.2 AVL树的平衡调整
6、字典的操作代码(C语言)
7、二分法检索算法(C语言)
1、字典与检索相关相关概念
1.1 字典:字典是由一些具有相同可辨认特性的数据元素(或记录)构成的集合。
1.2 关键字:是数据元素中某个数据项的值,用它可以标识(识别)一个数据元素。
1.3 检索:根据给定的某个值,在查找表中确定一个关键字等于给定值的数据元素。
- 1.基于线性表的检索:顺序检索、二分检索。
- 2.根据关键码值直接访问:散列检索,基于数组下标的直接检索。
- 3.树索引方法:二叉搜索树、字符树、B树。
1.4 平均查找长度ASL:查找过程中对关键字需要执行的平均比较次数。
n是数据元素的个数;Pi是查找第i个数据元素概率(通常取等概率,即Pi=1/n);Ci是找到第i个记录时所经历的比较次数。
2、查找方法
2.1静态查找
2.1.1顺序表的查找
- 思想:从顺序表的一端开始扫描,将给定的元素与每个数值比较成功查找长度ASL: ASL=(n+1)/2,若失败则ASL=n+1
- 优点:算法简单,且对顺序结构或链表结构均适用。
- 缺点:ASL 太大,时间效率太低。
- 存储:顺序表查找方法既适用于线性表的顺序存储结构,也适用于线性表的链式存储结构(单链表)
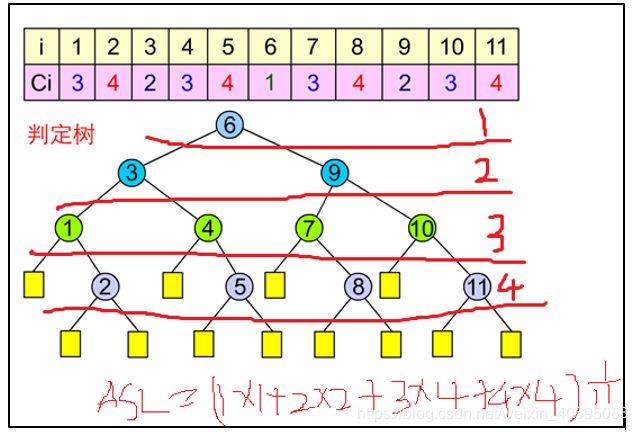
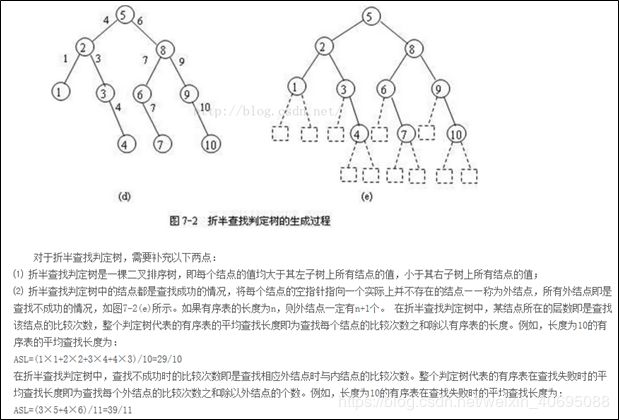
2.1.2 二分查找(折半查找)
- 基本思想:先给数据排序(例如按升序排好),形成有序表,然后再将key与正中元素相比,若key小,则缩小至前半部内查找;若key大,则缩小至后半部内查找。在每个区域内再取其中值比较,每次缩小1/2的范围,直到查找成功或失败为止。
- 对线性表的要求:要求线性表按关键字排序,排序本身是一种费时的运算,所以二分法的时间复杂度最好也是O(nlog 2 n),增加了算法的时间复杂度
- 算法ASL=log2 n
- 二分查找只适用于顺序存储结构的有序表,链表无法实现二分查找。
二分查找的比较次数(Ci)需要借用判定树来计算
判定树的画法:按照比较的次数生成判定树,比较1次的是根结点,比较2次的在第二层,比较3次的在第三层,.一次类推,也可以说是每次的mid即形成判定树的结点,左子树上的结点是有序表前半部分的所有结点,右子树是后半部分的结点.
