企业级Redis---------(redis结合lnmp架构做mysql的缓存服务器)以及(利用Gearmand做mysql缓存服务器)
企业级Redis---------(redis结合lnmp架构做mysql的缓存服务器)以及(利用Gearmand做mysql缓存服务器)
一、redis结合lnmp架构做mysql的缓存服务器
实验环境:server1中配置nginx和php,在server2中配置redis,在server3中配置数据库
[root@server1 ~]# killall redis-server
-bash: killall: command not found
[root@server1 ~]# yum whatprovides */killall
[root@server1 ~]# yum install -y psmisc-22.20-15.el7.x86_64
1.在server1中配置nginx
1. 编译安装nginx:
tar zxf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.16.1
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx
yum install gcc pcre-devel zlib-devel -y 解决依赖性
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx
make && make install
2.配置并启动nginx:
cd /usr/local/nginx/
ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/ #制作软连接
cd conf/
vim nginx.conf
修改以下内容:
2 user nginx nginx;
43 location / {
44 root html;
45 index index.php index.html index.htm;
46 }
65 location ~ \.php$ {
66 root html;
67 fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
68 fastcgi_index index.php;
69 # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
70 include fastcgi.conf;
71 }
useradd -u 900 nginx
nginx #启动
netstat -antlp
在server1中配置php
安装后启动:
systemctl start php-fpm
netstat -antlp
2.在server2中配置redis
注意:因为在之前的博客中server2做过redis的主从复制,所以此处还原实验环境
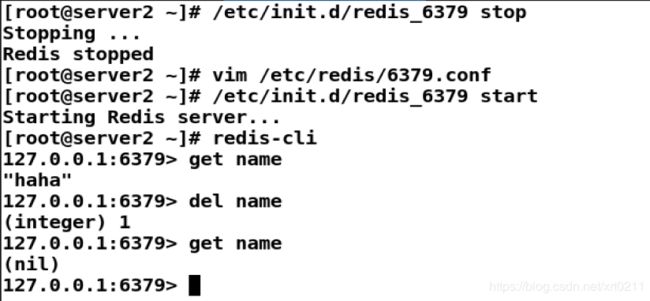
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop
vim /etc/redis/6379.conf #删除最后一行(1379 slaveof 192.168.43.71 6379)
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 start
测试redis:可以正常使用
[root@server2 ~]# redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> get name
"haha"
127.0.0.1:6379> del name
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> get name
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379>
3.在server3中配置数据库
rpm -qa | grep mysql #查看之前是否安装过mysql,如果安装过要卸载
yum install -y mariadb-server #实验不需要用mysql,安装mariadb即可
systemctl start mariadb
mysql_secure_installation #安全初始化
授权用户:
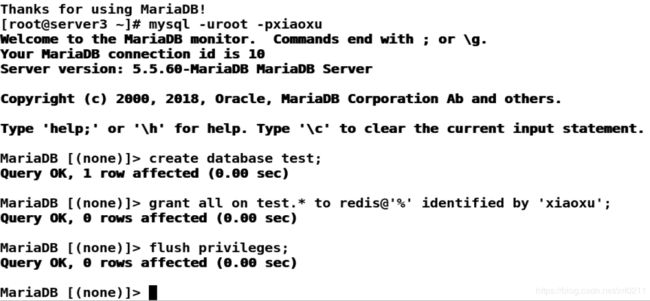
[root@server3 ~]# mysql -uroot -pxiaoxu
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 10
Server version: 5.5.60-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> create database test;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on test.* to redis@'%' identified by 'xiaoxu';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]>
在server1中:
配置测试页面:
cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
vim index.php
<?php
$redis = new Redis();
$redis->connect('192.168.43.72',6379) or die ("could net connect redis server"); #此处ip为安装redis的虚拟机ip(server2)
# $query = "select * from test limit 9";
$query = "select * from test";
for ($key = 1; $key < 10; $key++)
{
if (!$redis->get($key))
{
$connect = mysql_connect('192.168.43.73','redis','xiaoxu'); #此处ip为安装mariadb的虚拟机ip(server3);密码为数据库授权的用户密码
mysql_select_db(test);
$result = mysql_query($query);
//如果没有找到$key,就将该查询sql的结果缓存到redis
while ($row = mysql_fetch_assoc($result))
{
$redis->set($row['id'],$row['name']);
}
$myserver = 'mysql';
break;
}
else
{
$myserver = "redis";
$data[$key] = $redis->get($key);
}
}
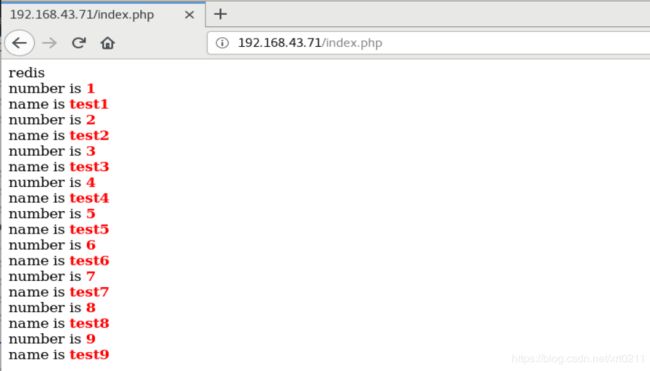
echo $myserver;
echo "
";
for ($key = 1; $key < 10; $key++)
{
echo "number is $key";
echo "
";
echo "name is $data[$key]";
echo "
";
}
?>
为server3上的mysql的test库加入一些数据:
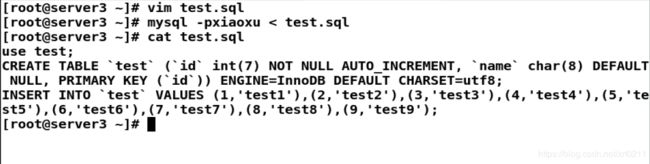
vim test.sql
use test;
CREATE TABLE `test` (`id` int(7) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` char(8) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `test` VALUES (1,'test1'),(2,'test2'),(3,'test3'),(4,'test4'),(5,'test5'),(6,'test6'),(7,'test7'),(8,'test8'),(9,'test9');
[root@server3 ~]# vim test.sql
[root@server3 ~]# mysql -pxiaoxu < test.sql
[root@server3 ~]# cat test.sql
use test;
CREATE TABLE `test` (`id` int(7) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` char(8) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `test` VALUES (1,'test1'),(2,'test2'),(3,'test3'),(4,'test4'),(5,'test5'),(6,'test6'),(7,'test7'),(8,'test8'),(9,'test9');
[root@server3 ~]#
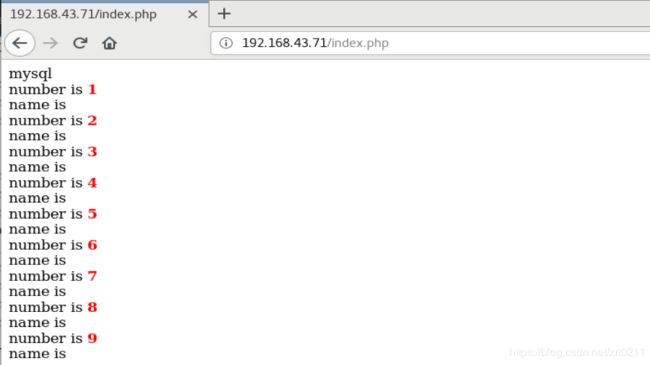
测试
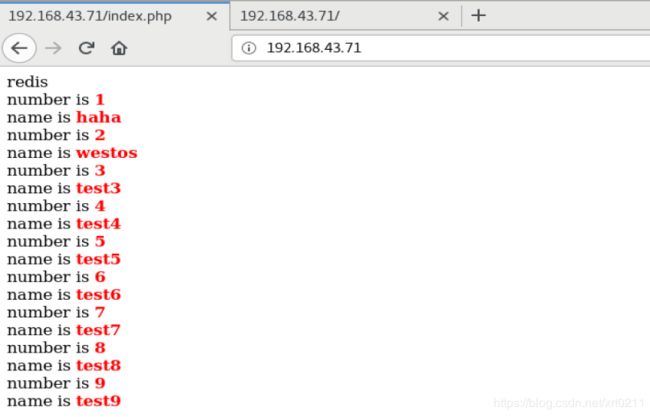
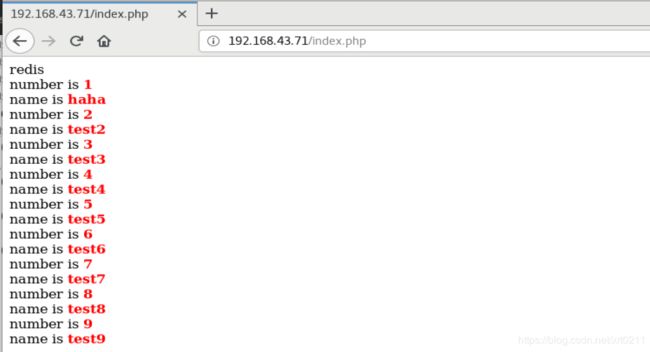
浏览器访问192.168.43.71
进入时查看到数据是从mysql获取到的;刷新后数据从redis中获取,再刷新也是从redis中获取
存在的问题
如果此时 mysql 数据发生变更,redis会同步吗?
测试:
修改数据库的数据信息:
MariaDB [(none)]> use test;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
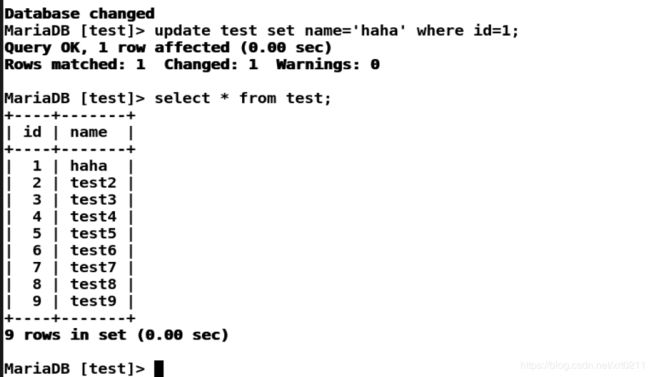
MariaDB [test]> update test set name='haha' where id=1;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
MariaDB [test]> select * from test;
+----+-------+
| id | name |
+----+-------+
| 1 | haha |
| 2 | test2 |
| 3 | test3 |
| 4 | test4 |
| 5 | test5 |
| 6 | test6 |
| 7 | test7 |
| 8 | test8 |
| 9 | test9 |
+----+-------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [test]>
[root@server2 ~]# redis-cli
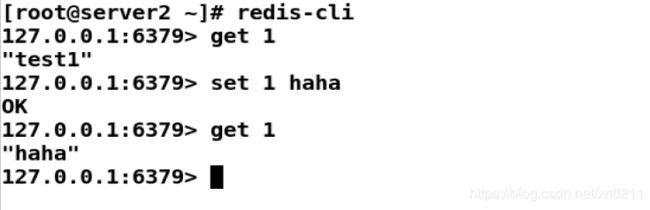
127.0.0.1:6379> get 1 #并没有修改为haha
"test1"
127.0.0.1:6379> set 1 haha #手动修改为haha
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get 1
"haha"
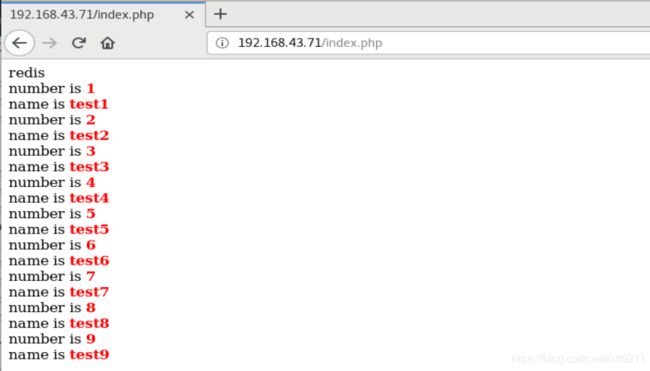
此时在刚才的测试页面中刷新查看,数据才更新了。
这是一个很大的弊端,我们必须时刻查看数据库的数据是否有更新,再手动在redis上更新,这显然不符合企业要求。
那么这个问题该如何解决呢?
需要用到gearmand
二、Redis—利用Gearmand做mysql缓存服务器
1.什么是Gearmand?
Gearmand是一个用来把工作委派给其它机器、分布式的调用更适合做某项工作的机器、并
发的做某项工作在多个调用间做负载均衡、或用来调用其它语言的函数的系统。
简单来讲,就是客户端程序把请求提交给gearmand,gearmand会把请求转发给合适的worker来处理这个请求,最后还通过gearmand返回结果。
运行流程:
Client --> Job --> Worker
- Client 请求发起者,客户端程序可以是任何一种语言:C 、PHP 、Perl 、Python等。
- Job 请求调度者,负载协调把 Client 发出的请求转发给合适的Worker。
- Worker 请求处理者,处理 Job 分发来的请求,可以是任何一种语言
2.部署过程
在server1中
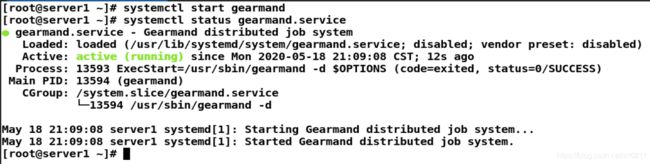
启动gearmand:
systemctl start gearmand
systemctl status gearmand
在server3中:
yum install unzip -y
unzip lib_mysqludf_json-master.zip 获取安装包lib
安装 mariadb-devel:
yum install -y mariadb-devel.x86_64
编译模块:
yum install gcc -y
cd lib_mysqludf_json-master
gcc $(mysql_config --cflags) -shared -fPIC -o lib_mysqludf_json.so lib_mysqludf_json.c
将模块放到mysql插件目录:
cp lib_mysqludf_json-master/lib_mysqludf_json.so /usr/lib64/mysql/plugin/
在数据库中查看:
MariaDB [(none)]> show global variables like 'plugin_dir';
注册udf函数:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE FUNCTION json_object RETURNS STRING SONAME'lib_mysqludf_json.so';
安装插件管理gearman的分布式队列:
tar zxf gearman-mysql-udf-0.6.tar.gz
yum install libevent-devel-2.0.21-4.el7.x86_64.rpm libgearman-* -y
cd gearman-mysql-udf-0.6
./configure --libdir=/usr/lib64/mysql/plugin/ --with-mysql
make && make install
注册udf函数:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE FUNCTION gman_do_background RETURNS STRING SONAME 'libgearman_mysql_udf.so';
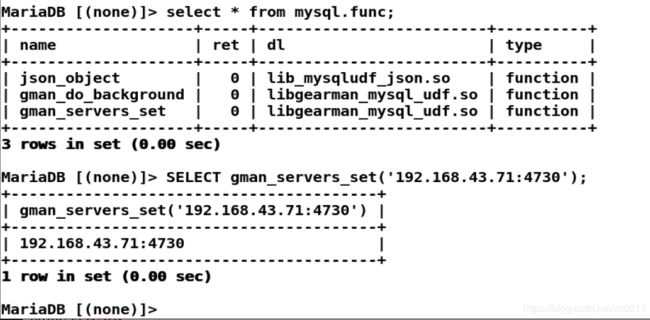
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE FUNCTION gman_servers_set RETURNS STRING SONAME 'libgearman_mysql_udf.so';
查看函数:
MariaDB [(none)]> select * from mysql.func;
指定gman服务信息:
MariaDB [(none)]> SELECT gman_servers_set('192.168.43.71:4730');
vim test.sql
use test;
#CREATE TABLE `test` (`id` int(7) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` char(8) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
#INSERT INTO `test` VALUES (1,'test1'),(2,'test2'),(3,'test3'),(4,'test4'),(5,'test5'),(6,'test6'),(7,'test7'),(8,'test8'),(9,'test9');
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER datatoredis AFTER UPDATE ON test FOR EACH ROW BEGIN
SET @RECV=gman_do_background('syncToRedis', json_object(NEW.id as `id`, NEW.name as `name`));
END$$
DELIMITER ;
导入数据:
mysql -pxiaoxu < test.sql
查看触发器:
MariaDB [(none)]> SHOW TRIGGERS FROM test;
在server1中:
编写gman的worker端:
cd /usr/local
vim worker.php
<?php
$worker = new GearmanWorker();
$worker->addServer();
$worker->addFunction('syncToRedis', 'syncToRedis');
$redis = new Redis();
$redis->connect('192.168.43.72', 6379);
while($worker->work());
function syncToRedis($job)
{
global $redis;
$workString = $job->workload();
$work = json_decode($workString);
if(!isset($work->id)){
return false;
}
$redis->set($work->id, $work->name);
}
?>
后台运行worker:
nohup php /usr/local/worker.php &> /dev/null &
测试
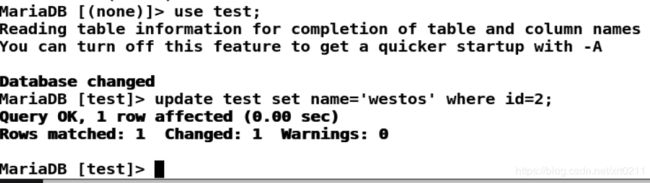
修改数据库内容:
MariaDB [test]> update test set name='westos' where id=2;
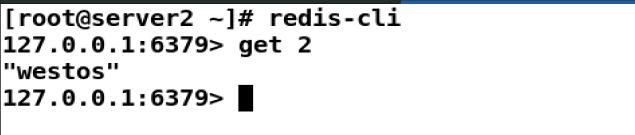
redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> get 2
"westos"