I2C总线浅析
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/pengliang528/article/details/79522644
参考链接: kernel/Documentation/i2c/dev-interface
参考链接:https://i2c.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Main_Page
一.I2C概念:
I2C是philips提出的外设总线.
I2C只有两条线,一条串行数据线:SDA,一条是时钟线SCL ,使用SCL,SDA这两根信号线就实现了设备之间的数据交互,它方便了工程师的布线。
因此, I2C总线被非常广泛地应用在EEPROM,实时钟,小型LCD等设备与CPU的接口中.
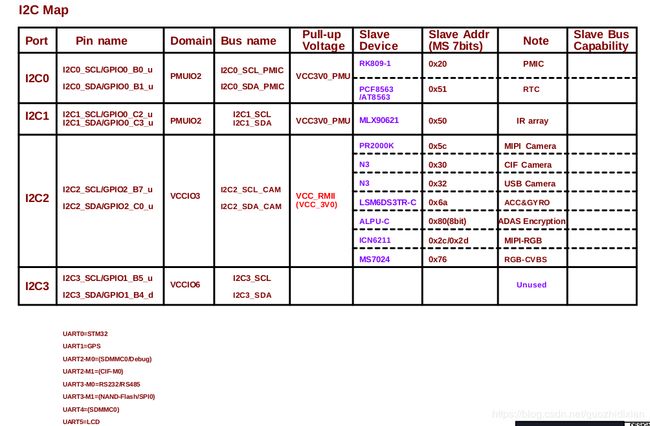
二.I2C硬件结构图
2.1 I2C组织结构:
当前很多ARM内部封装了I2C控制芯片,通过cpu引脚会将控制芯片相关接口暴露出来,通过查看CPU引脚手册会发现存在几组I2C控制引脚(从软件角度讲一个控制器对应一个adapter),将支持I2C设备的SDA与SCL与其中一个控制芯片的对应引脚连接在一起即从硬件上将设备挂载到了I2C控制芯片上,cpu即可通过软件的相关操作来与设备进行通信了
参考原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/pengliang528/article/details/79522644
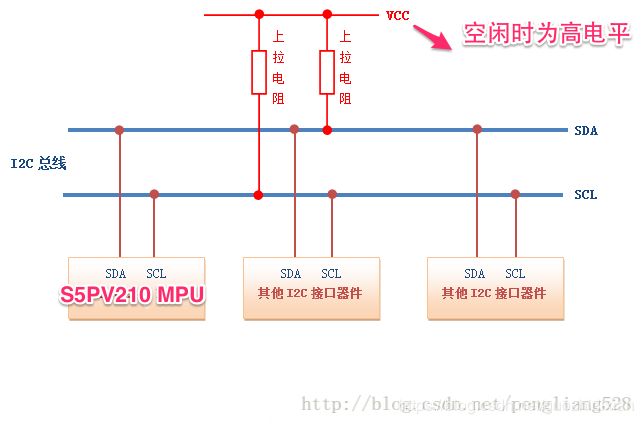
2.2 Soc芯片I2C控制器:
2.3 硬件的I2C映射:
2.4 Soc芯片总体架构
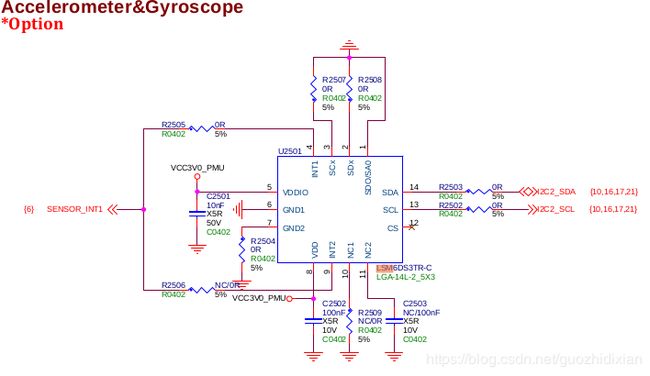
2.5 设备电路图(Accelerometer&Gyroscope :加速计和陀螺仪)
2.5.1: I2C设备分两类:(当前RTC芯片支持I2C通信)
1.采用GPIO模拟
2.设备支持I2C即存在SDA和SCL引脚
2.5.2:
如图2.2所示,控制器与设备是一对多的关系,那么控制器是如何寻找特定的设备呢?
从控制器的原理图我们看出控制器实际上只有SCL与SDA两个引脚,针对SDA采用分时复用,在和设备通讯时首先通过SDA发送设备的地址,然后再发送和设备交互的数据,此即与I2C协议挂钩了.
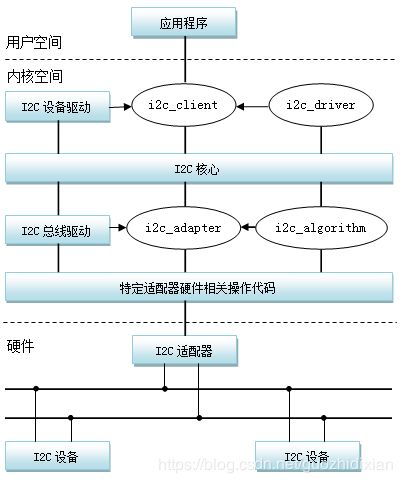
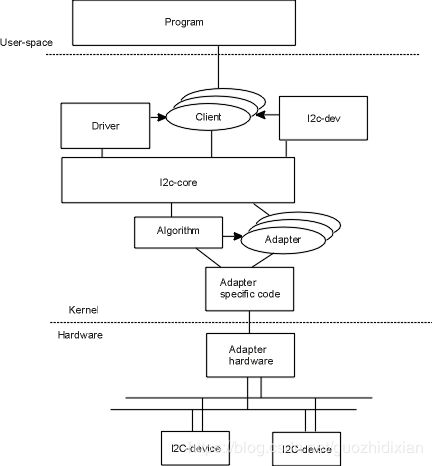
三. I2C子系统总线架构
3.1、三大组成部分
(1)I2C核心(i2c-core):I2C核心提供了I2C总线驱动(适配器)和设备驱动的注册、注销方法,I2C通信方法(”algorithm”)上层的,与具体硬件无关的代码以及探测设备
检测设备地址的上层代码等。。
(2)I2C总线驱动(I2Cadapter):I2C总线驱动是I2C适配器的软件实现,提供I2C适配器与从设备间完成数据通信的能力。I2C总线驱动由i2c_adapter和i2c_algorithm来描述
I2C适配器是SoC中内置i2c控制器的软件抽象,可以理解为他所代表的是一个I2C主机。
(3)I2C设备驱动(I2Cclient driver):包括两部分:设备的注册和设备驱动的注册
3.2、I2C子系统的主要目标是:
让驱动开发者可以在内核中方便的添加自己的I2C设备的驱动程序,让内核统一管理I2C设备,从而可以更容易的在linux下驱动自己的I2C接口硬件。
3.3、I2C子系统提供的两种驱动实现方法(源码中I2C相关的驱动均位于:drivers/i2c目录下)
(1)第一种叫i2c-dev,对应drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c,这种方法只是封装了主机(I2Cmaster,一般是SoC中内置的I2C控制器)的I2C基本操作,并且向应用层提供相应的操作
接口,应用层代码需要自己去实现对slave的控制和操作,所以这种I2C驱动相当于只是提供给应用层可以访问slave硬件设备的接口,本身并未对硬件做任何操作,应用需要实
现对硬件的操作,因此写应用的人必须对硬件非常了解,其实相当于传统的驱动中干的活儿丢给应用去做了,所以这种I2C驱动又叫做“应用层驱动”,这种方式并不主流,它的优势是
把差异化都放在应用中,这样在设备比较难缠(尤其是slave是非标准I2C时)时不用动驱动,而只需要修改应用就可以实现对各种设备的驱动。
(2)第二种I2C驱动是所有的代码都放在驱动层实现,直接向应用层提供最终结果。应用层甚至不需要知道这里面有I2C存在,譬如电容式触摸屏驱动,直接向应用层提供/dev/input/event1
的操作接口,应用层编程的人根本不知道event1中涉及到了I2C
3.4、关键文件(drivers\i2c)(1)i2c-core.c: i2c核心层
(2)busses目录:这个文件中是已经编写好的各种向i2c核心层注册的适配器
(3)algos目录:这个目录里面是一些I2C通信算法
3.5.从上面的分析其实可以知道:i2c子系统内部存在着2个匹配过程:
(1)platform总线下的匹配,soc的i2c控制器设备匹配soc的i2c控制器driver, 根据compatible匹配,匹配成功之后会将i2c adapter 适配器注册进内核
/**
-
platform_match - bind platform device to platform driver.
