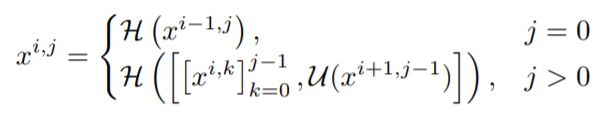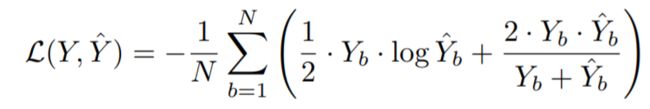【语义分割系列:六】Unet++ 论文阅读翻译笔记 医学图像 pytorch实现
UNet++
2018 CVPR
周纵苇,发表论文时是一个在读二年级的博士,在亚利桑那州立大学念生物信息学。
UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation
研习U-Net++
1、Introduce
UNet++与U-Net的区别:
- Re-designed skip pathways
- Deep supervision
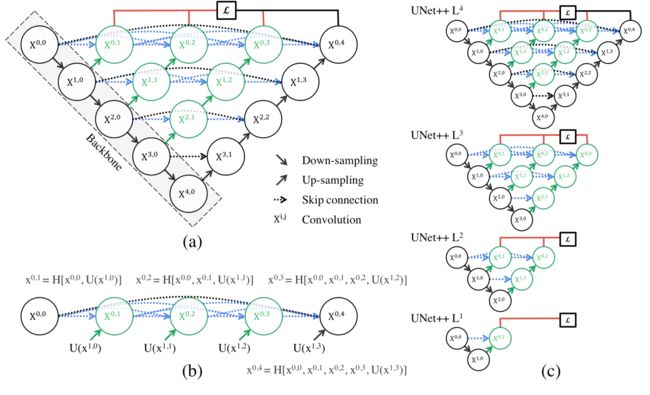
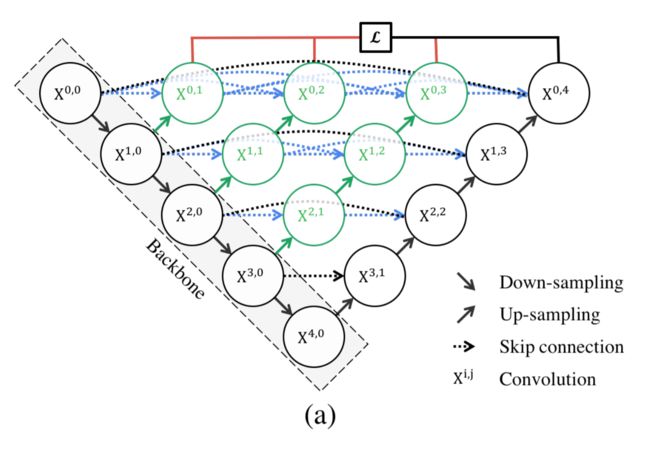
2、Network
- (a)黑色表示原始的Unet,绿色和蓝色表示skip pathways 上密集的卷积块,红色表示deep supervision
- (b) UNet++的第一个skip pathway 的详细分析。
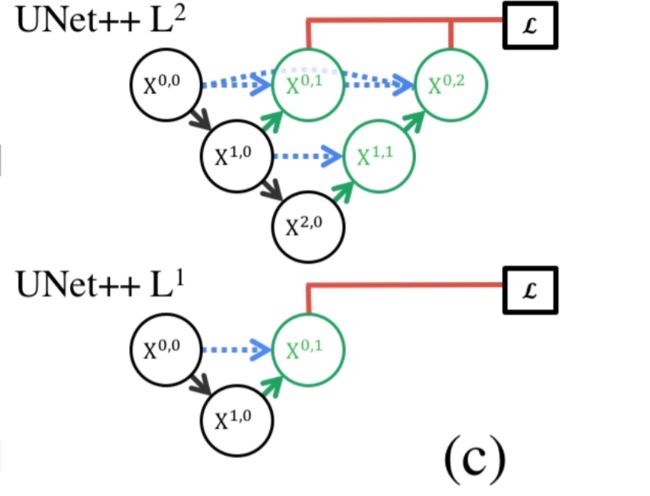
- (c) 如果经过deep supervision训练,UNet++可以在推理时进行修剪。
Re-designed skip pathways
在U-Net中,编码器的特征图在解码器中直接接收;然而,在UNet++中,它们经历了一个密集的卷积块,其卷积层数依赖于金字塔级。
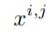 :denote the output of node
:denote the output of node 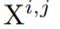
- i indexes the down-sampling layer along the encoder
- j indexes the convolution layer of the dense block along the skip pathway
-
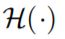 is a convolution operation followed by an activation function
is a convolution operation followed by an activation function -
nodes at level j = 0 :一个输入,来自上一层encoder
-
nodes at level j = 1 : 两个输入,其中 1 个输入为同一 skip pathway 前1个节点的输出, 1 个为 lower skip pathway 的 up-sampled 输出
-
nodes at level j > 1 : j+1 个输入,其中 j 个输入为同一 skip pathway 前 j 个节点的输出, 1 个为 lower skip pathway 的 up-sampled 输出
Deep supervisio
enabling the model to operate in two mode:
- accurate mode
the outputs from all segmentation branches are averaged - fast mode
the final segmentation map is selected from only one of the segmentation branches , the choice of which determines the extent of model pruning and speed gain
Fig. 1c shows how the choice of segmentation branch in fast mode results in architectures of varying complexit
Loss function
- a combination of binary cross-entropy and dice coefficient
- four semantic levels
Conclusion
Unet++ 和 Unet比改进了:
- having convolution layers on skip pathways (shown in green) which bridges the semantic gap between encoder and decoder feature maps;
- having dense skip connections on skip pathways (shown in blue), which improves gradient flow;
- having deep supervision (shown in red), which enables model pruning and improves or in the worst case achieves comparable performance to using only one loss layer.
