Android之对话框AlertDialog源码浅析
一、前述
我们在应用app开发中经常会使用对话框,基本都是使用AlertDialog来构建,使用方式如下:
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
builder.setTitle("Title").setMessage("Message").create().show();用法很简单并且是链式调用,非常美观,接下我们进入源码来分析下AlertDialog的实现原理。
二、AlertDialog源码分析
带着这句代码我们进入AlertDialog类:
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);会发现AlertDialog有个内部类Build,我们贴出它的代码,代码如下:
public static class Builder {
private final AlertController.AlertParams P;
private final int mTheme;
/**
* Creates a builder for an alert dialog that uses the default alert
* dialog theme.
*
* The default alert dialog theme is defined by
* {@link android.R.attr#alertDialogTheme} within the parent
* {@code context}'s theme.
*
* @param context the parent context
*/
public Builder(@NonNull Context context) {
this(context, resolveDialogTheme(context, 0));
}
/**
* Creates a builder for an alert dialog that uses an explicit theme
* resource.
*
* The specified theme resource ({@code themeResId}) is applied on top
* of the parent {@code context}'s theme. It may be specified as a
* style resource containing a fully-populated theme, such as
* {@link R.style#Theme_AppCompat_Dialog}, to replace all
* attributes in the parent {@code context}'s theme including primary
* and accent colors.
*
* To preserve attributes such as primary and accent colors, the
* {@code themeResId} may instead be specified as an overlay theme such
* as {@link R.style#ThemeOverlay_AppCompat_Dialog}. This will
* override only the window attributes necessary to style the alert
* window as a dialog.
*
* Alternatively, the {@code themeResId} may be specified as {@code 0}
* to use the parent {@code context}'s resolved value for
* {@link android.R.attr#alertDialogTheme}.
*
* @param context the parent context
* @param themeResId the resource ID of the theme against which to inflate
* this dialog, or {@code 0} to use the parent
* {@code context}'s default alert dialog theme
*/
public Builder(@NonNull Context context, @StyleRes int themeResId) {
P = new AlertController.AlertParams(new ContextThemeWrapper(
context, resolveDialogTheme(context, themeResId)));
mTheme = themeResId;
}
/**
* Returns a {@link Context} with the appropriate theme for dialogs created by this Builder.
* Applications should use this Context for obtaining LayoutInflaters for inflating views
* that will be used in the resulting dialogs, as it will cause views to be inflated with
* the correct theme.
*
* @return A Context for built Dialogs.
*/
@NonNull
public Context getContext() {
return P.mContext;
}
/**
* Set the title using the given resource id.
*
* @return This Builder object to allow for chaining of calls to set methods
*/
public Builder setTitle(@StringRes int titleId) {
P.mTitle = P.mContext.getText(titleId);
return this;
}
/**
* Set the title displayed in the {@link Dialog}.
*
* @return This Builder object to allow for chaining of calls to set methods
*/
public Builder setTitle(@Nullable CharSequence title) {
P.mTitle = title;
return this;
}
/**
* Set the title using the custom view {@code customTitleView}.
*
* The methods {@link #setTitle(int)} and {@link #setIcon(int)} should
* be sufficient for most titles, but this is provided if the title
* needs more customization. Using this will replace the title and icon
* set via the other methods.
*
* Note: To ensure consistent styling, the custom view
* should be inflated or constructed using the alert dialog's themed
* context obtained via {@link #getContext()}.
*
* @param customTitleView the custom view to use as the title
* @return this Builder object to allow for chaining of calls to set
* methods
*/
public Builder setCustomTitle(@Nullable View customTitleView) {
P.mCustomTitleView = customTitleView;
return this;
}
/**
* Set the message to display using the given resource id.
*
* @return This Builder object to allow for chaining of calls to set methods
*/
public Builder setMessage(@StringRes int messageId) {
P.mMessage = P.mContext.getText(messageId);
return this;
}
/**
* Set the message to display.
*
* @return This Builder object to allow for chaining of calls to set methods
*/
public Builder setMessage(@Nullable CharSequence message) {
P.mMessage = message;
return this;
}
/**
* Set the resource id of the {@link Drawable} to be used in the title.
*
* Takes precedence over values set using {@link #setIcon(Drawable)}.
*
* @return This Builder object to allow for chaining of calls to set methods
*/
public Builder setIcon(@DrawableRes int iconId) {
P.mIconId = iconId;
return this;
}
............
/**
* Creates an {@link AlertDialog} with the arguments supplied to this
* builder.