判定树求平均成功平均查找长度和不成功平均查找长度的方法:
二分查找对线性表的要求,会写二分检索算法:
int BinarySearch(SequenceList R,ElemType x)
{
int low=0,high=R.size-1,mid;
while(low<=high) {
mid=(low+high)/2;
if(R.list[mid].key==x.key) //判断mid是否=key
return mid; /*查找成功返回元素位置*/
if(R.list [mid].key>x.key) //若keymid则在mid右边的元素进行递归查找
low=mid+1;} //注意此时在设定low时不用加上mid
return -1 } /*当low>high时表示查找区间为空,查找失败*/
2.2动态查找
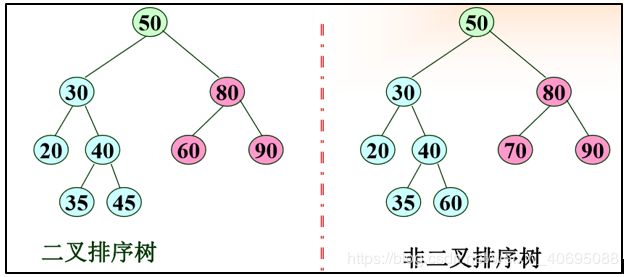
2.2.1 二叉排序树与二叉搜索树
(1)特征
a、若左子树非空,则左子树的所有元素均小于根元素。
b.若右子树非空,则右子树的所有元素均大于根元素。
c. 左右子树本身又各是一颗二叉排序树。
(2)二叉排序树可以通过树的中序周游获得关键字的有序序列。
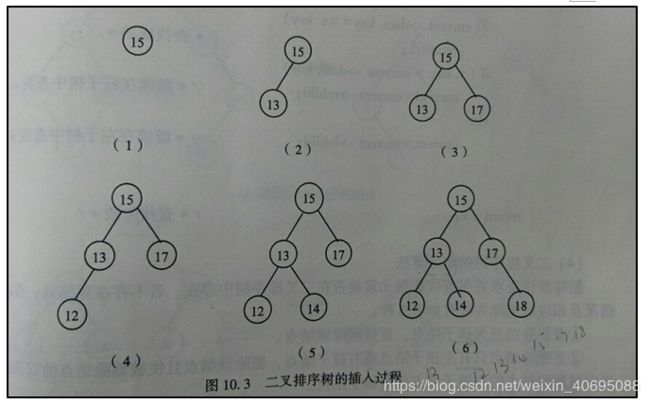
(3)二叉排序树的生成:每读入一个元素,建立一个新的结点,若二叉排序树为空,则新插入的结点成为二叉排序树的根;若二叉排序树为非空,则将新结点的值与根结点的值相比较,如果小于根结点的值,则插入到左子树中,若大于根结点的值,则插入到右子树中;若与根结点值相等,则停止插入。
(输入序列 15 13 17 12 14 18)
(4)二叉排序树的的查找
(5)二叉排序树的插入
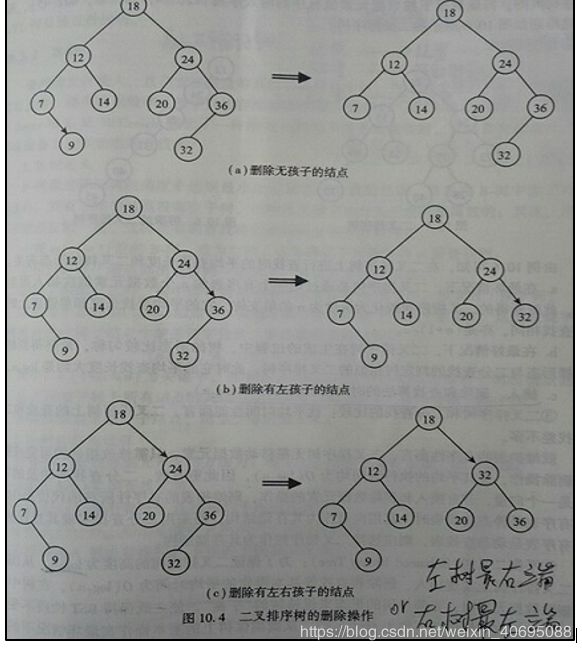
(6)二叉排序树的删除
1、要删除无孩子结点,直接删除该结点
2、要删除只有左孩子或右孩子结点,删除该结点,且使被删除结点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的左孩子结点或右孩子结点
3、要删除有左右孩子的结点,首先寻找数据元素的关键字值大于要删除结点数据元素关键字的最小值,即寻找要删除结点右子树的最左结点;然后把右子树的最左结点的数据元素值拷贝到要删除的结点上;最后删除右子树的最左结点。
(7)平均查找长度:ni 是每层结点个数; Ci 是结点所在层次数;m 为树深。
最坏情况:插入的n个元素从一开始就有序(单支树)ASL= (n+1)/2
