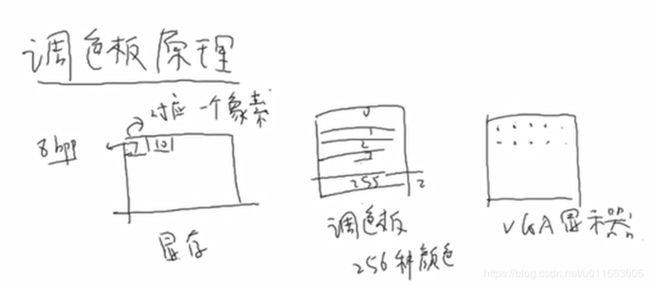
韦东山第3期嵌入式Linux项目-视频监控-3-在LCD上显示摄像头图像
一、在LCD上显示摄像头图像1_效果_框架_准备工作
1.准备工作:
(1) 准备虚拟机
(2)安装工具链
sudo tar xjf arm-linux-gcc-4.3.2.tar.bz2 -C /
设置环境变量:
sudo vi /etc/environment : PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/arm/4.3.2/bin"
(3)编译内核
① 首先解压缩内核:
tar xjf linux-3.4.2.tar.bz2
cd linux-3.4.2
② 打补丁:
可以使用我们制作好的补丁:
linux-3.4.2_camera_jz2440.patch
linux-3.4.2_camera_mini2440.patch
linux-3.4.2_camera_tq2440.patch
patch -p1 < …/linux-3.4.2_camera_jz2440.patch
③ 编译内核:
cp config_ok .config
make uImage
(重要)④ 另一种内核打补丁、编译的方法:
也可以从毕业班的内核补丁、驱动程序,自己修改、编译:
tar xjf linux-3.4.2.tar.bz2
cd linux-3.4.2
patch -p1 < ../linux-3.4.2_100ask.patch
把 lcd_4.3.c 复制到 /work/projects/linux-3.4.2/drivers/video中
修改/work/projects/linux-3.4.2/drivers/video/Makefile
#obj-$(CONFIG_FB_S3C2410) += s3c2410fb.o
obj-$(CONFIG_FB_S3C2410) += lcd_4.3.o
把dm9dev9000c.c、dm9000.h复制到/work/projects/linux-3.4.2/drivers/net/ethernet/davicom
修改/work/projects/linux-3.4.2/drivers/net/ethernet/davicom/Makefile
cp config_ok .config //config_ok中并没有加入UVC驱动程序,所以需要设置
make menuconfig
<*> Multimedia support --->
<*> Video For Linux
[*] Video capture adapters (NEW) --->
[*] V4L USB devices (NEW) --->
<*> USB Video Class (UVC)
// 如果你使用的是百问网自制的USB摄像头,
// 还需要参考第2课1.1.9节视频修改UVC驱动
make uImae
cp arch/arm/boot/uImage /work/nfs_root/uImage_new
(4) 文件系统:
cd /work/nfs_root
sudo tar xjf fs_mini_mdev_new.tar.bz2
sudo chown book:book fs_mini_mdev_new
(5)用新内核、新文件系统启动开发板
启动开发板至UBOOT
设置UBOOT的环境变量:
set ipaddr 192.168.1.148
set bootcmd ‘nfs 32000000 192.168.1.149:/work/nfs_root/uImage_new; bootm 32000000’
set bootargs console=ttySAC0,115200 root=/dev/nfs nfsroot=192.168.1.149:/work/nfs_root/fs_mini_mdev_new ip=192.168.1.148
save
boot
二、在LCD上显示摄像头图像2_实现摄像头模块
摄像头模块即video部分代码,这部分代码实现对设备的处理,具体做法是从摄像头中将视频数据读出供后续模块处理
(1)video_manage.h、video_manage.c模块
① video_manage.h:负责抽象出所有与设备有关的结构体
#ifndef _VIDEO_MANAGER_H
#define _VIDEO_MANAGER_H
#include
#include
#include
#define NB_BUFFER 4
/* 这里有一个问题:在VideoDevice 中引用了VideoOpr 结构体,同时在VideoOpr 结构体中的函数又引用了VideoDevice 结构体,这里交叉引用了。因此需要在最前面首先声明,后面就可以引用了 */
struct VideoDevice;
struct VideoOpr;
typedef struct VideoDevice T_VideoDevice, *PT_VideoDevice;
typedef struct VideoOpr T_VideoOpr, *PT_VideoOpr; //PT_VideoOpr为指向结构体的指针类型
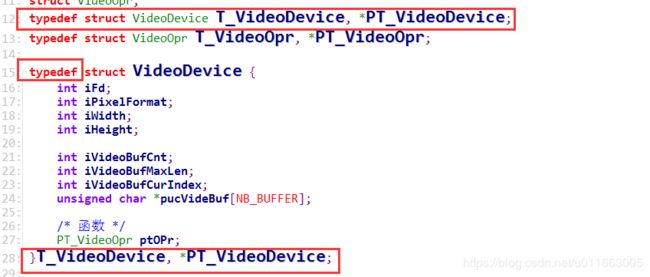
struct VideoDevice { //用该结构体表示这个设备
int iFd; //记录打开设备时的文件句柄
int iPixelFormat; //摄像头视频数据的格式
int iWidth; //分辨率的宽
int iHeight; //分辨率的高
int iVideoBufCnt;
int iVideoBufMaxLen;
int iVideoBufCurIndex;
unsigned char *pucVideBuf[NB_BUFFER]; //用来存放mmap之后的地址。
/* 函数 */
PT_VideoOpr ptOPr; //ptOPr指向VideoOpr 这个结构体
};
注释:当我们在程序中构造VideoDevice 实体时,就会让ptOPr这个结构体指向我们在v4l2.c文件中构造的VideoOpr 结构体
/* v4l2.c */
/* 构造一个VideoOpr结构体 */
static T_VideoOpr g_tV4l2VideoOpr = {
.name = "v4l2",
.InitDevice = V4l2InitDevice,
.ExitDevice = V4l2ExitDevice,
.GetFormat = V4l2GetFormat,
.GetFrame = V4l2GetFrameForStreaming,
.PutFrame = V4l2PutFrameForStreaming,
.StartDevice = V4l2StartDevice,
.StopDevice = V4l2StopDevice,
};
续注释前:
typedef struct VideoBuf { //该结构体负责储存从设备中读出的frame视频数据
T_PixelDatas tPixelDatas; //从摄像头读取到的视频数据
int iPixelFormat; //从摄像头读回来的视频数据的格式(YUV或MJPEG或RGB)
}T_VideoBuf, *PT_VideoBuf;
注释:tPixelDatas结构定义在:pic_operation.h中
/* 保存图片的象素数据 */
typedef struct PixelDatas {
int iWidth; /* 宽度: 一行有多少个象素 */
int iHeight; /* 高度: 一列有多少个象素 */
int iBpp; /* 一个象素用多少位来表示 */
int iLineBytes; /* 一行数据有多少字节 */
int iTotalBytes; /* 所有字节数 */
unsigned char *aucPixelDatas; /* 象素数据真正存储的地方 */
}T_PixelDatas, *PT_PixelDatas;
续注释前:
struct VideoOpr { //与操作设备相关的各种函数
char *name;
int (*InitDevice)(char *strDevName, PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice);
int (*ExitDevice)(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice);
/* 从ptVideoDevice设备上读取摄像头视频数据,然后存入ptVideoBuf中 */
int (*GetFrame)(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice, PT_VideoBuf ptVideo Buf);
int (*GetFormat)(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice);
int (*PutFrame)(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBuf);
int (*StartDevice)(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice); //使能设备
int (*StopDevice)(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice);
struct VideoOpr *ptNext;
};
int VideoDeviceInit(char *strDevName, PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice);
int V4l2Init(void);
int RegisterVideoOpr(PT_VideoOpr ptVideoOpr);
int VideoInit(void);
#endif /* _VIDEO_MANAGER_H */
② video_manage.c:(参考font_manage.c)
#include
#include
#include
static PT_VideoOpr g_ptVideoOprHead = NULL;
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: RegisterVideoOpr
* 功能描述: 注册"字体模块", 所谓字体模块就是取出字符位图的方法
* 输入参数: ptVideoOpr - 一个结构体,内含"取出字符位图"的操作函数
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: 0 - 成功, 其他值 - 失败
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
int RegisterVideoOpr(PT_VideoOpr ptVideoOpr)
//该函数负责完成将在v4l2.c文件中定义的VideoOpr结构体向video_manage.c注册的过程;
//所谓注册,就是将这个结构体放入一个链表中。
{
PT_VideoOpr ptTmp;
if (!g_ptVideoOprHead)
{
g_ptVideoOprHead = ptVideoOpr;
ptVideoOpr->ptNext = NULL;
}
else
{
ptTmp = g_ptVideoOprHead;
while (ptTmp->ptNext)
{
ptTmp = ptTmp->ptNext;
}
ptTmp->ptNext = ptVideoOpr;
ptVideoOpr->ptNext = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: ShowVideoOpr
* 功能描述: 显示本程序能支持的"字体模块"
* 输入参数: 无
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: 无
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
void ShowVideoOpr(void) //显示链表中的内容
{
int i = 0;
PT_VideoOpr ptTmp = g_ptVideoOprHead;
while (ptTmp)
{
printf("%02d %s\n", i++, ptTmp->name);
ptTmp = ptTmp->ptNext;
}
}
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: GetVideoOpr
* 功能描述: 根据名字取出指定的"字体模块"
* 输入参数: pcName - 名字
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: NULL - 失败,没有指定的模块,
* 非NULL - 字体模块的PT_VideoOpr结构体指针
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
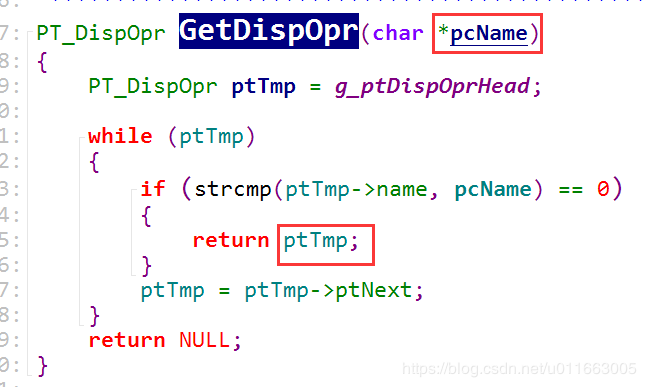
PT_VideoOpr GetVideoOpr(char *pcName) //通过名字将链表的内容取出
{
PT_VideoOpr ptTmp = g_ptVideoOprHead;
while (ptTmp)
{
if (strcmp(ptTmp->name, pcName) == 0)
{
return ptTmp;
}
ptTmp = ptTmp->ptNext;
}
return NULL;
}
int VideoDeviceInit(char *strDevName, PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice)
{
int iError;
PT_VideoOpr ptTmp = g_ptVideoOprHead;
while (ptTmp)
{
iError = ptTmp->InitDevice(strDevName, ptVideoDevice);
if (!iError)
{
return 0;
}
ptTmp = ptTmp->ptNext;
}
return -1;
}
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: FontsInit
* 功能描述: 调用各个字体模块的初始化函数
* 输入参数: 无
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: 0 - 成功, 其他值 - 失败
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
int VideoInit(void)
{
int iError;
iError = V4l2Init();
return iError;
}
(2)v4l2.c:
①构造一个VideoOpr结构体
②注册该结构体
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* 这些格式的宏都定义在:内核文件Videodev2.h中 */
static int g_aiSupportedFormats[] = {V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV, V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG, V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565};
static int V4l2GetFrameForReadWrite(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBuf);
static int V4l2PutFrameForReadWrite(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBuf);
static T_VideoOpr g_tV4l2VideoOpr; //全局变量结构体
static int isSupportThisFormat(int iPixelFormat)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(g_aiSupportedFormats)/sizeof(g_aiSupportedFormats[0]); i++)
{
if (g_aiSupportedFormats[i] == iPixelFormat)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/* 参考 luvcview */
/* (1)open
* (2)VIDIOC_QUERYCAP 确定它是否视频捕捉设备,支持哪种接口(streaming/read,write)
* (3)VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT 查询支持哪种格式
* (4)VIDIOC_S_FMT 设置摄像头使用哪种格式
* (5)VIDIOC_REQBUFS 申请buffer
对于 streaming:
* (6)VIDIOC_QUERYBUF 确定每一个buffer的信息 并且 mmap
* (7)VIDIOC_QBUF 放入队列
* (8)VIDIOC_STREAMON 启动设备
* (9)poll 等待有数据
* (10)VIDIOC_DQBUF 从队列中取出
* (11) 处理缓冲区中的数据
* (12)(处理过后再次放入队列中)VIDIOC_QBUF 放入队列
* ....一直进行9~12的循环
对于read,write:
read
处理....