3、Experiments
使用4个医学成像数据集进行模型评估,涵盖不同医学成像方式的病变/器官。
Baseline models
- original U-Net
- customized wide U-Net (with similar number of parameters as our U-Net++,ensure that the performance gain yielded by our architecture is not simply due to increased number of parameters)
Implementation details
- monitored the Dice coefficient and Intersection over Union (IoU)
- used early-stop mechanism on the validation set
- Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 3e-4
- All convolutional layers along a skip pathway
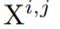 use k kernels of size 3×3
use k kernels of size 3×3 - To enable deep supervision, a 1×1 convolutional layer followed by a sigmoid activation function was appended to each of the target nodes:

Results
Unet++显著的性能提升
deep supervision is essential
UNet++ L3推理时间平均减少32.2%,IoU仅减少0.6个百分点
- 第一个优势就是精度的提升,这个应该它整合了不同层次的特征所带来的
- 第二个是灵活的网络结构配合深监督,让参数量巨大的深度网络在可接受的精度范围内大幅度的缩减参数量。
4、Train
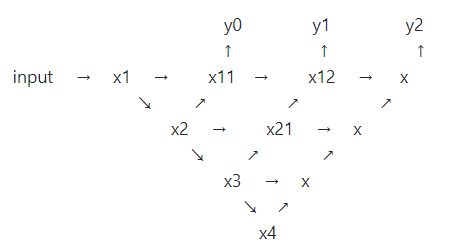
还有 x2 to x , x1 to x12 , x1 to x , x11 to x 没有画到图中
ReflectionPad2d
padding (int, tuple) uses the same padding in all boundaries.
nn.ReflectionPad2d((left_top_pad, right_bottom_pad, left_top_pad, right_bottom_pad))
4-tuple, (padding_left, padding_right, padding_top,padding_bottom)
代码地址
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class ConvSamePad2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels: int, out_channels: int, kernel_size: int, bias: bool = True):
super().__init__()
left_top_pad = right_bottom_pad = kernel_size // 2
if kernel_size % 2 == 0:
right_bottom_pad -= 1
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.ReflectionPad2d((left_top_pad, right_bottom_pad, left_top_pad, right_bottom_pad)),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, bias=bias)
)
def forward(self, inputs):
return self.layer(inputs)
class Conv3x3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, drop_rate=0.5):
super().__init__()
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
ConvSamePad2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3),
nn.Dropout2d(p=drop_rate),
ConvSamePad2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3),
nn.Dropout2d(p=drop_rate)
)
def forward(self, inputs):
return self.layer(inputs)
class Conv1x1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super().__init__()
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
ConvSamePad2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, inputs):
return self.layer(inputs)
class Unet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, n_classes, deep_supervision=True):
super().__init__()
self.deep_supervision = deep_supervision
filters = [32, 64, 128, 256, 512]
# j == 0
self.x_00 = Conv3x3(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=filters[0])
self.pool0 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.x_01 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[0] * 2, out_channels=filters[0])
self.x_02 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[0] * 3, out_channels=filters[0])
self.x_03 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[0] * 4, out_channels=filters[0])
self.x_04 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[0] * 5, out_channels=filters[0])
self.up_10_to_01 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[1], out_channels=filters[0], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.up_11_to_02 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[1], out_channels=filters[0], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.up_12_to_03 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[1], out_channels=filters[0], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.up_13_to_04 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[1], out_channels=filters[0], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# j == 1
self.x_10 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[0], out_channels=filters[1])
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.x_11 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[1] * 2, out_channels=filters[1])
self.x_12 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[1] * 3, out_channels=filters[1])
self.x_13 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[1] * 4, out_channels=filters[1])
