数据结构总结一——堆
数据结构总结——堆
-
- 1.堆的基本概念
- 2.代码讲解
-
- 1.堆的构建
- 2.插入元素
- 3.堆顶元素出列
- 4.完整代码及主函数
- 3.企业实战——堆排序
1.堆的基本概念
摘自百度百科:
堆(Heap)是计算机科学中一类特殊的数据结构的统称。堆通常是一个可以被看做一棵完全二叉树的数组对象。
1.堆中某个结点的值总是不大于(最大堆)或不小于(最小堆)其父结点的值;
2.堆总是一棵完全二叉树。
从结构上看,堆是一棵完全二叉树。但它实际上是以完全二叉树的数组映射形式储存在数组中的。树中每个结点的值总是不大于(最大堆)或不小于(最小堆)其父结点的值。所以堆顶元素总是所有元素中的最大值或最小值。已经构建好的最大堆或最小堆可以直接存放在数组中。
从功能上看,最大堆,最小堆的结构成就了它特有的功能,即能够很方便高效的取得数据中的最大值,最小值。
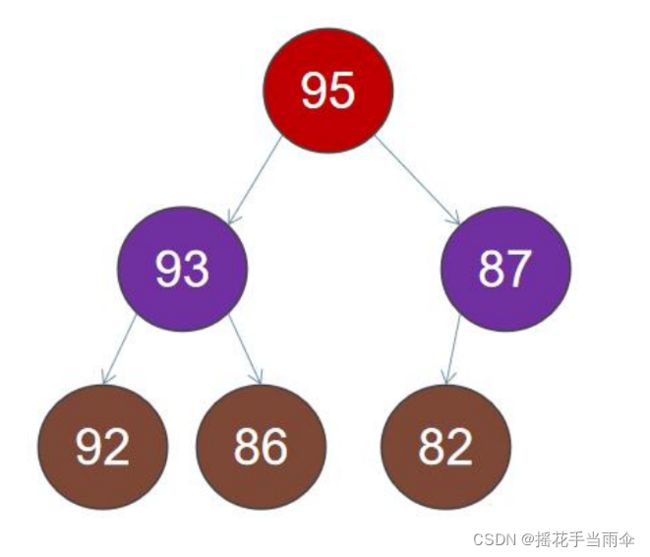
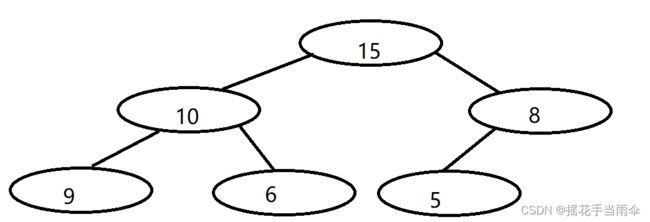
下图是一个已经构建好的最大堆。
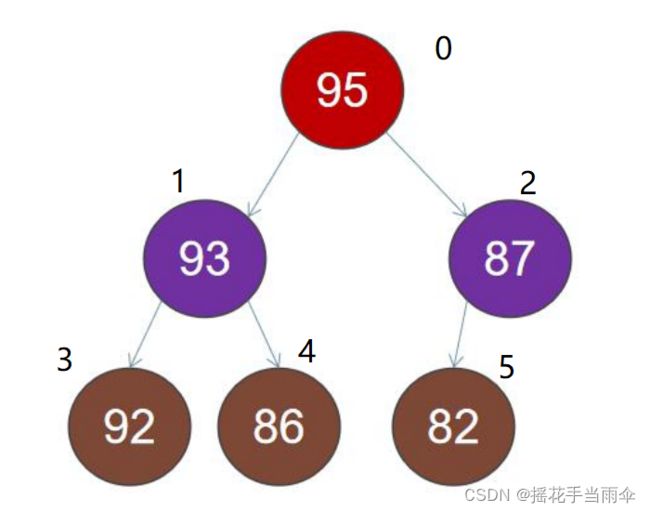
把上图所示已经构建好的最大堆中的节点分别编号。
如下图:
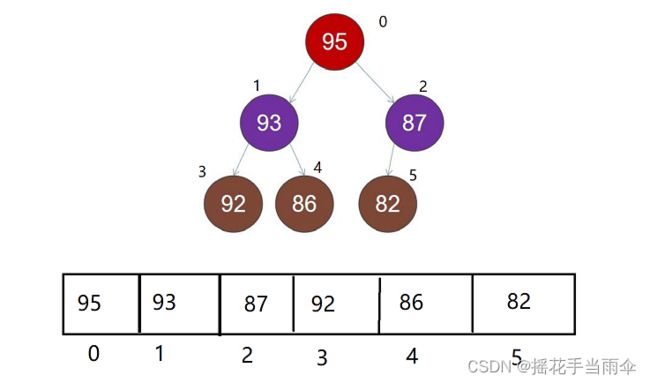
对于已经是最大堆或最小堆的堆,其各个元素是按顺序依次储存在数组中的。
知道一个堆元素在数组中的下标或在完全二叉树中的位置,就能找到它在完全二叉树映像中的父节点的下标。举个例子:数组下标为二的元素是87,那么它的父节点的下标应该为 ( 2 - 1 ) / 2,即0 。通用的公式应该是 (i-1) / 2。找到当前节点的子节点也很简单,直接给公式,左子节点 2i+1,右子节点 2i+2 。
2.代码讲解
注意下文都是以构建最大堆举例解释的。
值得注意的是,我们对堆的理解,很多都是建立在完全二叉树之上的,但实际上堆中元素都是储存在数组中的,我们也是在数组上进行操作的。
1.堆的构建
有一个无序数组,我们要把它构建成最大堆,应该怎么做呢?