read
* (13)VIDIOC_STREAMOFF 停止设备
*/
/* 摄像头设备初始化函数 */
static int V4l2InitDevice(char *strDevName, PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice)
{
int i;
int iFd;
int iError;
struct v4l2_capability tV4l2Cap;
struct v4l2_fmtdesc tFmtDesc;
struct v4l2_format tV4l2Fmt;
struct v4l2_requestbuffers tV4l2ReqBuffs;
struct v4l2_buffer tV4l2Buf;
int iLcdWidth;
int iLcdHeigt;
int iLcdBpp;
/* (1)open */
iFd = open(strDevName, O_RDWR);
if (iFd < 0)
{
DBG_PRINTF("can not open %s\n", strDevName);
return -1;
}
ptVideoDevice->iFd = iFd;
/* (2)VIDIOC_QUERYCAP 确定它是否视频捕捉设备,支持哪种接口(streaming/read,write) */
/* 如果在写APP的时候不清楚在调用具体每个ioctl时候的参数怎么去设置,
* 就可以在内核源码中搜索相应的ioctl的宏。
* 比如搜索:VIDIOC_QUERYCAP--->Uvc_v4l2.c:struct v4l2_capability *cap = arg(ioctl传入的参数)
* 这时候就知道了如果要去查询摄像头是否为视频捕捉设备(查询摄像头属性)而去调用ioctl函数的时候传入的
* 参数应该是v4l2_capability 类型的参数
*/
memset(&tV4l2Cap, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_capability));
iError = ioctl(iFd, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &tV4l2Cap);
if (iError) {
DBG_PRINTF("Error opening device %s: unable to query device.\n", strDevName);
goto err_exit;
}
/* 是否为视频捕捉设备 */
if (!(tV4l2Cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE))
{
DBG_PRINTF("%s is not a video capture device\n", strDevName);
goto err_exit;
}
/* 是否支持streaming接口 */
if (tV4l2Cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_STREAMING) {
DBG_PRINTF("%s supports streaming i/o\n", strDevName);
}
/* 是否支持read/write接口 */
if (tV4l2Cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_READWRITE) {
DBG_PRINTF("%s supports read i/o\n", strDevName);
}
/* (3)VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT 查询支持哪种格式 */
memset(&tFmtDesc, 0, sizeof(tFmtDesc));
tFmtDesc.index = 0; //查询第1种格式
tFmtDesc.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
while ((iError = ioctl(iFd, VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT, &tFmtDesc)) == 0) {
if (isSupportThisFormat(tFmtDesc.pixelformat)) //是否支持这种fmt,1支持,0不支持
{
ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat = tFmtDesc.pixelformat; //如果支持就将查询到的fmt赋给当前设备的fmt
break;
}
tFmtDesc.index++; //查询写一个fmt
}
if (!ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat) //该变量一直未设置,表明摄像头的格式不能支持
{
DBG_PRINTF("can not support the format of this device\n");
goto err_exit;
}
/*(4)VIDIOC_S_FMT 设置摄像头使用哪种格式 */
/* set format in */
GetDispResolution(&iLcdWidth, &iLcdHeigt, &iLcdBpp); //事先读出LCD的分辨率、位深度等信息。
//来自disp_manage.c
memset(&tV4l2Fmt, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_format));
tV4l2Fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
tV4l2Fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat;
tV4l2Fmt.fmt.pix.width = iLcdWidth;
tV4l2Fmt.fmt.pix.height = iLcdHeigt;
tV4l2Fmt.fmt.pix.field = V4L2_FIELD_ANY;
/* 如果驱动程序发现无法某些参数(比如分辨率),
* 它会调整这些参数, 并且返回给应用程序
*/
iError = ioctl(iFd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &tV4l2Fmt);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Unable to set format\n");
goto err_exit;
}
/* 当VIDIOC_S_FMT-->ioctl函数执行后,真正的分辨率应该再去读取出来 */
ptVideoDevice->iWidth = tV4l2Fmt.fmt.pix.width;
ptVideoDevice->iHeight = tV4l2Fmt.fmt.pix.height;
/* (5)VIDIOC_REQBUFS 申请buffer */
/* request buffers */
memset(&tV4l2ReqBuffs, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_requestbuffers));
tV4l2ReqBuffs.count = NB_BUFFER; //缓冲区的个数
tV4l2ReqBuffs.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
tV4l2ReqBuffs.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP; //可以通过mmap映射到用户程序空间
iError = ioctl(iFd, VIDIOC_REQBUFS, &tV4l2ReqBuffs);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Unable to allocate buffers.\n");
goto err_exit;
}
ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufCnt = tV4l2ReqBuffs.count; //实际申请到的缓冲区个数(申请的个数可能不等于实际分配的个数)
if (tV4l2Cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_STREAMING) //只有streaming接口的设备才需要mmap
{
/* map the buffers */
for (i = 0; i < ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufCnt; i++) //对于申请到的每一个buf
{
memset(&tV4l2Buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer));
tV4l2Buf.index = i; //查询哪一个buf
tV4l2Buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
tV4l2Buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
/* (6)VIDIOC_QUERYBUF 确定每一个buffer的信息 并且 mmap */
iError = ioctl(iFd, VIDIOC_QUERYBUF, &tV4l2Buf); //mmap之前先去查询每一个buf的信息,然后再来mmap
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Unable to query buffer.\n");
goto err_exit;
}
/* 接下来就是将tV4l2Buf 映射mmap到用户空间 */
ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufMaxLen = tV4l2Buf.length;
ptVideoDevice->pucVideBuf[i] = mmap(0 /* start anywhere */ ,
tV4l2Buf.length, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, iFd,
tV4l2Buf.m.offset);
if (ptVideoDevice->pucVideBuf[i] == MAP_FAILED)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Unable to map buffer\n");
goto err_exit;
}
}
/* (7)VIDIOC_QBUF 放入队列 */
/* Queue the buffers. */
for (i = 0; i < ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufCnt; i++)
{
memset(&tV4l2Buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer));
tV4l2Buf.index = i;
tV4l2Buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
tV4l2Buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
iError = ioctl(iFd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &tV4l2Buf);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Unable to queue buffer.\n");
goto err_exit;
}
}
}
else if (tV4l2Cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_READWRITE)
{
/* 如果是read/write接口,则在此处将g_tV4l2VideoOpr 结构体的成员变量赋值为read/write接口
* 对应的读写函数,为此需要在c文件开头之前就声明两个函数和g_tV4l2VideoOpr 结构体
*/
g_tV4l2VideoOpr.GetFrame = V4l2GetFrameForReadWrite;
g_tV4l2VideoOpr.PutFrame = V4l2PutFrameForReadWrite;
/* read(fd, buf, size) */
ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufCnt = 1; //对于读写接口也需要有一个buf
/* 在这个程序所能支持的格式里, 一个象素最多只需要4字节 */
ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufMaxLen = ptVideoDevice->iWidth * ptVideoDevice->iHeight * 4;
ptVideoDevice->pucVideBuf[0] = malloc(ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufMaxLen);
}
ptVideoDevice->ptOPr = &g_tV4l2VideoOpr;
return 0;
err_exit:
close(iFd);
return -1;
}
/* 摄像头设备退出函数 */
static int V4l2ExitDevice(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufCnt; i++)
{
if (ptVideoDevice->pucVideBuf[i])
{
munmap(ptVideoDevice->pucVideBuf[i], ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufMaxLen);
ptVideoDevice->pucVideBuf[i] = NULL;
}
}
close(ptVideoDevice->iFd);
return 0;
}
/* 摄像头设备启动函数,对应ioctl中的streamon */
static int V4l2StartDevice(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice)
{
int iType = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
int iError;
iError = ioctl(ptVideoDevice->iFd, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &iType);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Unable to start capture.\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