-
@dev: device.
-
@drv: driver.
-
Platform device IDs are assumed to be encoded like this:
-
“”, where is a short description of the type of
-
device, like “pci” or “floppy”, and is the enumerated
-
instance of the device, like ‘0’ or ‘42’. Driver IDs are simply
-
“”. So, extract the from the platform_device structure,
-
and compare it against the name of the driver. Return whether they match
-
or not.
*/
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);/* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */
if (pdev->driver_override)
return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);/* Attempt an OF style match first */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;/* Then try ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;/* Then try to match against the id table */
if (pdrv->id_table)
return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;/* fall-back to driver name match */
return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
}
(2)i2c总线下的匹配,i2c adapter适配器与i2c slave设备之间的匹配(通过适配器编号)
drivers/input/misc/lsm6ds3/lsm6ds3_i2c.c
static const struct i2c_device_id lsm6ds3_ids[] = {
{LSM6DS3_ACC_GYR_DEV_NAME, 0},
{ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(i2c, lsm6ds3_ids);
#ifdef CONFIG_OF
static const struct of_device_id lsm6ds3_id_table[] = {
{.compatible = “st,lsm6ds3”, },
{.compatible = “st,lsm6ds3h”, },
{ },
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, lsm6ds3_id_table);
#endif
/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/px30-recadas-p200.dts
&i2c2 {
status = “okay”;
clock-frequency = <100000>;
/* These are relatively safe rise/fall times; TODO: measure */
i2c-scl-falling-time-ns = <50>;
i2c-scl-rising-time-ns = <300>;
lsm6ds3: lsm6ds3@6a {
compatible = "st,lsm6ds3";---→i2c slave name(与i2c adapter name匹配)
reg = <0x6a>;-→i2c slave address(可以查看芯片原理图分配给各个i2c slave devices的设备地址)
};
}
3.6 I2C核心层 (drivers/i2c/i2c-core.c)
static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver;
if (!client)
return 0;
/* Attempt an OF style match */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);
/* match on an id table if there is one */
if (driver->id_table)
return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL;
return 0;
}
(1): I2C总线核心在于i2c-core.c,其注册方式与一般的总线注册方式一样,唯一的区别在于我们注册了一个空的dummy_driver,具体原因留给读者自己分析。
static const struct i2c_device_id dummy_id[] = {
{ “dummy”, 0 },
{ },
};
static int dummy_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
return 0;
}
static int dummy_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
{
return 0;
}
static struct i2c_driver dummy_driver = {
.driver.name = “dummy”,
.probe = dummy_probe,
.remove = dummy_remove,
.id_table = dummy_id,
};
static int __init i2c_init(void)
{
int retval;
retval = of_alias_get_highest_id("i2c");
down_write(&__i2c_board_lock);
if (retval >= __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num)
__i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num = retval + 1;
up_write(&__i2c_board_lock);
retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type);
if (retval)
return retval;
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
i2c_adapter_compat_class = class_compat_register(“i2c-adapter”);
if (!i2c_adapter_compat_class) {
retval = -ENOMEM;
goto bus_err;
}
#endif
retval = i2c_add_driver(&dummy_driver);
if (retval)
goto class_err;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC))
WARN_ON(of_reconfig_notifier_register(&i2c_of_notifier));
return 0;
class_err:
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class);
bus_err:
#endif
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
return retval;
}
static void __exit i2c_exit(void)
{
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC))
WARN_ON(of_reconfig_notifier_unregister(&i2c_of_notifier));
i2c_del_driver(&dummy_driver);
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class);
#endif
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
tracepoint_synchronize_unregister();
}
/* We must initialize early, because some subsystems register i2c drivers
- in subsys_initcall() code, but are linked (and initialized) before i2c.
*/
postcore_initcall(i2c_init);
module_exit(i2c_exit);
(2) 注意I2c总线初始化调用的是postcore_initcall(i2c_init);,查看其具体的宏我们得知其优先级为2,请留意该优先级,因为与后续的I2c设备驱动注册优先级存在强相关,必须要先有I2c总线,才能将i2c设备挂载到I2c总线上(稍后我们进行具体分析)
源码定义如下:
/*
- A “pure” initcall has no dependencies on anything else, and purely
- initializes variables that couldn’t be statically initialized.
- This only exists for built-in code, not for modules.
- Keep main.c:initcall_level_names[] in sync.
*/
#define pure_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 0)
#define core_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 1)
#define core_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 1s)
#define postcore_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 2)
#define postcore_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 2s)
#define arch_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 3)
#define arch_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 3s)
#define subsys_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 4)
#define subsys_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 4s)
#define fs_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 5)
#define fs_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 5s)
#define rootfs_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, rootfs)
#define device_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 6)
#define device_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 6s)
#define late_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 7)
#define late_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 7s)
(3 )注意导出dev的属性信息到kernel的sysfs的目录:
static ssize_t
show_name(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, “%s\n”, dev->type == &i2c_client_type ?
