街景字符识别—模型集成
目录
- 1. 集成学习方法
- 2. 深度学习中的集成学习
- 2.1 Dropout
- 2.2 TTA
- 2.3 Snapshot
- 3. 后处理
1. 集成学习方法
集成学习方法可以提高预测精度,常见的有Stacking、Bagging和Boosting。一般利用交叉验证法提高精度,如下所示。
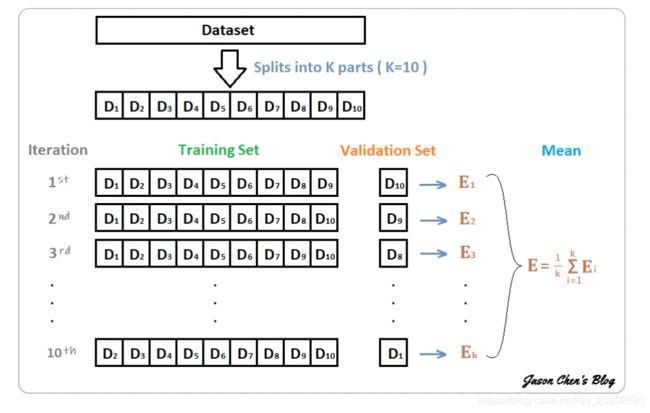
使用10折交叉验证法,得到10个CNN模型,可通过以下方法进行集成。
- 平均预测结果的概率值,然后解码为具体字符。
- 对预测的字符进行投票,得到最终字符。
2. 深度学习中的集成学习
2.1 Dropout
Dropout在训练过程中会随机选取一部分节点,令其停止工作,但在预测时又让所有节点参与工作。
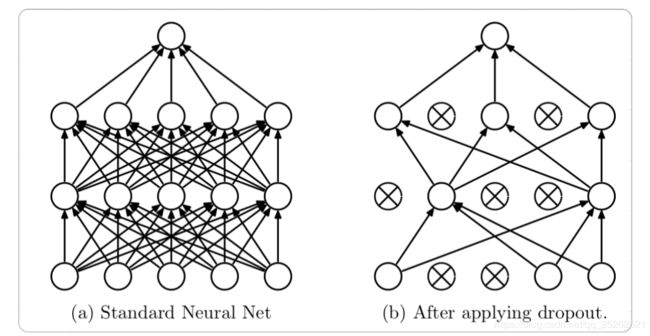
Dropout既能有效缓解过拟合问题,又能在预测时增加模型的精度。代码示例如下:
# 定义模型
class SVHN_Model1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SVHN_Model1, self).__init__()
# CNN提取特征模块
self.cnn = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.25),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.25),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
)
#
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(32*3*7, 11)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(32*3*7, 11)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(32*3*7, 11)
self.fc4 = nn.Linear(32*3*7, 11)
self.fc5 = nn.Linear(32*3*7, 11)
self.fc6 = nn.Linear(32*3*7, 11)
def forward(self, img):
feat = self.cnn(img)
feat = feat.view(feat.shape[0], -1)
c1 = self.fc1(feat)
c2 = self.fc2(feat)
c3 = self.fc3(feat)
c4 = self.fc4(feat)
c5 = self.fc5(feat)
c6 = self.fc6(feat)
return c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, c6
2.2 TTA
TTA,测试集数据扩增,在预测的时候进行数据扩增操作,比如对同一个样本预测三次,然后对三次结果进行平均。代码示例如下:
def predict(test_loader, model, tta=10):
model.eval()
test_pred_tta = None
# TTA 次数
for _ in range(tta):
test_pred = []
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (input, target) in enumerate(test_loader):
c0, c1, c2, c3, c4, c5 = model(data[0])
output = np.concatenate([c0.data.numpy(), c1.data.numpy(),
c2.data.numpy(), c3.data.numpy(),
c4.data.numpy(), c5.data.numpy()], axis=1)
test_pred.append(output)
test_pred = np.vstack(test_pred)
if test_pred_tta is None:
test_pred_tta = test_pred
else:
test_pred_tta += test_pred
return test_pred_tta
2.3 Snapshot
Snapshot是利用周期学习率来训练模型,保存多个高精度的测试点,最后将这些检查点进行模型集成。
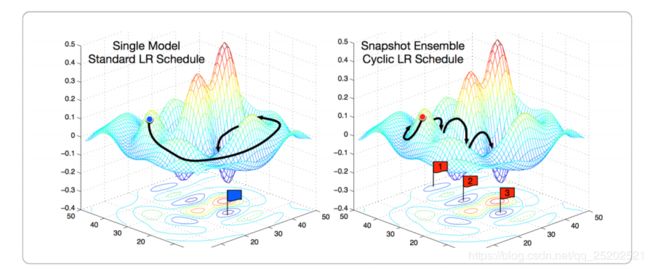
虽然此方法可以提高模型精度,但是需要更长的训练时间。
3. 后处理
对预测结果进行后处理的方法有:
- 统计图片中每个位置字符出现的概率,利用规则修正结果;
- 单独训练一个预测图片字符个数的模型,用于修正结果。
参考: Datawhale 零基础入门CV赛事-Task5 模型集成.