/* 摄像头设备关闭函数,对应ioctl中的streamoff */
static int V4l2StopDevice(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice)
{
int iType = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
int iError;
iError = ioctl(ptVideoDevice->iFd, VIDIOC_STREAMOFF, &iType);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Unable to stop capture.\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
/* 对于GetFrame来说,分为stream接口和read/write接口两种实现方式 */
/* 首先是对于stream接口 */
static int V4l2GetFrameForStreaming(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBuf)
{
struct pollfd tFds[1];
int iRet;
struct v4l2_buffer tV4l2Buf;
/* (1)首先利用poll函数查询是否有新数据到来 */
tFds[0].fd = ptVideoDevice->iFd; //当前打开的设备文件的句柄
tFds[0].events = POLLIN; //请求的事件是查询是否有数据可供读入
iRet = poll(tFds, 1, -1); //这里的“-1”表示永远等待
if (iRet <= 0)
{
DBG_PRINTF("poll error!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 如果poll函数的返回正确,说明有数据到来,这是从队列中将数据取出
* VIDIOC_DQBUF
*/
memset(&tV4l2Buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer));
tV4l2Buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
tV4l2Buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
iRet = ioctl(ptVideoDevice->iFd, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &tV4l2Buf);
/* 在DQBUF后,tV4l2Buf这个返回的参数中会含有一些值,从这些值就可以知道是关于buf 的信息 */
if (iRet < 0)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Unable to dequeue buffer.\n");
return -1;
}
/* 当前含有数据的buf指示标识 */
ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufCurIndex = tV4l2Buf.index;
/* 下面需要将传入的ptVideoBuf参数设置好 */
ptVideoBuf->iPixelFormat = ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iWidth = ptVideoDevice->iWidth;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iHeight = ptVideoDevice->iHeight;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iBpp = (ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV) ? 16 : \
(ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG) ? 0 : \
(ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565) ? 16 : \
0;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iLineBytes = ptVideoDevice->iWidth * ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iBpp / 8;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iTotalBytes = tV4l2Buf.bytesused;
//在设备初始化的时候DeviceInit中mmap后pucVideBuf[index]数组中就保存了视频数据的地址
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas = ptVideoDevice->pucVideBuf[tV4l2Buf.index];
return 0;
}
/* Getframe得到视频数据后,就是处理这些数据的工作 */
/* 处理完成后,将buf重新放入队列中 */
static int V4l2PutFrameForStreaming(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBuf)
{
/* VIDIOC_QBUF */
struct v4l2_buffer tV4l2Buf;
int iError;
memset(&tV4l2Buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer));
tV4l2Buf.index = ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufCurIndex;
tV4l2Buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
tV4l2Buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
iError = ioctl(ptVideoDevice->iFd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &tV4l2Buf);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Unable to queue buffer.\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
/* 对于read/write接口的设备来说: */
static int V4l2GetFrameForReadWrite(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBuf)
{
int iRet;
iRet = read(ptVideoDevice->iFd, ptVideoDevice->pucVideBuf[0], ptVideoDevice->iVideoBufMaxLen);
if (iRet <= 0) //表示没有读到数据
{
return -1;
}
/* 读到数据后,开始构造ptVideoBuf */
ptVideoBuf->iPixelFormat = ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iWidth = ptVideoDevice->iWidth;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iHeight = ptVideoDevice->iHeight;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iBpp = (ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV) ? 16 : \
(ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG) ? 0 : \
(ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565)? 16 : \
0;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iLineBytes = ptVideoDevice->iWidth * ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iBpp / 8;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.iTotalBytes = iRet;
ptVideoBuf->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas = ptVideoDevice->pucVideBuf[0];
return 0;
}
static int V4l2PutFrameForReadWrite(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBuf)
{
return 0;
}
static int V4l2GetFormat(PT_VideoDevice ptVideoDevice)
{
return ptVideoDevice->iPixelFormat;
}
/* 构造(定义)一个VideoOpr结构体,以后就用该结构体中的函数来读取摄像头中的数据 */
/* 这里把对v4l2设备的操作都封装起来了,就意味着可以根据需要完成不同的接口 */
static T_VideoOpr g_tV4l2VideoOpr = {
.name = "v4l2",
.InitDevice = V4l2InitDevice,
.ExitDevice = V4l2ExitDevice,
.GetFormat = V4l2GetFormat,
.GetFrame = V4l2GetFrameForStreaming,
.PutFrame = V4l2PutFrameForStreaming,
.StartDevice = V4l2StartDevice,
.StopDevice = V4l2StopDevice,
};
/* 注册这个结构体 */
int V4l2Init(void)
{
//该函数就是刚刚在 video_manage.c 中定义的RegisterVideoOpr函数。
return RegisterVideoOpr(&g_tV4l2VideoOpr);
}
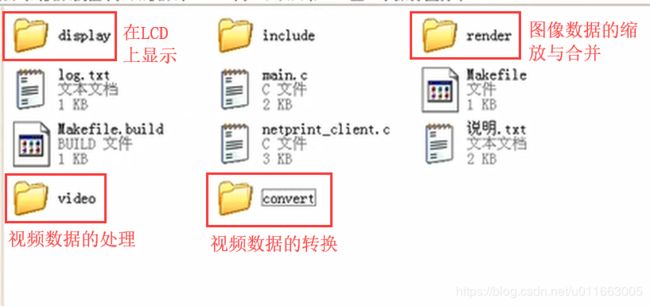
三、在LCD上显示摄像头图像3_实现视频转换模块
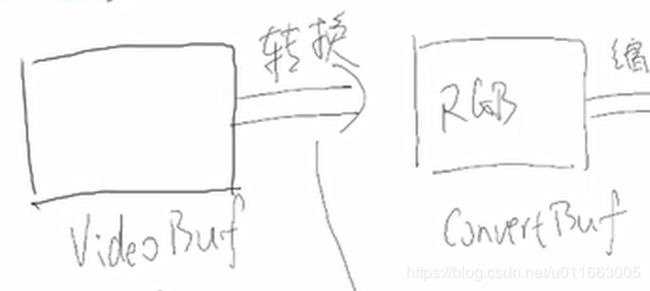
在上一步操作中(video模块),已经完成了将摄像头中的数据读出并存入VideoBuf中,但是因为读出的视频数据格式有可能不是能够在LCD上显示的标准RGB格式,因此现在需要将视频数据转换为RGB格式。
(1)convert_manege.h和convert_manege.c
① convert_manege.h
#ifndef _CONVERT_MANAGER_H
#define _CONVERT_MANAGER_H
#include
#include
#include
typedef struct VideoConvert {
char *name;
int (*isSupport)(int iPixelFormatIn, int iPixelFormatOut);
int (*Convert)(PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufIn, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufOut);
int (*ConvertExit)(PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufOut);
struct VideoConvert *ptNext;
}T_VideoConvert, *PT_VideoConvert;
PT_VideoConvert GetVideoConvertForFormats(int iPixelFormatIn, int iPixelFormatOut);
int VideoConvertInit(void);
int Yuv2RgbInit(void);
int Mjpeg2RgbInit(void);
int Rgb2RgbInit(void);
int RegisterVideoConvert(PT_VideoConvert ptVideoConvert);
#endif /* _CONVERT_MANAGER_H */
② convert_manege.c
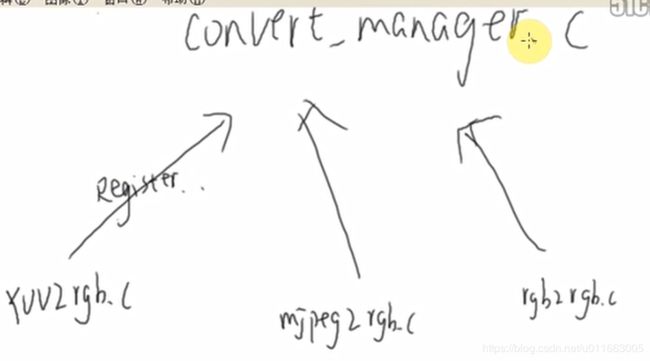
向上注册的过程需要模仿video_manage.c中在convert_manege.c实现一个链表结构。
#include
#include
#include
static PT_VideoConvert g_ptVideoConvertHead = NULL;
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: RegisterVideoConvert
* 功能描述: 注册"字体模块", 所谓字体模块就是取出字符位图的方法
* 输入参数: ptVideoConvert - 一个结构体,内含"取出字符位图"的操作函数
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: 0 - 成功, 其他值 - 失败
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
int RegisterVideoConvert(PT_VideoConvert ptVideoConvert)
{
PT_VideoConvert ptTmp;
if (!g_ptVideoConvertHead)
{
g_ptVideoConvertHead = ptVideoConvert;
ptVideoConvert->ptNext = NULL;
}
else
{
ptTmp = g_ptVideoConvertHead;
while (ptTmp->ptNext)
{
ptTmp = ptTmp->ptNext;
}
ptTmp->ptNext = ptVideoConvert;