最好情况:与折半查找中的判定树相同(即形态比较均衡)树的深度为[log2 n]+1 ASL=log 2(n+1) –1
(8)二叉树排序树的算法性能比较
- 二叉排序树的平均查找长度与二叉树的形态有关。N个节点不同序可能有n!中不同二叉树,其中有的二叉树形态相同。
- 最坏情况下退化为深度为n的单支树,ASL=(n+1)/2
- 最好情况下,二叉排序树的心态比较均匀,类似于完全二叉树,ASL=log2 n,所以需要使用平衡二叉树(见下)。
- 二叉排序树的插入,删除和查找算法的时间复杂度为O(log2 n)
3、散列法
3.1散列表的定义
散列表的目的:使用关键码直接找到记录存储地址。
散列表(哈希表):以关键码k为自变量,通过一定的函数关系h(k)计算 出对应数值的函数值,把这个值作为k的存储地址,检索时用同样的方法得到存储地址,然后得到相应的结点。
3.2 冲突(碰撞)及负载因子
冲突:是指两个不相等的关键码k1,k2,用散列函数h(k)得到的结果h(k1)=h(k2),这种现象称为冲突。发生碰撞的两个或多个关键码称为同义词。
3.3设计散列函数需要考虑的因素
- 计算哈希表函数所需时间
- 记录查找频率
- 关键字分布情况
- 哈希表长度(哈希地址范围)
- 关键字长度
3.4 散列表解决冲突的方法
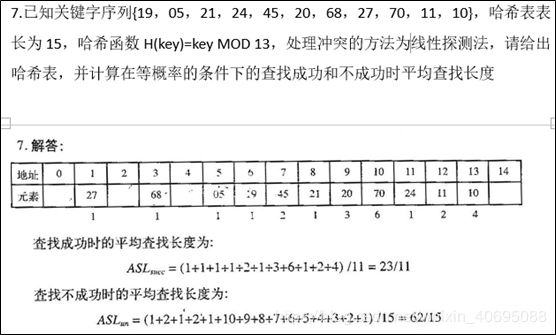
3.4.1开放地址法:指为发生冲突的关键码找到哈希表中的最近的另一个尚未被使用的位置。
- 找成功的平均查找长度为:ASL1= (N1+N1+…+N10)/空间大小,N为每个元素查找成功的比较次数。
- 计算第n位置查找不成功时的比较次数为,第n位置到第1个没有数据位置的距离。找不成功的平均查找长度ASL2=(n1+n2+…+ni)/A ,A位分配的所有空间,不是元素使用的空间(例如h(k)是%15,但是元素只使用了12格,则ASL1除以12,ASL2除以15)
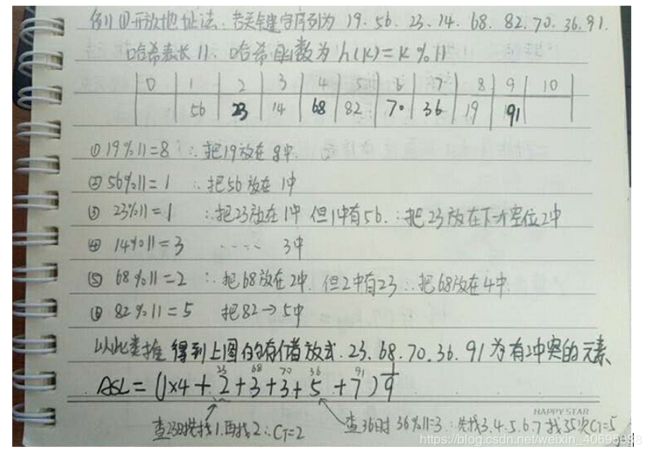
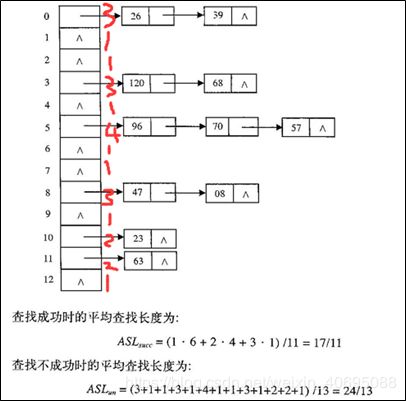
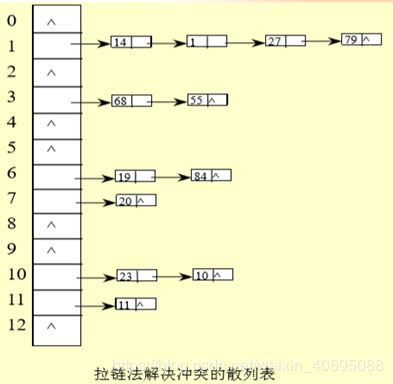
3.4.2拉链法:是把相互冲突的同义词用同一个单链表链接起来,若干组同义词可以组成若干个单链表
例题:给定关键字序列:19,14,23,1,68,20,84,27,55,11,10,79,h(k)=k%13,用拉链法解决冲突建立哈希表。
4、AVL树的生成过程与ASL的计算
4.1 AVL树即平衡二叉树
(1)特点:要么是一颗空树,若非空则一定满足左子树和右子树都是平衡二叉树且左右子树深度之差不大于1.
