Pid NameSpace浅分析
1.pid Namespace涉及的基本数据结构
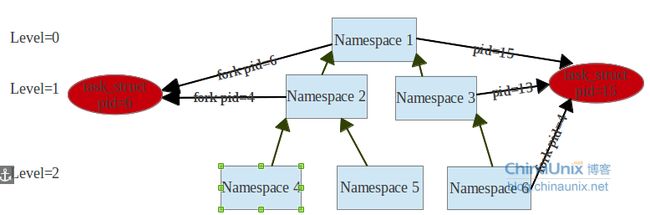
linux通过命名空间管理进程pid,对于同一进程(同一个task_struct),在不同的命名空间中,看到的pid号不相同,每个pid命名空间有一套自己的pid管理方法,所以在不同的命名空间中调用getpid(),看到的pid号是不同的。pid命名空间是一个父子关系的结构,系统初始只有一个pid命名空间,后面如果在fork进程的时候,加上新建pid命名空间的选项,那么这个新的命名空间的父命名空间就是初始的那个命名空间,在这个命名空间fork出的进程,在子命名空间和父命名空间都有一个pid号相对应到这个task_struct上。
从上图中可以看出,假设namespace有3层,如果在Namespace2中fork进程,产生的进程task_struct,如果pid是6,那么在根Namespace1中pid就是6,在Namespace2中pid就是4(自己的一套分配方式,递增方式,如果进程号被占用,就使用下一个空闲的id号,后面重点会说到id号的分配),在Namespace6中fork子进程,因为Namespace6来源于Namespace3,所以子命名空间fork的进程,这个命名空间的父命名空间都会看到这个进程,每个父命名空间根据自己id分配的情况,做一个task_struct到内部id号的映射关系,然后在相应的命名空间中调用getpid会使用当前命名空间中的id号,而不是task_struct中的pid。所以pid命名空间的作用就是,1个task_struct,在不同的命名空间看到的pid是不一样的。
关于pid namespace的管理,首先需要抽象出结构体pidNamespace:include/linux/pid_namespace.h
-
struct pid_namespace { struct kref kref; //引用计数 struct pidmap pidmap[PIDMAP_ENTRIES]; //pid分配的bitmap,如果位为1,表示这个pid已经分配了 int last_pid; //记录上次分配的pid,理论上,当前分配的pid=last_pid+1 struct task_struct *child_reaper; //表示进程结束后,需要这个child_reaper进程对这个进程进行托管 struct kmem_cache *pid_cachep; //高速缓存,这个不太清楚,待这块分析源代码 unsigned int level; //记录这个pid namespace的深度 struct pid_namespace *parent; //记录父pid namespace #ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS struct vfsmount *proc_mnt; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_BSD_PROCESS_ACCT struct bsd_acct_struct *bacct; #endif };
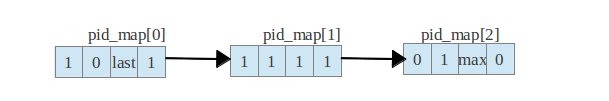
这里比较重要的成员变量就是pidmap,它表示在这个pid命名空间的pid的分配情况,pidmap是个数组,每一位代表这个这个偏移量的pid是否分配出去,初始这个数组只有一个元素。
pidmap的结构:include/linux/pid_namespace.h
-
struct pidmap { atomic_t nr_free;//表示这个bitmap还有多少位为0,就是说对应的pid没有被分配出去 void *page;//表示一段连续的内存空间,每位的0或1表示对应pid是否被分配 };
默认情况下pid最大是32768,那么默认正好是1页能保存下的pid使用情况,linux默认一页的大小是4k=4*1024*8位=32768,如果pid的最大值超过32768那么pidmap数组就用上了,多个pidmap就是为了pid限制大于32768来设计的。
child_reaper的作用见init进程对zombie进程的处理。这个child_reaper的作用就是当父进程先于子进程结束的时候,就把子进程的父进程更新为child_reaper。
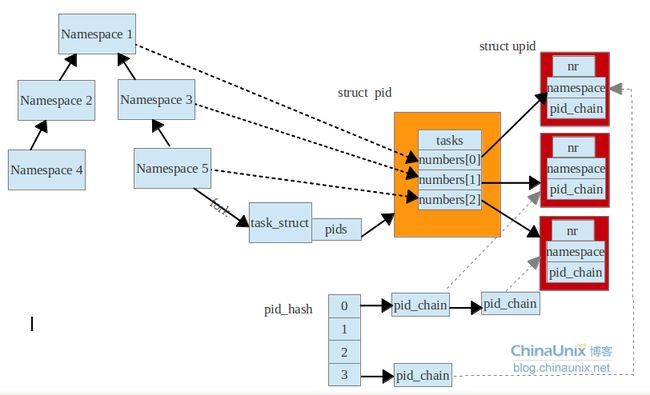
整体的pid管理结构图:
一个进程对应一个task_struct,但是这个进程在多个namespace中都可以看见不同的pid,那么就需要一个表示pid的结构体。代码:include/linux/pid.h
-