ptVideoConvert->ptNext = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: ShowVideoConvert
* 功能描述: 显示本程序能支持的"字体模块"
* 输入参数: 无
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: 无
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
void ShowVideoConvert(void)
{
int i = 0;
PT_VideoConvert ptTmp = g_ptVideoConvertHead;
while (ptTmp)
{
printf("%02d %s\n", i++, ptTmp->name);
ptTmp = ptTmp->ptNext;
}
}
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: GetVideoConvert
* 功能描述: 根据名字取出指定的"字体模块"
* 输入参数: pcName - 名字
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: NULL - 失败,没有指定的模块,
* 非NULL - 字体模块的PT_VideoConvert结构体指针
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
PT_VideoConvert GetVideoConvert(char *pcName)
{
PT_VideoConvert ptTmp = g_ptVideoConvertHead;
while (ptTmp)
{
if (strcmp(ptTmp->name, pcName) == 0)
{
return ptTmp;
}
ptTmp = ptTmp->ptNext;
}
return NULL;
}
PT_VideoConvert GetVideoConvertForFormats(int iPixelFormatIn, int iPixelFormatOut)
{
PT_VideoConvert ptTmp = g_ptVideoConvertHead;
while (ptTmp)
{
if (ptTmp->isSupport(iPixelFormatIn, iPixelFormatOut))
{
return ptTmp;
}
ptTmp = ptTmp->ptNext;
}
return NULL;
}
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: FontsInit
* 功能描述: 调用各个字体模块的初始化函数
* 输入参数: 无
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: 0 - 成功, 其他值 - 失败
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
int VideoConvertInit(void) //分别调用几个真正的转换函数
{
int iError;
iError = Yuv2RgbInit();
iError |= Mjpeg2RgbInit();
iError |= Rgb2RgbInit();
return iError;
}
(2)Yuv2RGB.c :实现Yuv2RGB的转换工作
#include
#include
#include "color.h"
static int isSupportYuv2Rgb(int iPixelFormatIn, int iPixelFormatOut)
{
if (iPixelFormatIn != V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV)
return 0;
if ((iPixelFormatOut != V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565) && (iPixelFormatOut != V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB32))
{
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
/* 参考了luvcview.c */
/* translate YUV422Packed to rgb24 */
static unsigned int
Pyuv422torgb565(unsigned char * input_ptr, unsigned char * output_ptr, unsigned int image_width, unsigned int image_height)
{
unsigned int i, size;
unsigned char Y, Y1, U, V;
unsigned char *buff = input_ptr;
unsigned char *output_pt = output_ptr;
unsigned int r, g, b;
unsigned int color;
size = image_width * image_height /2;
for (i = size; i > 0; i--) {
/* bgr instead rgb ?? */
Y = buff[0] ;
U = buff[1] ;
Y1 = buff[2];
V = buff[3];
buff += 4;
r = R_FROMYV(Y,V);
g = G_FROMYUV(Y,U,V); //b
b = B_FROMYU(Y,U); //v
/* 把r,g,b三色构造为rgb565的16位值 */
r = r >> 3;
g = g >> 2;
b = b >> 3;
color = (r << 11) | (g << 5) | b;
*output_pt++ = color & 0xff;
*output_pt++ = (color >> 8) & 0xff;
r = R_FROMYV(Y1,V);
g = G_FROMYUV(Y1,U,V); //b
b = B_FROMYU(Y1,U); //v
/* 把r,g,b三色构造为rgb565的16位值 */
r = r >> 3;
g = g >> 2;
b = b >> 3;
color = (r << 11) | (g << 5) | b;
*output_pt++ = color & 0xff;
*output_pt++ = (color >> 8) & 0xff;
}
return 0;
}
/* 参考了luvcview.c */
/* translate YUV422Packed to rgb24 */
static unsigned int
Pyuv422torgb32(unsigned char * input_ptr, unsigned char * output_ptr, unsigned int image_width, unsigned int image_height)
{
unsigned int i, size;
unsigned char Y, Y1, U, V;
unsigned char *buff = input_ptr;
unsigned int *output_pt = (unsigned int *)output_ptr;
unsigned int r, g, b;
unsigned int color;
size = image_width * image_height /2;
for (i = size; i > 0; i--) {
/* bgr instead rgb ?? */
Y = buff[0] ;
U = buff[1] ;
Y1 = buff[2];
V = buff[3];
buff += 4;
r = R_FROMYV(Y,V);
g = G_FROMYUV(Y,U,V); //b
b = B_FROMYU(Y,U); //v
/* rgb888 */
color = (r << 16) | (g << 8) | b;
*output_pt++ = color;
r = R_FROMYV(Y1,V);
g = G_FROMYUV(Y1,U,V); //b
b = B_FROMYU(Y1,U); //v
color = (r << 16) | (g << 8) | b;
*output_pt++ = color;
}
return 0;
}
/* 参考luvcview */
/* 根据之前的Pyuv422torgb565、Pyuv422torgb32来构造convert函数 */
static int Yuv2RgbConvert(PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufIn, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufOut)
{
PT_PixelDatas ptPixelDatasIn = &ptVideoBufIn->tPixelDatas;
PT_PixelDatas ptPixelDatasOut = &ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas;
ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth = ptPixelDatasIn->iWidth;
ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight = ptPixelDatasIn->iHeight;
if (ptVideoBufOut->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565)
{
ptPixelDatasOut->iBpp = 16;
//每一行的字节数
ptPixelDatasOut->iLineBytes = ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth * ptPixelDatasOut->iBpp / 8;
ptPixelDatasOut->iTotalBytes = ptPixelDatasOut->iLineBytes * ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight;
//如果存储数据的内存是空的,则为其分配空间
if (!ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas)
{
ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas = malloc(ptPixelDatasOut->iTotalBytes);
}
//输入数据转换为输出数据,需要的参数:输入、输出、宽度、高度
Pyuv422torgb565(ptPixelDatasIn->aucPixelDatas, ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas, ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth, ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight);
return 0;
}
else if (ptVideoBufOut->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB32)
{
ptPixelDatasOut->iBpp = 32;
ptPixelDatasOut->iLineBytes = ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth * ptPixelDatasOut->iBpp / 8;
ptPixelDatasOut->iTotalBytes = ptPixelDatasOut->iLineBytes * ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight;
if (!ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas)
{
ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas = malloc(ptPixelDatasOut->iTotalBytes);
}
Pyuv422torgb32(ptPixelDatasIn->aucPixelDatas, ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas, ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth, ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight);
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
//退出函数负责释放清理工作
static int Yuv2RgbConvertExit(PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufOut)
{
if (ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas)
{
free(ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas);
//一定要将释放后的指针设为NULL,防止野指针的出现
ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
/* 构造一个在convert_manage.h中定义的结构体 */
/* 并在该.c文件中实现其中的三个功能 函数 */
static T_VideoConvert g_tYuv2RgbConvert = {
.name = "yuv2rgb",
.isSupport = isSupportYuv2Rgb,
.Convert = Yuv2RgbConvert,
.ConvertExit = Yuv2RgbConvertExit,
};
extern void initLut(void); //声明外部函数
/* 注册 */
int Yuv2RgbInit(void)
{
initLut(); //该函数负责初始化在颜色操作过程中用到的那些宏中的变量
return RegisterVideoConvert(&g_tYuv2RgbConvert); //向上注册g_tYuv2RgbConvert结构体
}
(3)Mjpeg2Rgb.c :实现Mjpeg2Rgb的转换工作
MJPEG : 实质上每一帧数据都是一个完整的JPEG文件
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef struct MyErrorMgr
{
struct jpeg_error_mgr pub;
jmp_buf setjmp_buffer;