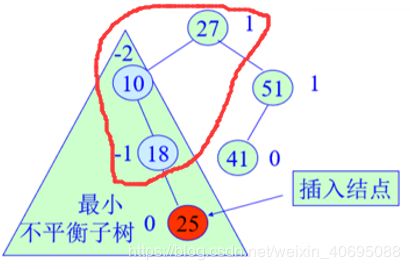
(2)平衡因子:当前节点的平衡因子定义为当前节点左子树的深度减右子树的深度。
(3)最小不平衡子树:离插入节点最近,且平衡因子的绝对值大于1的节点为根的子树
4.2 AVL树的平衡调整
- 目的:保证生成的二叉排序树的高度为log2 n,从而使二叉排序树的插入,删除,查找等操作的平均时间为O(log2 n)。所需调整的是最小不平衡子树,保证二叉树始终处于平衡状态。
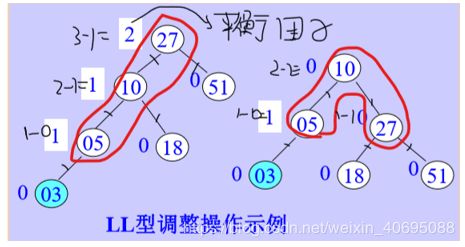
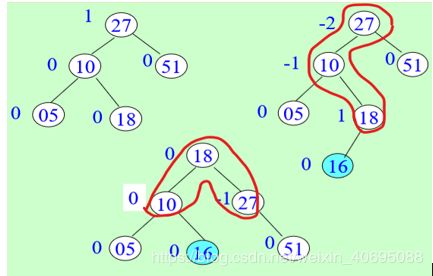
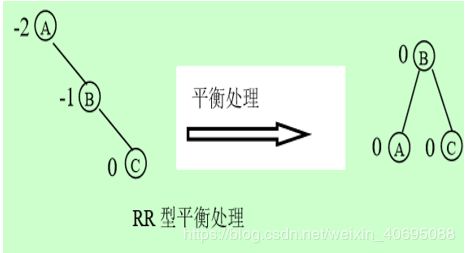
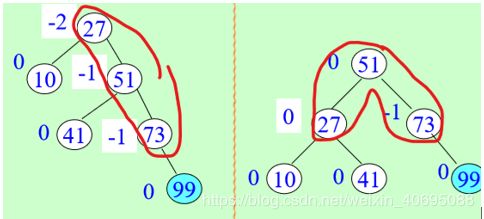
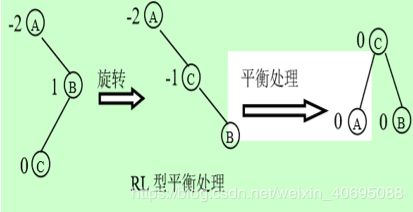
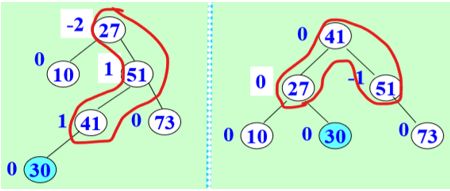
- 平衡调整模式:LL型调整,LR型调整,RR型调整,RL型调整
LL型调整:
LR型调整:
RR型调整:
RL型调整:
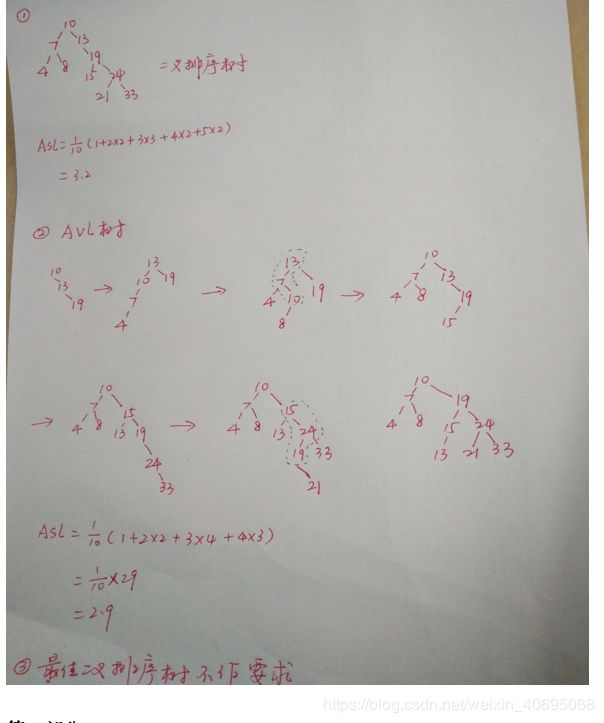
例题:关键字序列为:10,13,19,7,4,8,15,24,33,21试用二叉排序树和平衡二叉树进行检索,给出检索15时需要的比较次数及成功检索的平均检索长度。
6、字典的操作代码(C语言)
/* 二叉排序树的检索算法*/
#include
#include
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXNUM 100
typedef int KeyType;
typedef struct {
KeyType key; /* 字典元素的关键码字段 */
/*DataType value; /* 字典元素的属性字段 */
} DicElement;
typedef struct {
int n; /* n<=MAXNUM,为字典中元素的个数 */
DicElement element[MAXNUM];
} SeqDictionary;
struct BinTreeNode;
typedef struct BinTreeNode BinTreeNode, *PBinTreeNode;
struct BinTreeNode {
KeyType key; /* 结点的关键码字段 */
/*DataType value; 结点的属性字段 */
PBinTreeNode llink, rlink; /* 二叉树的左、右指针 */
};
typedef struct BinTreeNode * BinTree;
typedef BinTree * PBinTree;
int searchNode(PBinTree ptree, KeyType key, PBinTreeNode *position) {
PBinTreeNode p = *ptree, q = NULL;
while (p != NULL) {
q = p;
if(p->key == key) { /* 检索成功,设参数position使之指向找到的结点 */
*position = p; return TRUE;
}
else if (p->key > key) /* 进入左子树继续检索 */
p = p->llink;
else p = p->rlink; /* 进入右子树继续检索 */
}
*position = q; /* 检索失败时,position指向该结点应插入位置的父结点 */
return FALSE;
}
/* 创建新结点,无空间时返回NULL */
PBinTreeNode newNode(KeyType key) {
PBinTreeNode p = (PBinTreeNode)malloc(sizeof(BinTreeNode));
if (p == NULL) {
printf("Error!\n");
return NULL;
} /* 申请空间出错 */
p->key = key; /* 忽略对p->value的赋值 */
p->llink = p->rlink = NULL;
return p;
}
void insertNode(PBinTree ptree, KeyType key) {