struct pid { atomic_t count; //引用次数 unsigned int level; //这个pid的深度 /* lists of tasks that use this pid */ struct hlist_head tasks[PIDTYPE_MAX]; //引用pid的task,看了很多的文章始终搞不清楚什么条件下,会分配同一个pid结构,看了fork中的一些逻辑,发现每次都是创建新的pid结构,这个有待研究 struct rcu_head rcu; struct upid numbers[1]; //这个task_struct在多个命名空间的显示。一个upid就是一个namespace的pid的表示。 };
这里最重要的成员变量就是numbers,它是个数组,表示一个task_struct在每个namespace的id(这个id就是getpid()所得到的值),number[0]表示最顶层的namespace,level=0,number[1]表示level=1,以此类推。
代码:include/linux/pid.h
-
struct upid { /* Try to keep pid_chain in the same cacheline as nr for find_vpid * / int nr; //表示命名空间中的标识 struct pid_namespace *ns; //命名空间 struct hlist_node pid_chain; //hash表中的端点 };
这里nr和ns成对出现,表示进程的在这个ns命名空间的pid为nr。管理这些pid结构,通常把他们防止在hash表中,pid_chain是hash结构中的一个节点,所以pid_chain就是hash表和数据之间的桥梁。这里linux内核中广泛的使用这种hash表,hash表中每个元素都是hlist_node,那么取得每个元素所代表的value,就要通过指针和结构体,来倒推value的指针。实现机理通过函数container_of 代码:include/linux/kernel.h
-
/** * container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structu re * @ptr: the pointer to the member. * @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the member within the struct. * */ #define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \ const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \ (type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
这里ptr是结构体type中的成员变量member的指针,这个函数的实际含义是通过ptr指针根据结构体中member的具体偏移量来得到type结构体的首地址,然后在强转成type的指针。这里typeof是GCC内建函数,offsetof是获得结构体中member变量的指针的偏移量。这样member变量的内存地址减去member的偏移量就可以获得结构体的指针。
遗留的问题:不知道什么情况会多个进程会公用一个pid结构。
2.pid的分配
fork进程的时候,需要为这个进程分配pid,应该根据这个namespace中pidmap的pid分配情况,分配适合的id,大体的过程就是根据当前namespace中的last_pid+1,然后参照pidmap中这位是否为1,如果为1证明当前last_pid+1已经被使用(导致这种情况是id被分配到了最大值,然后再重头选择id,之前的进程如果有还没结束,就会导致last_pid+1,不可用),这时需要找到比last_pid大的值,取离它最近的。如果找不到,则分配失败。
分配pid的函数:kernel/pid.c
static int alloc_pidmap(struct pid_namespace *pid_ns)
{
int i, offset, max_scan, pid, last = pid_ns->last_pid; //取出last_pid
struct pidmap *map;
pid = last + 1; //这里last+1,取得备选pid
//如果pid到了pidmax,那么重头开始寻找可用的pid,从RESERVED_PIDS开始,保留RESERVED_PIDS之前的pid号,默认300
if (pid >= pid_max)
pid = RESERVED_PIDS;
offset = pid & BITS_PER_PAGE_MASK; //取得掩码,获得pidmap的掩码(取余数)。
map = &pid_ns->pidmap[pid/BITS_PER_PAGE]; //根据pid获得pidmap