}T_MyErrorMgr, *PT_MyErrorMgr;
extern void jpeg_mem_src_tj(j_decompress_ptr, unsigned char *, unsigned long);
/* 1. 是否支持的检查函数 */
static int isSupportMjpeg2Rgb(int iPixelFormatIn, int iPixelFormatOut)
{
if (iPixelFormatIn != V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG)
return 0;
if ((iPixelFormatOut != V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565) && (iPixelFormatOut != V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB32))
{
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
/* 2.2 出错之后终止运行 */
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: MyErrorExit
* 功能描述: 自定义的libjpeg库出错处理函数
* 默认的错误处理函数是让程序退出,我们当然不会使用它
* 参考libjpeg里的bmp.c编写了这个错误处理函数
* 输入参数: ptCInfo - libjpeg库抽象出来的通用结构体
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: 无
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
static void MyErrorExit(j_common_ptr ptCInfo)
{
static char errStr[JMSG_LENGTH_MAX];
PT_MyErrorMgr ptMyErr = (PT_MyErrorMgr)ptCInfo->err;
/* Create the message */
(*ptCInfo->err->format_message) (ptCInfo, errStr);
DBG_PRINTF("%s\n", errStr);
longjmp(ptMyErr->setjmp_buffer, 1);
}
/* 2.1 将一行数据从JPEG转换为RGB */
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: CovertOneLine
* 功能描述: 把已经从JPG文件取出的一行象素数据,转换为能在显示设备上使用的格式
* 输入参数: iWidth - 宽度,即多少个象素
* iSrcBpp - 已经从JPG文件取出的一行象素数据里面,一个象素用多少位来表示
* iDstBpp - 显示设备上一个象素用多少位来表示
* pudSrcDatas - 已经从JPG文件取出的一行象素数所存储的位置
* pudDstDatas - 转换所得数据存储的位置
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: 0 - 成功, 其他值 - 失败
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
static int CovertOneLine(int iWidth, int iSrcBpp, int iDstBpp, unsigned char *pudSrcDatas, unsigned char *pudDstDatas)
{
unsigned int dwRed;
unsigned int dwGreen;
unsigned int dwBlue;
unsigned int dwColor;
unsigned short *pwDstDatas16bpp = (unsigned short *)pudDstDatas;
unsigned int *pwDstDatas32bpp = (unsigned int *)pudDstDatas;
int i;
int pos = 0;
if (iSrcBpp != 24)
{
return -1;
}
if (iDstBpp == 24)
{
memcpy(pudDstDatas, pudSrcDatas, iWidth*3);
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < iWidth; i++)
{
dwRed = pudSrcDatas[pos++];
dwGreen = pudSrcDatas[pos++];
dwBlue = pudSrcDatas[pos++];
if (iDstBpp == 32)
{
dwColor = (dwRed << 16) | (dwGreen << 8) | dwBlue;
*pwDstDatas32bpp = dwColor;
pwDstDatas32bpp++;
}
else if (iDstBpp == 16)
{
/* 565 */
dwRed = dwRed >> 3;
dwGreen = dwGreen >> 2;
dwBlue = dwBlue >> 3;
dwColor = (dwRed << 11) | (dwGreen << 5) | (dwBlue);
*pwDstDatas16bpp = dwColor;
pwDstDatas16bpp++;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: GetPixelDatasFrmJPG
* 功能描述: 把JPG文件中的图像数据,取出并转换为能在显示设备上使用的格式
* 输入参数: ptFileMap - 内含文件信息
* 输出参数: ptPixelDatas - 内含象素数据
* ptPixelDatas->iBpp 是输入的参数, 它确定从JPG文件得到的数据要转换为该BPP
* 返 回 值: 0 - 成功, 其他值 - 失败
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2013/02/08 V1.0 韦东山 创建
***********************************************************************/
//以前是从文件中将JPEG格式的数据转换为RGB
//static int GetPixelDatasFrmJPG(PT_FileMap ptFileMap, PT_PixelDatas ptPixelDatas)
/* 2. 把内存里的JPEG图像转换为RGB图像 */
/* 借鉴数码相框中将JPEG数据转换为LCD能够显示的RGB图像的函数 */
static int Mjpeg2RgbConvert(PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufIn, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufOut)
{
struct jpeg_decompress_struct tDInfo;
//struct jpeg_error_mgr tJErr;
int iRet;
int iRowStride;
unsigned char *aucLineBuffer = NULL;
unsigned char *pucDest;
T_MyErrorMgr tJerr;
/* 首先得到我们输出的数据 */
PT_PixelDatas ptPixelDatas = &ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas;
// 分配和初始化一个decompression结构体
//tDInfo.err = jpeg_std_error(&tJErr);
tDInfo.err = jpeg_std_error(&tJerr.pub);
tJerr.pub.error_exit = MyErrorExit;
if(setjmp(tJerr.setjmp_buffer))
{
/* 如果程序能运行到这里, 表示JPEG解码出错 */
jpeg_destroy_decompress(&tDInfo);
if (aucLineBuffer)
{
free(aucLineBuffer);
}
if (ptPixelDatas->aucPixelDatas)
{
free(ptPixelDatas->aucPixelDatas);
}
return -1;
}
jpeg_create_decompress(&tDInfo);
// 以前用文件指针得到数据,用jpeg_read_header获得jpg信息
//jpeg_stdio_src(&tDInfo, ptFileMap->tFp);
/***********************************************************************/
/* 现在:把数据设为内存中的数据,有关用到的转换函数可以根据libjpeg.txt 文档中的说明来进行选择 */
/* 参1:jpeg实例结构体:;惨:输入数据存放的地址;参3:总共的字节数 */
jpeg_mem_src_tj (&tDInfo, ptVideoBufIn->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas, ptVideoBufIn->tPixelDatas.iTotalBytes);
iRet = jpeg_read_header(&tDInfo, TRUE);
// 设置解压参数,比如放大、缩小
tDInfo.scale_num = tDInfo.scale_denom = 1;
// 启动解压:jpeg_start_decompress
jpeg_start_decompress(&tDInfo);
// 一行的数据长度
iRowStride = tDInfo.output_width * tDInfo.output_components;
aucLineBuffer = malloc(iRowStride);
if (NULL == aucLineBuffer)
{
return -1;
}
ptPixelDatas->iWidth = tDInfo.output_width;
ptPixelDatas->iHeight = tDInfo.output_height;
//ptPixelDatas->iBpp = iBpp;
ptPixelDatas->iLineBytes = ptPixelDatas->iWidth * ptPixelDatas->iBpp / 8;
ptPixelDatas->iTotalBytes = ptPixelDatas->iHeight * ptPixelDatas->iLineBytes;
if (NULL == ptPixelDatas->aucPixelDatas) //如果存放输出数据的内存是空的,则分配空间
{
ptPixelDatas->aucPixelDatas = malloc(ptPixelDatas->iTotalBytes);
}
pucDest = ptPixelDatas->aucPixelDatas;
// 循环调用jpeg_read_scanlines来一行一行地获得解压的数据,读入一行数据,转换一行数据
while (tDInfo.output_scanline < tDInfo.output_height)
{
/* 得到一行数据,里面的颜色格式为0xRR, 0xGG, 0xBB */
(void) jpeg_read_scanlines(&tDInfo, &aucLineBuffer, 1);
// 转到ptPixelDatas去
CovertOneLine(ptPixelDatas->iWidth, 24, ptPixelDatas->iBpp, aucLineBuffer, pucDest);
pucDest += ptPixelDatas->iLineBytes;
}
free(aucLineBuffer);
jpeg_finish_decompress(&tDInfo);
jpeg_destroy_decompress(&tDInfo);
return 0;
}
static int Mjpeg2RgbConvertExit(PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufOut)
{
if (ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas)
{
free(ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas);
ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
/* 跟之前一样构造一个格式转换的结构体 */
static T_VideoConvert g_tMjpeg2RgbConvert = {
.name = "mjpeg2rgb",
.isSupport = isSupportMjpeg2Rgb,
.Convert = Mjpeg2RgbConvert,
.ConvertExit = Mjpeg2RgbConvertExit,
};
/* 注册 */
int Mjpeg2RgbInit(void)
{
return RegisterVideoConvert(&g_tMjpeg2RgbConvert);
}
(4)rgb2rgb.c :实现RGB2RGB的转换工作
#include
#include
#include
/* 1. 是否支持的检查函数 */
static int isSupportRgb2Rgb(int iPixelFormatIn, int iPixelFormatOut)
{
if (iPixelFormatIn != V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565)
return 0;
if ((iPixelFormatOut != V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565) && (iPixelFormatOut != V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB32))
{
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
/* 2. Rgb2Rgb转换函数 */
static int Rgb2RgbConvert(PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufIn, PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufOut)
{
PT_PixelDatas ptPixelDatasIn = &ptVideoBufIn->tPixelDatas;
PT_PixelDatas ptPixelDatasOut = &ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas;