to_i2c_client(dev)->name : to_i2c_adapter(dev)->name);
}
static DEVICE_ATTR(name, S_IRUGO, show_name, NULL);
static ssize_t
show_modalias(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct i2c_client *client = to_i2c_client(dev);
int len;
len = acpi_device_modalias(dev, buf, PAGE_SIZE -1);
if (len != -ENODEV)
return len;
return sprintf(buf, "%s%s\n", I2C_MODULE_PREFIX, client->name);
}
static DEVICE_ATTR(modalias, S_IRUGO, show_modalias, NULL);
static struct attribute i2c_dev_attrs[] = {
&dev_attr_name.attr,
/ modalias helps coldplug: modprobe $(cat …/modalias) */
&dev_attr_modalias.attr,
NULL
};
ATTRIBUTE_GROUPS(i2c_dev);
/-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define __ATTRIBUTE_GROUPS(_name)
static const struct attribute_group *_name##_groups[] = {
&_name##_group,
NULL,
}
#define ATTRIBUTE_GROUPS(_name)
static const struct attribute_group _name##_group = {
.attrs = _name##_attrs, ------->得到_i2c_dev_attrs
};
__ATTRIBUTE_GROUPS(_name)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define DEVICE_ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, store)
struct device_attribute dev_attr##_name = __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
#define __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) {
.attr = {.name = __stringify(_name),
.mode = VERIFY_OCTAL_PERMISSIONS(_mode) },
.show = _show, \ –-→相当于dev_attr_name.attr—>DEVICE_ATTR(name, S_IRUGO, show_name, NULL)
.store = _store,
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------/
3.7. Soc 侧I2C控制器层(drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-rk3x.c, platform总线,platform设备)
(1)控制器dts配置:
i2c2: i2c@ff1a0000 {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3399-i2c";
reg = <0x0 0xff1a0000 0x0 0x1000>;
clocks = <&cru SCLK_I2C2>, <&cru PCLK_I2C2>;
clock-names = "i2c", "pclk";
interrupts = ;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&i2c2_xfer>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
status = "disabled";
};
i2c2 {
i2c2_xfer: i2c2-xfer {
rockchip,pins =
<2 RK_PB7 RK_FUNC_2 &pcfg_pull_none_smt>,
<2 RK_PC0 RK_FUNC_2 &pcfg_pull_none_smt>;
};
};
(2)控制器驱动定义:
static struct platform_driver rk3x_i2c_driver = {
.probe = rk3x_i2c_probe,
.remove = rk3x_i2c_remove,
.driver = {
.name = “rk3x-i2c”,
.of_match_table = rk3x_i2c_match,
.pm = &rk3x_i2c_pm_ops,
},
};
static const struct of_device_id rk3x_i2c_match[] = {
{
.compatible = “rockchip,rk3066-i2c”,
.data = (void *)&rk3066_soc_data
},
{
.compatible = “rockchip,rk3188-i2c”,
.data = (void *)&rk3188_soc_data
},
{
.compatible = “rockchip,rk3228-i2c”,
.data = (void *)&rk3228_soc_data
},
{
.compatible = “rockchip,rk3288-i2c”,
.data = (void *)&rk3288_soc_data
},
{
.compatible = “rockchip,rk3399-i2c”,
.data = (void *)&rk3399_soc_data
},
{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, rk3x_i2c_match);
(3)控制器driver的加载
module_platform_driver(rk3x_i2c_driver);
–→platform_driver_register
---->__platform_driver_register
----→driver_register
------>bus_add_register
-----→async_schedule(driver_attach_async, drv)
----> driver_attach_async
-----→driver_attach
----→__driver_attach
—→driver_match_devices(drv,dev) ----(platform平台总线匹配)
/***************************************************************
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);
/* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */
if (pdev->driver_override)
return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);
/* Attempt an OF style match first */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try to match against the id table */
if (pdrv->id_table)
return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;
/* fall-back to driver name match */
return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
}
/
---->driver_probe_device
—→really_probe
—→drv→probe
/*****
(1.1)struct platform_device {
const char *name;
int id;
bool id_auto;
struct device dev;
u32 num_resources;
struct resource *resource;
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match */
/* MFD cell pointer */
struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;
/* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
bool prevent_deferred_probe;
};
^
|||
注:
platform总线匹配的时候,一般是对platform_driver_register的调用或者封装调用,platform的i2c控制器设备是platform_devices, 所以dev→bus == NULL,
platform的i2c控制器驱动really_probe中走的是drv→probe, 根据下图,最终走的是platform_drv_probe---->platform_driver->probe—> rk3x_i2c_probe
(1.2) i2c总线匹配的时候,一般是对device_add的调用或者封装调用,此时对应的devices是添加到内核的i2c_adaper devices设备,而且也挂载到了i2c 总线上,此时会和i2c devices的driver(i2c device driver)匹配,进入到了really_probe时,由于dev已经挂载到总线上,所以执行dev→bus→probe,然后走到i2c_device_probe, 然后走到driver→probe(client, i2c_match_id(driver→id_table, client));—>最终走到lsm6ds3_i2c_probe
static int i2c_register_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
adap->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;----→i2c adapter 挂载到了i2c 总线
adap->dev.type = &i2c_adapter_type;
res = device_register(&adap->dev);
}
static struct i2c_driver lsm6ds3_i2c_driver = {
.driver = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = LSM6DS3_ACC_GYR_DEV_NAME,
.pm = LSM6DS3_PM_OPS,
#ifdef CONFIG_OF
.of_match_table = lsm6ds3_id_table,
#endif
},
.probe = lsm6ds3_i2c_probe,
.remove = lsm6ds3_i2c_remove,
.id_table = lsm6ds3_ids,
};
struct i2c_driver {
unsigned int class;
/* Notifies the driver that a new bus has appeared. You should avoid
* using this, it will be removed in a near future.
*/
int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated;
/* Standard driver model interfaces */
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);
/* driver model interfaces that don't relate to enumeration */
void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);
/* Alert callback, for example for the SMBus alert protocol.
* The format and meaning of the data value depends on the protocol.
* For the SMBus alert protocol, there is a single bit of data passed
* as the alert response's low bit ("event flag").
*/
void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, unsigned int data);
/* a ioctl like command that can be used to perform specific functions
* with the device.
*/
int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table;
/* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */
int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *);
const unsigned short *address_list;
struct list_head clients;
};
struct device_driver {
const char *name;
struct bus_type *bus;
struct module *owner;
const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
enum probe_type probe_type;
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);
int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume) (struct device *dev);
const struct attribute_group **groups;
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
struct driver_private *p;
};
struct device {
struct device *parent;
struct device_private *p;
struct kobject kobj;
const char *init_name; /* initial name of the device */
const struct device_type *type;
struct mutex mutex; /* mutex to synchronize calls to
* its driver.