PBinTreeNode p, position;
if (*ptree == NULL) {
*ptree = newNode(key); /* 原树为空树 */
return;
}
if (searchNode(ptree, key, &position) == TRUE)
return;/* 已存在关键码为key的结点 */
p = newNode(key);
if (key < position->key)
position->llink = p; /* 插入position的左子树 */
else position->rlink = p; /* 插入position的右子树 */
}
void deleteNode(PBinTree ptree, KeyType key) {
PBinTreeNode parentp = NULL, p = *ptree, r;
while (p!=NULL) {
if (p->key == key) break; /* 找到了关键码为key的结点 */
parentp = p;
if(p->key>key)
p = p->llink; /* 进入左子树 */
else p=p->rlink; /* 进入右子树 */
}
if (p == NULL) return; /* 二叉排序树中无关键码为key的结点 */
if (p->llink == NULL) { /* 结点*p无左子树 */
if (parentp == NULL)
*ptree = p->rlink; /* 被删除的结点是原二叉排序树的根结点*/
else if(parentp->llink == p) /* *p是其父结点的左子女 */
parentp->llink = p->rlink; /* 将*p的右子树链到其父结点的左链上 */
else parentp->rlink = p->rlink;/* 将*p的右子树链到其父结点的右链上 */
}
else { /* 结点*p有左子树 */
r = p->llink;
while(r->rlink != NULL) /* 在*p的左子树中找最右下结点*r */
r = r->rlink;
r->rlink = p->rlink; /* 用*r的右指针指向*p的右子女 */
if (parentp == NULL) *ptree = p->llink;
else if(parentp->llink == p) /* 用*p的左子女代替*p */
parentp->llink = p->llink;
else parentp->rlink = p->llink;
}
free(p); /* 释放被删除结点 */
}
void creatBinTree (PBinTree ptree, SeqDictionary dic) {
int i;
*ptree = NULL; /* 这里假定了原来树中无结点 */
for(i = 0; i < dic.n; i++)
insertNode(ptree, dic.element[i].key); /* 将新结点插入树中 */
}
/* 释放整个二叉树。假定tree指向合法的二叉树 */
void destroyBinTree (BinTree tree) {
BinTree l, r;
if (tree == NULL) return;
l = tree->llink;
r = tree->rlink;
free(tree);
destroyBinTree(l);
destroyBinTree(r);
}
void printBinTree (BinTree tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return;
printBinTree(tree->llink);
printf("%d ", tree->key);
printBinTree(tree->rlink);
}
SeqDictionary dic = {11,
{18, 10, 73, 5, 68, 99, 27, 25, 41, 32, 51}
};
int main() {
BinTree tree = NULL;
creatBinTree(&tree, dic);
while(1){
int i, key;
PBinTreeNode position;
printf("Input 1 to insert element\n"