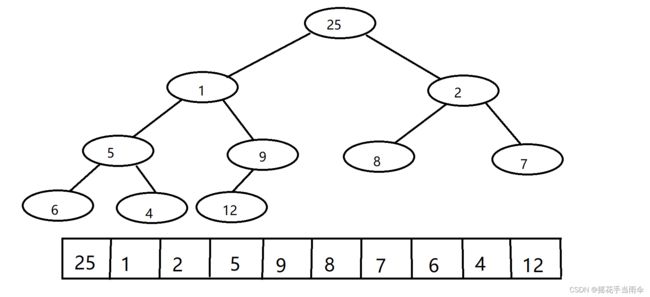
看下图(ps:这图画的也太丑了):
如图是一个无序数组映射成的完全二叉树映像。我们要将其改造成最大堆。改造方法是,从最后一个节点的父节点开始(即从上图12的父节点9开始),将父节点与子节点比较,如果父节点是父节点与子节点中最大的,则不变,如果不是,则将父节点与子节点中的较大者交换。处理完一个父节点,移动至上一个节点(即处理完节点9移动到节点5,处理完节点5移动到节点2 ,处理完2,移动到节点1,以此类推。),继续判断,直至处理完所有非叶子节点。
其实这很好理解,堆的性质决定了父节点必须小于或大于它的子节点,只要我们保证所有父节点都大于或小于它的子节点,那原二叉树就能被构建成一个堆。因为我们这里是构建最大堆,所以父节点需大于子节点。上述步骤就是遍历所有的父节点并让每一个父节点都大于它的子节点。
需要注意的是,交换后的父节点可能不能与新的子节点形成最大堆。举个例子,图中的1节点在与9交换后仍是小于它的新子节点12的。所以在这里我们应该进行迭代或递归处理,以确保交换下来的节点不会破坏已经处理好的节点。
#include 2.插入元素
插入元素的方法是先将堆元素个数加一,再将要插入的元素插入到堆的最后一个元素,再调整堆使之重新成为一个最大堆。
具体的调整方法是,将新插入的节点与父节点比较,如果大于父节点,则与父节点交换,再比较插入节点与新的父节点的值。重复这一步骤,直至插入节点小于父节点或插入节点已升至头节点。插入节点的时间复杂度为log n(即以2为底数的对数,不知道怎么输出一个小的2,汗)
#include 3.堆顶元素出列
堆顶元素出列,我们采取的方法是,先使用一个临时变量保存堆顶元素,再把堆中最后一个元素放到堆顶,堆元素个数减一。再调整堆使之再次成为一个最大堆。最后把临时变量作为返回值返回。
int adjust_down(Heap*& heap, int place, int length) { //递归函数,不断的调整节点位置
if (place >= length) {
return 1;
}
int max_ = 0;
if ((2 * place + 2) < length) { //如果父节点有两个子节点
max_ = heap->data[2 * place + 1] > heap->data[2 * place + 2] ? 2 * place + 1 : 2 * place + 2;
if (heap->data[max_] > heap->data[place]) {
swap(heap->data[max_], heap->data[place]);
adjust_down(heap, max_, length);
}
else {
return 1;
}
}
else if ((2 * place + 1) < length && (2 * place + 2) == length) { //如果父节点只有一个子节点
if (heap->data[2 * place + 1] > heap->data[place]) {
swap(heap->data[2 * place + 1], heap->data[place]);
adjust_down(heap, 2 * place + 1, length);
}
else {
return 1;
}
}
else { //如果父节点没有子节点
return 1;
}
}
int pop_heap(Heap*& heap) { //堆顶元素出列
if (heap->size == 0) {
cout << "堆中元素为空" << endl;
return -1;
}
int ret = 0;
ret = heap->data[0];
heap->data[0] = heap->data[heap->size - 1];
--heap->size;
adjust_down(heap, 0, heap->size); //末尾元素到了堆顶,最大堆被破坏,需重新调整
return ret;
}
4.完整代码及主函数
#include 结果:
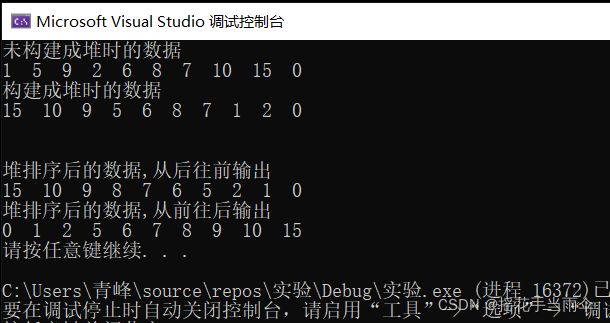
3.企业实战——堆排序
如果已经构建好了一个最大堆,并实现了堆中元素出列功能,那么堆排序就很简单了,只要让堆中所有元素出列,储存在一个新建的数组中,那么数组中的元素就是大小有序的。
但这样需要额外的数组空间,我们能不能利用堆中已有的空间实现呢?
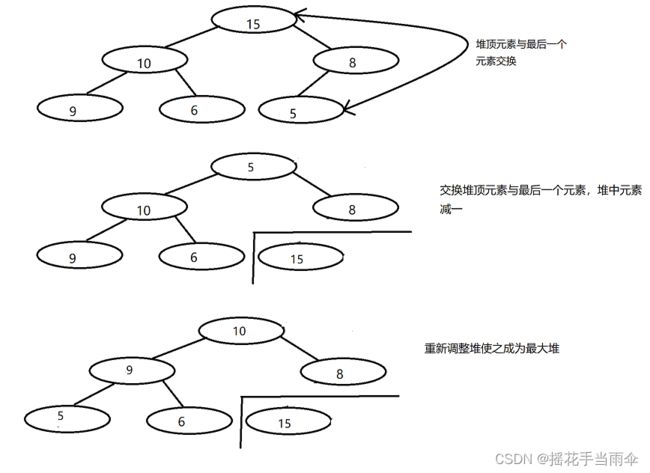
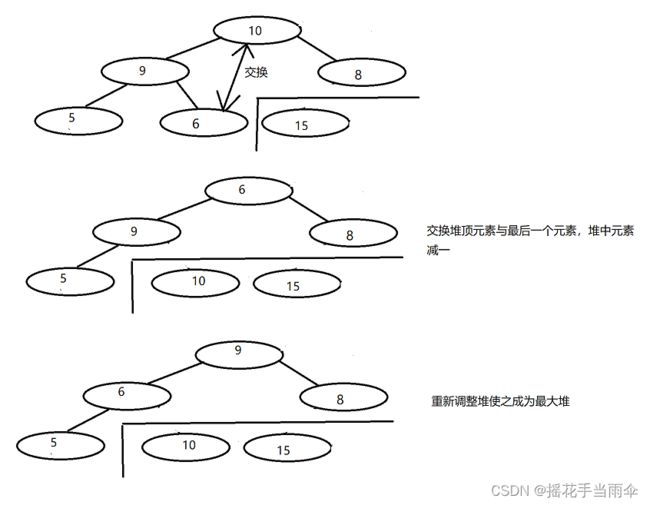
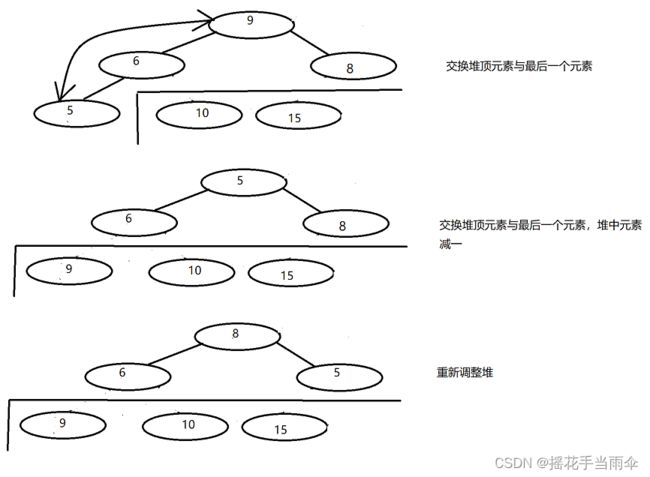
答案是肯定的,我们在实现堆中元素出列时,并不用一个临时变量保存堆顶元素,而是将其与最后一个元素交换,堆元素减一,重新调整堆使之成为最大堆。这样所有元素出列后,堆中就得到了一个有序序列。
举个例子:
第一步:
第三步:
直至最后堆会变为:
代码:
#include