*/
struct bus_type *bus; /* type of bus device is on */
struct device_driver *driver; /* which driver has allocated this
device */
void *platform_data; /* Platform specific data, device
core doesn't touch it */
void *driver_data; /* Driver data, set and get with
dev_set/get_drvdata */
struct dev_pm_info power;
struct dev_pm_domain *pm_domain;
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQ_DOMAIN
struct irq_domain *msi_domain;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PINCTRL
struct dev_pin_info *pins;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQ
struct list_head msi_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
int numa_node; /* NUMA node this device is close to */
#endif
u64 dma_mask; / dma mask (if dma’able device) /
u64 coherent_dma_mask;/ Like dma_mask, but for
alloc_coherent mappings as
not all hardware supports
64 bit addresses for consistent
allocations such descriptors. */
unsigned long dma_pfn_offset;
struct device_dma_parameters *dma_parms;
struct list_head dma_pools; /* dma pools (if dma'ble) */
struct dma_coherent_mem *dma_mem; /* internal for coherent mem
override */
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_CMA
struct cma cma_area; / contiguous memory area for dma
allocations /
#endif
/ arch specific additions */
struct dev_archdata archdata;
struct device_node *of_node; /* associated device tree node */
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode; /* firmware device node */
dev_t devt; /* dev_t, creates the sysfs "dev" */
u32 id; /* device instance */
spinlock_t devres_lock;
struct list_head devres_head;
struct klist_node knode_class;
struct class *class;
const struct attribute_group **groups; /* optional groups */
void (*release)(struct device *dev);
struct iommu_group *iommu_group;
bool offline_disabled:1;
bool offline:1;
};
********************************************************************/
---->platform_drv_probe
—→drv->probe
—>rk3x_i2c_probe
(4) rk3x_i2c_probe
static int rk3x_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device_node *np = pdev->dev.of_node;
const struct of_device_id *match;
struct rk3x_i2c *i2c;
struct resource *mem;
int ret = 0;
int bus_nr;
u32 value;
int irq;
unsigned long clk_rate;
/* 申请控制器结构体空间, 是各个厂商对i2c_adapter的封装 */
i2c = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(struct rk3x_i2c), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!i2c)
return -ENOMEM;
/* 搜索与device_node匹配的结构体, 根据compatibl匹配*/
match = of_match_node(rk3x_i2c_match, np);
i2c->soc_data = (struct rk3x_i2c_soc_data *)match->data;
/* use common interface to get I2C timing properties */
i2c_parse_fw_timings(&pdev->dev, &i2c->t, true);
/* struct i2c_adapter的由来 */
/* 设置i2c adapter的name */
strlcpy(i2c->adap.name, "rk3x-i2c", sizeof(i2c->adap.name));
i2c->adap.owner = THIS_MODULE;
/* 设置i2c adapter 的算法回调接口 */
i2c->adap.algo = &rk3x_i2c_algorithm;
/******************************************
static const struct i2c_algorithm rk3x_i2c_algorithm = {
.master_xfer = rk3x_i2c_xfer,
.functionality = rk3x_i2c_func,
};
****************************************/
i2c->adap.retries = 3;
i2c->adap.dev.of_node = np;
i2c->adap.algo_data = i2c;
/*******************************************
/*
* i2c_adapter is the structure used to identify a physical i2c bus along
* with the access algorithms necessary to access it.
*/
struct i2c_adapter {
struct module *owner;
unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */
const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */
struct device dev; /* the adapter device */
}
将i2c_adpater的dev设备(i2c adapter 设备)的父设备设置为pdev→dev(i2c 控制器设备)
**********************************************/
i2c->adap.dev.parent = &pdev->dev;
/*********************************************
@dev: device for this controller
struct rk3x_i2c {
struct i2c_adapter adap;
struct device *dev;
}
************************************************/
i2c->dev = &pdev->dev;
spin_lock_init(&i2c->lock);
init_waitqueue_head(&i2c->wait);
i2c->i2c_restart_nb.notifier_call = rk3x_i2c_restart_notify;
i2c->i2c_restart_nb.priority = 128;
ret = register_i2c_restart_handler(&i2c->i2c_restart_nb);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to setup i2c restart handler.\n");
return ret;
}
/*******************************
获取i2c adapter的内存空间
reg = <0x0 0xff1a0000 0x0 0x1000>;
***********************************************/
mem = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
i2c->regs = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, mem);
if (IS_ERR(i2c->regs))
return PTR_ERR(i2c->regs);
/* Try to set the I2C adapter number from dt */
bus_nr = of_alias_get_id(np, "i2c");
/*
* Switch to new interface if the SoC also offers the old one.
* The control bit is located in the GRF register space.
*/
if (i2c->soc_data->grf_offset >= 0) {
struct regmap *grf;
grf = syscon_regmap_lookup_by_phandle(np, "rockchip,grf");
if (IS_ERR(grf)) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev,
"rk3x-i2c needs 'rockchip,grf' property\n");
return PTR_ERR(grf);
}
if (bus_nr < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "rk3x-i2c needs i2cX alias");
return -EINVAL;
}
/* 27+i: write mask, 11+i: value */
value = BIT(27 + bus_nr) | BIT(11 + bus_nr);
ret = regmap_write(grf, i2c->soc_data->grf_offset, value);
if (ret != 0) {
dev_err(i2c->dev, "Could not write to GRF: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
}
/* IRQ setup : interrupts = ; */
irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);
if (irq < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot find rk3x IRQ\n");
return irq;
}
ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, irq, rk3x_i2c_irq,
0, dev_name(&pdev->dev), i2c);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot request IRQ\n");
return ret;
}
/* 将i2c 控制器设备与struct rk3x_i2c i2c(控制器回调接口)绑定 */
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, i2c);
if (i2c->soc_data->calc_timings == rk3x_i2c_v0_calc_timings) {
/* Only one clock to use for bus clock and peripheral clock */
i2c->clk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, NULL);
i2c->pclk = i2c->clk;
} else {
i2c->clk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "i2c");
i2c->pclk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "pclk");
}
if (IS_ERR(i2c->clk)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(i2c->clk);
if (ret != -EPROBE_DEFER)
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Can't get bus clk: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
if (IS_ERR(i2c->pclk)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(i2c->pclk);
if (ret != -EPROBE_DEFER)
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Can't get periph clk: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
ret = clk_prepare(i2c->clk);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Can't prepare bus clk: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
ret = clk_prepare(i2c->pclk);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Can't prepare periph clock: %d\n", ret);
goto err_clk;
}
i2c->clk_rate_nb.notifier_call = rk3x_i2c_clk_notifier_cb;
ret = clk_notifier_register(i2c->clk, &i2c->clk_rate_nb);
if (ret != 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Unable to register clock notifier\n");
goto err_pclk;
}
clk_rate = clk_get_rate(i2c->clk);
rk3x_i2c_adapt_div(i2c, clk_rate);
/* 将i2c adapter 挂上i2c bus , 设置i2c adapter 的类型 ,
然后调用device_add将i2c adapter 设备注册进内核*/
ret = i2c_add_adapter(&i2c->adap);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Could not register adapter\n");
goto err_clk_notifier;
}
dev_info(&pdev->dev, "Initialized RK3xxx I2C bus at %p\n", i2c->regs);
return 0;
err_clk_notifier:
clk_notifier_unregister(i2c->clk, &i2c->clk_rate_nb);
err_pclk:
clk_unprepare(i2c->pclk);
err_clk:
clk_unprepare(i2c->clk);
return ret;
}
3.8. i2c dev 或 dev-interface-to-userspace(kernel/drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c)
用户空间需要访问i2c devices, 通过这个文件去将i2c devices封装成/dev的i2c设备文件,以设备文件的接口形式提供给用户空间去访问
Refer to: kernel/Documentation/i2c/dev-interface
(1)添加i2c dev驱动
kernel/drivers/i2c/Makefile:
obj-$(CONFIG_I2C_CHARDEV) += i2c-dev.o
(2)配置kconfig以便执行make menuconfig可以配置成三态模式(buildin kernel/ compile module/ not compile)
kernel/drivers/i2c/Kconfig:
config I2C_CHARDEV
tristate “I2C device interface”
help
Say Y here to use i2c-* device files, usually found in the /dev
directory on your system. They make it possible to have user-space
programs use the I2C bus. Information on how to do this is
contained in the file
This support is also available as a module. If so, the module
will be called i2c-dev.
(3)源程序加载函数i2c_dev_init:
/*
- module load/unload record keeping
*/
static int __init i2c_dev_init(void)
{
int res;
printk(KERN_INFO "i2c /dev entries driver\n");
/* 注册I2C字符设备到内核,添加设备到系统中 module结构体链表中,使之模块立即生效,这个由 cdev_add去做,此后文件操作,可以正常使用*/
res = register_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c", &i2cdev_fops);
if (res)
goto out;
/*创建i2c dev的class目录*/
i2c_dev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "i2c-dev");
if (IS_ERR(i2c_dev_class)) {
res = PTR_ERR(i2c_dev_class);
goto out_unreg_chrdev;
}
i2c_dev_class->dev_groups = i2c_groups;
/* Keep track of adapters which will be added or removed later */
res = bus_register_notifier(&i2c_bus_type, &i2cdev_notifier);
if (res)
goto out_unreg_class;
/*************************************************
static struct notifier_block i2cdev_notifier = {
.notifier_call = i2cdev_notifier_call,
};
/-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
i2c_register_adapter-→device_register-→device_add
--→blocking_notifier_call_chain ---> i2cdev_notifier_call
/* Notify clients of device addition. This call must come
* after dpm_sysfs_add() and before kobject_uevent().
*/
if (dev->bus)
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE, dev);
–------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------/
static int i2cdev_notifier_call(struct notifier_block *nb, unsigned long action,
void *data)
{
struct device *dev = data;
switch (action) {
case BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE:
return i2cdev_attach_adapter(dev, NULL);
case BUS_NOTIFY_DEL_DEVICE:
return i2cdev_detach_adapter(dev, NULL);
}
return 0;
}
static int i2cdev_attach_adapter(struct device *dev, void *dummy)
{
struct i2c_adapter *adap;
struct i2c_dev *i2c_dev;
int res;
if (dev->type != &i2c_adapter_type)
return 0;
adap = to_i2c_adapter(dev);
i2c_dev = get_free_i2c_dev(adap);
if (IS_ERR(i2c_dev))
return PTR_ERR(i2c_dev);
/* ************************************************************
register this i2c device with the driver core , 在/dev目录下新建i2c的设备节点,
提供给用户空间去访问, 通过file_operations接口访问/dev目录下的设备节点
/dev目录下的节点不是在kernel里面建立的,kernel只是注册了kobject的uevent
的事件,待等到init.rc起来的时候,会建立/dev目录,用户空间的uevent机制
会检测到添加的uevent事件,从而在/dev目录下建立设备节点(如/dev/i2c-*)
//产生一个内核uevent事件,该事件可以被内核以及应用层捕获,属于linux设备模型中热插拔机制 //产生一个KOBJ_ADD的uevent事件,通过netlink机制和用户空间通信,这个driver_register中 已经分析过了
******************************************************************8/
i2c_dev->dev = device_create(i2c_dev_class, &adap->dev,
MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, adap->nr), NULL,
"i2c-%d", adap->nr);
if (IS_ERR(i2c_dev->dev)) {
res = PTR_ERR(i2c_dev->dev);
goto error;
}
pr_debug("i2c-dev: adapter [%s] registered as minor %d\n",
adap->name, adap->nr);
return 0;
error:
return_i2c_dev(i2c_dev);
return res;
}
****************************************************/
/* Bind to already existing adapters right away */
i2c_for_each_dev(NULL, i2cdev_attach_adapter);
return 0;
out_unreg_class:
class_destroy(i2c_dev_class);
out_unreg_chrdev:
unregister_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, “i2c”);
out:
printk(KERN_ERR “%s: Driver Initialisation failed\n”, FILE);
return res;
}
(4)UserSpace操作内核的/dev目录下的i2c设备节点:
static const struct file_operations i2cdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read = i2cdev_read,
.write = i2cdev_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = i2cdev_ioctl,
.open = i2cdev_open,
.release = i2cdev_release,
};
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/*
- After opening an instance of this character special file, a file
- descriptor starts out associated only with an i2c_adapter (and bus).
- Using the I2C_RDWR ioctl(), you can then immediately issue i2c_msg
- traffic to any devices on the bus used by that adapter. That’s because
- the i2c_msg vectors embed all the addressing information they need, and
- are submitted directly to an i2c_adapter. However, SMBus-only adapters
- don’t support that interface.
- To use read()/write() system calls on that file descriptor, or to use
- SMBus interfaces (and work with SMBus-only hosts!), you must first issue
- an I2C_SLAVE (or I2C_SLAVE_FORCE) ioctl. That configures an anonymous
- (never registered) i2c_client so it holds the addressing information
- needed by those system calls and by this SMBus interface.
*/
static ssize_t i2cdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *offset)
{
char *tmp;
int ret;
struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data;
if (count > 8192)
count = 8192;
tmp = kmalloc(count, GFP_KERNEL);
if (tmp == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
pr_debug("i2c-dev: i2c-%d reading %zu bytes.\n",
iminor(file_inode(file)), count);
ret = i2c_master_recv(client, tmp, count);
if (ret >= 0)
ret = copy_to_user(buf, tmp, count) ? -EFAULT : ret;
kfree(tmp);
return ret;
}
/**
-
i2c_master_recv - issue a single I2C message in master receive mode
-
@client: Handle to slave device
-
@buf: Where to store data read from slave
-
@count: How many bytes to read, must be less than 64k since msg.len is u16
-
Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes read.
*/
int i2c_master_recv(const struct i2c_client *client, char *buf, int count)
{
struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter;
struct i2c_msg msg;
int ret;msg.addr = client->addr;
msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN;
msg.flags |= I2C_M_RD;
msg.len = count;
msg.buf = buf;ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1);
/*
- If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg received), return #bytes received,
- else error code.
*/
return (ret == 1) ? count : ret;
}
/**
- i2c_transfer - execute a single or combined I2C message
- @adap: Handle to I2C bus
- @msgs: One or more messages to execute before STOP is issued to
- terminate the operation; each message begins with a START.
- @num: Number of messages to be executed.
- Returns negative errno, else the number of messages executed.
- Note that there is no requirement that each message be sent to
- the same slave address, although that is the most common model.
*/
int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
ret = __i2c_transfer(adap, msgs, num);
}
/**
-
__i2c_transfer - unlocked flavor of i2c_transfer
-
@adap: Handle to I2C bus
-
@msgs: One or more messages to execute before STOP is issued to
-
terminate the operation; each message begins with a START.
-
@num: Number of messages to be executed.
-
Returns negative errno, else the number of messages executed.
-
Adapter lock must be held when calling this function. No debug logging
-
takes place. adap->algo->master_xfer existence isn’t checked.
*/
int __i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
unsigned long orig_jiffies;
int ret, try;if (adap->quirks && i2c_check_for_quirks(adap, msgs, num))
return -EOPNOTSUPP;/* i2c_trace_msg gets enabled when tracepoint i2c_transfer gets
- enabled. This is an efficient way of keeping the for-loop from
- being executed when not needed.