max_scan = (pid_max + BITS_PER_PAGE - 1)/BITS_PER_PAGE - !offset; //后面单独讲
for (i = 0; i <= max_scan; ++i) {
if (unlikely(!map->page)) { //如果这个pidmap没有分配内存重新分配
void *page = kzalloc(PAGE_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
/* * Free the page if someone raced with us
* installing it:
*/
spin_lock_irq(&pidmap_lock);
if (!map->page) {
map->page = page;
page = NULL;
}
spin_unlock_irq(&pidmap_lock);
kfree(page);
if (unlikely(!map->page))
break;
}
//如果nr_free大于0表示map中还有空闲的pid的位
if (likely(atomic_read(&map->nr_free))) {
do {
//根据man->page基址,offset是偏移量,test_and_set_bit把offset位的值置为1,可以知道如果offset位如果是1,那么还是1,返回原来被set之前的值1,表示这位表示的pid已经被使用,如果返回0,表示之前这位表示的pid未被使用,同时将这位置为了1(这个函数的实现是,内嵌汇编,bts操作)返回0,表示这位未被使用
if (!test_and_set_bit(offset, map->page)) {
atomic_dec(&map->nr_free);//空闲计数减一
pid_ns->last_pid = pid; //重新设置last_pid
return pid;
}
//继续寻找offset之后,位为0的位置
offset = find_next_offset(map, offset);
//找到这个位置,根据map的序号和偏移量转换为pid
pid = mk_pid(pid_ns, map, offset);
/*
* find_next_offset() found a bit, the pid from it
* is in-bounds, and if we fell back to the last
* bitmap block and the final block was the same
* as the starting point, pid is before last_pid.
*/
//这里循环停止会有多种条件,如果偏移量找到了这个pid_map的最后那么就停止查找了,因为已经到了这个map的最后一位了,那么应该从下一个pid_map开始寻找,如果分配的pid大于允许分配最大pid的值,就该从第一个map开始寻找之前可能已经结束的进程,空闲出来的位置
} while (offset < BITS_PER_PAGE && pid < pid_max &&
(i != max_scan || pid < last ||
!((last+1) & BITS_PER_PAGE_MASK)));
}
//如果当前的pid_map没有到最后一个pid_map,就继续寻找下一个pid_map,这时offset=0,重头开始寻找
if (map < &pid_ns->pidmap[(pid_max-1)/BITS_PER_PAGE]) {
++map;
offset = 0;
} else {
//如果当前的pid_map到了最后一个pid_map,那么重头第一个pid_map开始寻找可用的pid,同时将offset设置成RESERVED_PIDS,RESERVED_PIDS之前的pid被保留了。
map = &pid_ns->pidmap[0];
offset = RESERVED_PIDS;
if (unlikely(last == offset))
break;
}
pid = mk_pid(pid_ns, map, offset);
}
return -1;
}代码:
max_scan = (pid_max + BITS_PER_PAGE - 1)/BITS_PER_PAGE - !offset;
这里max_scan代表最多去寻找几个pid_map,这里减去!offset的原因就是,如果offset为0,那么当前的pid_map不需要重新递归寻找掩码之前的空闲位置,因为掩码为0,没有再前面的位置了,如果掩码不为0,那么需要再次递归当前的pid_map,寻找掩码之前的位置的空闲位。
从上面的图看出来,如果last_pid位于第一个pid_map中的第三位,next就是第四位,那么max_scan=4,如果pid_map[1],pid_map[2]都没有空闲位,那么需要重新查找pid_map[0]中的空闲位,如果当前掩码是0,位于第一个pid_map,那么不需要回来查找pid_map[0]。
3.getpid函数的实现
getpid函数是获得当前进程id,如果线程调用这个函数,得到的是这个线程的task_group的pid,那么这个pid是当前namespace下的标识,并不是task_struct中的pid值。这个函数的具体实现在kernel/timer.c
-
SYSCALL_DEFINE0(getpid) { return task_tgid_vnr(current); }
系统调用直接到了这里,task_tgid_vnr的实现:include/linux/sched.h
-
static inline pid_t task_tgid_vnr(struct task_struct*tsk) { return pid_vnr(task_tgid(tsk)); }
这里task_tgid(tsk)函数就是获得当前进程的task_group(进程的task_group就是它自己,线程的task_group是它的父进程,调用pthread_create的那个进程)的pid结构
-
static inline struct pid*task_tgid(struct task_struct*task) { return task->group_leader->pids[PIDTYPE_PID].pid; }
获得pid结构,就应该根据当前namespace获得pid结构中对应的进程标识了,代码:kernel/pid.c
-
pid_t pid_vnr(struct pid*pid) { return pid_nr_ns(pid,current->nsproxy->pid_ns); }
current->nsproxy->pid_ns就是当前pid_namespace
-
pid_t pid_nr_ns(struct pid*pid,struct pid_namespace*ns) { struct upid*upid; pid_t nr=0; if(pid&&ns->level<=pid->level){ //根据namespace的level深度获得upid结构,这里的upid->nr就是这个进程在这个namespace下的进程标识 upid=&pid->numbers[ns->level]; if(upid->ns==ns) nr=upid->nr; } return nr; }
pid命名空间可以把一个进程在不同的命名空间pid管理隔离开,使得每个命名空间都有自己的一套pid命名规则,在看以上的代码后,有疑问:什么情况下多个进程才会共用一个pid结构?希望大家给点建议
上面的问题,在pid Namespace续中解释了问题,多个进程共用一个pid结构的时机:父进程fork出子线程,然后子线程去调用exec,在这调用exec函数的过程中,首先子线程发信号使得父进程停止,子线程去attach父进程pid结构,最后再release
父进程,在段代码中,父进程和子线程会共用一个pid结构。
2.多个进程共享一个pid结构
找了一遍代码,发现在fs/exec.c中有调用attach_pid调用,这个调用的条件是在一个进程fork出一个线程,同时这个线程调用了exec类函数,可以想到线程执行exec类函数,导致了整个线程组的内存结构的变化,线程在执行exec类函数时,调用了函数de_thread函数,这个函数的会杀死进程线程组中的其他的线程,包括主线程,同时把当前线程变成线程组中的主线程,同时把pid,attach到原来的主线程上。同时后面会在执行release_task,这个函数是释放进程zombie状态下剩余的内存结构。 也就是说在attach函数和release_task函数中间多个进程会共用一个pid结构。
引用一段源代码中的注释 2.6.35.13 fs/exec.c:880
880 /* Become a process group leader with the old leader's pid.
881 * The old leader becomes a thread of the this thread group .
882 * Note: The old leader also uses this pid until release_task
883 * is called. Odd but simple and correct.
884 */
下de_thread函数做的一些事情:
819 if (signal_group_exit(sig)) { //对整个group发退出信号
820 /*
821 * Another group action in progress, just
822 * return so that the signal is processed.
823 */
824 spin_unlock_irq(lock);
825 return -EAGAIN;
826 }
827
828 sig->group_exit_task = tsk; //group_exit_tas变量还没太明白搞
829 sig->notify_count = zap_other_threads(tsk); //等待线程组中除了tsk线程的退出
830 if (!thread_group_leader(tsk))
831 sig->notify_count--;
832
833 while (sig->notify_count) {
834 __set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
835 spin_unlock_irq(lock);
836 schedule();
837 spin_lock_irq(lock);
838 }
841 /*
842 * At this point all other threads have exited, all we have to
843 * do is to wait for the thread group leader to become inactive,
844 * and to assume its PID:
845 */
846 if (!thread_group_leader(tsk)) { //如果当前不是线程组主线程,后面会把当前pid,attach到主线程上
847 struct task_struct *leader = tsk->group_leader;
848
849 sig->notify_count = -1; /* for exit_notify() */
850 for (;;) {
851 write_lock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
852 if (likely(leader->exit_state)) //等待主线程的结束
853 break;
854 __set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
855 write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
856 schedule();
880 /* Become a process group leader with the old leader's pid.
881 * The old leader becomes a thread of the this thread group.
882 * Note: The old leader also uses this pid until release_task
883 * is called. Odd but simple and correct.
884 */
885 detach_pid(tsk, PIDTYPE_PID);
886 tsk->pid = leader->pid; //获得主线程的pid结构
887 attach_pid(tsk, PIDTYPE_PID, task_pid(leader)); //把当前线程的pid attach到主线程的pid上,这时pid的tasks会有多个线程结构(task_struct)
888 transfer_pid(leader, tsk, PIDTYPE_PGID);
889 transfer_pid(leader, tsk, PIDTYPE_SID);
890
891 list_replace_rcu(&leader->tasks, &tsk->tasks);
892 list_replace_init(&leader->sibling, &tsk->sibling);
893
894 tsk->group_leader = tsk;
895 leader->group_leader = tsk;
896
897 tsk->exit_signal = SIGCHLD;
898
899 BUG_ON(leader->exit_state != EXIT_ZOMBIE);
900 leader->exit_state = EXIT_DEAD;
901 write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
902
903 release_task(leader); //这时释放掉主线程的内存结构。说明一下:每个task_struct的thread_group字段是内核中hlist中的一个节点,也就是说通过这个字段,通过container_of函数来映射出task_struct结构体,在fork函数中会初始化这个thread_group,如果是fork的线程,那个会把这个task_struct,放到父进程(主线程)的thread_group中,也就是说每个线程的task_group中所代表的线程组中都有当前进程的task_struct,每个线程的主线程就是这些线程的父进程。
代码:Kernel/fork.c
1258 if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) { //线程
1259 current->signal->nr_threads++;
1260 atomic_inc(¤t->signal->live);
1261 atomic_inc(¤t->signal->sigcnt);
1262 p->group_leader = current->group_leader;
1263 list_add_tail_rcu(&p->thread_group, &p->group_leader->thread_group); //把当前的线程加入到父进程的线程组中
1264 } 3.寻找空闲的pid
没有说清楚的就是如何从一个bitmap中寻找位为0的位置。上篇的分析我们知道,pid的分配的情况被记在了pid_namespace中的pid_map中,pid_map被看做是一个bitmap,被用过的位置置为1,没有用过的位置位为0,寻找位为0的函数是find_next_zero_bit。这个函数的思想就是把bitmap切成多个long(连续64位)来看,然后根据位移屏蔽到一些无关的为1的位(offset之前的位不看),然后取反,可知,如果这个取反之前如果有一位为0,那么取反之后的long的值肯定会大于0,那么如果剩下的long的值大于0,就可以判断在64位中有为0的位,那么在用汇编bsf指令找出这个为0的位置。所以函数分为两个步骤,第一步是确定一个范围内有没有0的位,第二步就是如果有0的位置,把它从中找出来。
find_next_bit.c:
67 unsigned long find_next_zero_bit(const unsigned long *addr, unsigned long size,
68 unsigned long offset) //addr是pid_map的首地址,size是这个pid_map的规模,offset是从哪个位移开始寻找位为0的位置。
69 {
70 const unsigned long *p = addr + BITOP_WORD(offset);
71 unsigned long result = offset & ~(BITS_PER_LONG-1);
72 unsigned long tmp;
73
74 if (offset >= size)
75 return size;
76 size -= result; //2
77 offset %= BITS_PER_LONG;
78 if (offset) {
79 tmp = *(p++);
80 tmp |= ~0UL >> (BITS_PER_LONG - offset);
81 if (size < BITS_PER_LONG) //如果size不足1个long型变量,
82 goto found_first;
83 if (~tmp) //tmp取反如果大于0,代表在这段空间中有0位
84 goto found_middle;
85 size -= BITS_PER_LONG;
86 result += BITS_PER_LONG;
87 }
88 while (size & ~(BITS_PER_LONG-1)) { //遍历下一个64位空间
89 if (~(tmp = *(p++)))
90 goto found_middle;
91 result += BITS_PER_LONG;
92 size -= BITS_PER_LONG;
93 }
94 if (!size)
95 return result;
96 tmp = *p;
97
98 found_first:
99 tmp |= ~0UL << size;
100 if (tmp == ~0UL) /* Are any bits zero? */
101 return result + size; /* Nope. */
102 found_middle:
103 return result + ffz(tmp);
104 } 举例说明整个函数的思想:
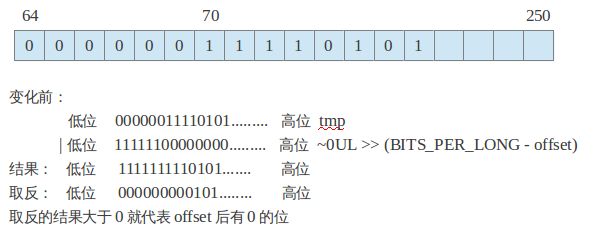
根据上图中假设上面有250位的内存地址空间,那么首地址就是addr,size是250,offset70,那么这个这个函数的目的就是寻找addr开始,最大位移为250的地址空间,从位移是70的位置开始寻找后面是否位是0的位置。
那么整个地址空间被切割成很多个64位来处理,因为可以把这64位转化为1个long型的变量,所以第一步就是取得包括位移为70的这个long型变量的首地址。如果这个offset这个位移求64位的掩码大于0,证明这个offset是在这个64位的中间位置(不是第一位),那么就到了tmp |= ~0UL >> (BITS_PER_LONG –offset);这里tmp就是long变量的值,~0UL操作就是64位1,然后向右移动64-6=58位,那么~0UL>> (BITS_PER_LONG –offset)结果就是高位58个0,和低位的6个1,那么这个tmp再和前面那个结果做与的操作,那么可以知道tmp的6个低位肯定都是1,tmp中后面58位该是什么还是什么。这时再对tmp取反操作,那么低位都变成0了,高位0变为1,1变为0,这个如果tmp大于0的话就代表高位58位有为0的位,那么对应到寻找pid_map中为0的位,那么就可以确定有0的位置了。
确认tmp中有1的位,那么就该寻找这个位究竟在什么位置了,通过fzz函数
361 static inline unsigned long ffz(unsigned long word)
362 {
363 asm("bsf %1,%0"
364 : "=r" (word)
365 : "r" (~word));
366 return word;
367 }从网上摘了一段关于bsf指令的说明:
bsfl汇编指令:
Intel汇编指令:bsf
oprd1,oprd2;
顺向位扫描(bitscan forward)
从右向左(从位0-->位15或位31)扫描字或双字操作数oprd2中第一个含"1"的位,并把扫描到的第一个含'1'的位的位号送操作数oprd1 。
参考文档:
1.http://blog.csdn.net/dog250/article/details/5303654
from: http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-27767798-id-3470592.html?page=2