Spring实战学习笔记
一、Spring之旅
1.1 简化Java开发
EJB和Spring都是为松耦合的POJOS提供中间件服务
EJB是重量级框架,代码侵入严重,强迫实现规范借口,类导致应用于框架绑死。Spring不会。
Spring做的是简化开发具体表现为四个方面:
- 基于POJO的轻量级和最小侵入性编程;
- 通过依赖注入和面向接口实现松耦合;
- 基于切面和惯例进行声明式编程;
- 通过切面和模板减少样板式代码。
通过DI(依赖注入),对象的依赖关系将由系统中负责协调各对像的第三方组件在创建的时候进行设定,对象无需自行创建或管理一俩关系。
面向切面编程(aspect-orientedprogramming,AOP)允许你把遍布应用各处的功能分离出来形成可重用的组件。
package student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import java.util.Scanner;
//加载应用上下文
public class ApplicationNew {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(student.StudentConfiguration.class);
Scanner scanner = applicationContext.getBean(Scanner.class);
int i = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
二、装配Bean
Spring容器提供了三种配置Bean的方式 :
- 在XML中显式配置
- 在JAVA中进行显式配置
- 隐式的bean发现机制和自动装配
自动装配、java显式装配
package student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}package student;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "student")
public class StudentConfiguration {
@Bean("PrintStream")
public PrintStream getScanner(){
return System.out;
}
}
package student;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = StudentConfiguration.class)
public class ApplicationTest {
@Autowired
private PrintStream printStream;
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@Test
public void test(){
studentService.sayHello();
printStream.println("hello");
}
}
使用Import及ImportResource导入配置
三、高级装配
环境与Profile
package student;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "student")
@Profile("dev")
public class StudentConfiguration {
@Bean("PrintStream")
public PrintStream getScanner(){
return System.out;
}
}
package student;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = StudentConfiguration.class)
@ActiveProfiles("dev")
public class ApplicationTest {
@Autowired
private PrintStream printStream;
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@Test
public void test(){
studentService.sayHello();
printStream.println("hello");
}
}
条件化的Bean
package student;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
public class StudentCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
return true;
}
}
package student;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Conditional(StudentCondition.class)
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}处理自动装配的歧义性
一个接口有多个实现bean,产生歧义。解决方法:
- Primary
package student;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Primary
public class StudentServiceImpl2 implements StudentService {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("start class");
}
}
- Qualifier限定
package student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Qualifier("2")
public class StudentServiceImpl2 implements StudentService {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("start class");
}
}
@Autowired
@Qualifier("2")
private StudentService studentService;
- 使用自定义限定符注解
package student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Qualifier("2")
@COde
public class StudentServiceImpl2 implements StudentService {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("start class");
}
}
@Autowired
@COde
private StudentService studentService;package student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR,ElementType.FIELD,
ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Qualifier
public @interface COde {
}
Bean的作用域
单例、原型、会话、请求
package student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Configurable;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Conditional(StudentCondition.class)
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}运行时值注入
- 注入外部的值
package student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:/student/app.properties")
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
Environment env;
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println(env.getProperty("a"));
}
}- 属性占位符
package student;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
@Component
public class MyProperty extends PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer {
public MyProperty() {
InputStream in = null;
in = MyProperty.class.getResourceAsStream("/student/app.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(in);
super.setProperties(properties);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Value("${a}")