int x, y;
int r, g, b;
int color;
unsigned short *pwSrc = (unsigned short *)ptPixelDatasIn->aucPixelDatas;
unsigned int *pdwDest;
if (ptVideoBufIn->iPixelFormat != V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565) //这里表示输入的格式只支持RGB565
{
return -1;
}
if (ptVideoBufOut->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565) //所需要的格式,可以直接拷贝无需处理
{
ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth = ptPixelDatasIn->iWidth;
ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight = ptPixelDatasIn->iHeight;
ptPixelDatasOut->iBpp = 16;
ptPixelDatasOut->iLineBytes = ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth * ptPixelDatasOut->iBpp / 8;
ptPixelDatasOut->iTotalBytes = ptPixelDatasOut->iLineBytes * ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight;
if (!ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas) //如果输出缓存是空的,则需要重新分配空间
{
ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas = malloc(ptPixelDatasOut->iTotalBytes);
}
/* memcpy函数的参1:目的;参2:源;参3:长度 */
memcpy(ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas, ptPixelDatasIn->aucPixelDatas, ptPixelDatasOut->iTotalBytes);
return 0;
}
else if (ptVideoBufOut->iPixelFormat == V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB32) //另外一个RGB32的分支
{
ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth = ptPixelDatasIn->iWidth;
ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight = ptPixelDatasIn->iHeight;
ptPixelDatasOut->iBpp = 32;
ptPixelDatasOut->iLineBytes = ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth * ptPixelDatasOut->iBpp / 8;
ptPixelDatasOut->iTotalBytes = ptPixelDatasOut->iLineBytes * ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight;
if (!ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas)
{
ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas = malloc(ptPixelDatasOut->iTotalBytes);
}
pdwDest = (unsigned int *)ptPixelDatasOut->aucPixelDatas;
for (y = 0; y < ptPixelDatasOut->iHeight; y++) //逐行处理数据
{
for (x = 0; x < ptPixelDatasOut->iWidth; x++) //将每个像素的数据取出来转换为RGB32
{
color = *pwSrc++;
//首先从源数据中取出16字节的数据(RGB565),之后把里面的红绿蓝解析出来
/* 从RGB565格式的数据中提取出R,G,B */
r = color >> 11;
g = (color >> 5) & (0x3f);
b = color & 0x1f;
/* 把r,g,b转为0x00RRGGBB的32位数据 */
color = ((r << 3) << 16) | ((g << 2) << 8) | (b << 3);
*pdwDest = color; //最后把转换后的数据放入目的地址中
pdwDest++;
}
}
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
static int Rgb2RgbConvertExit(PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufOut)
{
if (ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas)
{
free(ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas);
ptVideoBufOut->tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
/* 同理,需要首先构造结构转换操作函数的结构体 */
static T_VideoConvert g_tRgb2RgbConvert = {
.name = "rgb2rgb",
.isSupport = isSupportRgb2Rgb,
.Convert = Rgb2RgbConvert,
.ConvertExit = Rgb2RgbConvertExit,
};
/* 注册 */
int Rgb2RgbInit(void)
{
return RegisterVideoConvert(&g_tRgb2RgbConvert);
}
convert 目录完成
四、在LCD上显示摄像头图像4_整合代码
之前已经实现了摄像头读取数据的模块(video)和数据转换模块(convert)。后面的图像缩放、合并和显示用了数码相框中的源码。
现在要做的是将所有的代码整合起来,即写出main函数。
main函数中要做的事情:
- 首先是一系列的初始化
- 然后又一个while(1)循环:
2.1 读入摄像头数据
2.2 转换视频数据格式:转换为RGB数据
2.3 缩放图像大小:如果图像分辨率大于LCD的分辨率,则缩放
2.4 合并图像数据:合并进framebuffer中
2.5 把framebuffer中的数据刷到LCD上,显示
#include
#include
#include
#include
//三大模块:显示、视频数据读取和转换模块
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* video2lcd */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int iError;
T_VideoDevice tVideoDevice;
PT_VideoConvert ptVideoConvert;
int iPixelFormatOfVideo;
int iPixelFormatOfDisp;
PT_VideoBuf ptVideoBufCur; //指向当前正在使用的buf
T_VideoBuf tVideoBuf; //从摄像头中读取出的视频数据存放的buf
T_VideoBuf tConvertBuf; //转换后的视频数据存放的buf
T_VideoBuf tZoomBuf;
T_VideoBuf tFrameBuf;
int iLcdWidth;
int iLcdHeigt;
int iLcdBpp;
int iTopLeftX;
int iTopLeftY;
float k;
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage:\n");
printf("%s \n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 一系列的初始化 */
//1. 首先初始化LCD显示器
DisplayInit(); //注册显示设备:framebuffer的操作函数
/* 可能可支持多个显示设备: 选择和初始化指定的显示设备 */
SelectAndInitDefaultDispDev("fb");
//初始化后就要获得显示器的分辨率和bpp
GetDispResolution(&iLcdWidth, &iLcdHeigt, &iLcdBpp);
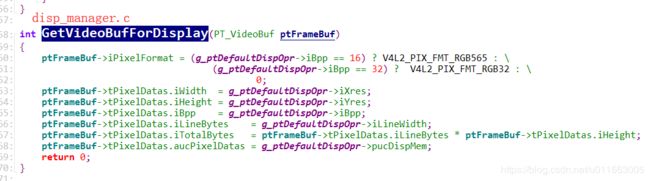
//获取用于显示的framebuffer:调用完GetVideoBufForDisplay函数后,tFrameBuf中就已经有了LCD显示器的格式
GetVideoBufForDisplay(&tFrameBuf);
/* LCD屏幕显示的图像格式 */
iPixelFormatOfDisp = tFrameBuf.iPixelFormat;
//设置转换后缓存的一些格式:如显示器的格式,显示器的bpp
memset(&tConvertBuf, 0, sizeof(tConvertBuf));
tConvertBuf.iPixelFormat = iPixelFormatOfDisp;
tConvertBuf.tPixelDatas.iBpp = iLcdBpp;
//2. 摄像头模块初始化
VideoInit();
/* VideoInit-->V4l2Init-->RegisterVideoOpr(&g_tV4l2VideoOpr)
* 主要是注册了VideoOpr结构体,其中有各种设备操作的函数
* 这里应该调用设备的初始化函数V4l2InitDevice,然后获得一个PT_VideoDevice结构体,之后就可以使用该结构体去读取视频数据了。
*/
video_manage.c中:
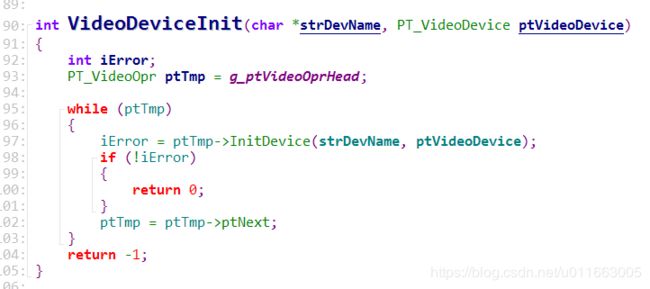
该函数就是去存放VideoOpr结构体的链表中把每一个结构体都取出来,然后调用其中的InitDevice函数初始化设备结构体。
iError = VideoDeviceInit(argv[1], &tVideoDevice);
/* VideoDeviceInit函数主要是打开某些设备验证是否成功,如果成功则会拿到tVideoDevice结构体
* 该结构体中除了有摄像头数据信息以外,还有PT_VideoOpr操作函数结构体,之后就可以用其中的函数进行一系列的设备操作了
* /
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("VideoDeviceInit for %s error!\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 获取摄像头传回视频数据的格式 */
iPixelFormatOfVideo = tVideoDevice.ptOPr->GetFormat(&tVideoDevice);
//3. 初始化格式转换函数,注册了一系列的转换操作函数结构体(YUV、MJPEG、RGB)
VideoConvertInit();
/* 在转换格式之前,首先要知道是从什么格式转换为什么格式,GetVideoConvertForFormats实现这个需要转换格式的读取: */
ptVideoConvert = GetVideoConvertForFormats(iPixelFormatOfVideo, iPixelFormatOfDisp);
if (NULL == ptVideoConvert)
{
DBG_PRINTF("can not support this format convert\n");
return -1;
}
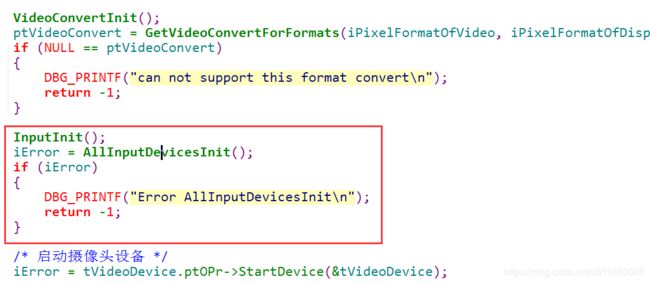
//4. 启动摄像头设备
iError = tVideoDevice.ptOPr->StartDevice(&tVideoDevice);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("StartDevice for %s error!\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
memset(&tVideoBuf, 0, sizeof(tVideoBuf)); //首先把存放数据的Videobuf清零。
memset(&tZoomBuf, 0, sizeof(tZoomBuf));
/* 初始化工作完成,现在开始循环完成摄像头显示 */
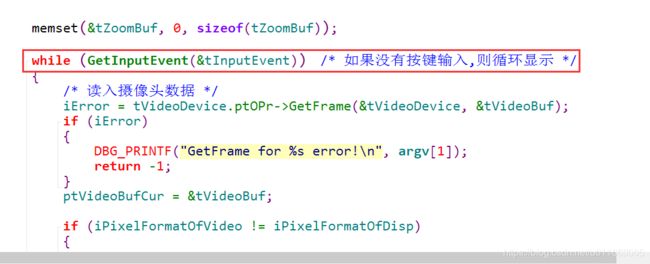
while (1)
{
/* 1. 读入摄像头数据 */
/* 面向对象的思想:所有的操作都可以调用tVideoDevice-->ptOPr中的函数 */
iError = tVideoDevice.ptOPr->GetFrame(&tVideoDevice, &tVideoBuf);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("GetFrame for %s error!\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
ptVideoBufCur = &tVideoBuf; //在转换之前首先让当前的buf指向刚从摄像头中读出的数据的缓冲区:tVideoBuf
//2. 如果摄像头的视频数据格式与LCD可以显示的视频格式不同,才需要转换
if (iPixelFormatOfVideo != iPixelFormatOfDisp)
{
/* 转换为RGB */
/* 将数据从VideoBuf中放入ConvertBuf中: */
iError = ptVideoConvert->Convert(&tVideoBuf, &tConvertBuf);
DBG_PRINTF("Convert %s, ret = %d\n", ptVideoConvert->name, iError);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("Convert for %s error!\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
ptVideoBufCur = &tConvertBuf;
}
/* 在此之前需要考虑:如果输入格式!=输出格式才需要转换,因此需要在之前定义一个指针指向当前提供数据的buf :ptVideoBufCur*/