"2 to search element\n"
"3 to delete element\n"
"4 to print (inorder) all element in the tree \n"
"5 to destroy all element in the tree \n"
"else to exit\nWhat do you want to do? ");
scanf("%d", &i);
if (i == 1) {
printf("Input the key you want to insert: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
insertNode(&tree, key);
}
else if (i == 2) {
printf("Input the key you want to search: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
if(searchNode(&tree, key, &position) == TRUE)
printf("It is in the dictionary.\n");
else printf("It is not in the dictionary!\n");
}
else if (i == 3) {
printf("Input the key you want to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
deleteNode(&tree, key);
}
else if (i == 4) {
printBinTree(tree);
putchar('\n');
}
else if (i == 5) {
destroyBinTree(tree);
tree = NULL;
putchar('\n');
}
else break;
}
return 0;
}
7、二分法检索算法
/* 本程序提供了用顺序表实现字典的情况下
的二分法检索算法*/
#include
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXNUM 100
typedef int KeyType ;
typedef struct {
KeyType key; /* 字典元素的关键码字段 */
/*DataType value; /* 字典元素的属性字段 */
} DicElement;
typedef struct {
int n; /* n<=MAXNUM,为字典中元素的个数 */
DicElement element[MAXNUM];
} SeqDictionary;
/* 在字典中用二分法查找关键码为key的元素 */
int binarySearch(SeqDictionary * pdic, KeyType key, int *position) {
int low = 0, high = pdic->n-1, mid;
while(low<=high) {
mid = (low+high)/2; /* 当前检索的中间位置 */
if(pdic->element[mid].key == key) { /* 检索成功 */
*position = mid; return TRUE;
}
else if (pdic->element[mid].key > key)
high = mid-1; /* 要检索的元素在左半区 */
else low = mid+1; /* 要检索的元素在右半区 */
}
*position=low;
return FALSE; /* 检索失败 */
}
SeqDictionary dic={
10, 1,3,5,7,9,11,13,19,21,30};
int main(){
int i, position;
while(1){
printf("Input the key you want to search: ");
scanf("%d",&i);
if(i==0)break;
if(binarySearch(&dic,i,&position)==TRUE)
printf("It is the %dth element!\n",position+1);
else printf("It is not in the dictionary!\n");
}
return 0;
}