String a;- SpringBidaodashi语言(SPEL)
@Value("#{1+2}")
Integer a;
四、面向切面的Spring
面向切面编程(AOP):通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
通知(Advice):就是需要进行加强的一些操作,方法。
连接点(Joinpoint):在程序执行过程中某个特定的点,比如某方法调用的时候或者处理异常的时候。在Spring AOP中,一个连接点总是表示一个方法的执行。
切入点(Pointcut):匹配连接点的断言。通知和一个切入点表达式关联,并在满足这个切入点的连接点上运行(例如,当执行某个特定名称的方法时)。切入点表达式如何和连接点匹配是AOP的核心:Spring缺省使用AspectJ切入点语法。
切面(Aspect):一个关注点的模块化,这个关注点可能会横切多个对象。事务管理是J2EE应用中一个关于横切关注点的很好的例子。在Spring AOP中,切面可以使用基于模式)或者基于@Aspect注解的方式来实现。
引入(Introduction):用来给一个类型声明额外的方法或属性(也被称为连接类型声明(inter-type declaration))。Spring允许引入新的接口(以及一个对应的实现)到任何被代理的对象。
目标对象(Target Object): 被一个或者多个切面所通知的对象。也被称做被通知(advised)对象。 既然Spring AOP是通过运行时代理实现的,这个对象永远是一个被代理(proxied)对象。
AOP代理(AOP Proxy):AOP框架创建的对象,用来实现切面契约(例如通知方法执行等等)。在Spring中,AOP代理可以是JDK动态代理或者CGLIB代理。
织入(Weaving):把切面连接到其它的应用程序类型或者对象上,并创建一个被通知的对象。这些可以在编译时(例如使用AspectJ编译器),类加载时和运行时完成。Spring和其他纯Java AOP框架一样,在运行时完成织入。
通知类型
前置通知(Before advice):在某连接点之前执行的通知,但这个通知不能阻止连接点之前的执行流程(除非它抛出一个异常)。
后置通知(After returning advice):在某连接点正常完成后执行的通知:例如,一个方法没有抛出任何异常,正常返回。
异常通知(After throwing advice):在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。
最终通知(After (finally) advice):当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。
环绕通知(Around Advice):包围一个连接点的通知,如方法调用。这是最强大的一种通知类型。环绕通知可以在方法调用前后完成自定义的行为。它也会选择是否继续执行连接点或直接返回它自己的返回值或抛出异常来结束执行。
通过切点来选择连接点
使用AspectJ的切点表达式语言定义切点。AspectJ的切点表达式一共有九种,
execution:用于匹配执行方法的连接点,这是Spring AOP中最主要的切入点指示符。该切入点的用法也相对复杂,execution表达式的格式如下:
execution(modifier-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern? name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
上面的格式中,execution是不变的,用于作为execution表达式的开头,整个表达式中几个参数的详细解释如下:
modifier-pattern:指定方法的修饰符,支持通配符,该部分可以省略
throw-pattern:指定方法声明抛出的异常,支持通配符,该部分可以省略
param-pattern:指定方法的形参列表,支持两个通配符,“*”和“..”,其中“*”代表一个任意类型的参数,而“..”代表0个或多个任意类型的参数。
name-pattern:指定匹配的方法名,支持通配符,可以使用“*”来通配所有的方法名
declaring-type-pattern:指定方法所属的类,支持通配符,该部分可以省略
ret-type-pattern:指定返回值类型,支持通配符,可以使用“*”来通配所有的返回值类型
如下是几个execution表达式:
execution(public * * (..))//匹配所有public方法
execution(* com.abc.service.AdviceManager.* (..))//匹配AdviceManager中任意方法
其余的八种表达式都是用来限定匹配的。
within:限定匹配特定类型的连接点,
within(com.abc.service.*)//匹配com.abc.service包中的任意连接点
@within:限定匹配特定注解类型的连接点
@within(com.learn.annotation.Secure)//匹配持有Secure注解的类方法;
this:用于指定AOP代理必须是指定类型的实例,用于匹配该对象的所有连接点。
this(com.abc.service.AdviceManager)//匹配实现了AdviceManager接口的代理对象的所有连接点
target:用于限定目标对象必须是指定类型的实例,用于匹配该对象的所有连接点。
target(com.abc.servcie.AdviceManager)//匹配实现了AdviceManager接口的目标对象的所有连接点,
@target:用于限定目标对象对应的类必须具有指定类型的注解
@target(com.learn.annotation.Secure)//匹配对象对应的类持有Secure注解的方法;
args:用于对连接点的参数类型进行限制,要求参数的类型时指定类型的实例。
args(java.io.Serializable)//匹配只接受一个参数,且参数类型是Serializable的所有连接点,
@args:用于对连接点的参数的注解进行限制,要求参数的注解是指定类型的实例。
@annotation:限定带有指定注解的连接点
表达式中可以使用&&符号表示与关系,使用||表示或关系、使用!表示非关系。在XML文件中使用and、or和not这三个符号。如excecution(* com.tianmaying.service.BlogService.updateBlog(..))&&within(concert.*)
在切点中引用Bean
Spring还提供了一个bean()描述符,用于在切点表达式中引用Spring Beans。例如:
excecution(* com.tianmaying.service.BlogService.updateBlog(..)) and bean('tianmayingBlog')
这表示将切面应用于BlogService的updateBlog方法上,但是仅限于ID为tianmayingBlog的Bean。
也可以排除特定的Bean:
excecution(* com.tianmaying.service.BlogService.updateBlog(..)) and !bean('tianmayingBlog')
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39326472/article/details/106543963 切入点定义
Spring提供四种AOP支持:
- 基于代理的经典Spring AOP
- 纯POJO切面
- @AspectJ注解驱动的切面
- 注入式AspectJ切面
使用注解创建切面
org.aspectj
aspectjrt
1.9.1
org.apache.geronimo.bundles
aspectjweaver
1.6.8_2
package student;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
//定义切面类
@Aspect
public class Advice {
@Before("execution(* student.StudentService.*(..))")
public void sayYes(){
System.out.println("Yes");
}
}
//开启
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class StudentConfiguration {PointCut使用
package student;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Aspect
public class Advice {
@Pointcut("execution(* student.StudentService.*(..))")
public void say(){
}
@Before("say()")
public void sayYes(){
System.out.println("Yes");
}
}
创建环绕通知
package student;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Aspect
public class Advice {
@Pointcut("execution(* student.StudentService.*(..))")