/* 3. 如果图像分辨率大于LCD, 缩放 */
if (ptVideoBufCur->tPixelDatas.iWidth > iLcdWidth || ptVideoBufCur->tPixelDatas.iHeight > iLcdHeigt)
{
/* 确定缩放后的分辨率,参考数相框代码 */
/* 把图片按比例缩放到VideoMem上, 居中显示
* 算出缩放后的大小,k为比例系数。
*/
//比例系数为原始数据的高度/原始数据的宽度
k = (float)ptVideoBufCur->tPixelDatas.iHeight / ptVideoBufCur->tPixelDatas.iWidth;
tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iWidth = iLcdWidth;
tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iHeight = iLcdWidth * k;
if ( tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iHeight > iLcdHeigt)
{
tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iWidth = iLcdHeigt / k;
tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iHeight = iLcdHeigt;
}
tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iBpp = iLcdBpp;
tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iLineBytes = tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iWidth * tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iBpp / 8;
tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iTotalBytes = tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iLineBytes * tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iHeight;
if (!tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas)
{
tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.aucPixelDatas = malloc(tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas.iTotalBytes);
}
//PicZoom就是缩放函数,参1表示原始数据的缓冲区;参2表示输出后的数据缓冲区,
//tZoomBuf是另外定义的缓冲区T_VideoBuf,同样需要在循环之前用memset做初始化
PicZoom(&ptVideoBufCur->tPixelDatas, &tZoomBuf.tPixelDatas);
ptVideoBufCur = &tZoomBuf; //缩放完成后,当前的Buf就是缩放后的Buf了。
}
/* 4. 合并进framebuffer,这时需要新定义一个framebuffer:tFrameBuf */
/* 并且对这个tFrameBuf进行一系列的设置: GetVideoBufForDisplay(&tFrameBuf);*/
/* 算出居中显示时左上角坐标 */
iTopLeftX = (iLcdWidth - ptVideoBufCur->tPixelDatas.iWidth) / 2;
iTopLeftY = (iLcdHeigt - ptVideoBufCur->tPixelDatas.iHeight) / 2;
PicMerge(iTopLeftX, iTopLeftY, &ptVideoBufCur->tPixelDatas, &tFrameBuf.tPixelDatas);
//最后tFrameBuf.tPixelDatas这个地址保存的就是最终缩放好的视频数据
/* 对于开发板来说,因为2440中有LCD控制器,我们将要显示的视频数据放入framebuffer
* 中后就可以直接显示了 。但是对于pc端来说,需要先将数据存在framebuffer中,然后将
* 其中的数据按照逐个像素的方式取出,然后在显示屏上描点来显示图像画面,需要FlushPixelDatasToDev这个函数完成这种效果。
*/
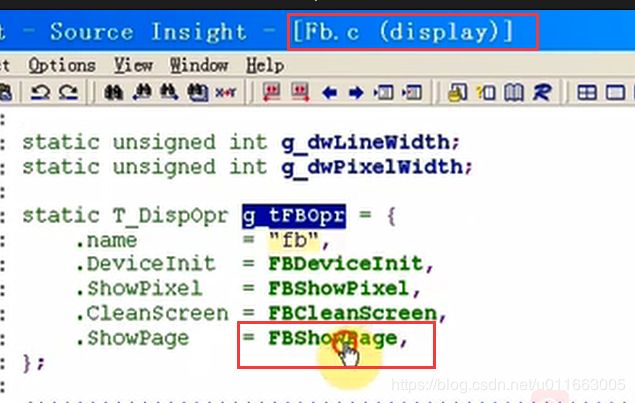
该函数中调用ShowPage函数来显示:


现在需要在fb.c文件中再次实现T_DispOpr结构体中的这个ShowPage这函数:



FlushPixelDatasToDev(&tFrameBuf.tPixelDatas);
//读取完数据后,将buf重新放入队列中,释放数据
iError = tVideoDevice.ptOPr->PutFrame(&tVideoDevice, &tVideoBuf);
if (iError)
{
DBG_PRINTF("PutFrame for %s error!\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 5. 把framebuffer的数据刷到LCD上, 显示 */
}
return 0;
}
五、在LCD上显示摄像头图像5_调试测试
1. 首先编写Makefile
本程序的Makefile分为3类:
- 顶层目录的Makefile
- 顶层目录的Makefile.build
- 各级子目录的Makefile
(1)各级子目录的Makefile:
它最简单,形式如下:
obj-y += file.o
obj-y += subdir/
"obj-y += file.o"表示把当前目录下的file.c编进程序里,
"obj-y += subdir/"表示要进入subdir这个子目录下去寻找文件来编进程序里,是哪些文件由subdir目录下的Makefile决定。
注意: "subdir/“中的斜杠”/"不可省略
(2)顶层目录的Makefile:
它除了定义obj-y来指定根目录下要编进程序去的文件、子目录外,主要是定义工具链、编译参数、链接参数──就是文件中用export导出的各变量。
源码:
CROSS_COMPILE = arm-linux-
AS = $(CROSS_COMPILE)as
LD = $(CROSS_COMPILE)ld
CC = $(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc
CPP = $(CC) -E
AR = $(CROSS_COMPILE)ar
NM = $(CROSS_COMPILE)nm
STRIP = $(CROSS_COMPILE)strip
OBJCOPY = $(CROSS_COMPILE)objcopy
OBJDUMP = $(CROSS_COMPILE)objdump
export AS LD CC CPP AR NM
export STRIP OBJCOPY OBJDUMP
CFLAGS := -Wall -Werror -O2 -g
CFLAGS += -I $(shell pwd)/include
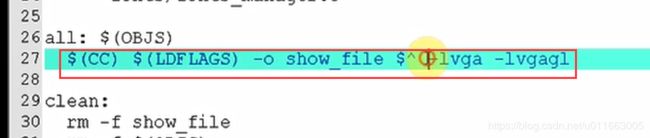
LDFLAGS := -lm -ljpeg
export CFLAGS LDFLAGS
TOPDIR := $(shell pwd)
export TOPDIR
(3)顶层目录的Makefile.build:
这是最复杂的部分,它的功能就是把某个目录及它的所有子目录中、需要编进程序去的文件都编译出来,打包为built-in.o
源码:
PHONY := __build
__build:
obj-y :=
subdir-y :=
include Makefile
# obj-y := a.o b.o c/ d/
# $(filter %/, $(obj-y)) : c/ d/
# __subdir-y : c d
# subdir-y : c d
__subdir-y := $(patsubst %/,%,$(filter %/, $(obj-y)))
subdir-y += $(__subdir-y)
# c/built-in.o d/built-in.o
subdir_objs := $(foreach f,$(subdir-y),$(f)/built-in.o)
# a.o b.o
cur_objs := $(filter-out %/, $(obj-y))
dep_files := $(foreach f,$(cur_objs),.$(f).d)
dep_files := $(wildcard $(dep_files))
ifneq ($(dep_files),)
include $(dep_files)
endif
PHONY += $(subdir-y)
__build : $(subdir-y) built-in.o
$(subdir-y):
make -C $@ -f $(TOPDIR)/Makefile.build
built-in.o : $(cur_objs) $(subdir_objs)
$(LD) -r -o $@ $^
dep_file = [email protected]
%.o : %.c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -Wp,-MD,$(dep_file) -c -o $@ $<
.PHONY : $(PHONY)
(4)怎么使用这套Makefile:
-
把顶层Makefile, Makefile.build放入程序的顶层目录
-
修改顶层Makefile
2.1 修改工具链
2.2 修改编译选项、链接选项
2.3 修改obj-y决定顶层目录下哪些文件、哪些子目录被编进程序
2.4 修改TARGET,这是用来指定编译出来的程序的名字 -
在各一个子目录下都建一个Makefile,形式为:
obj-y += file1.o
obj-y += file2.o
obj-y += subdir1/
obj-y += subdir2/ -
执行"make"来编译,执行"make clean"来清除,执行"make distclean"来彻底清除
2. 调试
- 结构体的重复定义:
- 宏未声明的解决:

需要找到这个宏的位置然后包含相应的头文件:
先通过工具链搜索的方法找到宏的位置,然后包含头文件即可。
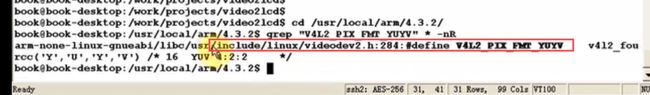
大部分遇到的函数、变量未声明的错误,只需要在相应的头文件中声明即可。
注意:所有在A.c文件中定义的函数fun1()如果想在B.c文件中调用,则有两种方法可以实现:
(1)在B.c文件中声明:extern fun1(); 然后就可以在B.c中调用了;
(2)在A.h头文件中声明:extern fun1(); 然后B.c包含A.h头文件,这样B.c中就可以调用fun1()了。
其中,这里的extern可以省略。
![]()
Debug完成之后,编译并拷贝 video2lcd 到网络文件系统中去。
启动开发板,接上USB摄像头,运行应用程序:
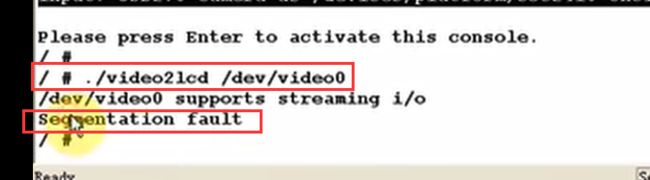
提示说出现段错误。
解决方案:

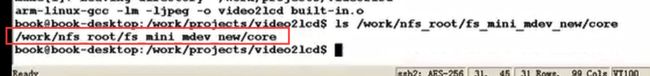
这时core文件已经生成成功。
在pc端使用gdb调试即可:

在gdb调试过程中执行backtrace命令得到:

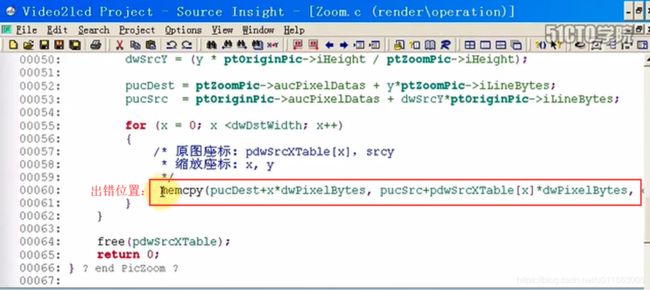
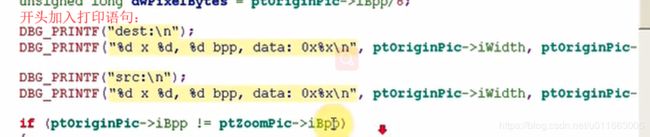
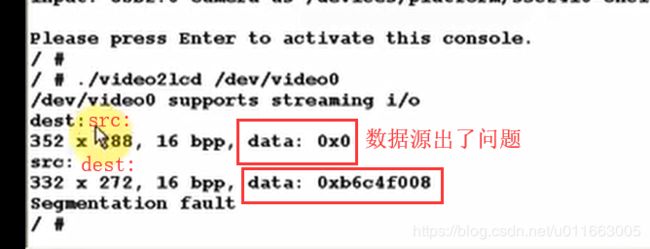
源数据来自convert:
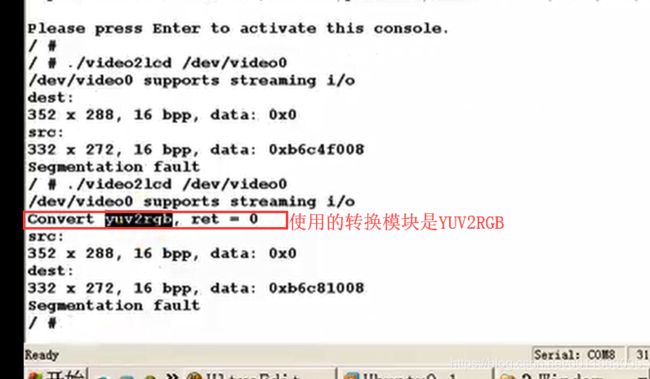
定位至Yuv2RgbConvert函数中:
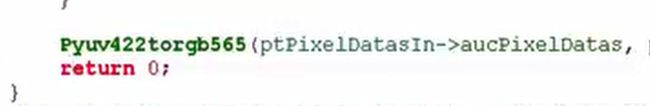
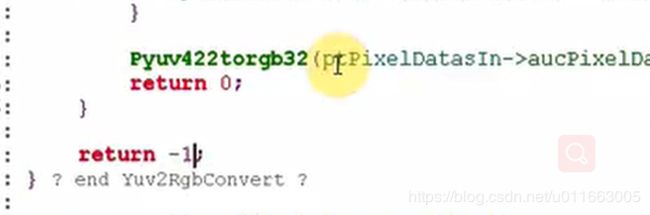

这时看到返回-1错误。也就是说在Yuv2RgbConvert函数中,输出格式ptVideoBufOut->iPixelFormat 既不等于V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565,也不等于 V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB32。
回到main.c的初始化部分代码:
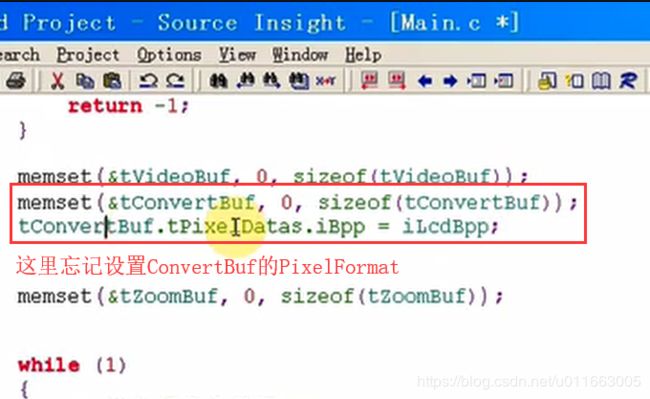

这里应该设置为显示器的格式。
可以正常显示了(使用了环宇飞扬YUV格式摄像头)。
现在接上自制的摄像头(输出MJPEG格式),测试也没问题。
六、在LCD上显示摄像头图像6_在PC(Ubuntu)上显示
应用程序以面向对象的思路来写,极大的增强了程序的可扩展性: 比如现在想在PC端显示摄像头的数据。之前负责在LCD上显示的文件是fb.c,现在只需要再构造一个crt.c即可。
参考之前的电子书源码crt.c:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
static GraphicsContext *physicalscreen;
static GraphicsContext *virtualscreen;
static int CRTDeviceInit(void);
static int CRTShowPixel(int iX, int iY, unsigned int dwColor);
static int CRTCleanScreen(unsigned int dwBackColor);
static int CRTDeviceExit(void);
static int CRTShowPage(PT_PixelDatas ptPixelDatas);
static T_DispOpr g_tCRTOpr = {
.name = "crt",
.DeviceInit = CRTDeviceInit,
.DeviceExit = CRTDeviceExit,
.ShowPixel = CRTShowPixel,
.CleanScreen = CRTCleanScreen,
.ShowPage = CRTShowPage,
};
/* 1. 首先初始化VGA接口 */
static int CRTDeviceInit(void)
{
vga_init();
vga_setmode(G640x480x64K);
gl_setcontextvga(G640x480x64K);
/* 获得"物理屏幕" */
physicalscreen = gl_allocatecontext();
gl_getcontext(physicalscreen);