*
* Calling this method does not display the dialog. If no additional
* processing is needed, {@link #show()} may be called instead to both
* create and display the dialog.
*/
public AlertDialog create() {
// We can't use Dialog's 3-arg constructor with the createThemeContextWrapper param,
// so we always have to re-set the theme
final AlertDialog dialog = new AlertDialog(P.mContext, mTheme);
P.apply(dialog.mAlert);
dialog.setCancelable(P.mCancelable);
if (P.mCancelable) {
dialog.setCanceledOnTouchOutside(true);
}
dialog.setOnCancelListener(P.mOnCancelListener);
dialog.setOnDismissListener(P.mOnDismissListener);
if (P.mOnKeyListener != null) {
dialog.setOnKeyListener(P.mOnKeyListener);
}
return dialog;
}
/**
* Creates an {@link AlertDialog} with the arguments supplied to this
* builder and immediately displays the dialog.
*
* Calling this method is functionally identical to:
*
* AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
* dialog.show();
*
*/
public AlertDialog show() {
final AlertDialog dialog = create();
dialog.show();
return dialog;
}
}public Builder(@NonNull Context context) {
this(context, resolveDialogTheme(context, 0));
}this(context,resolveDialogTheme(context,0))又调用了内部另外一个构造函数:
public Builder(@NonNull Context context, @StyleRes int themeResId) {
P = new AlertController.AlertParams(new ContextThemeWrapper(
context, resolveDialogTheme(context, themeResId)));
mTheme = themeResId;
}从构造函数中,有个变量P,追踪代码一看,它是Builder的一个成员变量,类型是AlertController.AlertParams。AlertParams也是AlertContoller的一个内部类,其代码如下:
public static class AlertParams {
public final Context mContext;
public final LayoutInflater mInflater;
public int mIconId = 0;
public Drawable mIcon;
public int mIconAttrId = 0;
public CharSequence mTitle;
public View mCustomTitleView;
public CharSequence mMessage;
public CharSequence mPositiveButtonText;
public DialogInterface.OnClickListener mPositiveButtonListener;
public CharSequence mNegativeButtonText;
public DialogInterface.OnClickListener mNegativeButtonListener;
public CharSequence mNeutralButtonText;
public DialogInterface.OnClickListener mNeutralButtonListener;
public boolean mCancelable;
public DialogInterface.OnCancelListener mOnCancelListener;
public DialogInterface.OnDismissListener mOnDismissListener;
public DialogInterface.OnKeyListener mOnKeyListener;
public CharSequence[] mItems;
public ListAdapter mAdapter;
public DialogInterface.OnClickListener mOnClickListener;
public int mViewLayoutResId;
public View mView;
public int mViewSpacingLeft;
public int mViewSpacingTop;
public int mViewSpacingRight;
public int mViewSpacingBottom;
public boolean mViewSpacingSpecified = false;
public boolean[] mCheckedItems;
public boolean mIsMultiChoice;
public boolean mIsSingleChoice;
public int mCheckedItem = -1;
public DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener mOnCheckboxClickListener;
public Cursor mCursor;
public String mLabelColumn;
public String mIsCheckedColumn;
public boolean mForceInverseBackground;
public AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener mOnItemSelectedListener;
public OnPrepareListViewListener mOnPrepareListViewListener;
public boolean mRecycleOnMeasure = true;
/**
* Interface definition for a callback to be invoked before the ListView
* will be bound to an adapter.
*/
public interface OnPrepareListViewListener {
/**
* Called before the ListView is bound to an adapter.
* @param listView The ListView that will be shown in the dialog.
*/
void onPrepareListView(ListView listView);
}
public AlertParams(Context context) {
mContext = context;
mCancelable = true;
mInflater = (LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
}
public void apply(AlertController dialog) {
if (mCustomTitleView != null) {
dialog.setCustomTitle(mCustomTitleView);
} else {
if (mTitle != null) {
dialog.setTitle(mTitle);
}
if (mIcon != null) {
dialog.setIcon(mIcon);
}
if (mIconId != 0) {
dialog.setIcon(mIconId);
}
if (mIconAttrId != 0) {
dialog.setIcon(dialog.getIconAttributeResId(mIconAttrId));
}
}
if (mMessage != null) {
dialog.setMessage(mMessage);
}
if (mPositiveButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_POSITIVE, mPositiveButtonText,
mPositiveButtonListener, null);
}
if (mNegativeButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEGATIVE, mNegativeButtonText,
mNegativeButtonListener, null);
}
if (mNeutralButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEUTRAL, mNeutralButtonText,
mNeutralButtonListener, null);
}
// For a list, the client can either supply an array of items or an
// adapter or a cursor
if ((mItems != null) || (mCursor != null) || (mAdapter != null)) {
createListView(dialog);
}
if (mView != null) {
if (mViewSpacingSpecified) {
dialog.setView(mView, mViewSpacingLeft, mViewSpacingTop, mViewSpacingRight,
mViewSpacingBottom);
} else {
dialog.setView(mView);
}
} else if (mViewLayoutResId != 0) {
dialog.setView(mViewLayoutResId);
}
/*
dialog.setCancelable(mCancelable);
dialog.setOnCancelListener(mOnCancelListener);
if (mOnKeyListener != null) {
dialog.setOnKeyListener(mOnKeyListener);
}
*/
}
............
}我们先回到Builder类的代码,它也有很多方法,诸如:setTitle()、setMessage()、setIcon()等,关键来看它的create()方法:
public AlertDialog create() {
// We can't use Dialog's 3-arg constructor with the createThemeContextWrapper param,
// so we always have to re-set the theme
final AlertDialog dialog = new AlertDialog(P.mContext, mTheme);
P.apply(dialog.mAlert);
dialog.setCancelable(P.mCancelable);
if (P.mCancelable) {
dialog.setCanceledOnTouchOutside(true);
}
dialog.setOnCancelListener(P.mOnCancelListener);
dialog.setOnDismissListener(P.mOnDismissListener);
if (P.mOnKeyListener != null) {
dialog.setOnKeyListener(P.mOnKeyListener);
}
return dialog;
}第4行代码new了一个AlertDialog对象,第5行调用P,也即是AlertController.AlertParams的apply方法,我们继续跟踪:
public void apply(AlertController dialog) {
if (mCustomTitleView != null) {
dialog.setCustomTitle(mCustomTitleView);
} else {
if (mTitle != null) {
dialog.setTitle(mTitle);
}
if (mIcon != null) {
dialog.setIcon(mIcon);
}
if (mIconId != 0) {
dialog.setIcon(mIconId);
}
if (mIconAttrId != 0) {
dialog.setIcon(dialog.getIconAttributeResId(mIconAttrId));
}
}
if (mMessage != null) {
dialog.setMessage(mMessage);
}
if (mPositiveButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_POSITIVE, mPositiveButtonText,
mPositiveButtonListener, null);
}
if (mNegativeButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEGATIVE, mNegativeButtonText,
mNegativeButtonListener, null);
}
if (mNeutralButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEUTRAL, mNeutralButtonText,
mNeutralButtonListener, null);
}
// For a list, the client can either supply an array of items or an
// adapter or a cursor
if ((mItems != null) || (mCursor != null) || (mAdapter != null)) {
createListView(dialog);
}
if (mView != null) {
if (mViewSpacingSpecified) {
dialog.setView(mView, mViewSpacingLeft, mViewSpacingTop, mViewSpacingRight,
mViewSpacingBottom);
} else {
dialog.setView(mView);
}
} else if (mViewLayoutResId != 0) {
dialog.setView(mViewLayoutResId);
}
/*
dialog.setCancelable(mCancelable);
dialog.setOnCancelListener(mOnCancelListener);
if (mOnKeyListener != null) {
dialog.setOnKeyListener(mOnKeyListener);
}
*/
}AlertController.AlertParams的apply方法主要做的事就是将AlertParams的属性值传给AlertController的对应属性,且AlertParams是AlertController的内部类,我们加到Build类,再看它的show()方法:
public AlertDialog show() {
final AlertDialog dialog = create();
dialog.show();
return dialog;
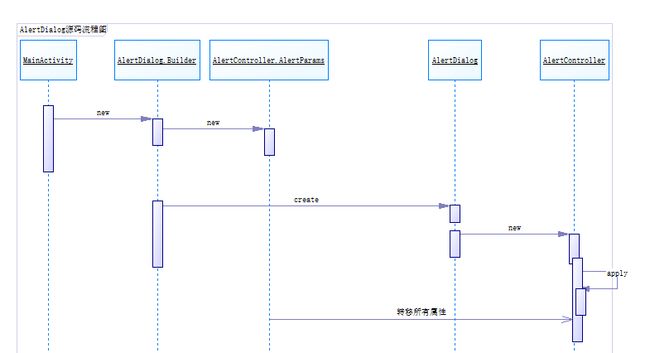
}三、AlertDialog源码UML顺序图
好了,AlertDialog的源码就简单分析完了,感谢大家的支持,谢谢!