self.up_20_to_11 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[2], out_channels=filters[1], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.up_21_to_12 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[2], out_channels=filters[1], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.up_22_to_13 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[2], out_channels=filters[1], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# j == 2
self.x_20 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[1], out_channels=filters[2])
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.x_21 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[2] * 2, out_channels=filters[2])
self.x_22 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[2] * 3, out_channels=filters[2])
self.up_30_to_21 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[3], out_channels=filters[2], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.up_31_to_22 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[3], out_channels=filters[2], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# j == 3
self.x_30 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[2], out_channels=filters[3])
self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.x_31 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[3] * 2, out_channels=filters[3])
self.up_40_to_31 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=filters[4], out_channels=filters[3], kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# j == 4
self.x_40 = Conv3x3(in_channels=filters[3], out_channels=filters[4])
# 1x1 conv layer
self.final_1x1_x01 = Conv1x1(in_channels=filters[0], out_channels=n_classes)
self.final_1x1_x02 = Conv1x1(in_channels=filters[0], out_channels=n_classes)
self.final_1x1_x03 = Conv1x1(in_channels=filters[0], out_channels=n_classes)
self.final_1x1_x04 = Conv1x1(in_channels=filters[0], out_channels=n_classes)
def forward(self, inputs, L=4):
if not (1 <= L <= 4):
raise ValueError("the model pruning factor `L` should be 1 <= L <= 4")
x_00_output = self.x_00(inputs)
x_10_output = self.x_10(self.pool0(x_00_output))
x_10_up_sample = self.up_10_to_01(x_10_output)
x_01_output = self.x_01(torch.cat([x_00_output, x_10_up_sample], 1))
nestnet_output_1 = self.final_1x1_x01(x_01_output)
if L == 1:
return nestnet_output_1
x_20_output = self.x_20(self.pool1(x_10_output))
x_20_up_sample = self.up_20_to_11(x_20_output)
x_11_output = self.x_11(torch.cat([x_10_output, x_20_up_sample], 1))
x_11_up_sample = self.up_11_to_02(x_11_output)
x_02_output = self.x_02(torch.cat([x_00_output, x_01_output, x_11_up_sample], 1))
nestnet_output_2 = self.final_1x1_x01(x_02_output)
if L == 2:
if self.deep_supervision:
# return the average of output layers
return (nestnet_output_1 + nestnet_output_2) / 2
else:
return nestnet_output_2
x_30_output = self.x_30(self.pool2(x_20_output))
x_30_up_sample = self.up_30_to_21(x_30_output)
x_21_output = self.x_21(torch.cat([x_20_output, x_30_up_sample], 1))
x_21_up_sample = self.up_21_to_12(x_21_output)
x_12_output = self.x_12(torch.cat([x_10_output, x_11_output, x_21_up_sample], 1))
x_12_up_sample = self.up_12_to_03(x_12_output)
x_03_output = self.x_03(torch.cat([x_00_output, x_01_output, x_02_output, x_12_up_sample], 1))
nestnet_output_3 = self.final_1x1_x01(x_03_output)
if L == 3:
# return the average of output layers
if self.deep_supervision:
return (nestnet_output_1 + nestnet_output_2 + nestnet_output_3) / 3
else:
return nestnet_output_3
x_40_output = self.x_40(self.pool3(x_30_output))
x_40_up_sample = self.up_40_to_31(x_40_output)
x_31_output = self.x_31(torch.cat([x_30_output, x_40_up_sample], 1))
x_31_up_sample = self.up_31_to_22(x_31_output)
x_22_output = self.x_22(torch.cat([x_20_output, x_21_output, x_31_up_sample], 1))
x_22_up_sample = self.up_22_to_13(x_22_output)
x_13_output = self.x_13(torch.cat([x_10_output, x_11_output, x_12_output, x_22_up_sample], 1))
x_13_up_sample = self.up_13_to_04(x_13_output)
x_04_output = self.x_04(torch.cat([x_00_output, x_01_output, x_02_output, x_03_output, x_13_up_sample], 1))
nestnet_output_4 = self.final_1x1_x01(x_04_output)
if L == 4:
if self.deep_supervision:
# return the average of output layers
return (nestnet_output_1 + nestnet_output_2 + nestnet_output_3 + nestnet_output_4) / 4
else:
return nestnet_output_4
if __name__ == '__main__':
inputs = torch.rand((3, 1, 96, 96)).cuda()
unet_plus_plus = Unet(in_channels=1, n_classes=3).cuda()
from datetime import datetime
st = datetime.now()
output = unet_plus_plus(inputs, L=1)
print(f"{(datetime.now() - st).total_seconds(): .4f}s")