public void say(){
}
@Around("say()")
public void sayYes(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("Yes");
try {
joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("OK");
}
}
处理通知中的参数
就是说,本来的函数是带有参数的,拦截的时候把参数也给拦下来,用在切面上。
package student;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Aspect
public class Advice {
@Pointcut("execution(* student.StudentService.*(String))&&args(s)")
public void say(String s){
}
@Before("say(s)")
public void sayYes(String s){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
通过注解引用新功能
引入HaveClass接口及其实现类:
package student;
public interface HaveClass {
void haveClass();
}
package student;
public class HaveClassImpl implements HaveClass {
public void haveClass() {
System.out.println("上课啦");
}
}
使用注解将新功能HavaClass注入StudentService:
package student;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
@Aspect
public class Advice {
@DeclareParents(value = "student.StudentService+",
defaultImpl = HaveClassImpl.class)
public static HaveClass haveClass;
}
使用时转换为不同的Bean:
package student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ApplicationNew {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(student.StudentConfiguration.class);
HaveClass haveClass = (HaveClass)applicationContext.getBean("StudentService");
haveClass.haveClass();
StudentService studentService = (StudentService)applicationContext.getBean("StudentService");
studentService.sayHello();
}
}
五、构建Spring Web应用程序
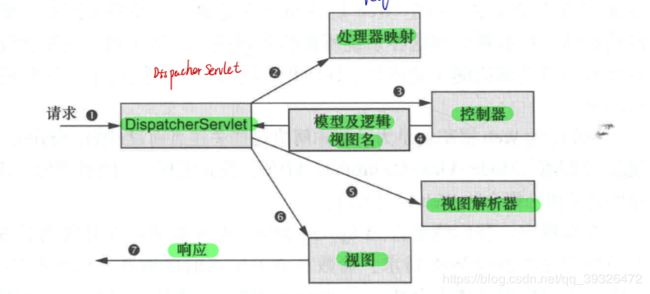
配置DispacherServlet:
package spittr.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
import spittr.web.WebConfig;
public class SpitterWebInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { RootConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Class[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { WebConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}WebConfig:
package spittr.web;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan("spittr.web")
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return resolver;
}
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
}
RootConfig:
package spittr.config;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan.Filter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.core.type.filter.RegexPatternTypeFilter;
import spittr.config.RootConfig.WebPackage;
@Configuration
@Import(DataConfig.class)
@ComponentScan(basePackages={"spittr"},
excludeFilters={
@Filter(type=FilterType.CUSTOM, value=WebPackage.class)
})
public class RootConfig {
public static class WebPackage extends RegexPatternTypeFilter {
public WebPackage() {
super(Pattern.compile("spittr\\.web"));
}
}
}
基本的控制器:
package spittr.web;
import static org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/")
public class HomeController {
@RequestMapping(method = GET)
public String home(Model model) {
return "home";
}
}
package spittr.web;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import spittr.Spittle;
import spittr.data.SpittleRepository;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/spittles")
public class SpittleController {
private static final String MAX_LONG_AS_STRING = "9223372036854775807";
private SpittleRepository spittleRepository;
@Autowired
public SpittleController(SpittleRepository spittleRepository) {
this.spittleRepository = spittleRepository;
}
//查询变量
@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.GET)
public List spittles(
@RequestParam(value="max", defaultValue=MAX_LONG_AS_STRING) long max,
@RequestParam(value="count", defaultValue="20") int count) {
return spittleRepository.findSpittles(max, count);
}
// 路径变量,Model,传递模型数据到视图
@RequestMapping(value="/{spittleId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String spittle(
@PathVariable("spittleId") long spittleId,
Model model) {
model.addAttribute(spittleRepository.findOne(spittleId));
return "spittle";
}
// 表单数据
@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveSpittle(SpittleForm form, Model model) throws Exception {
spittleRepository.save(new Spittle(null, form.getMessage(), new Date(),
form.getLongitude(), form.getLatitude()));
return "redirect:/spittles";
}
}
校验表单:
package spittr;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.EqualsBuilder;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.HashCodeBuilder;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;
public class Spitter {
private Long id;
@NotNull
@Size(min=5, max=16)
private String username;
@NotNull
@Size(min=5, max=25)
private String password;
@NotNull
@Size(min=2, max=30)
private String firstName;
@NotNull
@Size(min=2, max=30)
private String lastName;
@NotNull
@Email
private String email;
public Spitter() {}
public Spitter(String username, String password, String firstName, String lastName, String email) {
this(null, username, password, firstName, lastName, email);
}
public Spitter(Long id, String username, String password, String firstName, String lastName, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object that) {
return EqualsBuilder.reflectionEquals(this, that, "firstName", "lastName", "username", "password", "email");
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return HashCodeBuilder.reflectionHashCode(this, "firstName", "lastName", "username", "password", "email");
}
}
// 表单数据
@RequestMapping(value="/register", method=POST)
public String processRegistration(
@Valid Spitter spitter,
Errors errors) {
if (errors.hasErrors()) {
return "registerForm";
}