*/
if (static_key_false(&i2c_trace_msg)) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
if (msgs[i].flags & I2C_M_RD)
trace_i2c_read(adap, &msgs[i], i);
else
trace_i2c_write(adap, &msgs[i], i);
}
/* Retry automatically on arbitration loss */
orig_jiffies = jiffies;
for (ret = 0, try = 0; try <= adap->retries; try++) {
ret = adap->algo->master_xfer(adap, msgs, num);------→调用i2c adapter控制器的回调接口i2c_algorithm 的master_xfer接口,让i2c adpater去操作i2c的 读写
if (ret != -EAGAIN)
break;
if (time_after(jiffies, orig_jiffies + adap->timeout))
break;
}if (static_key_false(&i2c_trace_msg)) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < ret; i++)
if (msgs[i].flags & I2C_M_RD)
trace_i2c_reply(adap, &msgs[i], i);
trace_i2c_result(adap, i, ret);
}return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__i2c_transfer);
static const struct i2c_algorithm rk3x_i2c_algorithm = {
.master_xfer = rk3x_i2c_xfer,
.functionality = rk3x_i2c_func,
};
static int rk3x_i2c_xfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap,
struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
struct rk3x_i2c *i2c = (struct rk3x_i2c *)adap->algo_data;
unsigned long timeout, flags;
u32 val;
int ret = 0;
int i;
if (i2c->suspended)
return -EACCES;
spin_lock_irqsave(&i2c->lock, flags);
clk_enable(i2c->clk);
clk_enable(i2c->pclk);
i2c->is_last_msg = false;
/*
* Process msgs. We can handle more than one message at once (see
* rk3x_i2c_setup()).
*/
for (i = 0; i < num; i += ret) {
ret = rk3x_i2c_setup(i2c, msgs + i, num - i);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(i2c->dev, "rk3x_i2c_setup() failed\n");
break;
}
if (i + ret >= num)
i2c->is_last_msg = true;
rk3x_i2c_start(i2c);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&i2c->lock, flags);
timeout = wait_event_timeout(i2c->wait, !i2c->busy,
msecs_to_jiffies(WAIT_TIMEOUT));
spin_lock_irqsave(&i2c->lock, flags);
if (timeout == 0) {
dev_err(i2c->dev, "timeout, ipd: 0x%02x, state: %d\n",
i2c_readl(i2c, REG_IPD), i2c->state);
/* Force a STOP condition without interrupt */
i2c_writel(i2c, 0, REG_IEN);
val = i2c_readl(i2c, REG_CON) & REG_CON_TUNING_MASK;
val |= REG_CON_EN | REG_CON_STOP;
i2c_writel(i2c, val, REG_CON);
i2c->state = STATE_IDLE;
ret = -ETIMEDOUT;
break;
}
if (i2c->error) {
ret = i2c->error;
break;
}
}
clk_disable(i2c->pclk);
clk_disable(i2c->clk);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&i2c->lock, flags);
return ret < 0 ? ret : num;
}
3.9. I2C Client Devices(drivers/input/misc/lsm6ds3/lsm6ds3_i2c.c)
一般是外接的(没有封装到Soc芯片里面)i2c设备作为i2c client devices通过i2c 接口与soc侧的i2c adapter通信,比如TP, sensor,charge, camera,uvc, Accelerometer&Gyroscope等.
示例驱动: 有compatibe匹配,有2c_device_id的name和client->name匹配,根据匹配顺序,优先进行compatible匹配
drivers/input/misc/lsm6ds3/lsm6ds3_i2c.c
(1)dts配置
kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/px30-recadas-p200.dts
&i2c2 {
status = “okay”;
clock-frequency = <100000>;
/* These are relatively safe rise/fall times; TODO: measure */
i2c-scl-falling-time-ns = <50>;
i2c-scl-rising-time-ns = <300>;
lsm6ds3: lsm6ds3@6a {
compatible = "st,lsm6ds3";
reg = <0x6a>;
};
}
(2) i2c client drivers与i2c adapter devices匹配
i2c client driver的定义:
static struct i2c_driver lsm6ds3_i2c_driver = {
.driver = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = LSM6DS3_ACC_GYR_DEV_NAME,
.pm = LSM6DS3_PM_OPS,
#ifdef CONFIG_OF
.of_match_table = lsm6ds3_id_table,
#endif
},
.probe = lsm6ds3_i2c_probe,
.remove = lsm6ds3_i2c_remove,
.id_table = lsm6ds3_ids,
};
以compatibe匹配:
arch/arm64/configs/px30_recadas_p200_defconfig:1159:CONFIG_OF=y
#ifdef CONFIG_OF
static const struct of_device_id lsm6ds3_id_table[] = {
{.compatible = “st,lsm6ds3”, },
{.compatible = “st,lsm6ds3h”, },
{ },
};
i2c_device_id根据id 的name来匹配:
static const struct i2c_device_id lsm6ds3_ids[] = {
{LSM6DS3_ACC_GYR_DEV_NAME, 0},
{ }
};
#define LSM6DS3_ACC_GYR_DEV_NAME “lsm6ds3”
根据id 的name匹配的接口:
static const struct i2c_device_id *i2c_match_id(const struct i2c_device_id *id,
const struct i2c_client *client)
{
while (id->name[0]) {
if (strcmp(client->name, id->name) == 0)
return id;
id++;
}
return NULL;
}
i2c总线的定义:
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = {
.name = “i2c”,
.match = i2c_device_match,
.probe = i2c_device_probe,
.remove = i2c_device_remove,
.shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown,
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_bus_type);
static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver;
if (!client)
return 0;
/* Attempt an OF style match , 根据compatiblep匹配*/
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);
/* match on an id table if there is one , 根据id name来匹配*/
if (driver->id_table)
return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL;
return 0;
}
(3)
static int lsm6ds3_i2c_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
int err;
struct lsm6ds3_data *cdata;
cdata = kzalloc(sizeof(*cdata), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdata)
return -ENOMEM;
cdata->dev = &client->dev;
cdata->name = client->name;
cdata->tf = &lsm6ds3_tf_i2c;
i2c_set_clientdata(client, cdata);
err = lsm6ds3_common_probe(cdata, client->irq, BUS_I2C);
if (err < 0)
goto free_data;
return 0;
free_data:
kfree(cdata);
return err;
}
其中i2c_client的由来?
/**
- struct i2c_client - represent an I2C slave device
- @flags: I2C_CLIENT_TEN indicates the device uses a ten bit chip address;
- I2C_CLIENT_PEC indicates it uses SMBus Packet Error Checking
- @addr: Address used on the I2C bus connected to the parent adapter.
- @name: Indicates the type of the device, usually a chip name that’s
- generic enough to hide second-sourcing and compatible revisions.
- @adapter: manages the bus segment hosting this I2C device
- @dev: Driver model device node for the slave.
- @irq: indicates the IRQ generated by this device (if any)
- @detected: member of an i2c_driver.clients list or i2c-core’s
- userspace_devices list
- @slave_cb: Callback when I2C slave mode of an adapter is used. The adapter
- calls it to pass on slave events to the slave driver.
- An i2c_client identifies a single device (i.e. chip) connected to an
- i2c bus. The behaviour exposed to Linux is defined by the driver
- managing the device.
/
struct i2c_client {
unsigned short flags; / div., see below /
unsigned short addr; / chip address - NOTE: 7bit /
/ addresses are stored in the /
/ LOWER 7 bits */
char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE];
struct i2c_adapter adapter; / the adapter we sit on /
struct device dev; / the device structure /
int irq; / irq issued by device /
struct list_head detected;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_I2C_SLAVE)
i2c_slave_cb_t slave_cb; / callback for slave mode */
#endif
};
rk3x_i2c_probe
---->i2c_add_adapter
-----→__i2c_add_numbered_adapter
—→i2c_register_adapter
-----→of_i2c_register_devices
------->for_each_available_child_of_node
----→of_i2c_register_device
------>
/* OF support code */
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF)
static struct i2c_client *of_i2c_register_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap,
struct device_node *node)
{
struct i2c_client *result;
struct i2c_board_info info = {};
struct dev_archdata dev_ad = {};
const __be32 *addr_be;
u32 addr;
int len;
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: register %s\n", node->full_name);
/*****找到节点的compatible属性的字符串给info.type赋值*****/
if (of_modalias_node(node, info.type, sizeof(info.type)) < 0) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: modalias failure on %s\n",
node->full_name);
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
/* ******************************************************************************
**********************************************************************************8
获取dts的i2c client device的地址,即从机地址
&i2c2 {
lsm6ds3: lsm6ds3@6a {
compatible = "st,lsm6ds3";
reg = <0x6a>;
}
};
Device Tree文件结构描述就以上struct fdt_header、struct fdt_node_header及struct fdt_property三个结构体描述。kernel会根据Device Tree的结构解析出kernel能够使用的struct property结构体。kernel根据Device Tree中所有的属性解析出数据填充struct property结构体。struct property结构体描述如下:
struct property {
char name; / property full name /
int length;/ property value length /
/**** reg = <0x6a>; 这个返回的property→value 表示的是0x6a
void value; / property value */
struct property next; / next property under the same node */
unsigned long _flags;
unsigned int unique_id;
struct bin_attribute attr; /*属性文件,与sysfs文件系统挂接 */
};
*************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************/
addr_be = of_get_property(node, “reg”, &len);
if (!addr_be || (len < sizeof(*addr_be))) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, “of_i2c: invalid reg on %s\n”,
node->full_name);
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
addr = be32_to_cpup(addr_be);
if (addr & I2C_TEN_BIT_ADDRESS) {
addr &= ~I2C_TEN_BIT_ADDRESS;
info.flags |= I2C_CLIENT_TEN;
}
if (addr & I2C_OWN_SLAVE_ADDRESS) {
addr &= ~I2C_OWN_SLAVE_ADDRESS;
info.flags |= I2C_CLIENT_SLAVE;
}
if (i2c_check_addr_validity(addr, info.flags)) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: invalid addr=%x on %s\n",
addr, node->full_name);
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
/*****************************************************************
/**
* struct i2c_board_info - template for device creation
* @type: chip type, to initialize i2c_client.name
* @flags: to initialize i2c_client.flags
* @addr: stored in i2c_client.addr
* @platform_data: stored in i2c_client.dev.platform_data
* @archdata: copied into i2c_client.dev.archdata
* @of_node: pointer to OpenFirmware device node
* @fwnode: device node supplied by the platform firmware
* @irq: stored in i2c_client.irq
*
* I2C doesn't actually support hardware probing, although controllers and
* devices may be able to use I2C_SMBUS_QUICK to tell whether or not there's
* a device at a given address. Drivers commonly need more information than
* that, such as chip type, configuration, associated IRQ, and so on.
*
* i2c_board_info is used to build tables of information listing I2C devices
* that are present. This information is used to grow the driver model tree.
* For mainboards this is done statically using i2c_register_board_info();
* bus numbers identify adapters that aren't yet available. For add-on boards,
* i2c_new_device() does this dynamically with the adapter already known.
*/
struct i2c_board_info {
char type[I2C_NAME_SIZE];
unsigned short flags;
unsigned short addr;
void *platform_data;
struct dev_archdata *archdata;
struct device_node *of_node;
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode;
int irq;
};
************************************************************************/
info.addr = addr;
info.of_node = of_node_get(node);
info.archdata = &dev_ad;
if (of_get_property(node, "wakeup-source", NULL))
info.flags |= I2C_CLIENT_WAKE;
result = i2c_new_device(adap, &info);
if (result == NULL) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: Failure registering %s\n",
node->full_name);
of_node_put(node);
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
return result;
}
/**
-
i2c_new_device - instantiate an i2c device
-
@adap: the adapter managing the device
-
@info: describes one I2C device; bus_num is ignored
-
Context: can sleep
-
Create an i2c device. Binding is handled through driver model
-
probe()/remove() methods. A driver may be bound to this device when we
-
return from this function, or any later moment (e.g. maybe hotplugging will
-
load the driver module). This call is not appropriate for use by mainboard
-
initialization logic, which usually runs during an arch_initcall() long
-
before any i2c_adapter could exist.
-
This returns the new i2c client, which may be saved for later use with
-
i2c_unregister_device(); or NULL to indicate an error.
*/
struct i2c_client *
i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_board_info const *info)
{
struct i2c_client *client;
int status;client = kzalloc(sizeof *client, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!client)
return NULL;client->adapter = adap;
client->dev.platform_data = info->platform_data;
if (info->archdata)
client->dev.archdata = *info->archdata;client->flags = info->flags;
client->addr = info->addr;
client->irq = info->irq;/* 给client->name赋值,以便后面与i2c devices driver匹配可以根据
client->name与i2c devices driver的i2c_device_id->name匹配*/
strlcpy(client->name, info->type, sizeof(client->name));status = i2c_check_addr_validity(client->addr, client->flags);
if (status) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, “Invalid %d-bit I2C address 0x%02hx\n”,
client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_TEN ? 10 : 7, client->addr);
goto out_err_silent;
}/* Check for address business */status = i2c_check_addr_ex(adap, i2c_encode_flags_to_addr(client));
if (status != 0)
dev_err(&adap->dev, “%d i2c clients have been registered at 0x%02x”,
status, client->addr);
client->dev.parent = &client->adapter->dev;
client->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;
client->dev.type = &i2c_client_type;
client->dev.of_node = info->of_node;
client->dev.fwnode = info->fwnode;i2c_dev_set_name(adap, client, status);
status = device_register(&client->dev);
if (status)
goto out_err;dev_dbg(&adap->dev, “client [%s] registered with bus id %s\n”,
client->name, dev_name(&client->dev));return client;
out_err:
dev_err(&adap->dev, "Failed to register i2c client %s at 0x%02x "
“(%d)\n”, client->name, client->addr, status);
out_err_silent:
kfree(client);
return NULL;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_new_device);
3.10.示例驱动TP驱动: 无compatibe匹配,是根据2c_device_id的name和client->name匹配
drivers/input/touchscreen/gslx680.c
(1) DTS配置
arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3399.dtsi
i2c5: i2c@ff140000 {
compatible = “rockchip,rk3399-i2c”;
reg = <0x0 0xff140000 0x0 0x1000>;
clocks = <&cru SCLK_I2C5>, <&cru PCLK_I2C5>;
clock-names = “i2c”, “pclk”;
interrupts =
pinctrl-names = “default”;
pinctrl-0 = <&i2c5_xfer>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
status = “disabled”;
};
pinctrl: pinctrl {
compatible = “rockchip,rk3399-pinctrl”;
rockchip,grf = <&grf>;
rockchip,pmu = <&pmugrf>;
#address-cells = <0x2>;
#size-cells = <0x2>;
ranges;
i2c5 {
i2c5_xfer: i2c5-xfer {
rockchip,pins =
<3 11 RK_FUNC_2 &pcfg_pull_none>,
<3 10 RK_FUNC_2 &pcfg_pull_none>;
};
};
}
arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3399-tve1030g.dts
&i2c5 {
status = “okay”;
i2c-scl-rising-time-ns = <150>;
i2c-scl-falling-time-ns = <30>;
clock-frequency = <100000>;
gslx680: gslx680@40 {
compatible = "gslX680_tve";
reg = <0x40>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&tp_irq_gpio>;
touch-gpio = <&gpio3 RK_PB0 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING>;
reset-gpio = <&gpio4 RK_PC6 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
max-x = <1200>;
max-y = <1920>;
tp-size = <80>;
tp-supply = <&vcc3v0_tp>;
status = "okay";
};
};
(2) Driver配置
static const struct of_device_id gsl_ts_ids[] = {
{ .compatible = “gslX680”, .data = &gslx680_vr_cfg },
{ .compatible = “gslX680_tve”, .data = &gslx680_tve_cfg },
{}
};
static const struct i2c_device_id gsl_ts_id[] = {
{GSLX680_I2C_NAME, 0},
{}
};
#define GSLX680_I2C_NAME “gslX680”
static int gsl_ts_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
const struct of_device_id *match;
struct gsl_ts *ts;
int rc;
printk("GSLX680 Enter %s\n", __func__);
//wake_lock_init(&touch_wakelock, WAKE_LOCK_SUSPEND, "touch");
//wake_lock(&touch_wakelock); //system do not enter deep sleep
if (!i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter, I2C_FUNC_I2C)) {
dev_err(&client->dev, "gsl I2C functionality not supported\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
ts = devm_kzalloc(&client->dev, sizeof(*ts), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ts)
return -ENOMEM;
match = of_match_device(of_match_ptr(gsl_ts_ids), &client->dev);
if (!match)
return -EINVAL;
ts->ts_cfg = (const struct gsl_ts_cfg *)match->data;
ts->tp.tp_suspend = gsl_ts_early_suspend;
ts->tp.tp_resume = gsl_ts_late_resume;
tp_register_fb(&ts->tp);
ts->client = client;
i2c_set_clientdata(client, ts);
//ts->device_id = id->driver_data;
gslX680_init(ts);
rc = gslX680_ts_init(client, ts);
if (rc < 0) {
dev_err(&client->dev, "gsl GSLX680 init failed\n");
goto porbe_err_ret;
}
//#ifdef GSLX680_COMPATIBLE
// judge_chip_type(client);
//#endif
//printk("##################### probe [2]chip_type=%c .\n",chip_type);
init_chip(ts->client, ts);
check_mem_data(ts->client, ts);
spin_lock_init(&ts->irq_lock);
client->irq = gpio_to_irq(ts->irq);
rc = request_irq(client->irq, gsl_ts_irq, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING,
client->name, ts);
if (rc < 0) {
printk("gsl_probe: request irq failed\n");
goto porbe_err_ret;
}
/* create debug attribute */
//rc = device_create_file(&ts->input->dev, &dev_attr_debug_enable);
#ifdef CONFIG_HAS_EARLYSUSPEND
ts->early_suspend.level = EARLY_SUSPEND_LEVEL_BLANK_SCREEN + 1;
//ts->early_suspend.level = EARLY_SUSPEND_LEVEL_DISABLE_FB + 1;
ts->early_suspend.suspend = gsl_ts_early_suspend;
ts->early_suspend.resume = gsl_ts_late_resume;
register_early_suspend(&ts->early_suspend);
#endif
#ifdef GSL_MONITOR
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&ts->gsl_monitor_work, gsl_monitor_worker);
gsl_monitor_workqueue =
create_singlethread_workqueue("gsl_monitor_workqueue");
queue_delayed_work(gsl_monitor_workqueue, &ts->gsl_monitor_work, 1000);
#endif
#ifdef HAVE_CLICK_TIMER
sema_init(&my_sem, 1);
INIT_WORK(&ts->click_work, click_timer_worker);
gsl_timer_workqueue = create_singlethread_workqueue(“click_timer”);
queue_work(gsl_timer_workqueue, &ts->click_work);
#endif
#ifdef TPD_PROC_DEBUG
#if 0
gsl_config_proc = create_proc_entry(GSL_CONFIG_PROC_FILE, 0666, NULL);
printk("[tp-gsl] [%s] gsl_config_proc = %x \n", func,
gsl_config_proc);
if (gsl_config_proc == NULL) {
print_info(“create_proc_entry %s failed\n”,
GSL_CONFIG_PROC_FILE);
} else {
gsl_config_proc->read_proc = gsl_config_read_proc;
gsl_config_proc->write_proc = gsl_config_write_proc;
}
#else
i2c_client = client;
proc_create(GSL_CONFIG_PROC_FILE, 0666, NULL, &gsl_seq_fops);
#endif
gsl_proc_flag = 0;
#endif
//disable_irq_nosync(->irq);
printk("[GSLX680] End %s\n", func);
return 0;
porbe_err_ret:
return rc;
}
static int gsl_ts_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
{
struct gsl_ts *ts = i2c_get_clientdata(client);
#ifdef CONFIG_HAS_EARLYSUSPEND
unregister_early_suspend(&ts->early_suspend);
#endif
#ifdef GSL_MONITOR
cancel_delayed_work_sync(&ts->gsl_monitor_work);
destroy_workqueue(gsl_monitor_workqueue);
#endif
#ifdef HAVE_CLICK_TIMER
cancel_work_sync(&ts->click_work);
destroy_workqueue(gsl_timer_workqueue);
#endif
device_init_wakeup(&client->dev, 0);
cancel_work_sync(&ts->work);
free_irq(ts->client->irq, ts);
destroy_workqueue(ts->wq);
//device_remove_file(&ts->input->dev, &dev_attr_debug_enable);
return 0;
}
static const struct i2c_device_id gsl_ts_id[] = {
{GSLX680_I2C_NAME, 0},
{}
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(i2c, gsl_ts_id);
static struct i2c_driver gsl_ts_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = GSLX680_I2C_NAME,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(gsl_ts_ids),
},
#if 0 //ndef CONFIG_HAS_EARLYSUSPEND
.suspend = gsl_ts_suspend,
.resume = gsl_ts_resume,
#endif
.probe = gsl_ts_probe,
.remove = gsl_ts_remove,
.id_table = gsl_ts_id,
};
static int __init gsl_ts_init(void)
{
int ret;
ret = i2c_add_driver(&gsl_ts_driver);
return ret;
}
static void __exit gsl_ts_exit(void)
{
i2c_del_driver(&gsl_ts_driver);
return;
}
module_init(gsl_ts_init);
module_exit(gsl_ts_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE(“GPL”);
MODULE_DESCRIPTION(“GSLX680 touchscreen controller driver”);
MODULE_AUTHOR(“Guan Yuwei, [email protected]”);
MODULE_ALIAS(“platform:gsl_ts”);