/* 获得"虚拟屏幕" */
gl_setcontextvgavirtual(G640x480x64K);
virtualscreen = gl_allocatecontext();
gl_getcontext(virtualscreen);
/* 设置"虚拟屏幕"为当前所使用的"屏幕" */
gl_setcontext(virtualscreen);
g_tCRTOpr.iXres = 640;
g_tCRTOpr.iYres = 480;
g_tCRTOpr.iBpp = 32;
g_tCRTOpr.iLineWidth = g_tCRTOpr.iXres * g_tCRTOpr.iBpp / 8;
//申请显存
g_tCRTOpr.pucDispMem = malloc(g_tCRTOpr.iLineWidth * g_tCRTOpr.iYres);
return 0;
}
//退出函数,做清理工作
static int CRTDeviceExit(void)
{
free(g_tCRTOpr.pucDispMem);
gl_clearscreen(0);
vga_setmode(TEXT);
return 0;
}
//像素值显示函数,对于输入的每一个像素值,在显示器上进行显示
static int CRTShowPixel(int iX, int iY, unsigned int dwColor)
{
int iRed, iGreen, iBlue;
iRed = (dwColor >> 16) & 0xff;
iGreen = (dwColor >> 8) & 0xff;
iBlue = (dwColor >> 0) & 0xff;
// gl_setpalettecolor(5, iRed>>2, iGreen>>2, iBlue>>2); /* 0xE7DBB5 */ /* 泛黄的纸 */
// vga_setcolor(5);
// vga_drawpixel(iX, iY);
gl_setpixelrgb(iX, iY, iRed, iGreen, iBlue);
gl_copyscreen(physicalscreen);
return 0;
}
//清屏函数
static int CRTCleanScreen(unsigned int dwBackColor)
{
int iX;
int iY;
int iRed, iGreen, iBlue;
iRed = (dwBackColor >> 16) & 0xff;
iGreen = (dwBackColor >> 8) & 0xff;
iBlue = (dwBackColor >> 0) & 0xff;
// gl_setpalettecolor(4, iRed>>2, iGreen>>2, iBlue>>2); /* 0xE7DBB5 */ /* 泛黄的纸 */
// vga_setcolor(4);
for (iX = 0; iX < 320; iX++)
for (iY = 0; iY < 200; iY++)
gl_setpixelrgb(iX, iY, iRed, iGreen, iBlue);
gl_copyscreen(physicalscreen);
return 0;
}
/* 将显存中的数据刷到VGA显示器上去 */
static int CRTShowPage(PT_PixelDatas ptPixelDatas)
{
int x, y;
//pdwColor指向图像像素值所存放的地方
unsigned int *pdwColor = (unsigned int *)ptPixelDatas->aucPixelDatas;
//存放每个像素的颜色值
unsigned int dwColor;
unsigned int dwRed, dwGreen, dwBlue;
if (ptPixelDatas->iBpp != 32)
{
return -1;
}
for (y = 0; y < g_tCRTOpr.iYres; y++) //一行一行处理图像数据
{
for (x = 0; x < g_tCRTOpr.iXres; x++) //对每一行的每一个像素逐个处理
{
/* 0x00RRGGBB */
dwColor = *pdwColor++;
dwRed = (dwColor >> 16) & 0xff;
dwGreen = (dwColor >> 8) & 0xff;
dwBlue = (dwColor >> 0) & 0xff;
// CRTShowPixel(x, y, dwColor);
gl_setpixelrgb(x, y, dwRed, dwGreen, dwBlue);
}
}
gl_copyscreen(physicalscreen);
return 0;
}
int CRTInit(void)
{
return RegisterDispOpr(&g_tCRTOpr);
}
main函数中:


CRTinit同样是注册一个操作函数结构体。

在main函数中选择CRT作为显示器。
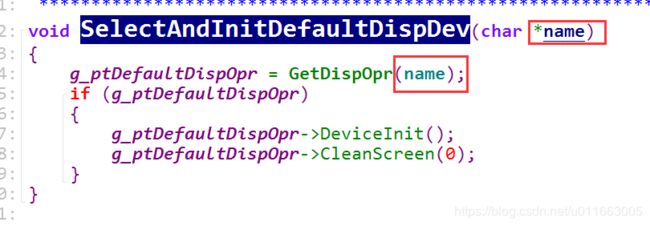
GetDispOpr函数根据name取出相应的操作函数结构体。
出现问题!!编译的时候找不到有关VGA的头文件,原因是缺少VGA有关的库,需要去安装。
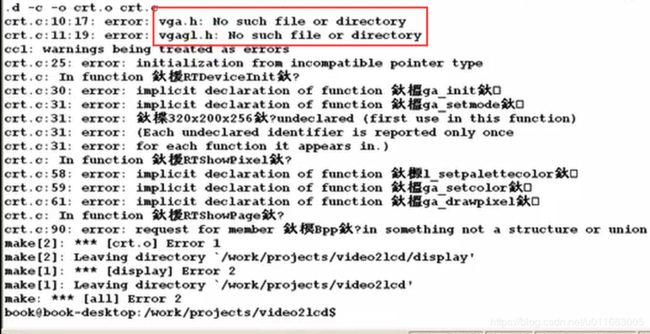
看之前的笔记:
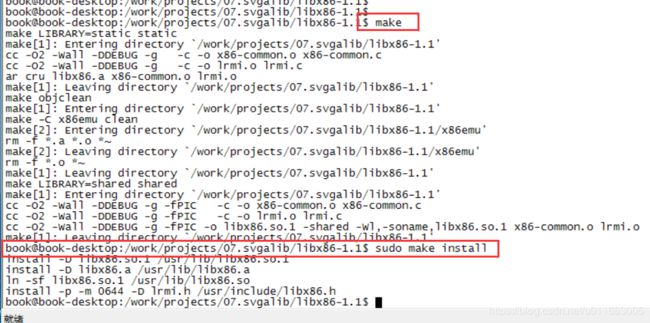
(1)首先安装libx86库
下载地址
http://packages.ubuntu.com/lucid/libx86-1
tar xzf libx86_1.1+ds1.orig.tar.gz
gunzip libx86_1.1+ds1-6.diff.gz
cd libx86-1.1/
patch -p1 < ../libx86_1.1+ds1-6.diff
make // 出错,修改lrmi.c,添加宏, 参考561491.patch
make
sudo make install
http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main//libx/libx86/
libx86_1.1+ds1.orig.tar.bz2 // 修改
sudo apt-get source libx86
(2)再安装svgalib库
下载地址:
https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/svgalib/1:1.4.3-30
svgalib_1.4.3.orig.tar.gz
svgalib_1.4.3-30.debian.tar.gz
svgalib_1.4.3-30.dsc
打补丁
tar xzf svgalib_1.4.3.orig.tar.gz
tar xzf svgalib_1.4.3-30.debian.tar.gz
cd svgalib-1.4.3.orig/
for file in ../debian/patches/*.patch; do patch -p1 < $file; done
编译安装:
sudo make install // 编译出错,需要安装libx86
再 sudo make install
注意:
在终端模式下(ctrl+alt+shift+f1,退出按下Alt+f7)执行应用程序时找不到libvga库,如下操作
sudo cp /usr/local/lib/libvga /lib -d*
查看源码Debug:
在PC端显示的过程中用到的核心函数是:CRTShowPixel函数

该函数的实现逻辑是:首先设置调色板;接着选择第5个调色板;最后画像素点。
这段代码是之前显示电子书的,只设置了一种调色板,且只设置了其中第5号颜色。
需要修改显示像素的代码,深入了解svgalib:参考SVGAlib Tutorials文档:
http://www.svgalib.org/jay/beginners_guide/beginners_guide.html
这里需要了解svgalib库中对VGA显示的实现方法:
在显示图像的时候,先将图像描绘在虚拟的屏幕上(virtualscreen),然后再将像素值拷贝至物理屏幕上进行显示(physicalscreen)。
这里只保留跟显示像素有关的代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* 1. 首先定义两个全局指针变量 */
static GraphicsContext *physicalscreen;
static GraphicsContext *virtualscreen;
static int CRTShowPixel(int iX, int iY, unsigned int dwColor);
static T_DispOpr g_tCRTOpr = {
.name = "crt",
.DeviceInit = CRTDeviceInit,
.DeviceExit = CRTDeviceExit,
.ShowPixel = CRTShowPixel,
.CleanScreen = CRTCleanScreen,
.ShowPage = CRTShowPage,
};
static int CRTDeviceInit(void)
{
/* 2. 参考SVGAlib Tutorials对VGA进行初始化 */
vga_init();
vga_setmode(G640x480x64K); //这种模式下不需要使用调色板
gl_setcontextvga(G640x480x64K);
/* 获得"物理屏幕" */
physicalscreen = gl_allocatecontext();
gl_getcontext(physicalscreen);
/* 获得"虚拟屏幕" */
gl_setcontextvgavirtual(G640x480x64K);
virtualscreen = gl_allocatecontext();
gl_getcontext(virtualscreen);
/* 设置"虚拟屏幕"为当前所使用的"屏幕" */
gl_setcontext(virtualscreen);
****************************************************************/
g_tCRTOpr.iXres = 640;
g_tCRTOpr.iYres = 480;
g_tCRTOpr.iBpp = 32;
g_tCRTOpr.iLineWidth = g_tCRTOpr.iXres * g_tCRTOpr.iBpp / 8;
g_tCRTOpr.pucDispMem = malloc(g_tCRTOpr.iLineWidth * g_tCRTOpr.iYres);
return 0;
}
static int CRTShowPixel(int iX, int iY, unsigned int dwColor)
{
int iRed, iGreen, iBlue;
iRed = (dwColor >> 16) & 0xff;
iGreen = (dwColor >> 8) & 0xff;
iBlue = (dwColor >> 0) & 0xff;
// gl_setpalettecolor(5, iRed>>2, iGreen>>2, iBlue>>2); /* 0xE7DBB5 */ /* 泛黄的纸 */
// vga_setcolor(5);
// vga_drawpixel(iX, iY);
gl_setpixelrgb(iX, iY, iRed, iGreen, iBlue);
gl_copyscreen(physicalscreen);
return 0;
}
static int CRTCleanScreen(unsigned int dwBackColor)
{
int iX;
int iY;
int iRed, iGreen, iBlue;
iRed = (dwBackColor >> 16) & 0xff;
iGreen = (dwBackColor >> 8) & 0xff;
iBlue = (dwBackColor >> 0) & 0xff;
// gl_setpalettecolor(4, iRed>>2, iGreen>>2, iBlue>>2); /* 0xE7DBB5 */ /* 泛黄的纸 */
// vga_setcolor(4);
for (iX = 0; iX < 320; iX++)
for (iY = 0; iY < 200; iY++)
gl_setpixelrgb(iX, iY, iRed, iGreen, iBlue);
gl_copyscreen(physicalscreen);
return 0;
}
static int CRTShowPage(PT_PixelDatas ptPixelDatas)
{
int x, y;
unsigned int *pdwColor = (unsigned int *)ptPixelDatas->aucPixelDatas;
unsigned int dwColor;
unsigned int dwRed, dwGreen, dwBlue;
if (ptPixelDatas->iBpp != 32)
{
return -1;
}
for (y = 0; y < g_tCRTOpr.iYres; y++)
{
for (x = 0; x < g_tCRTOpr.iXres; x++)
{
/* 0x00RRGGBB */
dwColor = *pdwColor++;
dwRed = (dwColor >> 16) & 0xff;
dwGreen = (dwColor >> 8) & 0xff;
dwBlue = (dwColor >> 0) & 0xff;
// CRTShowPixel(x, y, dwColor);
//把x,y坐标的点描为RGB三原色
gl_setpixelrgb(x, y, dwRed, dwGreen, dwBlue);
}
}
//设置完一帧(一幅图像)中每个像素色RGB颜色后,刷入屏幕。
gl_copyscreen(physicalscreen);
return 0;
}
还存在一个问题:就是无法正常退出:
(1)首先根据svgalib的说明在crt.c文件中加入退出函数:
static int CRTDeviceExit(void)
{
free(g_tCRTOpr.pucDispMem);
gl_clearscreen(0);
vga_setmode(TEXT);
return 0;
}
(2)在main函数中找到调用该退出函数的方法:参考之前的源码:
使用最简单的查询方式:
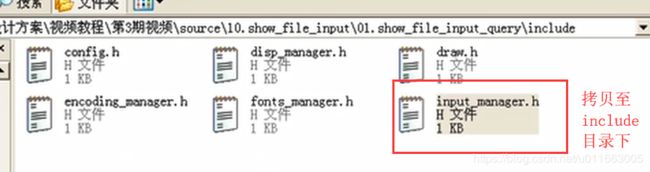
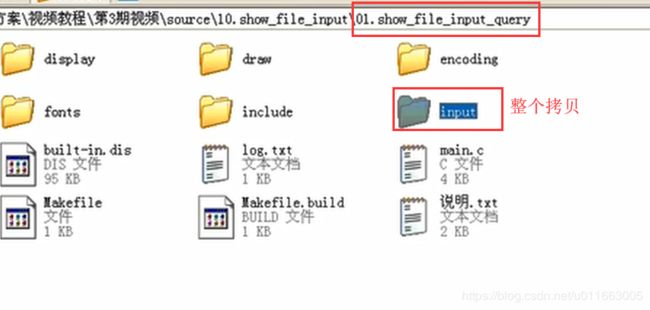
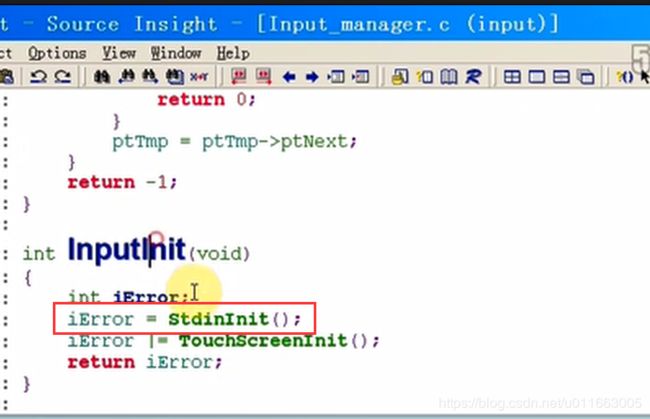
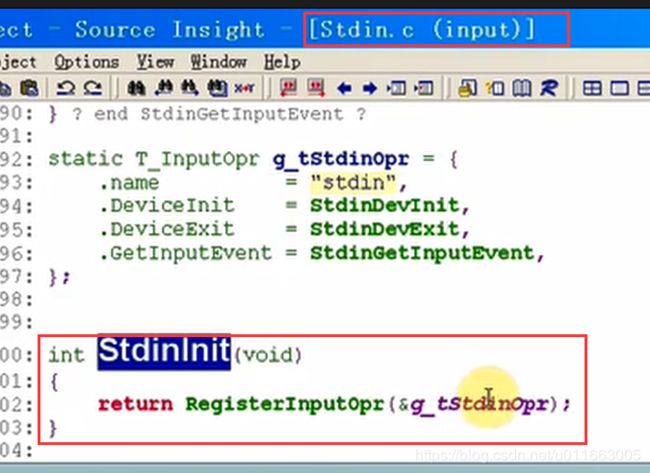
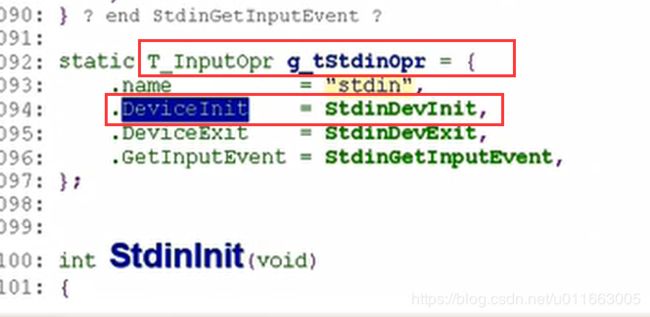
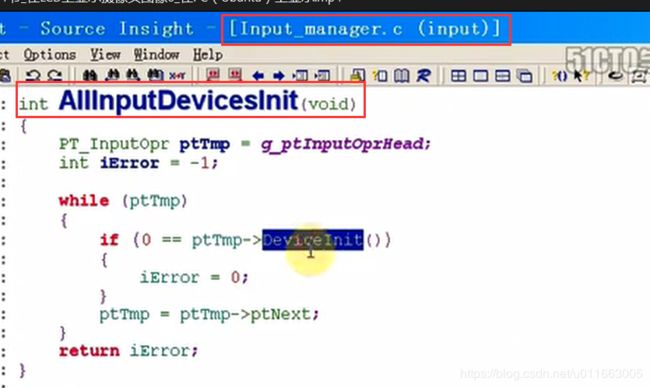
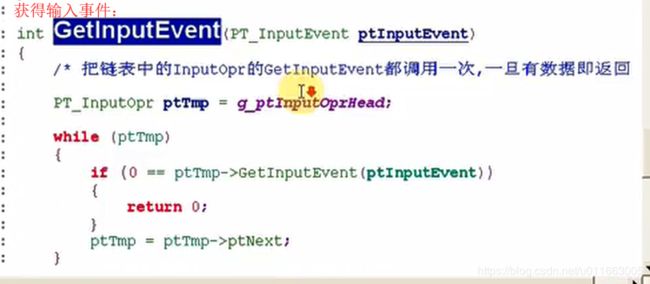
input文件夹中的input_manager.c和Stdin.c中的结构与之前的设计思想类似,都是用了模块坏的程序设计思想。
(1)input_manager.c: